Android 约束布局(ConstraintLayout)的使用
1. 概述
在Android中有许多的布局,比如 RelativeLayout,LinearLayout,FrameLayout 等,但是这些布局使用起来,需要一层层的嵌套。ConstraintLayout的诞生,是为了解决在开发中的复杂多层级布局的问题,在一定程度上进行布局的优化。这是Google的介绍:ConstraintLayout 官方文档
2. 导入 ConstraintLayout
在Android Studio 中(这里使用的是3.4),创建工程后,默认的布局都已经是 ConstraintLayout 了,系统已经默认导入 ConstraintLayout 所需要的库了:
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3'3. ConstraintLayout 的使用
在Android的官方介绍中,存在以下几种约束的类型:
- Relative positioning
- Margins
- Centering positioning
- Circular positioning
- Visibility behavior
- Dimension constraints
- Chains
3.1 Relative position 相对定位
ConstraintLayout具有RelativeLayout的能力,可以将一个控件置于相对于另一个控件的位置。
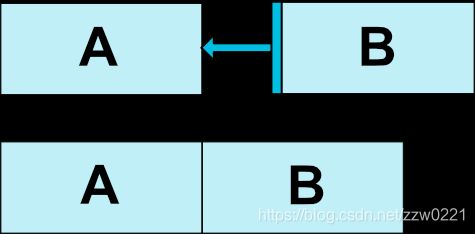
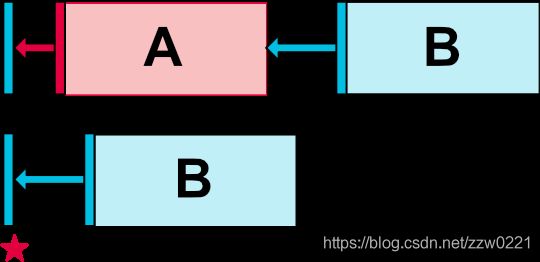
示例:将B按钮放在A按钮的右边
代码如下:
相对定位中控件的边界如图所示:
相对定位还有其他的属性:
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf
layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf
layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf
layout_constraintRight_toRightOf
layout_constraintTop_toTopOf
layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf
layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf
layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf
layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf
layout_constraintStart_toEndOf
layout_constraintStart_toStartOf
layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf
layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf从上面的属性中,可以看出相对定位属性的格式形如:
layout_constraint’DIRECTION’_to’TARGET DIRECTION’Of=”TARGET“
a. constraint’DIRECTION’ 里的 ‘DIRECTION’代表是这个子控件自身的哪条边
b. to’TARGET DIRECTION’Of 里的 ‘TARGET DIRECTION’ 代表的是和约束控件的哪条边发生约束
c. TARGET 为目标约束控件对应的 id(如果是外层的布局则 id 理解为 parent)
3.2 Margin 边距
margin指的是控件相对其他控件的距离,如图所示:
margin 常用的属性有:
android:layout_marginStart
android:layout_marginEnd
android:layout_marginLeft
android:layout_marginTop
android:layout_marginRight
android:layout_marginBottom注意:margin属性只对其相约束的View起作用,如果没有约束条件,则margin就会失效。
从下图可以看出margin属性失效了:
当加上相应的约束属性后:
margin 属性就生效了:
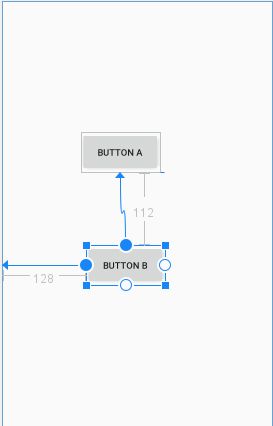
看一个栗子,Button B的位置依赖于 Button A,约束关系如下:
效果如图所示:
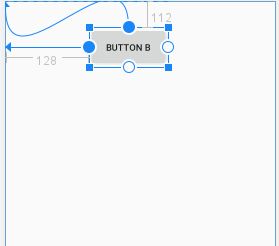
如果这时候 Button A 可见状态为gone的话,Button B会是神马样子呢?
从图上我们可以看出 Button B 的 margin-top 属性约束条件变成了与父布局的关系了。而有时候当被约束条件状态为 gone 以后,布局需要作出调整,这时候还有其他属性可以用。
效果:
可以看出 Button B 的上边距由原来的112dp 变成了40dp。
goneMargin相关的属性有如下几种:
layout_goneMarginStart
layout_goneMarginEnd
layout_goneMarginLeft
layout_goneMarginTop
layout_goneMarginRight
layout_goneMarginBottom3.3 Centering positioning 居中定位
在ConstraintLayout中没有直接的属性让一个控件者竖直居中或者竖直居中,可以使用如下方法:
效果:
可以设置bias属性,表示子控件相对父控件的位置倾向:
layout_constraintHorizontal_bias
layout_constraintVertical_bias居中情况下,bias的默认值为0.5,取值范围是0~1。
效果:
3.4 Circular positioning 圆形定位
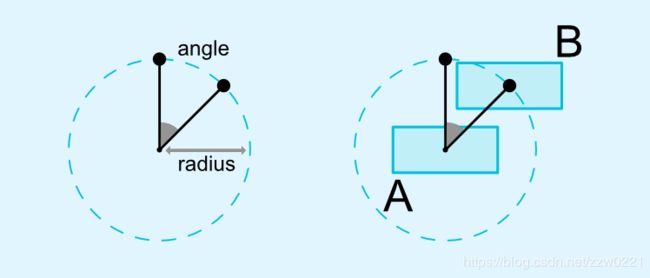
可以使用角度和距离来约束一个控件相对于另一个控件的位置。
相关的属性:
layout_constraintCircle:参照控件的id
layout_constraintCircleRadius:两个控件中心连线的距离
layout_constraintCircleAngle:当前View的中心与目标View的中心的连线与Y轴方向的夹角(取值:0~360)注意:此处的Y轴是数学坐标系中的Y轴。如下图所指示:
例子:
结果:
3.5 Visibility behavior 能见度行为
当控件设置了visibility属性为GONE属性后,控件就不会出现在布局中了,B控件对A控件的margin属性也就没有作用了。但是 ConstraintLayout 能对已经设置 GONE属性的控件进行特殊处理。当A控件设置 GONE之后,A控件相当于变成了一个点,B控件相对于对A的约束仍然是起作用的。
3.6 Dimensions constraints 尺寸约束
3.6.1 设置最小或最大尺寸
可以设置最小或者最大尺寸,有以下属性:
android:minWidth
android:minHeight
android:maxWidth
android:maxHeight 当控件的尺寸设置为 WRAP_CONTENT 的时候,这是属性才生效。
3.6.2 控件的尺寸约束
ConstraintLayout中有3中方式来设置子View的宽高尺寸:
a. Xdp,X为具体数值。
b. WARP_CONTENT。
c. 0dp,0dp代表MATCH_CONSTRAINT,ConstraintLayout不推荐使用MATCH_PARENT。
3.7 Chains 链
链能够对一组在水平或竖直方向互相关联的控件的属性进行统一管理。
在一个水平或者竖直方向上,一排view两两互相约束,即为链。
链的头部:
头部是水平链最左边的控件或者垂直链的最顶部的控件。
链的样式:
链有以下几种样式:
-
spread
默认模式,分布样式如上图 -
spread_inside
如图,和spread的区别是没算两端的约束 -
packed
所有元素挤在中间,也可以配合使用bias来改变位置偏移
例子:
结果:
例子中链的style设置为 packed,链的所有元素被打包在一起。
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/106e4282a383
https://www.cnblogs.com/angrycode/p/9739513.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/17ec9bd6ca8a
https://www.jianshu.com/p/502127a493fb