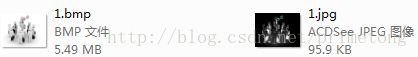【OpenCV图像处理入门学习教程一】OpenCV2 + 3的安装教程与VS2013的开发环境配置 + JPEG压缩源码分析与取反运算修改
OpenCV简介
OpenCV官网在此
OpenCV是大名鼎鼎的开源计算机视觉库,想做图像处理又不想用OpenCV的,不是大佬就是那啥,你懂的……
官网是这么介绍自己的:
OpenCV(开源计算机视觉库)是在BSD许可下发布的,因此它在学术和商业上的使用都是免费的。 它具有C ++,C,Python和Java接口,同时支持Windows,Linux,Mac OS,iOS和Android。OpenCV的设计目的是为了提高计算效率,并将重点放在实时应用程序上。采用优化的C / C ++编写,库可以利用多核处理。通过使用OpenCL,可以利用底层异构计算平台的硬件加速。OpenCV在世界各地被广泛采用,拥有超过4.7万人的用户群,预计下载量超过1400万。 其使用范围从交互式艺术到矿检,从网上拼接地图到高级机器人中都有它的身影。
来来来,敲黑板了,其实重点就是①开源②高效,心动不如行动,赶快下载吧!
一、OpenCV安装教程
IDE:Visual Studio 2013
语言:C++
依赖:OpenCV 2.4.9、3.3.0
- 安装教程网上已经有很多了,关于OpenCV2和3的争议也很多,我觉得不要想那么多,两个都装上就好嘛,2.4.9版本直接支持VS2013,安装比较简单,参考以下@浅墨_毛星云大大的教程即可:
- 【OpenCV入门教程之一】 安装OpenCV:OpenCV 3.0、OpenCV 2.4.8、OpenCV 2.4.9 +VS 开发环境配置
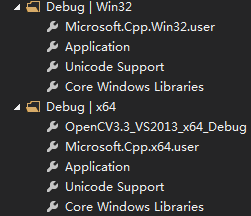
不管你是32位还是64位操作系统,只用管你用win32编译器还是X64 编译器。
其实配置选择什么跟64位还是32位系统没有直接的关系,而是在于你在编译你的程序的时候是使用那个编译器。
编译器是win32,就用x86
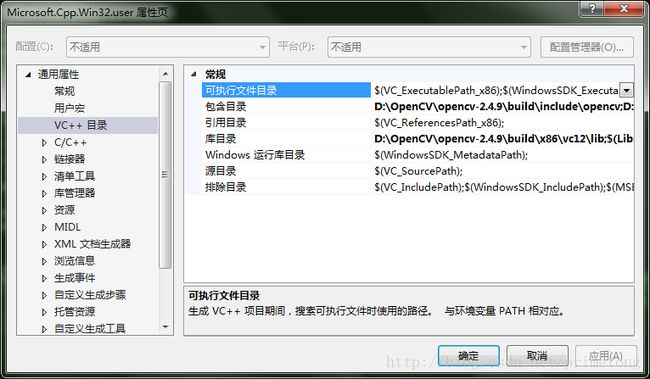
编译器是X64,就用X64。不过一般情况下,都是用的win32的X86编译器。因此将2.4.9版本添加进Win32的属性管理器:
将3.3.0版本添加进x64的属性管理器:
之后在使用中根据需要(一般默认是Win32也就是使用2.4.9版本),切换对应版本(想使用3.3.0就将配置好的x64的属性管理器添加进工程,然后在配置管理器中修改使用x64进行编译调试)
二、JPEG压缩源码分析
IDE:DEV-C++
语言:C
#include
#include
#include
#include "JTYPES.H"
#include "JGLOBALS.H"
#include "JTABLES.H"
void write_APP0info()
//Nothing to overwrite for APP0info
{
writeword(APP0info.marker);
writeword(APP0info.length);
writebyte('J');
writebyte('F');
writebyte('I');
writebyte('F');
writebyte(0);
writebyte(APP0info.versionhi);
writebyte(APP0info.versionlo);
writebyte(APP0info.xyunits);
writeword(APP0info.xdensity);
writeword(APP0info.ydensity);
writebyte(APP0info.thumbnwidth);
writebyte(APP0info.thumbnheight);
}
void write_SOF0info()
// We should overwrite width and height
{
writeword(SOF0info.marker);
writeword(SOF0info.length);
writebyte(SOF0info.precision);
writeword(SOF0info.height);
writeword(SOF0info.width);
writebyte(SOF0info.nrofcomponents);
writebyte(SOF0info.IdY);
writebyte(SOF0info.HVY);
writebyte(SOF0info.QTY);
writebyte(SOF0info.IdCb);
writebyte(SOF0info.HVCb);
writebyte(SOF0info.QTCb);
writebyte(SOF0info.IdCr);
writebyte(SOF0info.HVCr);
writebyte(SOF0info.QTCr);
}
/********************************************************************
写量化表的信息,这些以被赋予初始值
*********************************************************************/
void write_DQTinfo()
{
BYTE i;
writeword(DQTinfo.marker);
writeword(DQTinfo.length);
writebyte(DQTinfo.QTYinfo);
for (i=0; i<64; i++)
writebyte(DQTinfo.Ytable[i]);
writebyte(DQTinfo.QTCbinfo);
for (i=0; i<64; i++)
writebyte(DQTinfo.Cbtable[i]);
}
/************************************************************************************
设置量化表zigzag排序 109
*************************************************************************************/
void set_quant_table(BYTE *basic_table, BYTE scale_factor, BYTE *newtable) //设置量化表zigzag排序 109
// quantizSetation table and zigzag reorder it
{
BYTE i;
long temp;
for (i=0; i<64; i++)
{
temp = ((long) basic_table[i] * scale_factor + 50L) / 100L;
// limit the values to the valid range
if (temp <= 0L)
temp = 1L;
if (temp > 255L)
temp = 255L;
newtable[zigzag[i]] = (BYTE) temp;
}
}
/*********************************************************************************
量化因子的设定,按z秩序进行亮度与色度量化步长的排序
**********************************************************************************/
void set_DQTinfo()
{
BYTE scalefactor = 50;// scalefactor controls the visual quality of the image
// the smaller is the better image we'll get, and the smaller
// compression we'll achieve
DQTinfo.marker = 0xFFDB;
DQTinfo.length = 132;
DQTinfo.QTYinfo = 0;
DQTinfo.QTCbinfo = 1;
/******************************************************************************
四 重点讲解亮度表和色度表,注意量化因子
*******************************************************************************/
set_quant_table(std_luminance_qt, scalefactor, DQTinfo.Ytable);
set_quant_table(std_chrominance_qt, scalefactor, DQTinfo.Cbtable);
}
/*********************************************************************************
哈傅曼编码的量化排序
**********************************************************************************/
void write_DHTinfo()
{
BYTE i;
writeword(DHTinfo.marker);
writeword(DHTinfo.length);
writebyte(DHTinfo.HTYDCinfo);
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.YDC_nrcodes[i]);
for (i=0; i<12; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.YDC_values[i]);
writebyte(DHTinfo.HTYACinfo);
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.YAC_nrcodes[i]);
for (i=0; i<162; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.YAC_values[i]);
writebyte(DHTinfo.HTCbDCinfo);
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.CbDC_nrcodes[i]);
for (i=0; i<12; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.CbDC_values[i]);
writebyte(DHTinfo.HTCbACinfo);
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.CbAC_nrcodes[i]);
for (i=0; i< 162; i++)
writebyte(DHTinfo.CbAC_values[i]);
}
/***************************************************
同上
****************************************************/
void set_DHTinfo()
{
BYTE i;
// fill the DHTinfo structure [get the values from the standard Huffman tables]
DHTinfo.marker = 0xFFC4;
DHTinfo.length = 0x01A2;
DHTinfo.HTYDCinfo = 0;
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
DHTinfo.YDC_nrcodes[i] = std_dc_luminance_nrcodes[i+1];
for (i=0; i<12; i++)
DHTinfo.YDC_values[i] = std_dc_luminance_values[i];
DHTinfo.HTYACinfo = 0x10;
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
DHTinfo.YAC_nrcodes[i] = std_ac_luminance_nrcodes[i+1];
for (i=0; i<162; i++)
DHTinfo.YAC_values[i] = std_ac_luminance_values[i];
DHTinfo.HTCbDCinfo = 1;
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
DHTinfo.CbDC_nrcodes[i] = std_dc_chrominance_nrcodes[i+1];
for (i=0; i<12; i++)
DHTinfo.CbDC_values[i] = std_dc_chrominance_values[i];
DHTinfo.HTCbACinfo = 0x11;
for (i=0; i<16; i++)
DHTinfo.CbAC_nrcodes[i] = std_ac_chrominance_nrcodes[i+1];
for (i=0; i<162; i++)
DHTinfo.CbAC_values[i] = std_ac_chrominance_values[i];
}
/****************************************************************
设置编码开始的标记
*****************************************************************/
void write_SOSinfo()
//Nothing to overwrite for SOSinfo
{
writeword(SOSinfo.marker);
writeword(SOSinfo.length);
writebyte(SOSinfo.nrofcomponents);
writebyte(SOSinfo.IdY);
writebyte(SOSinfo.HTY);
writebyte(SOSinfo.IdCb);
writebyte(SOSinfo.HTCb);
writebyte(SOSinfo.IdCr);
writebyte(SOSinfo.HTCr);
writebyte(SOSinfo.Ss);
writebyte(SOSinfo.Se);
writebyte(SOSinfo.Bf);
}
void write_comment(BYTE *comment)
{
WORD i, length;
writeword(0xFFFE); // The COM marker
length = strlen((const char *)comment);
writeword(length + 2);
for (i=0; i=0
value = bs.value;
posval = bs.length - 1;
while (posval >= 0)
{
if (value & mask[posval])
bytenew |= mask[bytepos];
posval--;
bytepos--;
if (bytepos < 0)
{
// write it
if (bytenew == 0xFF)
{
// special case
writebyte(0xFF);
writebyte(0);
}
else
writebyte(bytenew);
// reinit
bytepos = 7;
bytenew = 0;
}
}
}
/********************************************************************************************
对准Huffman表的改变,利用静态数据作初始化
*********************************************************************************************/
void compute_Huffman_table(BYTE *nrcodes, BYTE *std_table, bitstring *HT) //修改标准Huffman码表,可以修改压缩率
{
BYTE k,j;
BYTE pos_in_table;
WORD codevalue;
codevalue = 0;
pos_in_table = 0;
for (k=1; k<=16; k++)
{
for (j=1; j<=nrcodes[k]; j++)
{
HT[std_table[pos_in_table]].value = codevalue;
HT[std_table[pos_in_table]].length = k;
pos_in_table++;
codevalue++;
}
codevalue <<= 1;
}
}
void init_Huffman_tables() //初始化Huffman编码表
{
// Compute the Huffman tables used for encoding //计算编码所需的Huffman码表
compute_Huffman_table(std_dc_luminance_nrcodes, std_dc_luminance_values, YDC_HT); //YDC-HT:亮度直流信号
compute_Huffman_table(std_ac_luminance_nrcodes, std_ac_luminance_values, YAC_HT); //YDC-HT:亮度交流信号
compute_Huffman_table(std_dc_chrominance_nrcodes, std_dc_chrominance_values, CbDC_HT);
compute_Huffman_table(std_ac_chrominance_nrcodes, std_ac_chrominance_values, CbAC_HT);
}
void exitmessage(char *error_message)
{
printf("%s\n",error_message);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/**************************************************************************
作用未知???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????
***************************************************************************/
void set_numbers_category_and_bitcode()
{
SDWORD nr;
SDWORD nrlower, nrupper;
BYTE cat;
category_alloc = (BYTE *)malloc(65535*sizeof(BYTE));
if (category_alloc == NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory.");
//allow negative subscripts
category = category_alloc + 32767;
bitcode_alloc=(bitstring *)malloc(65535*sizeof(bitstring));
if (bitcode_alloc==NULL)
exitmessage("Not enough memory.");
bitcode = bitcode_alloc + 32767;
nrlower = 1;
nrupper = 2;
for (cat=1; cat<=15; cat++)
{
//Positive numbers
for (nr=nrlower; nrycbcr的转换
*****************************************************************************/
void precalculate_YCbCr_tables() //RGB --> YCbCr
{
WORD R,G,B;
for (R=0; R<256; R++)
{
YRtab[R] = (SDWORD)(65536*0.299+0.5)*R;
CbRtab[R] = (SDWORD)(65536*-0.16874+0.5)*R;
CrRtab[R] = (SDWORD)(32768)*R;
}
for (G=0; G<256; G++)
{
YGtab[G] = (SDWORD)(65536*0.587+0.5)*G;
CbGtab[G] = (SDWORD)(65536*-0.33126+0.5)*G;
CrGtab[G] = (SDWORD)(65536*-0.41869+0.5)*G;
}
for (B=0; B<256; B++)
{
YBtab[B] = (SDWORD)(65536*0.114+0.5)*B;
CbBtab[B] = (SDWORD)(32768)*B;
CrBtab[B] = (SDWORD)(65536*-0.08131+0.5)*B;
}
}
// Using a bit modified form of the FDCT routine from IJG's C source:
// Forward DCT routine idea taken from Independent JPEG Group's C source for
// JPEG encoders/decoders
/* For float AA&N IDCT method, divisors are equal to quantization
coefficients scaled by scalefactor[row]*scalefactor[col], where
scalefactor[0] = 1
scalefactor[k] = cos(k*PI/16) * sqrt(2) for k=1..7
We apply a further scale factor of 8.
What's actually stored is 1/divisor so that the inner loop can
use a multiplication rather than a division. */
void prepare_quant_tables() //准备量化表。通过下面给出的参数修改标准量化表来定制自己所需的量化表
{
double aanscalefactor[8] = {1.0, 1.387039845, 1.306562965, 1.175875602,
1.0, 0.785694958, 0.541196100, 0.275899379};
BYTE row, col;
BYTE i = 0;
//8*8的宏块设置
for (row = 0; row < 8; row++)
{
for (col = 0; col < 8; col++)
{
fdtbl_Y[i] = (float) (1.0 / ((double) DQTinfo.Ytable[zigzag[i]] *
aanscalefactor[row] * aanscalefactor[col] * 8.0));
fdtbl_Cb[i] = (float) (1.0 / ((double) DQTinfo.Cbtable[zigzag[i]] *
aanscalefactor[row] * aanscalefactor[col] * 8.0));
i++;
}
}
}
/************************************************************************************
快速离散余弦变换(fdct) 先行变换,8行变换后,再按列变换,按时域抽取来划分
*************************************************************************************/
void fdct_and_quantization(SBYTE *data, float *fdtbl, SWORD *outdata) //使用快速离散余弦变换方法实现(FDCT)来实现离散余弦变化并量化
{
float tmp0, tmp1, tmp2, tmp3, tmp4, tmp5, tmp6, tmp7;
float tmp10, tmp11, tmp12, tmp13;
float z1, z2, z3, z4, z5, z11, z13;
float *dataptr;
float datafloat[64];
float temp;
SBYTE ctr;
BYTE i;
for (i=0; i<64; i++)
datafloat[i] = data[i];
/* Pass 1: process rows. */
dataptr = datafloat;
for (ctr = 7; ctr >= 0; ctr--)
{
tmp0 = dataptr[0] + dataptr[7];
tmp7 = dataptr[0] - dataptr[7];
tmp1 = dataptr[1] + dataptr[6];
tmp6 = dataptr[1] - dataptr[6];
tmp2 = dataptr[2] + dataptr[5];
tmp5 = dataptr[2] - dataptr[5];
tmp3 = dataptr[3] + dataptr[4];
tmp4 = dataptr[3] - dataptr[4];
/* Even part */
tmp10 = tmp0 + tmp3; /* phase 2 */
tmp13 = tmp0 - tmp3;
tmp11 = tmp1 + tmp2;
tmp12 = tmp1 - tmp2;
dataptr[0] = tmp10 + tmp11; /* phase 3 */
dataptr[4] = tmp10 - tmp11;
z1 = (tmp12 + tmp13) * ((float) 0.707106781); /* c4 */
dataptr[2] = tmp13 + z1; /* phase 5 */
dataptr[6] = tmp13 - z1;
/* Odd part */
tmp10 = tmp4 + tmp5; /* phase 2 */
tmp11 = tmp5 + tmp6;
tmp12 = tmp6 + tmp7;
/* The rotator is modified from fig 4-8 to avoid extra negations. */
z5 = (tmp10 - tmp12) * ((float) 0.382683433); /* c6 */
z2 = ((float) 0.541196100) * tmp10 + z5; /* c2-c6 */
z4 = ((float) 1.306562965) * tmp12 + z5; /* c2+c6 */
z3 = tmp11 * ((float) 0.707106781); /* c4 */
z11 = tmp7 + z3; /* phase 5 */
z13 = tmp7 - z3;
dataptr[5] = z13 + z2; /* phase 6 */
dataptr[3] = z13 - z2;
dataptr[1] = z11 + z4;
dataptr[7] = z11 - z4;
dataptr += 8; /* advance pointer to next row */
}
/* Pass 2: process columns. */
dataptr = datafloat;
for (ctr = 7; ctr >= 0; ctr--)
{
tmp0 = dataptr[0] + dataptr[56];
tmp7 = dataptr[0] - dataptr[56];
tmp1 = dataptr[8] + dataptr[48];
tmp6 = dataptr[8] - dataptr[48];
tmp2 = dataptr[16] + dataptr[40];
tmp5 = dataptr[16] - dataptr[40];
tmp3 = dataptr[24] + dataptr[32];
tmp4 = dataptr[24] - dataptr[32];
/* Even part */
tmp10 = tmp0 + tmp3; /* phase 2 */
tmp13 = tmp0 - tmp3;
tmp11 = tmp1 + tmp2;
tmp12 = tmp1 - tmp2;
dataptr[0] = tmp10 + tmp11; /* phase 3 */
dataptr[32] = tmp10 - tmp11;
z1 = (tmp12 + tmp13) * ((float) 0.707106781); /* c4 */
dataptr[16] = tmp13 + z1; /* phase 5 */
dataptr[48] = tmp13 - z1;
/* Odd part */
tmp10 = tmp4 + tmp5; /* phase 2 */
tmp11 = tmp5 + tmp6;
tmp12 = tmp6 + tmp7;
/* The rotator is modified from fig 4-8 to avoid extra negations. */
z5 = (tmp10 - tmp12) * ((float) 0.382683433); /* c6 */
z2 = ((float) 0.541196100) * tmp10 + z5; /* c2-c6 */
z4 = ((float) 1.306562965) * tmp12 + z5; /* c2+c6 */
z3 = tmp11 * ((float) 0.707106781); /* c4 */
z11 = tmp7 + z3; /* phase 5 */
z13 = tmp7 - z3;
dataptr[40] = z13 + z2; /* phase 6 */
dataptr[24] = z13 - z2;
dataptr[8] = z11 + z4;
dataptr[56] = z11 - z4;
dataptr++; /* advance pointer to next column */
}
/* Quantize/descale the coefficients, and store into output array */
for (i = 0; i < 64; i++)
{
/* Apply the quantization and scaling factor */
temp = datafloat[i] * fdtbl[i];
/* Round to nearest integer.
Since C does not specify the direction of rounding for negative
quotients, we have to force the dividend positive for portability.
The maximum coefficient size is +-16K (for 12-bit data), so this
code should work for either 16-bit or 32-bit ints.
*/
outdata[i] = (SWORD) ((SWORD)(temp + 16384.5) - 16384);
}
}
/************************************************************************************
FDCT变换,DC,AC量化编码(Z扫描),哈夫曼编码存储
*************************************************************************************/
void process_DU(SBYTE *ComponentDU,float *fdtbl,SWORD *DC, bitstring *HTDC,bitstring *HTAC)
{
bitstring EOB = HTAC[0x00];
bitstring M16zeroes = HTAC[0xF0];
BYTE i;
BYTE startpos;
BYTE end0pos;
BYTE nrzeroes;
BYTE nrmarker;
SWORD Diff;
fdct_and_quantization(ComponentDU, fdtbl, DU_DCT); //使用快速离散余弦变换方法实现(FDCT)来实现离散余弦变化并量化
{
// zigzag reorder
for (i=0; i<64; i++) //使用zigzag方式对数据进行排序
DU[zigzag[i]]=DU_DCT[i];
// Encode DC //对直流分量进行专门的差分编码
Diff = DU[0] - *DC;
*DC = DU[0];
/****************************************************************************************
哈夫曼编码存储
*****************************************************************************************/
if (Diff == 0)
writebits(HTDC[0]); //Diff might be 0
else
{
writebits(HTDC[category[Diff]]);
writebits(bitcode[Diff]);
}
// Encode ACs //对交流分量进行按zigzag顺序编码
for (end0pos=63; (end0pos>0)&&(DU[end0pos]==0); end0pos--) ;
//end0pos = first element in reverse order != 0
i = 1;
while (i <= end0pos)
{
startpos = i;
for (; (DU[i]==0) && (i<=end0pos); i++) ;
nrzeroes = i - startpos;
if (nrzeroes >= 16)
{
for (nrmarker=1; nrmarker<=nrzeroes/16; nrmarker++)
writebits(M16zeroes);
nrzeroes = nrzeroes%16;
}
writebits(HTAC[nrzeroes*16+category[DU[i]]]);
writebits(bitcode[DU[i]]);
i++;
}
if (end0pos != 63)
writebits(EOB);
}
}
/***************************************************************************
按块64*64从rgb缓存中读取数据
****************************************************************************/
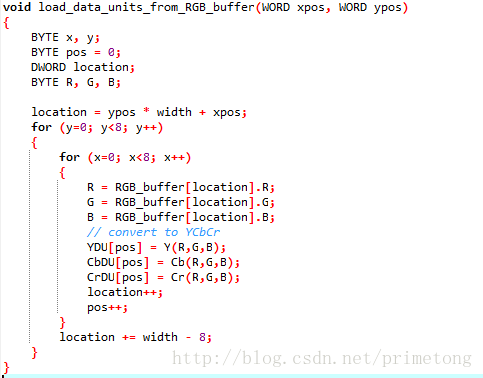
void load_data_units_from_RGB_buffer(WORD xpos, WORD ypos)
{
BYTE x, y;
BYTE pos = 0;
DWORD location;
BYTE R, G, B;
location = ypos * width + xpos;
for (y=0; y<8; y++)
{
for (x=0; x<8; x++) //图像取反前的注释
{
R = RGB_buffer[location].R;
G = RGB_buffer[location].G;
B = RGB_buffer[location].B;
// for (x=0; x<8; x++) //图像取反处理
// {
// R = 0xff - RGB_buffer[location].R;
// G = 0xff - RGB_buffer[location].G;
// B = 0xff - RGB_buffer[location].B;
// convert to YCbCr
YDU[pos] = Y(R,G,B);
CbDU[pos] = Cb(R,G,B);
CrDU[pos] = Cr(R,G,B);
location++;
pos++;
}
location += width - 8;
}
}
void main_encoder() //
{
SWORD DCY = 0, DCCb = 0, DCCr = 0; //DC coefficients used for differential encoding
WORD xpos, ypos;
for (ypos=0; yposnrline_dn; nrline_up--,nrline_dn++)
{
memcpy(tmpline, RGB_buffer+nrline_up*width, dimline);
memcpy(RGB_buffer+nrline_up*width, RGB_buffer+nrline_dn*width, dimline);
memcpy(RGB_buffer+nrline_dn*width, tmpline, dimline);
}
// Y completion:
memcpy(tmpline, RGB_buffer+(height-1)*width, dimline);
for (nrline=height; nrline1)
{
strcpy(BMP_filename,argv[1]);
if (argc>2)
strcpy(JPG_filename,argv[2]);
else
{
// replace ".bmp" with ".jpg"
strcpy(JPG_filename, BMP_filename);
len_filename=strlen(BMP_filename);
strcpy(JPG_filename+(len_filename-3),"jpg");
}
}
else
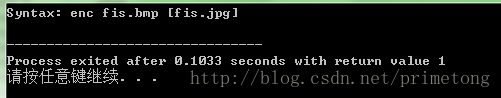
exitmessage("Syntax: enc fis.bmp [fis.jpg]");
//BMP_filename="";
/*************************************************************************
二:讲解如何跳转和回到重前,设置断点及调试,查看当前运行情况
**************************************************************************/
load_bitmap(BMP_filename, &width_original, &height_original);
fp_jpeg_stream = fopen(JPG_filename,"wb");
init_all();
/*************************************************************************
桢图像开始的标记sof
**************************************************************************/
SOF0info.width = width_original;
SOF0info.height = height_original;
/*************************************************************************
图像开始的标记soi
**************************************************************************/
writeword(0xFFD8); // SOI
/****************************************************************
版本信息
*****************************************************************/
write_APP0info();
// write_comment("Cris made this JPEG with his own encoder");
/******************************************************************
定义量化表
*******************************************************************/
write_DQTinfo();
/******************************************************************
*******************************************************************/
write_SOF0info();
write_DHTinfo();
write_SOSinfo();
// init global variables
bytenew = 0; // current byte
bytepos = 7; // bit position in this byte
main_encoder();
// Do the bit alignment of the EOI marker
if (bytepos >= 0)
{
fillbits.length = bytepos + 1;
fillbits.value = (1<<(bytepos+1)) - 1;
writebits(fillbits);
}
writeword(0xFFD9); // EOI
free(RGB_buffer);
free(category_alloc);
free(bitcode_alloc);
fclose(fp_jpeg_stream);
} 1.通过对以上BMP转JPEG的源码的分析来熟悉JPEG压缩和解压缩流程:
①主程序中先是声明变量的过程,接着通过字符串操作把主程序参数输入图像的后缀由.bmp改成了.jpg,这步主要就是获取到输入图像的名字。如果没有读到图像,则会打印出一串错误信息:
②接着装载图片,将原始图像读入内存,并且进行字节对齐处理,把长宽定为8的倍数以便下一步的宏模块分割,然后将图像作倒置(X,Y轴)处理。之后通过fopen函数在当前目录下打开输入的图片赋给文件指针fp_jpeg_stream,并设置为wb即写二进制文件操作。
③初始化:初始化各种量化表,这里面调用了好多量化排序的函数(根据亮度表色度表以及哈傅曼编码)、把RGB转换成YCbCr、滤波,就是JPEG中预处理的过程,在初始化中的prepare_quant_tables()函数中还有一个8*8的宏模块设置(还在空间域)
④接着标记图像的帧开始、版本信息、定义量化表(量化因子选的是50)的过程
⑤接下来进行快速离散余弦变化并量化(分别处理三个分量Y、Cb、Cr,使用zigzag方式对数据进行排序,对直流分量进行专门的差分编码,交流分量进行按zigzag顺序编码,霍夫曼编码存储)
⑥释放缓冲区、空间、IO流
(2)编译并用测试照片(工程目录下的1.bmp)进行实验,观察源文件和生成jpg文件大小,计算出压缩率:
压缩率 = (95.9/(5.49*1024)) * 100% ≈1.7%
2.熟悉图像处理程序框架,完成图像取反运算。
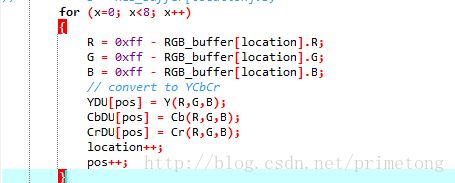
在源码中,有个函数:load_data_units_from_RGB_buffer,是负责从RGB缓存中读取数据的,只需对这段函数中RGB的值稍作修改即可完成图像取反运算。
就是拿255去减RGB值,出来的就是取反图像:
BMP转JPEG压缩源码与取反运算修改及分析,整个工程文件见下载页面
OpenCV图像处理入门学习教程系列,下一篇第二篇:不同阈值二值化图像