像React,Vue这类的框架,响应式是其最核心的特性之一。通过响应式可以实现当改变数据的时候,视图会自动变化,反之,视图变化,数据也随之更新。避免了繁琐的dom操作,让开发者在开发的时候只需要关注数据本身,而不需要关注数据如何渲染到视图。
实现原理
2.x
在vue2.0中通过Object.defineProperty方法实现数据拦截,也就是为每个属性添加get和set方法,当获取属性值和修改属性值的时候会触发get和set方法。
let vue = {}
let data = {
msg: 'foo'
}
Object.defineProperty(vue, 'msg', {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
console.log('正在获取msg属性对应的值')
return data.msg
},
set(newValue) {
if(newValue === data.msg) {
return
}
console.log('正在为msg属性赋值')
data.msg = newValue
}
})
console.log(vue.msg)
vue.msg = 'bar'Object.defineProperty添加的数据拦截在针对数组的时候会出现问题,也就是当属性值为一个数组的时候,如果进行push,shift等操作的时候,虽然修改了数组,但不会触发set拦截。
为了解决这个问题,vue在内部重写了原生的数组操作方法,以支持响应式。
3.x
在vue3.0版本中使用ES6新增的Proxy对象替换了Object.defineProperty,不仅简化了添加拦截的语法,同时也可以支持数组。
let data = {
msg: 'foo'
}
let vue = new Proxy(data, {
get(target, key) {
console.log('正在获取msg属性对应的值')
return target[key]
},
set(target, key, newValue) {
if(newValue === target[key]) {
return
}
console.log('正在为msg属性赋值')
target[key] = newValue
}
})
console.log(vue.msg)
vue.msg = 'bar'依赖的开发模式
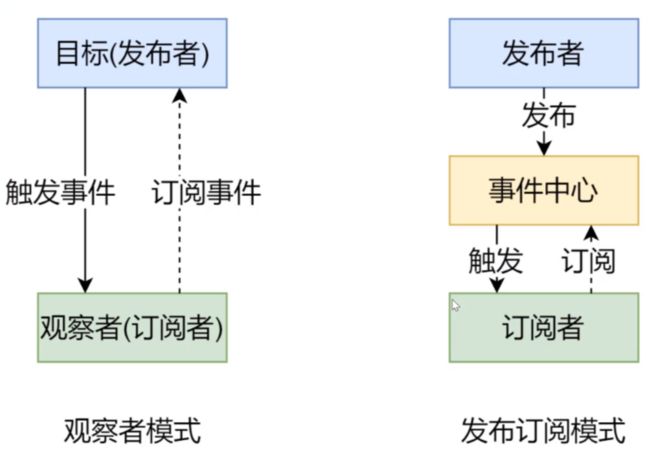
在vue实现响应式的代码中,使用了观察者模式。
观察者模式
观察者模式中,包含两个部分:
- 观察者watcher
观察者包含一个update方法,此方法表示当事件发生变化的时候需要做的事情
class Watcher {
update() {
console.log('执行操作')
}
}- 目标dep
目标包含一个属性和两个方法:
- subs属性:用于存储所有注册的观察者。
- addSub方法: 用于添加观察者。
- notify方法: 当事件变化的时候,用于轮询subs中所有的观察者,并执行其update方法。
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subs = []
}
addSub(watcher) {
if (watcher.update) {
this.subs.push(watcher)
}
}
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(watcher => {
watcher.update()
})
}
}- 使用方式
// 创建观察者和目标对象
const w = new Watcher()
const d = new Dep()
// 添加观察者
d.addSub(w)
// 触发变化
d.notify()发布订阅模式
与观察者模式很相似的是发布订阅模式,该模式包含三个方面:
- 订阅者
订阅者类似观察者模式中的观察者,当事件发生变化的时候,订阅者会执行相应的操作。
- 发布者
发布者类似观察者模式中的目标,其用于发布变化。
- 事件中心
在事件中心中存储着事件对应的所有订阅者,当发布者发布事件变化后,事件中心会通知所有的订阅者执行相应操作。
与观察者模式相比,发布订阅模式多了一个事件中心,其作用是隔离订阅者和发布者之间的依赖。
vue中的on和emit就是实现的发布订阅模式,因为其和响应式原理关系不大,所以此处不再详细说明。
自实现简版vue
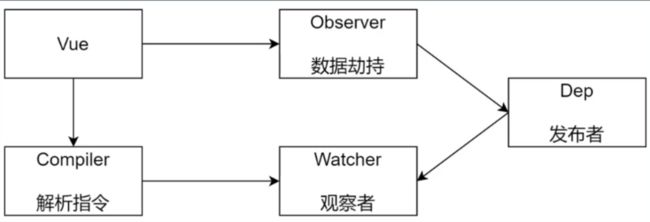
简化版的vue核心包含5大类,如下图:
通过实现这5大类,就可以一窥Vue内部如何实现响应式。
vue
vue是框架的入口,负责存储用户变量、添加数据拦截,启动模版编译。
Vue类:
- 属性
$options 存储初始化Vue实例时传递的参数$data 存储响应式数据$methods 存储传入的所有函数$el 编译的模版节点
- 方法
_proxyData 私有方法,负责将data中所有属性添加到Vue实例上。
_proxyMethods 私有方法,遍历传入的函数,将非声明周期函数添加到Vue实例上。
directive 静态方法,用于向Vue注入指令。
- 实现
// 所有声明周期方法名称
const hooks = ['beforeCreate', 'created', 'beforeMount', 'mounted',
'beforeUpdate', 'updated', 'activated', 'deactivated', 'beforeDestroy', 'destroyed']
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = Object.assign(Vue.options || {}, options || {})
this.$data = options.data || {}
this.$methods = options.methods || {}
if (options && options.el) {
this.$el = typeof options.el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
}
this._proxyData(this.$data)
this._proxyMethods(this.$methods)
// 实现数据拦截
// 启动模版编译
}
_proxyMethods(methods) {
let obj = {}
Object.keys(methods).forEach(key => {
if (hooks.indexOf(key) === -1 && typeof methods[key] === 'function') {
obj[key] = methods[key].bind(this)
}
})
this._proxyData(obj)
}
_proxyData(data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
// 数据未发生任何变化,不需要处理
if (newValue === data[key]) {
return
}
data[key] = newValue
}
})
})
}
// 用于注册指令的方法
static directive(name, handle) {
if (!Vue.options) {
Vue.options = {
directives: {}
}
}
Vue.options.directives[name] = {
bind: handle,
update: handle
}
}
}observer
observer类负责为data对象添加数据拦截。
- 方法
walk 轮询对象属性,调用defineReactive方法为每个属性添加setter和getter。defineReactive 添加setter和getter。
- 实现
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data)
}
// 轮询对象
walk(data) {
// 只有data为object对象时,才轮询其属性
if (data && typeof data === 'object') {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
}
// 添加拦截
defineReactive(data, key, val) {
const that = this
// 如果val是一个对象,为对象的每一个属性添加拦截
this.walk(val)
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return val
},
set(newValue) {
if (val === newValue) {
return
}
// 如果赋值为一个对象,为对象的每一个属性添加拦截
that.walk(newValue)
val = newValue
}
})
}
}在Vue的constructor构造函数中添加Observer:
constructor(options) {
this.$options = Object.assign(Vue.options || {}, options || {})
this.$data = options.data || {}
this.$methods = options.methods || {}
if (options && options.el) {
this.$el = typeof options.el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
}
this._proxyData(this.$data)
this._proxyMethods(this.$methods)
// 实现数据拦截
new Observer(this.$data)
// 启动模版编译
new Compiler(this)
}directive
由于在compiler编译模版的时候,需要用到指令解析,所以此处模拟一个指令初始化方法,用于向vue实例添加内置指令。
在此处模拟实现了四个指令:
// v-text
Vue.directive('text', function (el, binding) {
const { value } = binding
el.textContent = value
})
// v-model
Vue.directive('model', function (el, binding) {
const { value, expression } = binding
el.value = value
// 实现双向绑定
el.addEventListener('input', () => {
el.vm[expression] = el.value
})
})
// v-html
Vue.directive('html', function (el, binding) {
const { value } = binding
el.innerHTML = value
})
// v-on
Vue.directive('on', function (el, binding) {
const { value, argument } = binding
el.addEventListener(argument, value)
})compiler
compiler负责html模版编译,解析模版中的插值表达式和指令等。
- 属性
el 保存编译的目标元素vm 保存编译时用到的vue上下文信息。
- 方法
compile 负责具体的html编译。
- 实现
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.vm = vm
this.el = vm.$el
// 构造函数中执行编译
this.compile(this.el)
}
compile(el) {
if (!el) {
return
}
const children = el.childNodes
Array.from(children).forEach(node => {
if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
this.compileElement(node)
} else if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
this.compileText(node)
}
// 递归处理node下面的子节点
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
compileElement(node) {
const directives = this.vm.$options.directives
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
// 判断是否是指令
let attrName = attr.name
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// v-text --> text
// 获取指令的相关数据
let attrNames = attrName.substr(2).split(':')
let name = attrNames[0]
let arg = attrNames[1]
let key = attr.value
// 获取注册的指令并执行
if (directives[name]) {
node.vm = this.vm
// 执行指令绑定
directives[name].bind(node, {
name: name,
value: this.vm[key],
argument: arg,
expression: key
})
}
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
// 利用正则表达式匹配插值表达式
let reg = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/
const value = node.textContent
if (reg.test(value)) {
let key = RegExp.$1.trim()
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key])
}
}
// 判断元素属性是否是指令,简化vue原来逻辑,现在默认只有v-开头的属性是指令
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith('v-')
}
// 判断节点是否是文本节点
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3
}
// 判断节点是否是元素节点
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}修改vue的构造函数,启动模版编译。
constructor(options) {
this.$options = Object.assign(Vue.options || {}, options || {})
this.$data = options.data || {}
this.$methods = options.methods || {}
if (options && options.el) {
this.$el = typeof options.el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
}
this._proxyData(this.$data)
this._proxyMethods(this.$methods)
// 实现数据拦截
new Observer(this.$data)
// 启动模版编译
new Compiler(this)
}dep
dep负责收集某个属性的所有观察者,当属性值发生变化的时候,会依次执行观察者的update方法。
- 属性
subs 记录所有的观察者
- 方法
addSub 添加观察者notify 触发执行所有观察者的update方法
- 实现
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 存储所有的观察者
this.subs = []
}
// 添加观察者
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// 发送通知
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
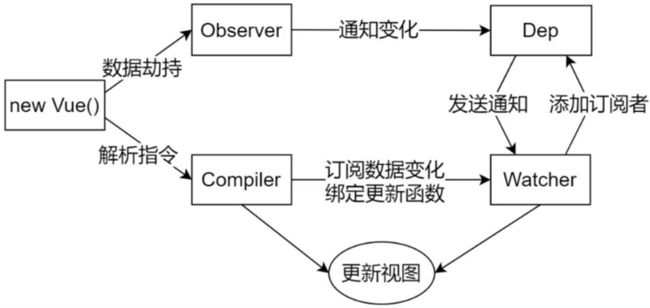
}现在的问题是何时添加观察者,何时触发更新?
从上图可以看出,应该在Observer中触发拦截的时候对Dep进行操作,也就是get的时候添加观察者,set时触发更新。
修改observer的defineReactive方法:
defineReactive(data, key, val) {
const that = this
// 创建dep对象
const dep = new Dep()
// 如果val是一个对象,为对象的每一个属性添加拦截
this.walk(val)
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
// 添加依赖
// 在watcher中,获取属性值的时候,会把相应的观察者添加到Dep.target属性上
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
return val
},
set(newValue) {
if (val === newValue) {
return
}
// 如果赋值为一个对象,为对象的每一个属性添加拦截
that.walk(newValue)
val = newValue
// 触发更新
dep.notify()
}
})
}watcher
watcher是观察者对象,在vue对象的属性发生变化的时候执行相应的更新操作。
- 方法
update 执行具体的更新操作
- 实现
class Watcher {
// vm: vue实例
// key: 监控的属性键值
// cb: 回调函数,执行具体更新
constructor(vm, key, cb) {
this.vm = vm
this.key = key
this.cb = cb
// 指定在这个执行环境下的watcher实例
Dep.target = this
// 获取旧的数据,触发get方法中Dep.addSub
this.oldValue = vm[key]
// 删除target,等待下一次赋值
Dep.target = null
}
update() {
let newValue = this.vm[this.key]
if (this.oldValue === newValue) {
return
}
this.cb(newValue)
this.oldValue = newValue
}
}由于需要数据双向绑定,在compiler编译模版的时候,创建Watcher实例,并指定具体如何更新页面。
compileElement(node) {
const directives = this.vm.$options.directives
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
// 判断是否是指令
let attrName = attr.name
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// v-text --> text
// 获取指令的相关数据
let attrNames = attrName.substr(2).split(':')
let name = attrNames[0]
let arg = attrNames[1]
let key = attr.value
// 获取注册的指令并执行
if (directives[name]) {
node.vm = this.vm
// 执行指令绑定
directives[name].bind(node, {
name: name,
value: this.vm[key],
argument: arg,
expression: key
})
new Watcher(this.vm, key, () => {
directives[name].update(node, {
name: name,
value: this.vm[key],
argument: arg,
expression: key
})
})
}
}
})
}