第三周作业(图论--BFS与DFS相关)
第三周作业(图论–BFS与DFS相关)
目录:
- 本周完成题目
- 主要过程思路
- 相关代码
- 感想与总结
一、本周完成题目
本周共完成2道题目,2道Medium。针对于本周所学的知识选择了Graph分类下的题目。 Graph
具体完成题目及难度如下表:
| # | Title | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| 207 | Course Schedule | Medium |
| 399 | Evaluate Division | Medium |
题目内容
1、Course Schedule
There are a total of n courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to n - 1.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example to take course 0 you have to first take course 1, which is expressed as a pair: [0,1]
Given the total number of courses and a list of prerequisite pairs, is it possible for you to finish all courses?
For example:
2, [[1,0]]
There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
题目大意:有n门可选课程,从0到n-1编号。其中课程之间存在先后顺序关系,问满足先后顺序的情况下课程是否都能上完。
2、Evaluate Division
Equations are given in the format A / B = k, where A and B are variables represented as strings, and k is a real number (floating point number). Given some queries, return the answers. If the answer does not exist, return -1.0.
Example:
Given a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0.
queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? .
return [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ].
题目大意:给定几组除法关系,如A/B=k。根据所给关系计算出所问除法关系的答案。(无法计算则输出-1)
二、主要过程思路
这两道题都是图论相关的题目,可以使用BFS(广度优先搜索)或者DFS(深度优先搜索)算法进行处理。
BFS:
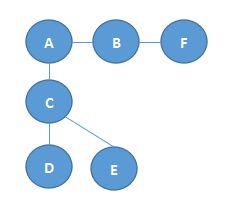
其英文全称是Breadth First Search,对于某个顶点s,算法会首先搜索和s距离为k的所有顶点,然后再去搜索和S距离为k+l的其他顶点。类似于逐层搜索的情况。以下图为例,如从A开始。则会继续搜索B、C。然后再下一层,搜索F、D、E。
DFS:
其英文全称为Depth First Search,图的深度遍历原则:访问一个邻接的未访问的节点,标记它,并把它放入栈中。当不能再访问时,如果栈不为空,则从栈中弹出一个元素。直到所有元素都被访问到,遍历结束。
以下图为例,如从A开始,首先访问B、F,之后访问C、D。最后访问E。
Course Schedule
本题的问题可以进行转化,实质上是求有向图是否有环存在,若存在则返回false,不存在则返回true。在读入数字之后建立一个邻接表,之后对于从0开始的每个元素进行逐次判断,看以该数字起始的子元素中是否存在环。
本题在这一部分使用的是DFS,对于每个数字进行遍历。
首先对于数字状态进行设定。
(1)visit[i]=0,说明i未被遍历过;
(2)visit[i]=-1,说明i正在遍历中,即i为当前元素的前置元素;
(3)visit[i]=1,说明i已经遍历完成且没有出现环。
遍历具体规则如下:
1.当前数字没有子元素,visit[i]标记为1,return true。
2.当前数字有子元素,对于每个子元素,判断该元素的visit值是否为-1,若为-1,说明产生了环,return false。
若为0,说明子元素未被访问过,标记为-1,对该元素继续进行DFS。若为1,跳过该元素。
3.遍历完所有子元素则标记该元素为1,代表已经完成子元素的遍历且不存在环。
Evaluate Division
首先,使用map存储每个元素和剩余其他元素之间的商。之后对于要求的式子进行判断,两个元素有不存在的元素,返回-1;两个元素存在且相同,返回1;否则,需要进行遍历判断两个元素是否存在递进的商的关系。
本题使用的是BFS算法。假设最后要求的式子是s1/s2。以s1作为搜索起点,进行广度优先遍历,每次将所有的子元素都压到队列中,同时更新每个子元素的商,遍历完一个节点的子元素后该节点商置为-1。
逐层遍历,若找到s2则返回相乘结果。若没有找到则返回-1。
三、相关代码
Course Schedule
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses, vectorint , int> >& prerequisites) {
vector<vector<int> > graph(numCourses); //保存邻接表
for(int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); ++ i){
int s1=prerequisites[i].first,s2=prerequisites[i].second;
graph[s1].push_back(s2);
}
int visit[numCourses] = { 0 };
for (int i=0;iif(visit[i]!=1){
if(!DFS(graph,i,visit)){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
//DFS部分,递归遍历
bool DFS(vector<vector<int> > &graph, int current, int *visit) {
if (graph[current].size() == 0) {
visit[current] = 1; //当前数字没有子元素,标记为1
return true;
}
visit[current] = -1; //表示正在遍历中
//遍历子元素
for (int i = 0; i < graph[current].size(); i++) {
int index = graph[current][i];
if (visit[index] == -1) {
return false; //遍历到正在遍历的元素中,环出现
} else if (visit[index] == 0) {
visit[index] = -1;
if (!DFS(graph, graph[current][i], visit)) {
return false;
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
visit[current] = 1; //遍历完成
return true;
}
}; Evaluate Division
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> calcEquation(vectorstring , string> > equations, vector<double>& values, vectorstring , string> > queries) {
vector<double> result;
//使用map存储每个元素和剩余其他元素之间的商
map<string,map<string,double> > graph;
for(int i=0;istring s1 = equations[i].first, s2 = equations[i].second;
graph[s1].insert(map<string,double>::value_type(s2,values[i]));
graph[s2].insert(map<string,double>::value_type(s1,1/values[i]));
}
for(int i=0;istring s1 = queries[i].first, s2 = queries[i].second;
if(graph.find(s1)==graph.end()||graph.find(s2)==graph.end()){
result.push_back(-1.0); //两个元素有不存在的元素,返回-1
}else if(s1==s2){
result.push_back(1.0); //两个元素存在且相同,返回1
}else{
result.push_back(BFS(s1,s2,graph)); //利用BFS计算结果
}
}
return result;
}
double BFS(string s1,string s2,map<string,map<string,double> > graph){
int len=graph.size();
map<string,double> visit; //用于保存从s1到其他元素的商
queue<string> q;
q.push(s1);
visit.insert(map<string,double>::value_type(s1,1));
while(!q.empty()){
string str=q.front();
q.pop();
double num=visit[str];
if(num==-1){
continue;
}
map<string,double>::iterator my_Itr;
if(graph[str].find(s2)!=graph[str].end()){
return graph[str][s2]*num;
}
//将当前元素的子元素压入队列,计算到子元素的总共的商
for(my_Itr=graph[str].begin(); my_Itr!=graph[str].end(); ++my_Itr) {
q.push(my_Itr->first);
visit.insert(map<string,double>::value_type(my_Itr->first,my_Itr->second*num));
}
visit[str]=-1; //标记已遍历过的元素
}
return -1;
}
}; 四、感想与总结
本周主要进行了图论中BFS和DFS的练习,通过具体的题目对于这两种遍历算法都进行了复习。在弄懂了题目之后相对而言还是比较简单的。但是在做第一题的时候出现了Memory Limited的问题。这是由于开始的时候使用了map形式且没有进行引用调用,空间损耗比较大。