导读
喵喵的,一个大坑。本文分为吐槽和干货两部分。
一、吐槽
大周末的,被导师扣下加班,嗨气,谁叫本狗子太弱鸡呢,看起来很简单的任务倒腾了两天还没完,不扣你扣谁?
自己刚接到微调Inception-v3的任务时,也是觉得小意思不是,不就下载预训练模型然后finetune?
当然,本狗子是不可能自己写代码的,毕竟弱鸡自己造轮胎从来都漏气。打开网页,眼花缭乱,选定了个看起来算比较简单的博客开始动手,嗯就这个。
事实证明,该博客的方法不仅该说的没说不该说的瞎说还最后有巨坑。
此处截出来进行diss,博主请假装没看到。不然,“我魏璎珞,从来脾气爆,天生不好惹...”。
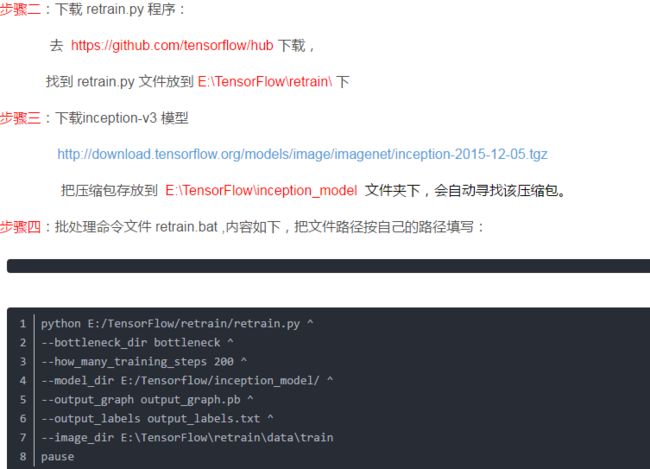
好了,说说上图的事。本狗子最后调通了该博主的训练代码,证明:
1)上图中代码导入tensorflow-hub这个包,需要事先安装,而博主文中一毛钱都没有提到。(安装tensorflow-hub是一个大坑,本狗子折腾一天最后换了台电脑才爬出来...
2)上图中说上面链接下载Inception-v3模型,其实并不需要,亲测。原因是代码中采用的是tensorflow-hub封装的Inception-v3。
3)代码中需要的Inception-v3模型,需要FQ下载,该下载过程是利用代码实现的,国内一般ubuntu系统(为了使用gpu训练模型方便)并不能主动FQ,因此模型无法下载,代码无法运行。(本狗子因该代码倒腾了一上午的FQ问题,然而并没有解决。最终手动下载tensorflow-hub模型并修改代码才得以解决。
4)上图第四步,运行也是报错的。正确做法是,在代码的main函数中改默认参数,而默认参数改的并不是图上这几个。(该问题本狗子没有仔细验证,但是该脚本参数不能运行是确定的。
在踩完上面一片大坑,用该博主代码测试时才发现更有一大坑,且该坑无法解决,只能换代码训练。出现的问题是:
遂,该博文方法终结。
总结下来过程是,该文漏了很多东西,漏的东西里无数大坑,全坑踩完最终测试宣告该方法无解。
二、干货
下面就直接上现在拿到的确定能跑通的代码,内容参考链接。
1.训练数据准备
train_data_dir/class_i/*.jpg,如 data/train/n012345678/1.jpg....
2.训练
直接上代码:(路径根据个人情况修改)
1 # Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 #
3 # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 #
7 # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 #
9 # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 # limitations under the License.
14 # ==============================================================================
15 r"""Simple transfer learning with Inception v3 or Mobilenet models.
16
17 With support for TensorBoard.
18
19 This example shows how to take a Inception v3 or Mobilenet model trained on
20 ImageNet images, and train a new top layer that can recognize other classes of
21 images.
22
23 The top layer receives as input a 2048-dimensional vector (1001-dimensional for
24 Mobilenet) for each image. We train a softmax layer on top of this
25 representation. Assuming the softmax layer contains N labels, this corresponds
26 to learning N + 2048*N (or 1001*N) model parameters corresponding to the
27 learned biases and weights.
28
29 Here's an example, which assumes you have a folder containing class-named
30 subfolders, each full of images for each label. The example folder flower_photos
31 should have a structure like this:
32
33 ~/flower_photos/daisy/photo1.jpg
34 ~/flower_photos/daisy/photo2.jpg
35 ...
36 ~/flower_photos/rose/anotherphoto77.jpg
37 ...
38 ~/flower_photos/sunflower/somepicture.jpg
39
40 The subfolder names are important, since they define what label is applied to
41 each image, but the filenames themselves don't matter. Once your images are
42 prepared, you can run the training with a command like this:
43
44
45 bash:
46 bazel build tensorflow/examples/image_retraining:retrain && \
47 bazel-bin/tensorflow/examples/image_retraining/retrain \
48 --image_dir ~/flower_photos
49
50
51 Or, if you have a pip installation of tensorflow, `retrain.py` can be run
52 without bazel:
53
54 bash:
55 python tensorflow/examples/image_retraining/retrain.py \
56 --image_dir ~/flower_photos
57
58
59 You can replace the image_dir argument with any folder containing subfolders of
60 images. The label for each image is taken from the name of the subfolder it's
61 in.
62
63 This produces a new model file that can be loaded and run by any TensorFlow
64 program, for example the label_image sample code.
65
66 By default this script will use the high accuracy, but comparatively large and
67 slow Inception v3 model architecture. It's recommended that you start with this
68 to validate that you have gathered good training data, but if you want to deploy
69 on resource-limited platforms, you can try the `--architecture` flag with a
70 Mobilenet model. For example:
71
72 bash:
73 python tensorflow/examples/image_retraining/retrain.py \
74 --image_dir ~/flower_photos --architecture mobilenet_1.0_224
75
76
77 There are 32 different Mobilenet models to choose from, with a variety of file
78 size and latency options. The first number can be '1.0', '0.75', '0.50', or
79 '0.25' to control the size, and the second controls the input image size, either
80 '224', '192', '160', or '128', with smaller sizes running faster. See
81 https://research.googleblog.com/2017/06/mobilenets-open-source-models-for.html
82 for more information on Mobilenet.
83
84 To use with TensorBoard:
85
86 By default, this script will log summaries to /tmp/retrain_logs directory
87
88 Visualize the summaries with this command:
89
90 tensorboard --logdir /tmp/retrain_logs
91
92 """
93 from __future__ import absolute_import
94 from __future__ import division
95 from __future__ import print_function
96
97 import argparse
98 from datetime import datetime
99 import hashlib
100 import os.path
101 import random
102 import re
103 import sys
104 import tarfile
105
106 import numpy as np
107 from six.moves import urllib
108 import tensorflow as tf
109
110 from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util
111 from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
112 from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile
113 from tensorflow.python.util import compat
114
115 FLAGS = None
116
117 # These are all parameters that are tied to the particular model architecture
118 # we're using for Inception v3. These include things like tensor names and their
119 # sizes. If you want to adapt this script to work with another model, you will
120 # need to update these to reflect the values in the network you're using.
121 MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS = 2 ** 27 - 1 # ~134M
122
123
124 def create_image_lists(image_dir, testing_percentage, validation_percentage):
125 """Builds a list of training images from the file system.
126
127 Analyzes the sub folders in the image directory, splits them into stable
128 training, testing, and validation sets, and returns a data structure
129 describing the lists of images for each label and their paths.
130
131 Args:
132 image_dir: String path to a folder containing subfolders of images.
133 testing_percentage: Integer percentage of the images to reserve for tests.
134 validation_percentage: Integer percentage of images reserved for validation.
135
136 Returns:
137 A dictionary containing an entry for each label subfolder, with images split
138 into training, testing, and validation sets within each label.
139 """
140 if not gfile.Exists(image_dir):
141 tf.logging.error("Image directory '" + image_dir + "' not found.")
142 return None
143 result = {}
144 sub_dirs = [x[0] for x in gfile.Walk(image_dir)]
145 # The root directory comes first, so skip it.
146 is_root_dir = True
147 for sub_dir in sub_dirs:
148 if is_root_dir:
149 is_root_dir = False
150 continue
151 extensions = ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'JPG', 'JPEG']
152 file_list = []
153 dir_name = os.path.basename(sub_dir)
154 if dir_name == image_dir:
155 continue
156 tf.logging.info("Looking for images in '" + dir_name + "'")
157 for extension in extensions:
158 file_glob = os.path.join(image_dir, dir_name, '*.' + extension)
159 file_list.extend(gfile.Glob(file_glob))
160 if not file_list:
161 tf.logging.warning('No files found')
162 continue
163 if len(file_list) < 20:
164 tf.logging.warning(
165 'WARNING: Folder has less than 20 images, which may cause issues.')
166 elif len(file_list) > MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS:
167 tf.logging.warning(
168 'WARNING: Folder {} has more than {} images. Some images will '
169 'never be selected.'.format(dir_name, MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS))
170 label_name = re.sub(r'[^a-z0-9]+', ' ', dir_name.lower())
171 training_images = []
172 testing_images = []
173 validation_images = []
174 for file_name in file_list:
175 base_name = os.path.basename(file_name)
176 # We want to ignore anything after '_nohash_' in the file name when
177 # deciding which set to put an image in, the data set creator has a way of
178 # grouping photos that are close variations of each other. For example
179 # this is used in the plant disease data set to group multiple pictures of
180 # the same leaf.
181 hash_name = re.sub(r'_nohash_.*$', '', file_name)
182 # This looks a bit magical, but we need to decide whether this file should
183 # go into the training, testing, or validation sets, and we want to keep
184 # existing files in the same set even if more files are subsequently
185 # added.
186 # To do that, we need a stable way of deciding based on just the file name
187 # itself, so we do a hash of that and then use that to generate a
188 # probability value that we use to assign it.
189 hash_name_hashed = hashlib.sha1(compat.as_bytes(hash_name)).hexdigest()
190 percentage_hash = ((int(hash_name_hashed, 16) %
191 (MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS + 1)) *
192 (100.0 / MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS))
193 if percentage_hash < validation_percentage:
194 validation_images.append(base_name)
195 elif percentage_hash < (testing_percentage + validation_percentage):
196 testing_images.append(base_name)
197 else:
198 training_images.append(base_name)
199 result[label_name] = {
200 'dir': dir_name,
201 'training': training_images,
202 'testing': testing_images,
203 'validation': validation_images,
204 }
205 return result
206
207
208 def get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, index, image_dir, category):
209 """"Returns a path to an image for a label at the given index.
210
211 Args:
212 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
213 label_name: Label string we want to get an image for.
214 index: Int offset of the image we want. This will be moduloed by the
215 available number of images for the label, so it can be arbitrarily large.
216 image_dir: Root folder string of the subfolders containing the training
217 images.
218 category: Name string of set to pull images from - training, testing, or
219 validation.
220
221 Returns:
222 File system path string to an image that meets the requested parameters.
223
224 """
225 if label_name not in image_lists:
226 tf.logging.fatal('Label does not exist %s.', label_name)
227 label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
228 if category not in label_lists:
229 tf.logging.fatal('Category does not exist %s.', category)
230 category_list = label_lists[category]
231 if not category_list:
232 tf.logging.fatal('Label %s has no images in the category %s.',
233 label_name, category)
234 mod_index = index % len(category_list)
235 base_name = category_list[mod_index]
236 sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
237 full_path = os.path.join(image_dir, sub_dir, base_name)
238 return full_path
239
240
241 def get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index, bottleneck_dir,
242 category, architecture):
243 """"Returns a path to a bottleneck file for a label at the given index.
244
245 Args:
246 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
247 label_name: Label string we want to get an image for.
248 index: Integer offset of the image we want. This will be moduloed by the
249 available number of images for the label, so it can be arbitrarily large.
250 bottleneck_dir: Folder string holding cached files of bottleneck values.
251 category: Name string of set to pull images from - training, testing, or
252 validation.
253 architecture: The name of the model architecture.
254
255 Returns:
256 File system path string to an image that meets the requested parameters.
257 """
258 return get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, index, bottleneck_dir,
259 category) + '_' + architecture + '.txt'
260
261
262 def create_model_graph(model_info):
263 """"Creates a graph from saved GraphDef file and returns a Graph object.
264
265 Args:
266 model_info: Dictionary containing information about the model architecture.
267
268 Returns:
269 Graph holding the trained Inception network, and various tensors we'll be
270 manipulating.
271 """
272 with tf.Graph().as_default() as graph:
273 model_path = os.path.join(FLAGS.model_dir, model_info['model_file_name'])
274 with gfile.FastGFile(model_path, 'rb') as f:
275 graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
276 graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
277 bottleneck_tensor, resized_input_tensor = (tf.import_graph_def(
278 graph_def,
279 name='',
280 return_elements=[
281 model_info['bottleneck_tensor_name'],
282 model_info['resized_input_tensor_name'],
283 ]))
284 return graph, bottleneck_tensor, resized_input_tensor
285
286
287 def run_bottleneck_on_image(sess, image_data, image_data_tensor,
288 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
289 bottleneck_tensor):
290 """Runs inference on an image to extract the 'bottleneck' summary layer.
291
292 Args:
293 sess: Current active TensorFlow Session.
294 image_data: String of raw JPEG data.
295 image_data_tensor: Input data layer in the graph.
296 decoded_image_tensor: Output of initial image resizing and preprocessing.
297 resized_input_tensor: The input node of the recognition graph.
298 bottleneck_tensor: Layer before the final softmax.
299
300 Returns:
301 Numpy array of bottleneck values.
302 """
303 # First decode the JPEG image, resize it, and rescale the pixel values.
304 resized_input_values = sess.run(decoded_image_tensor,
305 {image_data_tensor: image_data})
306 # Then run it through the recognition network.
307 bottleneck_values = sess.run(bottleneck_tensor,
308 {resized_input_tensor: resized_input_values})
309 bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values)
310 return bottleneck_values
311
312
313 def maybe_download_and_extract(data_url):
314 """Download and extract model tar file.
315
316 If the pretrained model we're using doesn't already exist, this function
317 downloads it from the TensorFlow.org website and unpacks it into a directory.
318
319 Args:
320 data_url: Web location of the tar file containing the pretrained model.
321 """
322 dest_directory = FLAGS.model_dir
323 if not os.path.exists(dest_directory):
324 os.makedirs(dest_directory)
325 filename = data_url.split('/')[-1]
326 filepath = os.path.join(dest_directory, filename)
327 if not os.path.exists(filepath):
328
329 def _progress(count, block_size, total_size):
330 sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' %
331 (filename,
332 float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0))
333 sys.stdout.flush()
334
335 filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(data_url, filepath, _progress)
336 print()
337 statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
338 tf.logging.info('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size,
339 'bytes.')
340 tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dest_directory)
341
342
343 def ensure_dir_exists(dir_name):
344 """Makes sure the folder exists on disk.
345
346 Args:
347 dir_name: Path string to the folder we want to create.
348 """
349 if not os.path.exists(dir_name):
350 os.makedirs(dir_name)
351
352
353 bottleneck_path_2_bottleneck_values = {}
354
355
356 def create_bottleneck_file(bottleneck_path, image_lists, label_name, index,
357 image_dir, category, sess, jpeg_data_tensor,
358 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
359 bottleneck_tensor):
360 """Create a single bottleneck file."""
361 tf.logging.info('Creating bottleneck at ' + bottleneck_path)
362 image_path = get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, index,
363 image_dir, category)
364 if not gfile.Exists(image_path):
365 tf.logging.fatal('File does not exist %s', image_path)
366 image_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read()
367 try:
368 bottleneck_values = run_bottleneck_on_image(
369 sess, image_data, jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor,
370 resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
371 except Exception as e:
372 raise RuntimeError('Error during processing file %s (%s)' % (image_path,
373 str(e)))
374 bottleneck_string = ','.join(str(x) for x in bottleneck_values)
375 with open(bottleneck_path, 'w') as bottleneck_file:
376 bottleneck_file.write(bottleneck_string)
377
378
379 def get_or_create_bottleneck(sess, image_lists, label_name, index, image_dir,
380 category, bottleneck_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
381 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
382 bottleneck_tensor, architecture):
383 """Retrieves or calculates bottleneck values for an image.
384
385 If a cached version of the bottleneck data exists on-disk, return that,
386 otherwise calculate the data and save it to disk for future use.
387
388 Args:
389 sess: The current active TensorFlow Session.
390 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
391 label_name: Label string we want to get an image for.
392 index: Integer offset of the image we want. This will be modulo-ed by the
393 available number of images for the label, so it can be arbitrarily large.
394 image_dir: Root folder string of the subfolders containing the training
395 images.
396 category: Name string of which set to pull images from - training, testing,
397 or validation.
398 bottleneck_dir: Folder string holding cached files of bottleneck values.
399 jpeg_data_tensor: The tensor to feed loaded jpeg data into.
400 decoded_image_tensor: The output of decoding and resizing the image.
401 resized_input_tensor: The input node of the recognition graph.
402 bottleneck_tensor: The output tensor for the bottleneck values.
403 architecture: The name of the model architecture.
404
405 Returns:
406 Numpy array of values produced by the bottleneck layer for the image.
407 """
408 label_lists = image_lists[label_name]
409 sub_dir = label_lists['dir']
410 sub_dir_path = os.path.join(bottleneck_dir, sub_dir)
411 ensure_dir_exists(sub_dir_path)
412 bottleneck_path = get_bottleneck_path(image_lists, label_name, index,
413 bottleneck_dir, category, architecture)
414 if not os.path.exists(bottleneck_path):
415 create_bottleneck_file(bottleneck_path, image_lists, label_name, index,
416 image_dir, category, sess, jpeg_data_tensor,
417 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
418 bottleneck_tensor)
419 with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file:
420 bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read()
421 did_hit_error = False
422 try:
423 bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')]
424 except ValueError:
425 tf.logging.warning('Invalid float found, recreating bottleneck')
426 did_hit_error = True
427 if did_hit_error:
428 create_bottleneck_file(bottleneck_path, image_lists, label_name, index,
429 image_dir, category, sess, jpeg_data_tensor,
430 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
431 bottleneck_tensor)
432 with open(bottleneck_path, 'r') as bottleneck_file:
433 bottleneck_string = bottleneck_file.read()
434 # Allow exceptions to propagate here, since they shouldn't happen after a
435 # fresh creation
436 bottleneck_values = [float(x) for x in bottleneck_string.split(',')]
437 return bottleneck_values
438
439
440 def cache_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, image_dir, bottleneck_dir,
441 jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor,
442 resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor, architecture):
443 """Ensures all the training, testing, and validation bottlenecks are cached.
444
445 Because we're likely to read the same image multiple times (if there are no
446 distortions applied during training) it can speed things up a lot if we
447 calculate the bottleneck layer values once for each image during
448 preprocessing, and then just read those cached values repeatedly during
449 training. Here we go through all the images we've found, calculate those
450 values, and save them off.
451
452 Args:
453 sess: The current active TensorFlow Session.
454 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
455 image_dir: Root folder string of the subfolders containing the training
456 images.
457 bottleneck_dir: Folder string holding cached files of bottleneck values.
458 jpeg_data_tensor: Input tensor for jpeg data from file.
459 decoded_image_tensor: The output of decoding and resizing the image.
460 resized_input_tensor: The input node of the recognition graph.
461 bottleneck_tensor: The penultimate output layer of the graph.
462 architecture: The name of the model architecture.
463
464 Returns:
465 Nothing.
466 """
467 how_many_bottlenecks = 0
468 ensure_dir_exists(bottleneck_dir)
469 for label_name, label_lists in image_lists.items():
470 for category in ['training', 'testing', 'validation']:
471 category_list = label_lists[category]
472 for index, unused_base_name in enumerate(category_list):
473 get_or_create_bottleneck(
474 sess, image_lists, label_name, index, image_dir, category,
475 bottleneck_dir, jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor,
476 resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor, architecture)
477
478 how_many_bottlenecks += 1
479 if how_many_bottlenecks % 100 == 0:
480 tf.logging.info(
481 str(how_many_bottlenecks) + ' bottleneck files created.')
482
483
484 def get_random_cached_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, how_many, category,
485 bottleneck_dir, image_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
486 decoded_image_tensor, resized_input_tensor,
487 bottleneck_tensor, architecture):
488 """Retrieves bottleneck values for cached images.
489
490 If no distortions are being applied, this function can retrieve the cached
491 bottleneck values directly from disk for images. It picks a random set of
492 images from the specified category.
493
494 Args:
495 sess: Current TensorFlow Session.
496 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
497 how_many: If positive, a random sample of this size will be chosen.
498 If negative, all bottlenecks will be retrieved.
499 category: Name string of which set to pull from - training, testing, or
500 validation.
501 bottleneck_dir: Folder string holding cached files of bottleneck values.
502 image_dir: Root folder string of the subfolders containing the training
503 images.
504 jpeg_data_tensor: The layer to feed jpeg image data into.
505 decoded_image_tensor: The output of decoding and resizing the image.
506 resized_input_tensor: The input node of the recognition graph.
507 bottleneck_tensor: The bottleneck output layer of the CNN graph.
508 architecture: The name of the model architecture.
509
510 Returns:
511 List of bottleneck arrays, their corresponding ground truths, and the
512 relevant filenames.
513 """
514 class_count = len(image_lists.keys())
515 bottlenecks = []
516 ground_truths = []
517 filenames = []
518 if how_many >= 0:
519 # Retrieve a random sample of bottlenecks.
520 for unused_i in range(how_many):
521 label_index = random.randrange(class_count)
522 label_name = list(image_lists.keys())[label_index]
523 image_index = random.randrange(MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS + 1)
524 image_name = get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, image_index,
525 image_dir, category)
526 bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(
527 sess, image_lists, label_name, image_index, image_dir, category,
528 bottleneck_dir, jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor,
529 resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor, architecture)
530 ground_truth = np.zeros(class_count, dtype=np.float32)
531 ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
532 bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
533 ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
534 filenames.append(image_name)
535 else:
536 # Retrieve all bottlenecks.
537 for label_index, label_name in enumerate(image_lists.keys()):
538 for image_index, image_name in enumerate(
539 image_lists[label_name][category]):
540 image_name = get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, image_index,
541 image_dir, category)
542 bottleneck = get_or_create_bottleneck(
543 sess, image_lists, label_name, image_index, image_dir, category,
544 bottleneck_dir, jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor,
545 resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor, architecture)
546 ground_truth = np.zeros(class_count, dtype=np.float32)
547 ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
548 bottlenecks.append(bottleneck)
549 ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
550 filenames.append(image_name)
551 return bottlenecks, ground_truths, filenames
552
553
554 def get_random_distorted_bottlenecks(
555 sess, image_lists, how_many, category, image_dir, input_jpeg_tensor,
556 distorted_image, resized_input_tensor, bottleneck_tensor):
557 """Retrieves bottleneck values for training images, after distortions.
558
559 If we're training with distortions like crops, scales, or flips, we have to
560 recalculate the full model for every image, and so we can't use cached
561 bottleneck values. Instead we find random images for the requested category,
562 run them through the distortion graph, and then the full graph to get the
563 bottleneck results for each.
564
565 Args:
566 sess: Current TensorFlow Session.
567 image_lists: Dictionary of training images for each label.
568 how_many: The integer number of bottleneck values to return.
569 category: Name string of which set of images to fetch - training, testing,
570 or validation.
571 image_dir: Root folder string of the subfolders containing the training
572 images.
573 input_jpeg_tensor: The input layer we feed the image data to.
574 distorted_image: The output node of the distortion graph.
575 resized_input_tensor: The input node of the recognition graph.
576 bottleneck_tensor: The bottleneck output layer of the CNN graph.
577
578 Returns:
579 List of bottleneck arrays and their corresponding ground truths.
580 """
581 class_count = len(image_lists.keys())
582 bottlenecks = []
583 ground_truths = []
584 for unused_i in range(how_many):
585 label_index = random.randrange(class_count)
586 label_name = list(image_lists.keys())[label_index]
587 image_index = random.randrange(MAX_NUM_IMAGES_PER_CLASS + 1)
588 image_path = get_image_path(image_lists, label_name, image_index, image_dir,
589 category)
590 if not gfile.Exists(image_path):
591 tf.logging.fatal('File does not exist %s', image_path)
592 jpeg_data = gfile.FastGFile(image_path, 'rb').read()
593 # Note that we materialize the distorted_image_data as a numpy array before
594 # sending running inference on the image. This involves 2 memory copies and
595 # might be optimized in other implementations.
596 distorted_image_data = sess.run(distorted_image,
597 {input_jpeg_tensor: jpeg_data})
598 bottleneck_values = sess.run(bottleneck_tensor,
599 {resized_input_tensor: distorted_image_data})
600 bottleneck_values = np.squeeze(bottleneck_values)
601 ground_truth = np.zeros(class_count, dtype=np.float32)
602 ground_truth[label_index] = 1.0
603 bottlenecks.append(bottleneck_values)
604 ground_truths.append(ground_truth)
605 return bottlenecks, ground_truths
606
607
608 def should_distort_images(flip_left_right, random_crop, random_scale,
609 random_brightness):
610 """Whether any distortions are enabled, from the input flags.
611
612 Args:
613 flip_left_right: Boolean whether to randomly mirror images horizontally.
614 random_crop: Integer percentage setting the total margin used around the
615 crop box.
616 random_scale: Integer percentage of how much to vary the scale by.
617 random_brightness: Integer range to randomly multiply the pixel values by.
618
619 Returns:
620 Boolean value indicating whether any distortions should be applied.
621 """
622 return (flip_left_right or (random_crop != 0) or (random_scale != 0) or
623 (random_brightness != 0))
624
625
626 def add_input_distortions(flip_left_right, random_crop, random_scale,
627 random_brightness, input_width, input_height,
628 input_depth, input_mean, input_std):
629 """Creates the operations to apply the specified distortions.
630
631 During training it can help to improve the results if we run the images
632 through simple distortions like crops, scales, and flips. These reflect the
633 kind of variations we expect in the real world, and so can help train the
634 model to cope with natural data more effectively. Here we take the supplied
635 parameters and construct a network of operations to apply them to an image.
636
637 Cropping
638 ~~~~~~~~
639
640 Cropping is done by placing a bounding box at a random position in the full
641 image. The cropping parameter controls the size of that box relative to the
642 input image. If it's zero, then the box is the same size as the input and no
643 cropping is performed. If the value is 50%, then the crop box will be half the
644 width and height of the input. In a diagram it looks like this:
645
646 < width >
647 +---------------------+
648 | |
649 | width - crop% |
650 | < > |
651 | +------+ |
652 | | | |
653 | | | |
654 | | | |
655 | +------+ |
656 | |
657 | |
658 +---------------------+
659
660 Scaling
661 ~~~~~~~
662
663 Scaling is a lot like cropping, except that the bounding box is always
664 centered and its size varies randomly within the given range. For example if
665 the scale percentage is zero, then the bounding box is the same size as the
666 input and no scaling is applied. If it's 50%, then the bounding box will be in
667 a random range between half the width and height and full size.
668
669 Args:
670 flip_left_right: Boolean whether to randomly mirror images horizontally.
671 random_crop: Integer percentage setting the total margin used around the
672 crop box.
673 random_scale: Integer percentage of how much to vary the scale by.
674 random_brightness: Integer range to randomly multiply the pixel values by.
675 graph.
676 input_width: Horizontal size of expected input image to model.
677 input_height: Vertical size of expected input image to model.
678 input_depth: How many channels the expected input image should have.
679 input_mean: Pixel value that should be zero in the image for the graph.
680 input_std: How much to divide the pixel values by before recognition.
681
682 Returns:
683 The jpeg input layer and the distorted result tensor.
684 """
685
686 jpeg_data = tf.placeholder(tf.string, name='DistortJPGInput')
687 decoded_image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(jpeg_data, channels=input_depth)
688 decoded_image_as_float = tf.cast(decoded_image, dtype=tf.float32)
689 decoded_image_4d = tf.expand_dims(decoded_image_as_float, 0)
690 margin_scale = 1.0 + (random_crop / 100.0)
691 resize_scale = 1.0 + (random_scale / 100.0)
692 margin_scale_value = tf.constant(margin_scale)
693 resize_scale_value = tf.random_uniform(tensor_shape.scalar(),
694 minval=1.0,
695 maxval=resize_scale)
696 scale_value = tf.multiply(margin_scale_value, resize_scale_value)
697 precrop_width = tf.multiply(scale_value, input_width)
698 precrop_height = tf.multiply(scale_value, input_height)
699 precrop_shape = tf.stack([precrop_height, precrop_width])
700 precrop_shape_as_int = tf.cast(precrop_shape, dtype=tf.int32)
701 precropped_image = tf.image.resize_bilinear(decoded_image_4d,
702 precrop_shape_as_int)
703 precropped_image_3d = tf.squeeze(precropped_image, squeeze_dims=[0])
704 cropped_image = tf.random_crop(precropped_image_3d,
705 [input_height, input_width, input_depth])
706 if flip_left_right:
707 flipped_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(cropped_image)
708 else:
709 flipped_image = cropped_image
710 brightness_min = 1.0 - (random_brightness / 100.0)
711 brightness_max = 1.0 + (random_brightness / 100.0)
712 brightness_value = tf.random_uniform(tensor_shape.scalar(),
713 minval=brightness_min,
714 maxval=brightness_max)
715 brightened_image = tf.multiply(flipped_image, brightness_value)
716 offset_image = tf.subtract(brightened_image, input_mean)
717 mul_image = tf.multiply(offset_image, 1.0 / input_std)
718 distort_result = tf.expand_dims(mul_image, 0, name='DistortResult')
719 return jpeg_data, distort_result
720
721
722 def variable_summaries(var):
723 """Attach a lot of summaries to a Tensor (for TensorBoard visualization)."""
724 with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
725 mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
726 tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)
727 with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
728 stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
729 tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)
730 tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
731 tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
732 tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var)
733
734
735 def add_final_training_ops(class_count, final_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor,
736 bottleneck_tensor_size):
737 """Adds a new softmax and fully-connected layer for training.
738
739 We need to retrain the top layer to identify our new classes, so this function
740 adds the right operations to the graph, along with some variables to hold the
741 weights, and then sets up all the gradients for the backward pass.
742
743 The set up for the softmax and fully-connected layers is based on:
744 https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/master/tutorials/mnist/beginners/index.html
745
746 Args:
747 class_count: Integer of how many categories of things we're trying to
748 recognize.
749 final_tensor_name: Name string for the new final node that produces results.
750 bottleneck_tensor: The output of the main CNN graph.
751 bottleneck_tensor_size: How many entries in the bottleneck vector.
752
753 Returns:
754 The tensors for the training and cross entropy results, and tensors for the
755 bottleneck input and ground truth input.
756 """
757 with tf.name_scope('input'):
758 bottleneck_input = tf.placeholder_with_default(
759 bottleneck_tensor,
760 shape=[None, bottleneck_tensor_size],
761 name='BottleneckInputPlaceholder')
762
763 ground_truth_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,
764 [None, class_count],
765 name='GroundTruthInput')
766
767 # Organizing the following ops as `final_training_ops` so they're easier
768 # to see in TensorBoard
769 layer_name = 'final_training_ops'
770 with tf.name_scope(layer_name):
771 with tf.name_scope('weights'):
772 initial_value = tf.truncated_normal(
773 [bottleneck_tensor_size, class_count], stddev=0.001)
774
775 layer_weights = tf.Variable(initial_value, name='final_weights')
776
777 variable_summaries(layer_weights)
778 with tf.name_scope('biases'):
779 layer_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([class_count]), name='final_biases')
780 variable_summaries(layer_biases)
781 with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
782 logits = tf.matmul(bottleneck_input, layer_weights) + layer_biases
783 tf.summary.histogram('pre_activations', logits)
784
785 final_tensor = tf.nn.softmax(logits, name=final_tensor_name)
786 tf.summary.histogram('activations', final_tensor)
787
788 with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
789 cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
790 labels=ground_truth_input, logits=logits)
791 with tf.name_scope('total'):
792 cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
793 tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy_mean)
794
795 with tf.name_scope('train'):
796 optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(FLAGS.learning_rate)
797 train_step = optimizer.minimize(cross_entropy_mean)
798
799 return (train_step, cross_entropy_mean, bottleneck_input, ground_truth_input,
800 final_tensor)
801
802
803 def add_evaluation_step(result_tensor, ground_truth_tensor):
804 """Inserts the operations we need to evaluate the accuracy of our results.
805
806 Args:
807 result_tensor: The new final node that produces results.
808 ground_truth_tensor: The node we feed ground truth data
809 into.
810
811 Returns:
812 Tuple of (evaluation step, prediction).
813 """
814 with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
815 with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
816 prediction = tf.argmax(result_tensor, 1)
817 correct_prediction = tf.equal(
818 prediction, tf.argmax(ground_truth_tensor, 1))
819 with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
820 evaluation_step = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
821 tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', evaluation_step)
822 return evaluation_step, prediction
823
824
825 def save_graph_to_file(sess, graph, graph_file_name):
826 output_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
827 sess, graph.as_graph_def(), [FLAGS.final_tensor_name])
828 with gfile.FastGFile(graph_file_name, 'wb') as f:
829 f.write(output_graph_def.SerializeToString())
830 return
831
832
833 def prepare_file_system():
834 # Setup the directory we'll write summaries to for TensorBoard
835 if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.summaries_dir):
836 tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.summaries_dir)
837 tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.summaries_dir)
838 if FLAGS.intermediate_store_frequency > 0:
839 ensure_dir_exists(FLAGS.intermediate_output_graphs_dir)
840 return
841
842
843 def create_model_info(architecture):
844 """Given the name of a model architecture, returns information about it.
845
846 There are different base image recognition pretrained models that can be
847 retrained using transfer learning, and this function translates from the name
848 of a model to the attributes that are needed to download and train with it.
849
850 Args:
851 architecture: Name of a model architecture.
852
853 Returns:
854 Dictionary of information about the model, or None if the name isn't
855 recognized
856
857 Raises:
858 ValueError: If architecture name is unknown.
859 """
860 architecture = architecture.lower()
861 if architecture == 'inception_v3':
862 # pylint: disable=line-too-long
863 data_url = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/models/image/imagenet/inception-2015-12-05.tgz'
864 # pylint: enable=line-too-long
865 bottleneck_tensor_name = 'pool_3/_reshape:0'
866 bottleneck_tensor_size = 2048
867 input_width = 299
868 input_height = 299
869 input_depth = 3
870 resized_input_tensor_name = 'Mul:0'
871 model_file_name = 'classify_image_graph_def.pb'
872 input_mean = 128
873 input_std = 128
874 elif architecture.startswith('mobilenet_'):
875 parts = architecture.split('_')
876 if len(parts) != 3 and len(parts) != 4:
877 tf.logging.error("Couldn't understand architecture name '%s'",
878 architecture)
879 return None
880 version_string = parts[1]
881 if (version_string != '1.0' and version_string != '0.75' and
882 version_string != '0.50' and version_string != '0.25'):
883 tf.logging.error(
884 """"The Mobilenet version should be '1.0', '0.75', '0.50', or '0.25',
885 but found '%s' for architecture '%s'""",
886 version_string, architecture)
887 return None
888 size_string = parts[2]
889 if (size_string != '224' and size_string != '192' and
890 size_string != '160' and size_string != '128'):
891 tf.logging.error(
892 """The Mobilenet input size should be '224', '192', '160', or '128',
893 but found '%s' for architecture '%s'""",
894 size_string, architecture)
895 return None
896 if len(parts) == 3:
897 is_quantized = False
898 else:
899 if parts[3] != 'quantized':
900 tf.logging.error(
901 "Couldn't understand architecture suffix '%s' for '%s'", parts[3],
902 architecture)
903 return None
904 is_quantized = True
905 data_url = 'http://download.tensorflow.org/models/mobilenet_v1_'
906 data_url += version_string + '_' + size_string + '_frozen.tgz'
907 bottleneck_tensor_name = 'MobilenetV1/Predictions/Reshape:0'
908 bottleneck_tensor_size = 1001
909 input_width = int(size_string)
910 input_height = int(size_string)
911 input_depth = 3
912 resized_input_tensor_name = 'input:0'
913 if is_quantized:
914 model_base_name = 'quantized_graph.pb'
915 else:
916 model_base_name = 'frozen_graph.pb'
917 model_dir_name = 'mobilenet_v1_' + version_string + '_' + size_string
918 model_file_name = os.path.join(model_dir_name, model_base_name)
919 input_mean = 127.5
920 input_std = 127.5
921 else:
922 tf.logging.error("Couldn't understand architecture name '%s'", architecture)
923 raise ValueError('Unknown architecture', architecture)
924
925 return {
926 'data_url': data_url,
927 'bottleneck_tensor_name': bottleneck_tensor_name,
928 'bottleneck_tensor_size': bottleneck_tensor_size,
929 'input_width': input_width,
930 'input_height': input_height,
931 'input_depth': input_depth,
932 'resized_input_tensor_name': resized_input_tensor_name,
933 'model_file_name': model_file_name,
934 'input_mean': input_mean,
935 'input_std': input_std,
936 }
937
938
939 def add_jpeg_decoding(input_width, input_height, input_depth, input_mean,
940 input_std):
941 """Adds operations that perform JPEG decoding and resizing to the graph..
942
943 Args:
944 input_width: Desired width of the image fed into the recognizer graph.
945 input_height: Desired width of the image fed into the recognizer graph.
946 input_depth: Desired channels of the image fed into the recognizer graph.
947 input_mean: Pixel value that should be zero in the image for the graph.
948 input_std: How much to divide the pixel values by before recognition.
949
950 Returns:
951 Tensors for the node to feed JPEG data into, and the output of the
952 preprocessing steps.
953 """
954 jpeg_data = tf.placeholder(tf.string, name='DecodeJPGInput')
955 decoded_image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(jpeg_data, channels=input_depth)
956 decoded_image_as_float = tf.cast(decoded_image, dtype=tf.float32)
957 decoded_image_4d = tf.expand_dims(decoded_image_as_float, 0)
958 resize_shape = tf.stack([input_height, input_width])
959 resize_shape_as_int = tf.cast(resize_shape, dtype=tf.int32)
960 resized_image = tf.image.resize_bilinear(decoded_image_4d,
961 resize_shape_as_int)
962 offset_image = tf.subtract(resized_image, input_mean)
963 mul_image = tf.multiply(offset_image, 1.0 / input_std)
964 return jpeg_data, mul_image
965
966
967 def main(_):
968 # Needed to make sure the logging output is visible.
969 # See https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/3047
970 tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
971
972 # Prepare necessary directories that can be used during training
973 prepare_file_system()
974
975 # Gather information about the model architecture we'll be using.
976 model_info = create_model_info(FLAGS.architecture)
977 if not model_info:
978 tf.logging.error('Did not recognize architecture flag')
979 return -1
980
981 # Set up the pre-trained graph.
982 maybe_download_and_extract(model_info['data_url'])
983 graph, bottleneck_tensor, resized_image_tensor = (
984 create_model_graph(model_info))
985
986 # Look at the folder structure, and create lists of all the images.
987 image_lists = create_image_lists(FLAGS.image_dir, FLAGS.testing_percentage,
988 FLAGS.validation_percentage)
989 class_count = len(image_lists.keys())
990 if class_count == 0:
991 tf.logging.error('No valid folders of images found at ' + FLAGS.image_dir)
992 return -1
993 if class_count == 1:
994 tf.logging.error('Only one valid folder of images found at ' +
995 FLAGS.image_dir +
996 ' - multiple classes are needed for classification.')
997 return -1
998
999 # See if the command-line flags mean we're applying any distortions.
1000 do_distort_images = should_distort_images(
1001 FLAGS.flip_left_right, FLAGS.random_crop, FLAGS.random_scale,
1002 FLAGS.random_brightness)
1003
1004 with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess:
1005 # Set up the image decoding sub-graph.
1006 jpeg_data_tensor, decoded_image_tensor = add_jpeg_decoding(
1007 model_info['input_width'], model_info['input_height'],
1008 model_info['input_depth'], model_info['input_mean'],
1009 model_info['input_std'])
1010
1011 if do_distort_images:
1012 # We will be applying distortions, so setup the operations we'll need.
1013 (distorted_jpeg_data_tensor,
1014 distorted_image_tensor) = add_input_distortions(
1015 FLAGS.flip_left_right, FLAGS.random_crop, FLAGS.random_scale,
1016 FLAGS.random_brightness, model_info['input_width'],
1017 model_info['input_height'], model_info['input_depth'],
1018 model_info['input_mean'], model_info['input_std'])
1019 else:
1020 # We'll make sure we've calculated the 'bottleneck' image summaries and
1021 # cached them on disk.
1022 cache_bottlenecks(sess, image_lists, FLAGS.image_dir,
1023 FLAGS.bottleneck_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
1024 decoded_image_tensor, resized_image_tensor,
1025 bottleneck_tensor, FLAGS.architecture)
1026
1027 # Add the new layer that we'll be training.
1028 (train_step, cross_entropy, bottleneck_input, ground_truth_input,
1029 final_tensor) = add_final_training_ops(
1030 len(image_lists.keys()), FLAGS.final_tensor_name, bottleneck_tensor,
1031 model_info['bottleneck_tensor_size'])
1032
1033 # Create the operations we need to evaluate the accuracy of our new layer.
1034 evaluation_step, prediction = add_evaluation_step(
1035 final_tensor, ground_truth_input)
1036
1037 # Merge all the summaries and write them out to the summaries_dir
1038 merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
1039 train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.summaries_dir + '/train',
1040 sess.graph)
1041
1042 validation_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(
1043 FLAGS.summaries_dir + '/validation')
1044
1045 # Set up all our weights to their initial default values.
1046 init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
1047 sess.run(init)
1048
1049 # Run the training for as many cycles as requested on the command line.
1050 for i in range(FLAGS.how_many_training_steps):
1051 # Get a batch of input bottleneck values, either calculated fresh every
1052 # time with distortions applied, or from the cache stored on disk.
1053 if do_distort_images:
1054 (train_bottlenecks,
1055 train_ground_truth) = get_random_distorted_bottlenecks(
1056 sess, image_lists, FLAGS.train_batch_size, 'training',
1057 FLAGS.image_dir, distorted_jpeg_data_tensor,
1058 distorted_image_tensor, resized_image_tensor, bottleneck_tensor)
1059 else:
1060 (train_bottlenecks,
1061 train_ground_truth, _) = get_random_cached_bottlenecks(
1062 sess, image_lists, FLAGS.train_batch_size, 'training',
1063 FLAGS.bottleneck_dir, FLAGS.image_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
1064 decoded_image_tensor, resized_image_tensor, bottleneck_tensor,
1065 FLAGS.architecture)
1066 # Feed the bottlenecks and ground truth into the graph, and run a training
1067 # step. Capture training summaries for TensorBoard with the `merged` op.
1068 train_summary, _ = sess.run(
1069 [merged, train_step],
1070 feed_dict={bottleneck_input: train_bottlenecks,
1071 ground_truth_input: train_ground_truth})
1072 train_writer.add_summary(train_summary, i)
1073
1074 # Every so often, print out how well the graph is training.
1075 is_last_step = (i + 1 == FLAGS.how_many_training_steps)
1076 if (i % FLAGS.eval_step_interval) == 0 or is_last_step:
1077 train_accuracy, cross_entropy_value = sess.run(
1078 [evaluation_step, cross_entropy],
1079 feed_dict={bottleneck_input: train_bottlenecks,
1080 ground_truth_input: train_ground_truth})
1081 tf.logging.info('%s: Step %d: Train accuracy = %.1f%%' %
1082 (datetime.now(), i, train_accuracy * 100))
1083 tf.logging.info('%s: Step %d: Cross entropy = %f' %
1084 (datetime.now(), i, cross_entropy_value))
1085 validation_bottlenecks, validation_ground_truth, _ = (
1086 get_random_cached_bottlenecks(
1087 sess, image_lists, FLAGS.validation_batch_size, 'validation',
1088 FLAGS.bottleneck_dir, FLAGS.image_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
1089 decoded_image_tensor, resized_image_tensor, bottleneck_tensor,
1090 FLAGS.architecture))
1091 # Run a validation step and capture training summaries for TensorBoard
1092 # with the `merged` op.
1093 validation_summary, validation_accuracy = sess.run(
1094 [merged, evaluation_step],
1095 feed_dict={bottleneck_input: validation_bottlenecks,
1096 ground_truth_input: validation_ground_truth})
1097 validation_writer.add_summary(validation_summary, i)
1098 tf.logging.info('%s: Step %d: Validation accuracy = %.1f%% (N=%d)' %
1099 (datetime.now(), i, validation_accuracy * 100,
1100 len(validation_bottlenecks)))
1101
1102 # Store intermediate results
1103 intermediate_frequency = FLAGS.intermediate_store_frequency
1104
1105 if (intermediate_frequency > 0 and (i % intermediate_frequency == 0)
1106 and i > 0):
1107 intermediate_file_name = (FLAGS.intermediate_output_graphs_dir +
1108 'intermediate_' + str(i) + '.pb')
1109 tf.logging.info('Save intermediate result to : ' +
1110 intermediate_file_name)
1111 save_graph_to_file(sess, graph, intermediate_file_name)
1112
1113 # We've completed all our training, so run a final test evaluation on
1114 # some new images we haven't used before.
1115 test_bottlenecks, test_ground_truth, test_filenames = (
1116 get_random_cached_bottlenecks(
1117 sess, image_lists, FLAGS.test_batch_size, 'testing',
1118 FLAGS.bottleneck_dir, FLAGS.image_dir, jpeg_data_tensor,
1119 decoded_image_tensor, resized_image_tensor, bottleneck_tensor,
1120 FLAGS.architecture))
1121 test_accuracy, predictions = sess.run(
1122 [evaluation_step, prediction],
1123 feed_dict={bottleneck_input: test_bottlenecks,
1124 ground_truth_input: test_ground_truth})
1125 tf.logging.info('Final test accuracy = %.1f%% (N=%d)' %
1126 (test_accuracy * 100, len(test_bottlenecks)))
1127
1128 if FLAGS.print_misclassified_test_images:
1129 tf.logging.info('=== MISCLASSIFIED TEST IMAGES ===')
1130 for i, test_filename in enumerate(test_filenames):
1131 if predictions[i] != test_ground_truth[i].argmax():
1132 tf.logging.info('%70s %s' %
1133 (test_filename,
1134 list(image_lists.keys())[predictions[i]]))
1135
1136 # Write out the trained graph and labels with the weights stored as
1137 # constants.
1138 save_graph_to_file(sess, graph, FLAGS.output_graph)
1139 with gfile.FastGFile(FLAGS.output_labels, 'w') as f:
1140 f.write('\n'.join(image_lists.keys()) + '\n')
1141
1142
1143 if __name__ == '__main__':
1144 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
1145 parser.add_argument(
1146 '--image_dir',
1147 type=str,
1148 default='data/train',
1149 help='Path to folders of labeled images.'
1150 )
1151 parser.add_argument(
1152 '--output_graph',
1153 type=str,
1154 default='tmp/output_graph.pb',
1155 help='Where to save the trained graph.'
1156 )
1157 parser.add_argument(
1158 '--intermediate_output_graphs_dir',
1159 type=str,
1160 default='tmp/intermediate_graph/',
1161 help='Where to save the intermediate graphs.'
1162 )
1163 parser.add_argument(
1164 '--intermediate_store_frequency',
1165 type=int,
1166 default=0,
1167 help="""\
1168 How many steps to store intermediate graph. If "0" then will not
1169 store.\
1170 """
1171 )
1172 parser.add_argument(
1173 '--output_labels',
1174 type=str,
1175 default='tmp/output_labels.txt',
1176 help='Where to save the trained graph\'s labels.'
1177 )
1178 parser.add_argument(
1179 '--summaries_dir',
1180 type=str,
1181 default='tmp/retrain_logs',
1182 help='Where to save summary logs for TensorBoard.'
1183 )
1184 parser.add_argument(
1185 '--how_many_training_steps',
1186 type=int,
1187 default=200,
1188 help='How many training steps to run before ending.'
1189 )
1190 parser.add_argument(
1191 '--learning_rate',
1192 type=float,
1193 default=0.01,
1194 help='How large a learning rate to use when training.'
1195 )
1196 parser.add_argument(
1197 '--testing_percentage',
1198 type=int,
1199 default=10,
1200 help='What percentage of images to use as a test set.'
1201 )
1202 parser.add_argument(
1203 '--validation_percentage',
1204 type=int,
1205 default=10,
1206 help='What percentage of images to use as a validation set.'
1207 )
1208 parser.add_argument(
1209 '--eval_step_interval',
1210 type=int,
1211 default=10,
1212 help='How often to evaluate the training results.'
1213 )
1214 parser.add_argument(
1215 '--train_batch_size',
1216 type=int,
1217 default=100,
1218 help='How many images to train on at a time.'
1219 )
1220 parser.add_argument(
1221 '--test_batch_size',
1222 type=int,
1223 default=-1,
1224 help="""\
1225 How many images to test on. This test set is only used once, to evaluate
1226 the final accuracy of the model after training completes.
1227 A value of -1 causes the entire test set to be used, which leads to more
1228 stable results across runs.\
1229 """
1230 )
1231 parser.add_argument(
1232 '--validation_batch_size',
1233 type=int,
1234 default=100,
1235 help="""\
1236 How many images to use in an evaluation batch. This validation set is
1237 used much more often than the test set, and is an early indicator of how
1238 accurate the model is during training.
1239 A value of -1 causes the entire validation set to be used, which leads to
1240 more stable results across training iterations, but may be slower on large
1241 training sets.\
1242 """
1243 )
1244 parser.add_argument(
1245 '--print_misclassified_test_images',
1246 default=False,
1247 help="""\
1248 Whether to print out a list of all misclassified test images.\
1249 """,
1250 action='store_true'
1251 )
1252 parser.add_argument(
1253 '--model_dir',
1254 type=str,
1255 default='tmp/imagenet',
1256 help="""\
1257 Path to classify_image_graph_def.pb,
1258 imagenet_synset_to_human_label_map.txt, and
1259 imagenet_2012_challenge_label_map_proto.pbtxt.\
1260 """
1261 )
1262 parser.add_argument(
1263 '--bottleneck_dir',
1264 type=str,
1265 default='tmp/bottleneck',
1266 help='Path to cache bottleneck layer values as files.'
1267 )
1268 parser.add_argument(
1269 '--final_tensor_name',
1270 type=str,
1271 default='final_result',
1272 help="""\
1273 The name of the output classification layer in the retrained graph.\
1274 """
1275 )
1276 parser.add_argument(
1277 '--flip_left_right',
1278 default=False,
1279 help="""\
1280 Whether to randomly flip half of the training images horizontally.\
1281 """,
1282 action='store_true'
1283 )
1284 parser.add_argument(
1285 '--random_crop',
1286 type=int,
1287 default=0,
1288 help="""\
1289 A percentage determining how much of a margin to randomly crop off the
1290 training images.\
1291 """
1292 )
1293 parser.add_argument(
1294 '--random_scale',
1295 type=int,
1296 default=0,
1297 help="""\
1298 A percentage determining how much to randomly scale up the size of the
1299 training images by.\
1300 """
1301 )
1302 parser.add_argument(
1303 '--random_brightness',
1304 type=int,
1305 default=0,
1306 help="""\
1307 A percentage determining how much to randomly multiply the training image
1308 input pixels up or down by.\
1309 """
1310 )
1311 parser.add_argument(
1312 '--architecture',
1313 type=str,
1314 default='inception_v3',
1315 help="""\
1316 Which model architecture to use. 'inception_v3' is the most accurate, but
1317 also the slowest. For faster or smaller models, chose a MobileNet with the
1318 form 'mobilenet__[_quantized]'. For example,
1319 'mobilenet_1.0_224' will pick a model that is 17 MB in size and takes 224
1320 pixel input images, while 'mobilenet_0.25_128_quantized' will choose a much
1321 less accurate, but smaller and faster network that's 920 KB on disk and
1322 takes 128x128 images. See https://research.googleblog.com/2017/06/mobilenets-open-source-models-for.html
1323 for more information on Mobilenet.\
1324 """)
1325 FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
1326 tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)
3.测试
直接上代码:(路径根据个人情况修改)
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 """
3 Created on Fri Oct 13 16:15:16 2017
4 use_output_graph
5 使用retrain所训练的迁移后的inception模型来测试
6 @author: Dexter
7 """
8 import tensorflow as tf
9 import numpy as np
10 import os
11 from PIL import Image
12 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
13
14 model_name = 'tmp/output_graph.pb'
15 image_dir = 'data/validation'
16 label_filename = 'tmp/output_labels.txt'
17
18 # 读取并创建一个图graph来存放Google训练好的Inception_v3模型(函数)
19 def create_graph():
20 with tf.gfile.FastGFile( model_name, 'rb') as f:
21 # 使用tf.GraphDef()定义一个空的Graph
22 graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
23 graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
24 # Imports the graph from graph_def into the current default Graph.
25 tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name='')
26
27 # 读取标签labels
28 def load_labels(label_file_dir):
29 if not tf.gfile.Exists(label_file_dir):
30 # 预先检测地址是否存在
31 tf.logging.fatal('File does not exist %s', label_file_dir)
32 else:
33 # 读取所有的标签返并回一个list
34 labels = tf.gfile.GFile(label_file_dir).readlines()
35 for i in range(len(labels)):
36 labels[i] = labels[i].strip('\n')
37 return labels
38
39 # 创建graph
40 create_graph()
41
42 # 创建会话,因为是从已有的Inception_v3模型中恢复,所以无需初始化
43 with tf.Session() as sess:
44 # Inception_v3模型的最后一层final_result:0的输出
45 softmax_tensor = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name('final_result:0')
46
47 # 遍历目录
48 for root, dirs, files in os.walk(image_dir):
49 for file in files:
50 # 载入图片
51 image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(os.path.join(root, file), 'rb').read()
52 # 输入图像(jpg格式)数据,得到softmax概率值(一个shape=(1,1008)的向量)
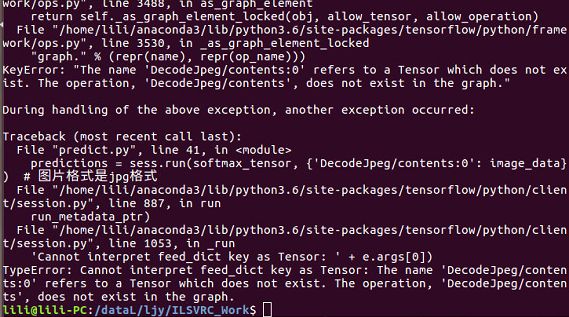
53 predictions = sess.run(softmax_tensor,{'DecodeJpeg/contents:0': image_data})
54 # 将结果转为1维数据
55 predictions = np.squeeze(predictions)
56
57 # 打印图片路径及名称
58 image_path = os.path.join(root, file)
59 print(image_path)
60 # 显示图片
61 img = Image.open(image_path)
62 plt.imshow(img)
63 plt.axis('off')
64 plt.show()
65
66 # 排序,取出前5个概率最大的值(top-5),本数据集一共就5个
67 # argsort()返回的是数组值从小到大排列所对应的索引值
68 top_5 = predictions.argsort()[-5:][::-1]
69 for label_index in top_5:
70 # 获取分类名称
71 label_name = load_labels(label_filename)[label_index]
72 # 获取该分类的置信度
73 label_score = predictions[label_index]
74 print('%s (score = %.5f)' % (label_name, label_score))
75 print()
完。