python if 条件语句
Python程序语言指定任何非0和非空(null)值为true,0 或者 null为false。
Python 编程中 if 语句用于控制程序的执行,基本形式为(注意书写格式以及缩进,冒号):
if 判断条件:
执行语句……
else:
执行语句……
其中"判断条件"成立时(非零),则执行后面的语句,而执行内容可以多行,以缩进来区分表示同一范围。
else 为可选语句,当需要在条件不成立时执行内容则可以执行相关语句
if 语句的判断条件可以用>(大于)、<(小于)、==(等于)、>=(大于等于)、<=(小于等于)来表示其关系。
当判断条件为多个值时,可以使用以下形式:
if 判断条件1:
执行语句1……
elif 判断条件2:
执行语句2……
elif 判断条件3:
执行语句3……
else:
执行语句4……
综合练习: 年龄猜测
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
dwl = 22
guess_age = int(input("guess age:"))
if guess_age == dwl:
print("yes,you get it!")
elif guess_age > dwl:
print("think smaller!")
else:
print("think biger")Python While 循环语句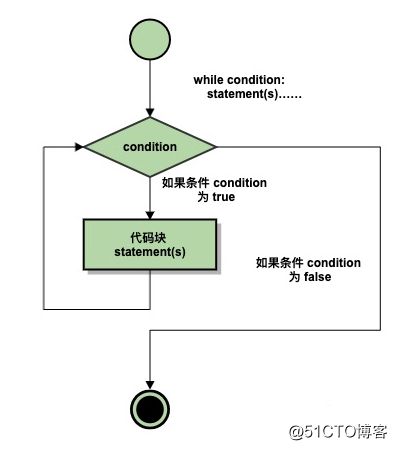
while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件(condition):
执行语句(statements)……
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"判断条件"还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
# continue 和 break 用法
i = 1
while i < 10:
i += 1
if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出
continue
print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10
i = 1
while 1: # 循环条件为1必定成立
print i # 输出1~10
i += 1
if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环
break无限循环 while true,以及while … else 在循环条件为 false 时执行 else 语句块
#!/usr/bin/python
count = 0
while count < 5:
print count, " is less than 5"
count = count + 1
else:
print count, " is not less than 5"while if 嵌套练习
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
dwl = 22
count = 0 ##申明计时变量
while count < 3: ##控制猜想的次数
guess_age = int(input("guess age num:"))
if guess_age == dwl:
print("yes,you got it!!")
break ##猜中即跳出循环
elif guess_age < dwl:
print("think bigger....")
else:
print("think smaller")
count +=1
if count ==3: ##3次判断后是否继续 继续就重置计数器
continue_keep = input("do you want keep on game?")
if continue_keep != "n":
count =0
# else:
# print("you have tired too many times..")Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。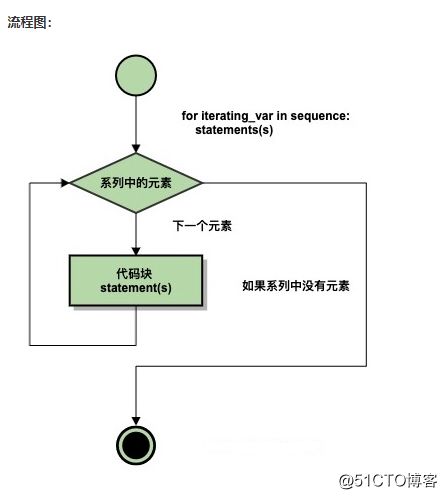
序列循环实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for letter in 'Python': # 第一个实例
print '当前字母 :', letter
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例
print '当前水果 :', fruit
print "Good bye!"通过序列索引迭代
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for index in range(len(fruits)): ##len 函数统计序列数,在使用rang函数生成计数
print '当前水果 :', fruits[index] ##切片表示
print "Good bye!"循环嵌套实例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字
for i in range(2,num): # 根据因子迭代
if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子
j=num/i # 计算第二个因子
print '%d 等于 %d * %d' % (num,i,j)
break # 跳出当前循环 继续下一个循环
else: # 循环的 else 部分
print num, '是一个质数'