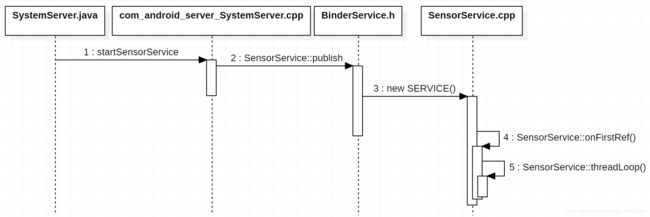
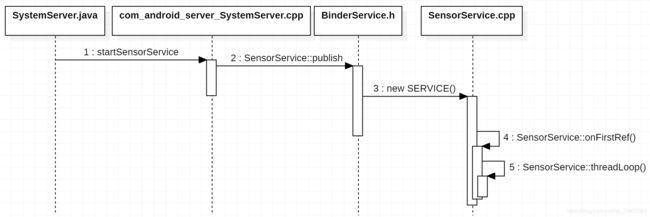
SensorService启动
SensorService启动
SystemServer进程启动SensorService
系统启动system_server进程,SystemServer.java 负责启动 startSensorService()
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
system_server进程启动 new SystemServer().run()
private void run() {
// ... ...
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
// ... ...
}
在引导服务 startBootstrapServices 中启动 startSensorService()
/**
* Start the sensor service. This is a blocking call and can take time.
*/
private static native void startSensorService();
// ... ...
private void startBootstrapServices() {
// ... ...
traceBeginAndSlog("StartSensorPrivacyService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new SensorPrivacyService(mSystemContext));
traceEnd();
if (SystemProperties.getInt("persist.sys.displayinset.top", 0) > 0) {
// DisplayManager needs the overlay immediately.
mActivityManagerService.updateSystemUiContext();
LocalServices.getService(DisplayManagerInternal.class).onOverlayChanged();
}
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
// Start sensor service in a separate thread. Completion should be checked
// before using it.
mSensorServiceStart = SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(() -> {
TimingsTraceLog traceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(
SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_ASYNC_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
traceLog.traceBegin(START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
startSensorService();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
}
1、SensorService 需要访问 PKMS服务,AppOpsService服务和PermissionsService服务,因此在它们之后启动SensorService。
2、SystemServerInitThreadPool在单独的线程中启动传感器服务
3、native 调用 startSensorService()
native 调用 startSensorService()
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp
SensorService::publish 启动
static void android_server_SystemServer_startSensorService(JNIEnv* /* env */, jobject /* clazz */) {
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
SensorService::publish(false /* allowIsolated */,
IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
}
}
SensorService 实例创建
SensorService继承
frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorService.h
继承BinderService、BnSensorServer、Thread
class SensorService :
public BinderService<SensorService>,
public BnSensorServer,
protected Thread
1、BinderService:frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/BinderService.h
BinderService 是 Android Service 框架的主要类,是个模板类,它提供了 Service 的生命周期管理、进程间通信、请求响应处理等功能。Android 中的绝大部分 Service 都会继承此类。
new SERVICE():new一个SensorService,然后 以 “sensorservice”为key,把sensorservice实例加入到ServiceManaer
2、BnSensorServer:frameworks/native/libs/sensor/include/sensor/ISensorServer.h
和 BinderService 主要实现IPC跨进程通信,实际继承BnInterface
3、Thread:继承 Thread 启动 threadLoop
SensorService 创建 onFirstRef
当 SensorService 第一个实例创建时,其 onFirstRef 接口将会被调用
① 在 SensorDevice 的构造函数中,会调用 hw_get_module 接口加载 Sensor HAL 的动态库
② 通过 SensorDevice,调用 Sensor HAL 提供的 get_sensors_list 接口,获取所支持的 Sensor 信息获,调用registerSensor函数把Sensor保存起来
③ SensorFusion功能,传感融合。它的主要作用就是,按照一定的算法计算系统的多个传感器对某一个值的上报的数据,得到更准确的值。
④ registerVirtualSensor注册虚拟传感器:这些虚拟的传感器步会产生真的数据,而是通过SensorFusion功能计算得到的值,作为虚拟传感的数据。分发过程中会有分析到。
⑤ 初始化一些Buffer,用他们保存sensor硬件上报的数据
⑥ 创建一个 Looper 和 SensorEventAckReceiver。其中 Looper 用于 enable sensor 后,进行数据的接收;而 SensorEventAckReceiver 则用于在 dispatch wake up sensor event 给上层后,接收上层返回的确认 ACK。
⑦ SensorService 不仅是一个服务,而且他还是一个线程,初始化工作的最后就是启动该线程执行threadLoop函数。threadLoop函数主要的工作就是,循环读取sensor硬件上传上来的数据,然后分发给应用。
void SensorService::onFirstRef() {
// ① 在 SensorDevice 的构造函数中,会调用 hw_get_module 接口加载 Sensor HAL 的动态库
SensorDevice& dev(SensorDevice::getInstance());
//.......
if (dev.initCheck() == NO_ERROR) {
// ② 通过 SensorDevice,调用 Sensor HAL 提供的 get_sensors_list 接口,获取所支持的 Sensor 信息获,调用registerSensor函数把Sensor保存起来
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = dev.getSensorList(&list);
//.......
for (ssize_t i=0 ; i<count ; i++) {
//.......
if (useThisSensor) {
registerSensor( new HardwareSensor(list[i]) );
}
}
// ③ SensorFusion功能,传感融合。它的主要作用就是,按照一定的算法计算系统的多个传感器对某一个值的上报的数据,得到更准确的值。
// it's safe to instantiate the SensorFusion object here
// (it wants to be instantiated after h/w sensors have been
// registered)
SensorFusion::getInstance();
// ④ 注册虚拟传感器:这些虚拟的传感器步会产生真的数据,而是通过SensorFusion功能计算得到的值,作为虚拟传感的数据。
//.......
registerSensor(new RotationVectorSensor(), !needRotationVector, true);
registerSensor(new OrientationSensor(), !needRotationVector, true);
registerSensor(new LinearAccelerationSensor(list, count),
!needLinearAcceleration, true);
registerSensor( new CorrectedGyroSensor(list, count), true, true);
registerSensor( new GyroDriftSensor(), true, true);
//.......
registerSensor(new GravitySensor(list, count), !needGravitySensor, true);
//.......
registerSensor(new GameRotationVectorSensor(), !needGameRotationVector, true);
//.......
registerSensor(new GeoMagRotationVectorSensor(), !needGeoMagRotationVector, true);
//.......
// ⑤ 初始化一些Buffer,用他们保存sensor硬件上报的数据
mLooper = new Looper(false);
const size_t minBufferSize = SensorEventQueue::MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT;
mSensorEventBuffer = new sensors_event_t[minBufferSize];
mSensorEventScratch = new sensors_event_t[minBufferSize];
mMapFlushEventsToConnections = new wp<const SensorEventConnection> [minBufferSize];
mCurrentOperatingMode = NORMAL;
//.......
// ⑥ 创建一个 Looper 和 SensorEventAckReceiver。其中 Looper 用于 enable sensor 后,进行数据的接收;而 SensorEventAckReceiver 则用于在 dispatch wake up sensor event 给上层后,接收上层返回的确认 ACK。
mAckReceiver = new SensorEventAckReceiver(this);
mAckReceiver->run("SensorEventAckReceiver", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
// ⑦ SensorService 不仅是一个服务,而且他还是一个线程,初始化工作的最后就是启动该线程执行threadLoop函数。threadLoop函数主要的工作就是,循环读取sensor硬件上传上来的数据,然后分发给应用。
run("SensorService", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
//.......
}
SensorService::threadLoop()
1、通过poll往hal层取sensor数据, 若没有数据的时候就一直阻塞(该阻塞功能由HAL层实现),当有数据时该函数就会返回
2、virtual sensors 相关数据计算后上报
3、通过SensorEventConnection中 sendEvents 将数据给到每个应用,每个应用都有自己的SensorEventConnection
bool SensorService::threadLoop() {
ALOGD("nuSensorService thread starting...");
//.......
SensorDevice& device(SensorDevice::getInstance());
const int halVersion = device.getHalDeviceVersion();
do {
// ① 通过poll往hal层取sensor数据, 若没有数据的时候就一直阻塞(该阻塞功能由HAL层实现),当有数据时该函数就会返回
ssize_t count = device.poll(mSensorEventBuffer, numEventMax);//①
if (count < 0) {
if(count == DEAD_OBJECT && device.isReconnecting()) {
device.reconnect();
continue;
} else {
ALOGE("sensor poll failed (%s)", strerror(-count));
break;
}
}
//.......
// handle virtual sensors
if (count && vcount) {
sensors_event_t const * const event = mSensorEventBuffer;
if (!mActiveVirtualSensors.empty()) {
size_t k = 0;
SensorFusion& fusion(SensorFusion::getInstance());
if (fusion.isEnabled()) {
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
fusion.process(event[i]);
}
}
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) && k<minBufferSize ; i++) {
for (int handle : mActiveVirtualSensors) {
if (count + k >= minBufferSize) {
ALOGE("buffer too small to hold all events: "
"count=%zd, k=%zu, size=%zu",
count, k, minBufferSize);
break;
}
sensors_event_t out;
sp<SensorInterface> si = mSensors.getInterface(handle);
if (si == nullptr) {
ALOGE("handle %d is not an valid virtual sensor", handle);
continue;
}
// ② virtual sensors 相关数据计算后上报
if (si->process(&out, event[i])) {
mSensorEventBuffer[count + k] = out;
k++;
}
}
}
if (k) {
// record the last synthesized values
recordLastValueLocked(&mSensorEventBuffer[count], k);
count += k;
// sort the buffer by time-stamps
sortEventBuffer(mSensorEventBuffer, count);
}
}
}
//.......
// Send our events to clients. Check the state of wake lock for each client and release the
// lock if none of the clients need it.
bool needsWakeLock = false;
for (const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection : activeConnections) {
// ② 通过SensorEventConnection 将数据给到每个应用,每个应用都有自己的SensorEventConnection
connection->sendEvents(mSensorEventBuffer, count, mSensorEventScratch,
mMapFlushEventsToConnections); //②
needsWakeLock |= connection->needsWakeLock();
// If the connection has one-shot sensors, it may be cleaned up after first trigger.
// Early check for one-shot sensors.
if (connection->hasOneShotSensors()) {
cleanupAutoDisabledSensorLocked(connection, mSensorEventBuffer, count);
}
}
if (mWakeLockAcquired && !needsWakeLock) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(false);
}
} while (!Thread::exitPending());
ALOGW("Exiting SensorService::threadLoop => aborting...");
abort();
return false;
}