Atcoder Grand Contest 011F - Train Service Planning
Problem Statement
There is a railroad in Takahashi Kingdom. The railroad consists of N sections, numbered 1, 2, ..., N, and N+1 stations, numbered 0, 1, ..., N. Section i directly connects the stations i−1 and i. A train takes exactly Ai minutes to run through section i, regardless of direction. Each of the N sections is either single-tracked over the whole length, or double-tracked over the whole length. If Bi=1, section i is single-tracked; if Bi=2, section i is double-tracked. Two trains running in opposite directions can cross each other on a double-tracked section, but not on a single-tracked section. Trains can also cross each other at a station.
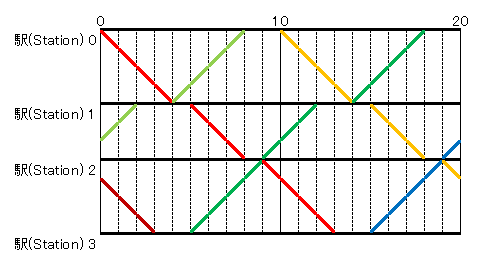
Snuke is creating the timetable for this railroad. In this timetable, the trains on the railroad run every K minutes, as shown in the following figure. Here, bold lines represent the positions of trains running on the railroad. (See Sample 1 for clarification.)
When creating such a timetable, find the minimum sum of the amount of time required for a train to depart station 0 and reach station N, and the amount of time required for a train to depart station N and reach station 0. It can be proved that, if there exists a timetable satisfying the conditions in this problem, this minimum sum is always an integer.
Formally, the times at which trains arrive and depart must satisfy the following:
- Each train either departs station 0 and is bound for station N, or departs station N and is bound for station 0.
- Each train takes exactly Ai minutes to run through section i. For example, if a train bound for station N departs station i−1 at time t, the train arrives at station iexactly at time t+Ai.
- Assume that a train bound for station N arrives at a station at time s, and departs the station at time t. Then, the next train bound for station N arrives at the station at time s+K, and departs the station at time t+K. Additionally, the previous train bound for station N arrives at the station at time s−K, and departs the station at time t−K. This must also be true for trains bound for station 0.
- Trains running in opposite directions must not be running on the same single-tracked section (except the stations at both ends) at the same time.
Constraints
- 1≤N≤100000
- 1≤K≤109
- 1≤Ai≤109
- Ai is an integer.
- Bi is either 1 or 2.
Partial Score
- In the test set worth 500 points, all the sections are single-tracked. That is, Bi=1.
- In the test set worth another 500 points, N≤200.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K A1 B1 A2 B2 : AN BN
Output
Print an integer representing the minimum sum of the amount of time required for a train to depart station 0 and reach station N, and the amount of time required for a train to depart station N and reach station 0. If it is impossible to create a timetable satisfying the conditions, print −1 instead.
Sample Input 1
3 10 4 1 3 1 4 1
Sample Output 1
26
For example, the sum of the amount of time in question will be 26 minutes in the following timetable:
In this timetable, the train represented by the red line departs station 0 at time 0, arrives at station 1 at time 4, departs station 1 at time 5, arrives at station 2 at time 8, and so on.
Sample Input 2
1 10 10 1
Sample Output 2
-1
Sample Input 3
6 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 3
12
Sample Input 4
20 987654321 129662684 2 162021979 1 458437539 1 319670097 2 202863355 1 112218745 1 348732033 1 323036578 1 382398703 1 55854389 1 283445191 1 151300613 1 693338042 2 191178308 2 386707193 1 204580036 1 335134457 1 122253639 1 824646518 2 902554792 2
Sample Output 4
14829091348
题意:
有n+1个站台,标号为0到n,相邻两个站台之间通过需要的时间为A[i],有B[i]段轨道,两种车分别从0到n(车1),从n到0(车2)
要求给出一个时间表(例如样例的图),使得时间表以K为一个循环,并且B[i]=1的轨道同一时刻只有一辆车
现在要最小化从0到n的车在途中用的时间和从n到0的车在途中用的时间之和,或者输出-1表示不可能
题解:
首先我们记P[i]表示在i这个站台车1等待的时间
对于车2,我们不这样记
我们假设它在站台0等了-Q[0]的时间,然后经过-A[1]的时间到达站台1...
这一步转化特别喵
考虑B[i]=1的轨道的限制,就是说
车1在i轨道上的区间(∑A[1 to i - 1] + ∑P[0 to i - 1], ∑A[1 to i] + ∑P[0 to i - 1])
车2对应的区间是(-∑A[1 to i - 1] - ∑Q[0 to i - 1], -∑A[1 to i] - ∑Q[0 to i - 1])没有交
这里的区间是模K意义下的
显然如果A[i]*2>K应该直接输出-1
然后两个区间没有交不好做,我们可以转化为每个端点不在另一个区间中
移项可得∑P[0 to i - 1] + ∑Q[0 to i - 1]不在区间(-2∑A[1 to i], -2∑A[1 to i - 1])中
记录P[]+Q[]的前缀和x,那么就是最小化x[n-1] - x[0],并且x[i]在区间L[i],R[i]中,那么一定是x[i]一直在L[j]或者R[j],在j之后贪心改变
这个用一个很简单的线段树优化DP即可完成
我离散化端点数组没开2倍调了好久
#include
#define xx first
#define yy second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define fill( x, y ) memset( x, y, sizeof x )
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair < int, int > pa;
const int MAXN = 100010;
const LL INF = 1e18;
int n, K, A[MAXN], L[MAXN], R[MAXN];
int ls[MAXN << 1], tot, type[MAXN], e[MAXN << 2], sum;
LL f[MAXN], g[MAXN], ans = INF;
inline void modify(int x, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int v)
{
if( l == ql && r == qr ) { e[ x ] = v; return ; }
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if( qr <= mid ) modify( x << 1, l, mid, ql, qr, v );
else if( ql > mid ) modify( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, v );
else modify( x << 1, l, mid, ql, mid, v ), modify( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, qr, v );
}
inline int querymin(int x, int l, int r, int v)
{
if( l == r ) return e[ x ];
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if( v <= mid ) return min( e[ x ], querymin( x << 1, l, mid, v ) );
return min( e[ x ], querymin( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, v ) );
}
inline void add(int x, int l, int r, int ql, int qr)
{
if( l == ql && r == qr ) { e[ x ]++; return ; }
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if( qr <= mid ) add( x << 1, l, mid, ql, qr );
else if( ql > mid ) add( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, ql, qr );
else add( x << 1, l, mid, ql, mid ), add( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, mid + 1, qr );
}
inline int querysum(int x, int l, int r, int v)
{
if( l == r ) return e[ x ];
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if( v <= mid ) return e[ x ] + querysum( x << 1, l, mid, v );
return e[ x ] + querysum( x << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, v );
}
int main()
{
#ifdef wxh010910
freopen( "data.in", "r", stdin );
#endif
scanf( "%d%d", &n, &K );
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ )
{
scanf( "%d%d", &A[ i ], &type[ i ] );
if( A[ i ] * 2 > K && type[ i ] == 1 ) return printf( "-1\n" ), 0;
if( type[ i ] == 2 ) L[ i ] = 0, R[ i ] = K - 1;
else L[ i ] = sum, R[ i ] = ( ( L[ i ] - 2 * A[ i ] ) % K + K ) % K;
sum = ( ( sum - 2 * A[ i ] ) % K + K ) % K;
}
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ) ls[ ++tot ] = L[ i ], ls[ ++tot ] = R[ i ];
sort( ls + 1, ls + tot + 1 ); tot = unique( ls + 1, ls + tot + 1 ) - ls - 1;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ) L[ i ] = lower_bound( ls + 1, ls + tot + 1, L[ i ] ) - ls, R[ i ] = lower_bound( ls + 1, ls + tot + 1, R[ i ] ) - ls;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= ( n << 2 ) ; i++ ) e[ i ] = n + 1;
for( int i = n, pos ; i ; i-- )
{
pos = querymin( 1, 1, tot, L[ i ] );
if( pos != n + 1 ) f[ i ] = f[ pos ] + ( ls[ L[ pos ] ] - ls[ L[ i ] ] + K ) % K;
pos = querymin( 1, 1, tot, R[ i ] );
if( pos != n + 1 ) g[ i ] = f[ pos ] + ( ls[ L[ pos ] ] - ls[ R[ i ] ] + K ) % K;
if( L[ i ] <= R[ i ] )
{
if( R[ i ] < tot ) modify( 1, 1, tot, R[ i ] + 1, tot, i );
if( L[ i ] > 1 ) modify( 1, 1, tot, 1, L[ i ] - 1, i );
}
else if( R[ i ] + 1 < L[ i ] ) modify( 1, 1, tot, R[ i ] + 1, L[ i ] - 1, i );
}
for( int i = 1 ; i <= ( n << 2 ) ; i++ ) e[ i ] = 0;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ )
{
if( querysum( 1, 1, tot, L[ i ] ) == i - 1 )
ans = min( ans, f[ i ] );
if( querysum( 1, 1, tot, R[ i ] ) == i - 1 )
ans = min( ans, g[ i ] );
if( L[ i ] <= R[ i ] ) add( 1, 1, tot, L[ i ], R[ i ] );
else add( 1, 1, tot, L[ i ], tot ), add( 1, 1, tot, 1, R[ i ] );
}
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ) ans += A[ i ] << 1;
cout << ans << endl;
}