Lottie的使用和源码详解
一、说在前面的话
在Android开发中,Coder要兼顾各个模块的建设维护,当然也少不了动画的制作,为了让界面使用更为友善,一般会由设计狮的一番设计后交由开发者在App重现出来。开发着在开发动画的同时会带来很多的问题,比如:图像适配性、大小占用空间等。
早在Android5.0的时候,Google已经提供对vector矢量图的支持,并且这种矢量图还可以“动起来”。
解决问题的同时,又带来了新坑,暂总结如下:
- 在Android4.x中,是无法解析vector的路径变换动画
- 在Android4.x中,只能使用系统自带的插值器,不能自定义
- 制作动态vector动画,并不容易。制作静态vector路径,再实现动态vector的路径变化值,很繁琐的一个过程。
以上,直接后果就是,几乎各大App中不存在动态vector的影子,然而直到Lottie的出现。
二、LOTTIE简介
1、效果展示(要想抓住你的心,必须抓住你的眼)
2、Lottie是什么?
-
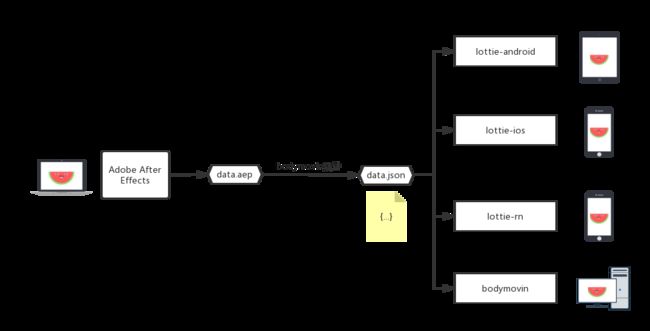
Lottie是Airbnb开源的一个动画渲染库,同时支持Android、IOS、React Native和Web平台,Lottie目前只支持渲染播放After Effects动画。Lottie使用bobymovin(After Effects插件)导出的json数据作为动画数据源。使用Lottie可以让动画显示变得简单方便。
-
工作流程:
- 设计师使用Affer Effects制作动画并导出json文件,可以将json文件放到Bodymovin网站上运行看效果,也可以放在lottiefiles网站上运行看效果,lottiefiles有很多免费动画json资源可以下载看。
- 各端开发使用相应的LottieSDK实现动画效果,GitHub下载地址:Lottie Android, Lottie IOS ,React Native,Web
-
注意事项:
设计师同学制作各个平台(Android、IOS、React Netive)动画时需要查看Lottie在不同平台支持的特性,否则制作出来的动画显示可能会有问题,设计同学制作动画参考: 不同平台Lottie支持特性
3、为什么要使用LOTTIE?
-
先看看在没有Lottie之前我们实现复杂动画的方式:
- 使用GIF,占用空间大,有些动画显示效果不佳,需要适配分辨率,Android原生不支持GIF动画的显示。
- 使用帧动画,占用空间大,依然会遇到不同分辨率适配的问题。
- 组合式动画,通过大量代码实现复杂的动画效果。
-
使用Lottie可以解决的问题:
- 开发无需编写动画,只需加载
- Android, iOS, 和React Native多平台支持
- 可手动设置进度,绑定手势,事件等
- 可网络加载,动态控制播放速度等
- 降低动画设计和开发成本
- 解决设计提供动画效果与实现不一致问题
- 占用空间更小
- 不同的手机分辨率不需要适配
4、LOTTIE适用于哪些场景?
- 启动(splash)动画:典型场景是APP logo动画的播放
- 上下拉刷新(refresh)动画:所有APP都必备的功能,利用 Lottie可以做的更加简单酷炫了
- 加载(loading)动画:典型场景是网络请求的loading动画
- 提示(tips)动画:典型场景是空白页的提示
- 按钮(button)动画:典型场景如switch按钮、编辑按钮、播放按钮等按钮的
- 礼物(gift)动画:典型场景是直播类APP的高级动画播放
5、我们想要使用LOTTIE替代哪些动画?
- 首先并不是在APP中所有的动画都要用Lottie来替换
- 一些可以通过属性动画来实现的简单动画就不需要用Lottie来实现了
- 替代一些通过代码不好实现的动画效果
- 替代GIF动画和帧动画
三、LottieAndroid的使用
1、集成到项目中(以2.2.0版本为例)
-
添加依赖:compile ‘com.airbnb.android:lottie:2.2.0’
Lottie版本号参考: Maven库查看Lottie各版本号
-
Gradle依赖修改:
最低版本:MIN_SDK_VERSION = 16
编译版本:COMPILE_SDK_VERSION = 25
所有的兼容包需要升级到版本号为25.3.1
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support:cardview-v7:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support:design:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support:palette-v7:25.3.1'
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:25.3.1'
2、使用方法
-
Lottie基本用法查看官方文档
-
在布局中添加LottieAnimationView控件:
如上图,如果json文件在assets子文件夹中,lottie_fileName=“lottieani/stars.json”(也可以使用zip格式的压缩文件)
<com.airbnb.lottie.LottieAnimationView android:id="@+id/animationView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" airbnb:lottie_fileName="lottieani/stars.json" airbnb:lottie_autoPlay="true" airbnb:lottie_loop="true"/>LottieAnimationView可以设置的属性如下:
<declare-styleable name="LottieAnimationView"> //切记这个名字不能随便改,这个是官方命名 <attr name="lottie_fileName" format="string" /> //值得一提的是:lottie_fileName和lottie_rawRes不能同时设置,不然会报错。 <attr name="lottie_rawRes" format="reference" /> <attr name="lottie_url" format="string" /> <attr name="lottie_autoPlay" format="boolean" /> <attr name="lottie_loop" format="boolean" /> <attr name="lottie_repeatMode" format="enum"> <enum name="restart" value="1" /> <enum name="reverse" value="2" /> </attr> <attr name="lottie_repeatCount" format="integer" /> <attr name="lottie_imageAssetsFolder" format="string" /> <attr name="lottie_progress" format="float" /> <attr name="lottie_enableMergePathsForKitKatAndAbove" format="boolean" /> <attr name="lottie_colorFilter" format="color" /> <attr name="lottie_scale" format="float" /> </declare-styleable>- 得到LottieAnimationView对象进行动画操作:
LottieAnimationView animationView = (LottieAnimationView)findViewById(R.id.animation_view); // 布局中不指定文件可以在此设置,路径设置同布局文件 animationView.setAnimation("hello-world.json"); // 是否循环播放 animationView.loop(true); // 设置播放速率,例如:2代表播放速率是不设置时的二倍 animationView.setSpeed(2f); // 开始播放 animationView.playAnimation(); // 暂停播放 animationView.pauseAnimation(); // 取消播放 animationVIew.cancelAnimation(); // 设置播放进度 animationView.setProgress(0.5f); // 判断是否正在播放 animationView.isAnimating();setAnimation()有六种方法,可以直接设置动画的Json对象,或者设置Json文件相对路径名:
setAnimation(@RawRes final int rawRes) setAnimation(final String assetName) setAnimationFromJson(String jsonString) //不建议使用 setAnimationFromJson(String jsonString, @Nullable String cacheKey) setAnimation(JsonReader reader, @Nullable String cacheKey) setAnimationFromUrl(String url)playAnimation()有一种方法:
public void playAnimation()大家在低版本可能会看到CacheStrategy这个属性,这是指定缓存类型,这个在高版本(V2.7.0)已经移除,官方解释为:
This cleans up a number of things related to the LottieCompositionFactory.
It:
Handled task caching at the LottieCompositionFactory level so it is guaranteed to work everywhere. The existing architecture left several instances where compositions would not be cached.
Simplified the way tasks are handled in LottieAnimationView
Fixes #958 in which different cache keys are used for rawRes animations
Removed deprecated factory APIs- 添加动画监听
animationView.addAnimatorListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationStart : " + animation.getDuration()); } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationEnd"); } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationCancel"); } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationRepeat"); }}); mAnimationView.addAnimatorUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { @Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { //Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationUpdate : " + animation.getCurrentPlayTime()); } });
四、源码解析
1、从Json到动画显示的实现思路
-
设计狮把一个复杂的图片使用多个图层来表示,每个图层展示一部分内容,图层中的内容也可以拆分为多个元素。拆分元素之后,根据动画需求,可以单独对图层或者图层中的元素做平移、旋转、收缩等动画(主要是通过Canvas绘制以及对Matrix进行操作)

-
Json文件中数据转成LottieComposition数据对象,LottieDrawable负责将数据绘制成drawable,LottieAnimationView负责将LottieDrawable显示出来。LottieAnimationView继承自AppCompatImageView,LottieDrawable继承自Drawable。

2、先看看生成的Json数据
Lottie的使用的资源是需要先通过bodymovin(bodymovin插件本身是用于网页上呈现各种AE效果的一个开源库)将 Adobe After Effects (AE)生成的aep动画工程文件转换为通用的json格式描述文件。Lottie则负责解析动画的数据,计算每个动画在某个时间点的状态,准确地绘制到屏幕上。
这段JSON取自Lottie单元测试
{
"v": "4.11.1", //使用bodymovin的版本
"fr": 60, //帧率
"ip": 0, //起始关键帧
"op": 180, //结束关键帧
"w": 300, //视图的宽度
"h": 300, //视图的高度
"nm": "Comp 1", //从源码中未看到对此字段解析
"ddd": 0,
"assets": [], //图片集合
"layers": [ //图层集合
{
"ddd": 0,
"ind": 1, //layer的Id,唯一
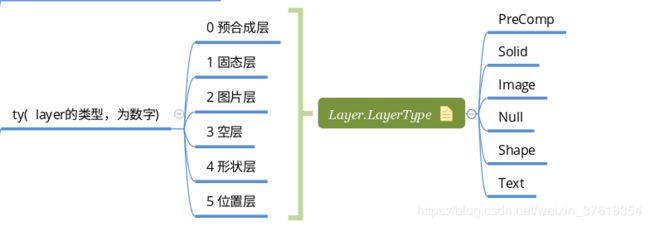
"ty": 4, //layer的类型,为数字
"nm": "Shape Layer 1", //layer的名称,在ae中生成唯一
"sr": 1,
"ks": {}, //外观信息
"ao": 0,
"shapes": [], //矢量图形图层的数组
"ip": 0, // 该图层的起始关键帧
"op": 180, //该图层的结束关键帧
"st": 0,
"bm": 0
},
{...},
{...},
{...},
]
}
这里有详细的字段解释:bodymovin Json分析
3、如何加载JSON数据并显示图像的?
animationView.setAnimation(“hello-world.json”);
通过setAnimation()来看看,上面json数据到显示图像的过程。源码时序图如下:
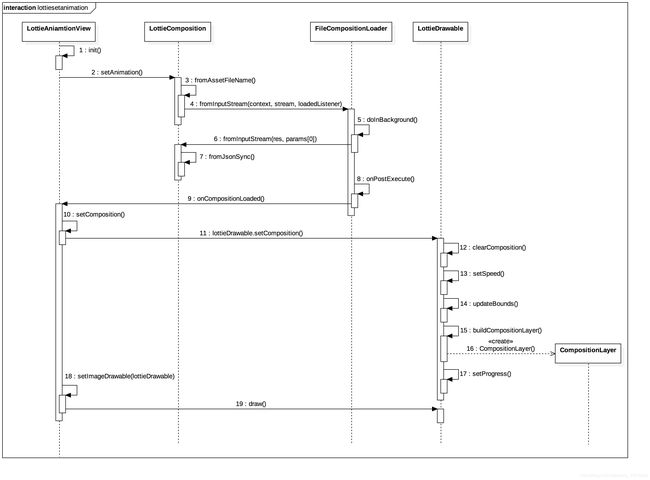
- 1、LottieAnimationView初始化的时候会首先创建LottieDrawable对象,init()函数中进行初始化的时候,解析xml设置的属性。
创建LottieDrawable对象代码段:
@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "WeakerAccess"})
public class LottieAnimationView extends AppCompatImageView {
private static final String TAG = LottieAnimationView.class.getSimpleName();
private final LottieListener<LottieComposition> loadedListener = new LottieListener<LottieComposition>() {
@Override public void onResult(LottieComposition composition) {
setComposition(composition);
}
};
private final LottieListener<Throwable> failureListener = new LottieListener<Throwable>() {
@Override public void onResult(Throwable throwable) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to parse composition", throwable);
}
};
private final LottieDrawable lottieDrawable = new LottieDrawable();
...
init()函数的代码段:
private void init(@Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray ta = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.LottieAnimationView);
if (!isInEditMode()) {
boolean hasRawRes = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_rawRes);
boolean hasFileName = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_fileName);
boolean hasUrl = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_url);
if (hasRawRes && hasFileName) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("lottie_rawRes and lottie_fileName cannot be used at " +
"the same time. Please use only one at once.");
} else if (hasRawRes) {
int rawResId = ta.getResourceId(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_rawRes, 0);
if (rawResId != 0) {
setAnimation(rawResId);
}
} else if (hasFileName) {
String fileName = ta.getString(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_fileName);
if (fileName != null) {
setAnimation(fileName);
}
} else if (hasUrl) {
String url = ta.getString(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_url);
if (url != null) {
setAnimationFromUrl(url);
}
}
}
....
}
- 2、setAnimation(String assetName),加载JSON文件。主要是通过LottieCompositionFactory和LottieComposition.Factory这两个类加载,其中LottieComposition.Factory官方已经不建议使用。
其中setAnimation()函数代码:
public void setAnimation(final String assetName) {
this.animationName = assetName;
animationResId = 0;
setCompositionTask(LottieCompositionFactory.fromAsset(getContext(), assetName)); //它是异步加载资源,加载成功后,会有相应回调
}
setCompositionTask函数代码段:
private void setCompositionTask(LottieTask<LottieComposition> compositionTask) {
clearComposition();
cancelLoaderTask();
this.compositionTask = compositionTask
.addListener(loadedListener)
.addFailureListener(failureListener);
}
- 3、通过异步加载,最终会调用到fromJsonSync()对Json文件进行解析。
LottieCompositionFactory.fromAsset()函数代码:
public static LottieTask<LottieComposition> fromAsset(Context context, final String fileName) {
// Prevent accidentally leaking an Activity.
final Context appContext = context.getApplicationContext();
return cache(fileName, new Callable<LottieResult<LottieComposition>>() { //在这里它会先从缓存中去找,如果找不到才会去加载资源
@Override public LottieResult<LottieComposition> call() {
return fromAssetSync(appContext, fileName);
}
});
}
- 4、解析结果通过LottieListener->onResult回调到主线程,然后会将Json数据转换成LottieComposition对象。
LottieTask类中回调代码段:
private void notifyListeners() {
// Listeners should be called on the main thread.
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (result == null || task.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
// Local reference in case it gets set on a background thread.
LottieResult<T> result = LottieTask.this.result;
if (result.getValue() != null) {
notifySuccessListeners(result.getValue());
} else {
notifyFailureListeners(result.getException());
}
}
});
}
LottieListener->onResult()代码段:
@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "WeakerAccess"}) public class LottieAnimationView extends AppCompatImageView {
private static final String TAG = LottieAnimationView.class.getSimpleName();
private final LottieListener<LottieComposition> loadedListener = new LottieListener<LottieComposition>() {
@Override public void onResult(LottieComposition composition) {
setComposition(composition);
}
};
private final LottieListener<Throwable> failureListener = new LottieListener<Throwable>() {
@Override public void onResult(Throwable throwable) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to parse composition", throwable);
}
};
...
- 5、lottieDrawable.setComposition(),将LottieComposition对象设置给LottieDrawable。
public void setComposition(@NonNull LottieComposition composition) {
if (L.DBG) {
Log.v(TAG, "Set Composition \n" + composition);
}
lottieDrawable.setCallback(this);
this.composition = composition;
boolean isNewComposition = lottieDrawable.setComposition(composition);
enableOrDisableHardwareLayer();
if (getDrawable() == lottieDrawable && !isNewComposition) {
// We can avoid re-setting the drawable, and invalidating the view, since the composition
// hasn't changed.
return;
}
// If you set a different composition on the view, the bounds will not update unless
// the drawable is different than the original.
setImageDrawable(null);
setImageDrawable(lottieDrawable);
requestLayout();
for (LottieOnCompositionLoadedListener lottieOnCompositionLoadedListener : lottieOnCompositionLoadedListeners) {
lottieOnCompositionLoadedListener.onCompositionLoaded(composition);
}
}
- 6、通过LottieDrawable生成CompositionLayer对象,并初始化基本的属性
public boolean setComposition(LottieComposition composition) {
if (this.composition == composition) {
return false;
}
clearComposition();
this.composition = composition;
buildCompositionLayer();
animator.setComposition(composition);
setProgress(animator.getAnimatedFraction());
setScale(scale);
updateBounds();
...
}
- 7、CompositionLayer会根据层的类型不同而生成不同的层
这个是对所有层进行管理的一个类,例如:创建、绘制、更新进度、管理等。这个类也是继承自BaseLayer(BaseLayer是所有层的父类)。
其中会在CompositionLayer构造函数里面初始化不同的Layer:
public CompositionLayer(LottieDrawable lottieDrawable, Layer layerModel, List<Layer> layerModels,
LottieComposition composition) {
...
BaseLayer mattedLayer = null;
for (int i = layerModels.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Layer lm = layerModels.get(i);
BaseLayer layer = BaseLayer.forModel(lm, lottieDrawable, composition);
if (layer == null) {
continue;
}
layerMap.put(layer.getLayerModel().getId(), layer);
if (mattedLayer != null) {
mattedLayer.setMatteLayer(layer);
mattedLayer = null;
} else {
layers.add(0, layer);
switch (lm.getMatteType()) {
case Add:
case Invert:
mattedLayer = layer;
break;
}
}
}
...
}
根据不同的LayerType绘制不同的图层
BaseLayer.java
static BaseLayer forModel(
Layer layerModel, LottieDrawable drawable, LottieComposition composition) {
switch (layerModel.getLayerType()) {
case Shape:
return new ShapeLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case PreComp:
return new CompositionLayer(drawable, layerModel,
composition.getPrecomps(layerModel.getRefId()), composition);
case Solid:
return new SolidLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case Image:
return new ImageLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case Null:
return new NullLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case Text:
return new TextLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case Unknown:
default:
// Do nothing
L.warn("Unknown layer type " + layerModel.getLayerType());
return null;
}
}
- 8、通过setImageDrawable(lottieDrawable)将图像显示出来,显示第一帧动画。
4、动画如何运行起来的?
animationView.playAnimation();
调用playAnimation()动画是如何动起来的,源码时序图如下:
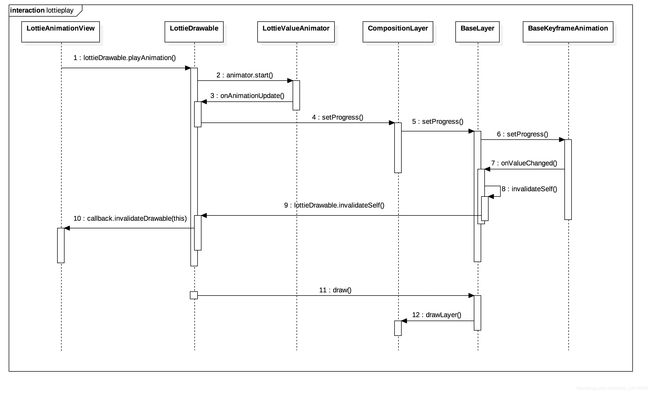
- 1、利用属性动画计算进度
在初始化LottieDrawable的同时也会创建LottieValueAnimator,LottieValueAnimator继承至ValueAnimator,Lottie的动画是用到了属性动画来产生一个0~1的插值,根据不同的插值来设置当前动画进度。
初始化代码:
public class LottieDrawable extends Drawable implements Drawable.Callback, Animatable {
private static final String TAG = LottieDrawable.class.getSimpleName();
private interface LazyCompositionTask {
void run(LottieComposition composition);
}
private final Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
private LottieComposition composition;
private final LottieValueAnimator animator = new LottieValueAnimator();
...
在LottieDrawable构造函数中注册监听进度回调:
public LottieDrawable() {
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
if (compositionLayer != null) {
compositionLayer.setProgress(animator.getAnimatedValueAbsolute());
}
}
});
}
当执行LottieDrawable.playAnimation方法时,也是调用animator.playAnimation()
public void playAnimation() {
if (compositionLayer == null) {
lazyCompositionTasks.add(new LazyCompositionTask() {
@Override public void run(LottieComposition composition) {
playAnimation();
}
});
return;
}
animator.playAnimation();
}
- 2、通过CompositionLayer将setProgress实现的显示具体进度动画
代码如下:
@Override
public void setProgress(@FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float progress) {
super.setProgress(progress);
if (timeRemapping != null) {
float duration = lottieDrawable.getComposition().getDuration();
long remappedTime = (long) (timeRemapping.getValue() * 1000);
progress = remappedTime / duration;
}
if (layerModel.getTimeStretch() != 0) {
progress /= layerModel.getTimeStretch();
}
progress -= layerModel.getStartProgress();
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
layers.get(i).setProgress(progress);
}
}
- 3、通知进度改变
public void setProgress(@FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float progress) {
if (progress < getStartDelayProgress()) {
progress = getStartDelayProgress();
} else if (progress > getEndProgress()) {
progress = getEndProgress();
}
if (progress == this.progress) {
return;
}
this.progress = progress;
notifyListeners();
}
其中notifyListeners中代码:
public void notifyListeners() {
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.size(); i++) {
listeners.get(i).onValueChanged();
}
}
- 4、最终回调到LottieAnimationView的invalidateDrawable
@Override public void invalidateDrawable(@NonNull Drawable dr) {
if (getDrawable() == lottieDrawable) {
// We always want to invalidate the root drawable so it redraws the whole drawable.
// Eventually it would be great to be able to invalidate just the changed region.
super.invalidateDrawable(lottieDrawable);
} else {
// Otherwise work as regular ImageView
super.invalidateDrawable(dr);
}
}
- 5、最后触发LottieDrawable重绘
@Override public void draw(@NonNull Canvas canvas) {
L.beginSection("Drawable#draw");
if (compositionLayer == null) {
return;
}
...
matrix.reset();
matrix.preScale(scale, scale);
compositionLayer.draw(canvas, matrix, alpha);
L.endSection("Drawable#draw");
...
}
其中CompositionLayer.draw函数:
@Override void drawLayer(Canvas canvas, Matrix parentMatrix, int parentAlpha) {
L.beginSection("CompositionLayer#draw");
canvas.save();
newClipRect.set(0, 0, layerModel.getPreCompWidth(), layerModel.getPreCompHeight());
parentMatrix.mapRect(newClipRect);
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
boolean nonEmptyClip = true;
if (!newClipRect.isEmpty()) {
nonEmptyClip = canvas.clipRect(newClipRect);
}
if (nonEmptyClip) {
BaseLayer layer = layers.get(i);
layer.draw(canvas, parentMatrix, parentAlpha);
}
}
canvas.restore();
L.endSection("CompositionLayer#draw");
}
5、原理简单总结:
- 首先会通过LottieComposition.Factory的对应类型设置json资源文件
- 然后再fromJsonSync方法里面会把json文件解析出图层的大小并且绘制相应的图片资源文件和图层
- 资源加载完后,会在回调里面设置LottieAnimationView的Composition,从而调用LottieDrawable的setComposition()方法
- 在setComposition方法里面会通过buildCompositionLayer()方法去创建一个CompositionLayer图层
- 其中CompositionLayer继承BaseLayer,通过BaseLayer的forModel()静态方法获取不同的图层类型
- 然后LottieDrawable的setComposition()方法里面会开始执行一个ValueAnimation动画
- 这个动画会驱使aseLayer的draw()方法不断执行,通过Matrix的矩阵形式不断的绘制各个图层从而形成动画
- 而这些图层的矩阵变换的数据来源于BaseKeyframeAnimation里面有一个Keyframe对象会去Json里面获取相应得数据。
五、性能问题
1、官方说明
-
如果没有mask和mattes,那么性能和内存非常好,没有bitmap创建,大部分操作都是简单的cavas绘制。
-
如果存在mattes,将会创建2~3个bitmap。bitmap在动画加载到window时被创建,被window删除时回收。所以不宜在RecyclerView中使用包涵mattes或者mask的动画,否则会引起bitmap抖动。除了内存抖动,mattes和mask中必要的bitmap.eraseColor()和canvas.drawBitmap()也会降低动画性能。对于简单的动画,在实际使用时性能不太明显。
-
硬件加速
Android可以使用硬件或软件加速来渲染动画。 硬件加速通常要快得多,但有一些限制。 以下功能的支持有限:
- Anti aliasing (API 16+ only)
- Clip to composition bounds (API 18+ only)
- Stroke caps (API 19+ only)