Netty中的内存分配分析
1.ByteBuf的继承类图
1.1 AbstractBytebuf的实现
int readerIndex;
int writerIndex;
private int markedReaderIndex;
private int markedWriterIndex;
private int maxCapacity;
主要实现了index的实现,定义了_getByte和_setByte由其子类实现
1.2 ByteBuf分类 可以分为3类
Pooled和Unpooled分类
区别:pooled 是从已经分配好的内存中来分配一块内存;UnPooled是每次都是新分配地址
Unsafe和非UnSafe
区别:是否依赖与底层的Unsafe对象(可以直接获取到内存地址)来分配内存
Heap和Direct
区别:heap是在jvm堆内存上进行分配,受jvm管理,会被Gc,不用手动释放;Direct是在堆外进行的内存分配,需要手动释放,否则会导致能使用的内存越来越少.
1.3 ByteBufAllocator分析
public abstract class AbstractByteBufAllocator implements ByteBufAllocator
AbstractByteBufAllocator 定义了两个方法
/**
* Create a heap {@link ByteBuf} with the given initialCapacity and maxCapacity.
*/
protected abstract ByteBuf newHeapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity);
/**
* Create a direct {@link ByteBuf} with the given initialCapacity and maxCapacity.
*/
protected abstract ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity);
这两个方法有两个实现

注意:UnSaf和非UnSafe是Netty自己判断的
2.UnPooledByteBufAllocator分析
2.1 heap内存分配
2.2 direct内存分配
3 PooledByteBufAllocator分析
3.1 newDirectBuffer
@Override
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get();
PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;
ByteBuf buf;
if (directArena != null) {
buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
if (PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
buf = UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
} else {
buf = new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
}
return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);
}
1.PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get(), 拿到当前线程的一个对象
2. 拿到当前对象的directArena
3. directArena.allocate 分配内存

这里的heapArenas和directArenas 一般来说是2倍的cpu和数
3.2 directArena分配direct内存的流程
2.从缓存上进行内存分配
3.如果第2步失败,则从内存堆里面进行内存分配
代码如下


4 内存规格介绍

4.1 MemoryRegionCache介绍

4.2 命中缓存的分配流程
1.找到对应size的MemoryRegionCache
2.从queue中弹出一个entry给ByteBuf初始化
3.将弹出的entry扔到对象池中进行复用
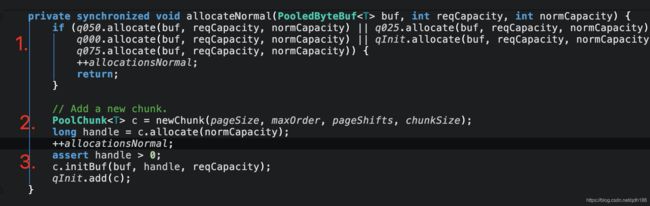
4.3 page级别的内存分配 allocateNormal()
1.尝试在现有的chunk上分配
2.创建一个chunk进行内存分配
3.初始化内存
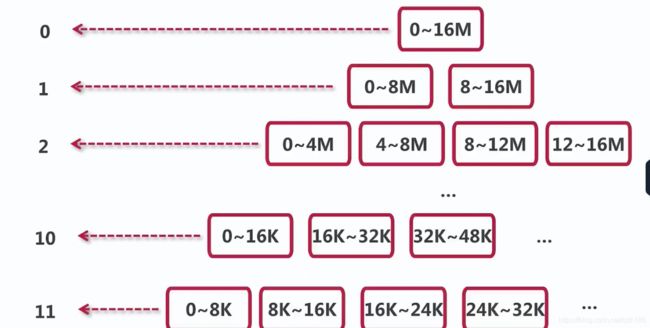
4.4 subpage级别的内存分配:allocateTiny()
1.定位Subpage对象
2.初始化Subpage
3.初始化PooledByteBuf
4.5ByteBuf的释放
1.连续内存区段加到缓存
2.标记连续内存区段为未使用(page级别用二叉树的方式标记,subPage使用bitMap来标记)
3.ByteBuf加到对象池