吴恩达机器学习作业——多元分类及神经网络
第四周作业
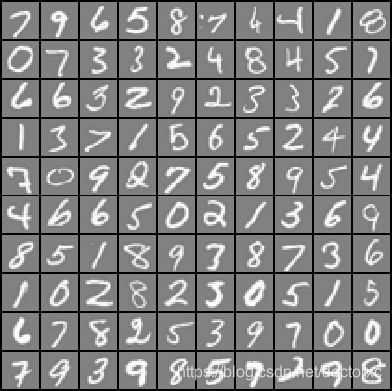
多元分类问题:识别手写数字0~9(0替换为10),5000个样本,20*20共400像素。
多元分类Logistic回归
1参数初始化
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this part of the exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
2加载数据并可视化
%% =========== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data =============
% We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.
% You will be working with a dataset that contains handwritten digits.
%
% Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
load('ex3data1.mat'); % training data stored in arrays X, y
m = size(X, 1);%返回矩阵X的行数。(若size(X,2)返回X的列数)
% Randomly select 100 data points to display
rand_indices = randperm(m);%将1到5000整数随机置换。
sel = X(rand_indices(1:100), :);%先打乱再选取100行向量,即100个数字。display显示10*10数字矩阵。
displayData(sel);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
displayData函数如下:
function [h, display_array] = displayData(X, example_width)
%DISPLAYDATA Display 2D data in a nice grid
% [h, display_array] = DISPLAYDATA(X, example_width) displays 2D data
% stored in X in a nice grid. It returns the figure handle h and the
% displayed array if requested.
% Set example_width automatically if not passed in
if ~exist('example_width', 'var') || isempty(example_width)
example_width = round(sqrt(size(X, 2)));%四舍五入求出图片的宽度
end
% Gray Image
colormap(gray);%将图片定义为灰色系
% Compute rows, cols
[m n] = size(X);
example_height = (n / example_width);%求出图片的高度
% Compute number of items to display
display_rows = floor(sqrt(m));%计算出每行每列展示多少个数字图片
display_cols = ceil(m / display_rows);
% Between images padding
pad = 1;%图片之间间隔
% Setup blank display 创建要展示的图片像素大小,空像素,数字图片之间有1像素间隔
display_array = - ones(pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad), ...
pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad));
% Copy each example into a patch on the display array 将像素点填充进去
curr_ex = 1;
for j = 1:display_rows
for i = 1:display_cols
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
% Copy the patch
% Get the max value of the patch
max_val = max(abs(X(curr_ex, :)));
display_array(pad + (j - 1) * (example_height + pad) + (1:example_height), ...
pad + (i - 1) * (example_width + pad) + (1:example_width)) = ...
reshape(X(curr_ex, :), example_height, example_width) / max_val;
curr_ex = curr_ex + 1;
end
if curr_ex > m,
break;
end
end
% Display Image
h = imagesc(display_array, [-1 1]);%将像素点画为图片
% Do not show axis
axis image off %不显示坐标轴
drawnow; %刷新屏幕
end
图像显示(由于程序中randperm函数,图像中数字随机):
3一对多样本训练
%% ============ Part 2b: One-vs-All Training ============
fprintf('\nTraining One-vs-All Logistic Regression...\n')
lambda = 0.1;
[all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;oneVsAll函数如下:
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
m = size(X, 1);%X的行数
n = size(X, 2);%X的列数
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50); %‘Gradobj’指用户自定义的目标函数梯度;‘MaxITer’指最大迭代次数,‘50’也就是最大迭代次数,这一项只能为整数。
for c=1:num_labels
all_theta(c,:)=fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y==c), lambda)), all_theta(c,:)', options)'; %fmincg函数与fminunc函数相似,用于求代价函数,对fmincg对大数据处理更有效率。
end
endfmincg函数:
fmincg函数与fminunc函数相似,用于求解代价函数最小值,但fmincg对大数据处理更有效率。
function [X, fX, i] = fmincg(f, X, options, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5)
if exist('options', 'var') && ~isempty(options) && isfield(options, 'MaxIter')
length = options.MaxIter;
else
length = 100;
end
RHO = 0.01; % a bunch of constants for line searches
SIG = 0.5; % RHO and SIG are the constants in the Wolfe-Powell conditions
INT = 0.1; % don't reevaluate within 0.1 of the limit of the current bracket
EXT = 3.0; % extrapolate maximum 3 times the current bracket
MAX = 20; % max 20 function evaluations per line search
RATIO = 100; % maximum allowed slope ratio
argstr = ['feval(f, X']; % compose string used to call function
for i = 1:(nargin - 3)
argstr = [argstr, ',P', int2str(i)];
end
argstr = [argstr, ')'];
if max(size(length)) == 2, red=length(2); length=length(1); else red=1; end
S=['Iteration '];
i = 0; % zero the run length counter
ls_failed = 0; % no previous line search has failed
fX = [];
[f1 df1] = eval(argstr); % get function value and gradient
i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?!
s = -df1; % search direction is steepest
d1 = -s'*s; % this is the slope
z1 = red/(1-d1); % initial step is red/(|s|+1)
while i < abs(length) % while not finished
i = i + (length>0); % count iterations?!
X0 = X; f0 = f1; df0 = df1; % make a copy of current values
X = X + z1*s; % begin line search
[f2 df2] = eval(argstr);
i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?!
d2 = df2'*s;
f3 = f1; d3 = d1; z3 = -z1; % initialize point 3 equal to point 1
if length>0, M = MAX; else M = min(MAX, -length-i); end
success = 0; limit = -1; % initialize quanteties
while 1
while ((f2 > f1+z1*RHO*d1) || (d2 > -SIG*d1)) && (M > 0)
limit = z1; % tighten the bracket
if f2 > f1
z2 = z3 - (0.5*d3*z3*z3)/(d3*z3+f2-f3); % quadratic fit
else
A = 6*(f2-f3)/z3+3*(d2+d3); % cubic fit
B = 3*(f3-f2)-z3*(d3+2*d2);
z2 = (sqrt(B*B-A*d2*z3*z3)-B)/A; % numerical error possible - ok!
end
if isnan(z2) || isinf(z2)
z2 = z3/2; % if we had a numerical problem then bisect
end
z2 = max(min(z2, INT*z3),(1-INT)*z3); % don't accept too close to limits
z1 = z1 + z2; % update the step
X = X + z2*s;
[f2 df2] = eval(argstr);
M = M - 1; i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?!
d2 = df2'*s;
z3 = z3-z2; % z3 is now relative to the location of z2
end
if f2 > f1+z1*RHO*d1 || d2 > -SIG*d1
break; % this is a failure
elseif d2 > SIG*d1
success = 1; break; % success
elseif M == 0
break; % failure
end
A = 6*(f2-f3)/z3+3*(d2+d3); % make cubic extrapolation
B = 3*(f3-f2)-z3*(d3+2*d2);
z2 = -d2*z3*z3/(B+sqrt(B*B-A*d2*z3*z3)); % num. error possible - ok!
if ~isreal(z2) || isnan(z2) || isinf(z2) || z2 < 0 % num prob or wrong sign?
if limit < -0.5 % if we have no upper limit
z2 = z1 * (EXT-1); % the extrapolate the maximum amount
else
z2 = (limit-z1)/2; % otherwise bisect
end
elseif (limit > -0.5) && (z2+z1 > limit) % extraplation beyond max?
z2 = (limit-z1)/2; % bisect
elseif (limit < -0.5) && (z2+z1 > z1*EXT) % extrapolation beyond limit
z2 = z1*(EXT-1.0); % set to extrapolation limit
elseif z2 < -z3*INT
z2 = -z3*INT;
elseif (limit > -0.5) && (z2 < (limit-z1)*(1.0-INT)) % too close to limit?
z2 = (limit-z1)*(1.0-INT);
end
f3 = f2; d3 = d2; z3 = -z2; % set point 3 equal to point 2
z1 = z1 + z2; X = X + z2*s; % update current estimates
[f2 df2] = eval(argstr);
M = M - 1; i = i + (length<0); % count epochs?!
d2 = df2'*s;
end % end of line search
if success % if line search succeeded
f1 = f2; fX = [fX' f1]';
fprintf('%s %4i | Cost: %4.6e\r', S, i, f1);
s = (df2'*df2-df1'*df2)/(df1'*df1)*s - df2; % Polack-Ribiere direction
tmp = df1; df1 = df2; df2 = tmp; % swap derivatives
d2 = df1'*s;
if d2 > 0 % new slope must be negative
s = -df1; % otherwise use steepest direction
d2 = -s'*s;
end
z1 = z1 * min(RATIO, d1/(d2-realmin)); % slope ratio but max RATIO
d1 = d2;
ls_failed = 0; % this line search did not fail
else
X = X0; f1 = f0; df1 = df0; % restore point from before failed line search
if ls_failed || i > abs(length) % line search failed twice in a row
break; % or we ran out of time, so we give up
end
tmp = df1; df1 = df2; df2 = tmp; % swap derivatives
s = -df1; % try steepest
d1 = -s'*s;
z1 = 1/(1-d1);
ls_failed = 1; % this line search failed
end
if exist('OCTAVE_VERSION')
fflush(stdout);
end
end
fprintf('\n');4一对多预测
pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);predictOneVsAll函数如下:
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1);
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
index=0;
pre=zeros(num_labels,1); %存储每个样本对应数字1-10的预测值
for c=1:m
for d=1:num_labels
pre(d)=sigmoid(X(c,:)*(all_theta(d,:)'));
end
[maxnum index]=max(pre);
p(c)=index; %找到该样本最大的预测值所对应的数字,作为实际预测值
end
endlogistic回归只是线性分类,不能用于图像等复杂的预测,因此本例运用神经网络。
三层神经网络,输入层400个单元(像素20*20),隐藏层25个单元,输出层10个单元(数字1~10)
程序如下:
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
% Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
load('ex3data1.mat');
m = size(X, 1);
% Randomly select 100 data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, 1));
sel = sel(1:100);
displayData(X(sel, :));
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
fprintf('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n')
% Load the weights into variables Theta1 and Theta2
load('ex3weights.mat'); %训练好的theta1和theta2
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
% Randomly permute examples
rp = randperm(m);
for i = 1:m
% Display
fprintf('\nDisplaying Example Image\n');
displayData(X(rp(i), :));
pred = (Theta1, Theta2, X(rp(i),:));
fprintf('\nNeural Network Prediction: %d (digit %d)\n', pred, mod(pred, 10));
% Pause with quit option
s = input('Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:','s');
if s == 'q'
break
end
endpredict函数如下:
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1);
X=[ones(m,1) X];
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
for i=1:m
a2 = sigmoid(Theta1*X(i,:)');
a2 = [1;a2];
a3 = sigmoid(Theta2*a2);
[manum index]=max(a3); %求出哪个数字的预测值最大
p(i)=index; %得出预测值
end
end