基于树莓派3Beric6+PyQt5搭建步进电机控制
在之前的文章中讲述了在树莓派3B中基于python3.4搭建eric6IDE以及如何利用树莓派控制28步进电机。因此楼主搭建了简单步进电机控制界面,与大家分享。
写这篇文章的目的在于熟悉Eric6的操作以及利用PyQt5编辑软件界面的简单步骤。实现难度不大,但需要运行第二线程运行输出脉冲的程序。
首先,推荐一下PyQt5和Eric6的学习资料连接如下,一些简单的操作讲述的很细致。
https://blog.csdn.net/weiaitaowang/article/category/6334249
本文只介绍界面部即代码部分的操作,树莓派与步进电机硬件部分的连接见是一篇文章。
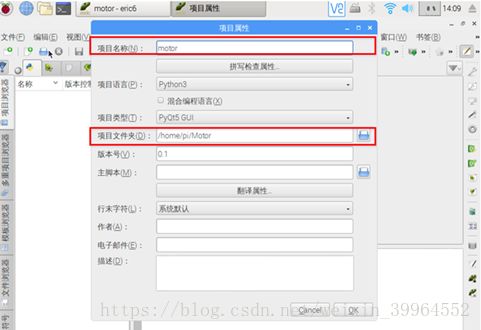
首先打eric6新建一个工程
然后编辑项目名称以及选择工作文件夹
然后所有操作选择确认即可
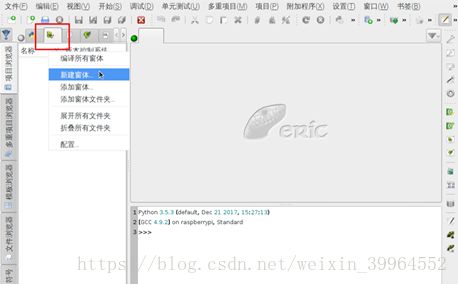
然后点击窗体图标,选择新建窗体。
在弹出对话框中选择主窗口,然后会自动弹出QTdesigner界面
选择按钮控件拖拽到主界面中,并双击修改文字,改为“Open door”,然后点击保存。
返回Eric6界面,选择刚刚创建的界面,右键单击选择编译窗体。会显示编译成功,会自动生成显示界面的.py文件。
点击窗体图标,并右键单击刚才生成的.ui文件,选择生成对话框选项,并找到按钮触发选项,点击生成。
产生对话.py文件。生成的.py文本如下所示:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot, QThread, pyqtSignal
from Ui_motormain import .Ui_MainWindow
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_MainWindow):
"""
Class documentation goes here.
"""
def __init__(self, parent=None):
"""
Constructor
@param parent reference to the parent widget
@type QWidget
"""
super(MainWindow, self).__init__(parent)
@pyqtSlot()
def on_pushButton_clicked(self):
"""
Slot documentation goes here.
"""
将 from Ui_motormain import .Ui_MainWindow 中的‘.’去掉
变为
from Ui_motormain import Ui_MainWindow然后在代码末尾添加如下代码,保证可运行刚才编辑好的界面。
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = MainWindow()
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())由于要调用树莓派的管脚并发送脉冲所以要导入GPIO和time库
所以在代码开头添加
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot, QThread, pyqtSignal
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time然后由于输出脉冲是一个循环程序,所以需要开启另一个线程,防止循环阻塞界面的运行,因此重新定义QThread类中的的run()方法。
class O_doorThread(QThread):
trigger = pyqtSignal()
def __int__(self, parent=None):
super(O_doorThread,self).__init__(parent)
def setdirecton(self, opendoor):
if opendoor:
GPIO.output(38,False)
else:
GPIO.output(38,True)
def run(self):
"""
第二线程运行函数
"""
n=0
while True:
n=n+1
time.sleep(0.00005) #设置脉冲频率
GPIO.output(40,False)
time.sleep(0.00005)
GPIO.output(40,True)
# print(n)
if n==9800:
break
self.trigger.emit()然后重写按钮触发方法,完成第二线程的开启
def on_pushButton_clicked(self):
"""
点击按钮运行
"""
self.doorThread=O_doorThread() #将O_doorThread()实例
self.doorThread.setdirecton( self.opendoor) #设置电机运行方向
time.sleep(0.5)
self.doorThread.trigger.connect(self.changedirecton)
self.doorThread.start() #第二线程开启下面给出全部代码:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot, QThread, pyqtSignal
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
from Ui_motormain import Ui_MainWindow
class O_doorThread(QThread):
trigger = pyqtSignal()
def __int__(self, parent=None):
super(O_doorThread,self).__init__(parent)
def setdirecton(self, opendoor):
if opendoor:
GPIO.output(38,False)
else:
GPIO.output(38,True)
def run(self):
"""
第二线程运行
"""
n=0
while True:
n=n+1
time.sleep(0.00005)
GPIO.output(40,False)
time.sleep(0.00005)
GPIO.output(40,True)
# print(n)
if n==9800:
break
self.trigger.emit()
class MainWindow(QMainWindow, Ui_MainWindow):
"""
Class documentation goes here.
"""
def __init__(self, parent=None):
"""
Constructor
@param parent reference to the parent widget
@type QWidget
"""
super(MainWindow, self).__init__(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
self.opendoor=True
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(38,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(40,GPIO.OUT)
@pyqtSlot()
def on_pushButton_clicked(self):
"""
Slot documentation goes here.
"""
self.doorThread=O_doorThread()
self.doorThread.setdirecton( self.opendoor)
time.sleep(0.5)
self.doorThread.trigger.connect(self.changedirecton)
self.doorThread.start()
def changedirecton(self):
# print('done')
if self.opendoor: #改变电机运转方向
self.opendoor=False
self.pushButton.setText('close door') #改变按钮文字
else:
self.opendoor=True
self.pushButton.setText('open door')
# self.doorThread.setdirecton( self.opendoor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = MainWindow()
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
楼主用这段代码控制步进电机驱动了一个装置的开门和拉门。