Pytorch的学习——批标准化
批标准化
批标准化是一种将分散的数据统一的标准,也是优化神经网络的一种方法。为什么要批标准化?当神经网络深度很深的时候,在误差反向传递时,神经网络开始几层会学到一些东西,而到后面几层时很可能会出现神经网络没有东西可学的情况,这时候可以通过批标准化解决这个问题。
列子
这里小编通过一个列子来更加直观的了解批标准化
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
import torch.utils.data as Data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
N_SAMPLES = 2000
BATCH_SIZE = 64 # 批处理时,每次提取的数据个数
EPOCH = 12 # 批处理的次数
LR = 0.03 # 学习效率
N_HIDDEN = 8 # 隐藏层数量
ACTIVATION = torch.tanh # 使用的激励函数
B_INIT = -0.2 # 使用错误的偏置常数初始值,让神经网络更加偏向于负数区间,更加容易体现经过批标准化和没有经过批标准化的区别
# train数据
x = np.linspace(-7, 10, N_SAMPLES)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 2, x.shape)
y = np.square(x) - 5 + noise
# test数据
test_x = np.linspace(-7, 10, 200)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 2, test_x.shape)
test_y = np.square(test_x) - 5 + noise
# 转换数据类型
train_x, train_y = torch.from_numpy(x).float(), torch.from_numpy(y).float()
test_x = torch.from_numpy(test_x).float()
test_y = torch.from_numpy(test_y).float()
train_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(train_x, train_y)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=2,)
# 可视化
plt.scatter(train_x.numpy(), train_y.numpy(), c='#FF9359', s=50, alpha=0.2, label='train')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, batch_normalization=False):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.do_bn = batch_normalization
self.fcs = []
self.bns = []
self.bn_input = nn.BatchNorm1d(1, momentum=0.5) # 对输入数据进行批标准化,0.5是更新批标准化的缩减参数和平移参数的频率
for i in range(N_HIDDEN): # 构建隐藏层和BN层
input_size = 1 if i == 0 else 10
fc = nn.Linear(input_size, 10)
setattr(self, 'fc%i' % i, fc)
self._set_init(fc) # 参数初始化
self.fcs.append(fc)
if self.do_bn:
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(10, momentum=0.5)
setattr(self, 'bn%i' % i, bn)
self.bns.append(bn)
self.predict = nn.Linear(10, 1) # 输出层
self._set_init(self.predict) # 参数初始化
def _set_init(self, layer):
init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0., std=.1)
init.constant_(layer.bias, B_INIT)
def forward(self, x):
pre_activation = [x]
if self.do_bn: x = self.bn_input(x) # 输入批标准化
layer_input = [x]
for i in range(N_HIDDEN):
x = self.fcs[i](x)
pre_activation.append(x)
if self.do_bn: x = self.bns[i](x) # 批标准化
x = ACTIVATION(x)
layer_input.append(x)
out = self.predict(x)
return out, layer_input, pre_activation
# 初始化两个神经网络,一进行批标准化,一个没有
nets = [Net(batch_normalization=False), Net(batch_normalization=True)]
# 选择优化器
opts = [torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=LR) for net in nets]
# 选择计算误差的工具
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# 用来可视化
def plot_histogram(l_in, l_in_bn, pre_ac, pre_ac_bn):
for i, (ax_pa, ax_pa_bn, ax, ax_bn) in enumerate(zip(axs[0, :], axs[1, :], axs[2, :], axs[3, :])):
[a.clear() for a in [ax_pa, ax_pa_bn, ax, ax_bn]]
if i == 0:
p_range = (-7, 10)
the_range = (-7, 10)
else:
p_range = (-4, 4)
the_range = (-1, 1)
ax_pa.set_title('L' + str(i))
ax_pa.hist(pre_ac[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=p_range, color='#FF9359', alpha=0.5)
ax_pa_bn.hist(pre_ac_bn[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=p_range, color='#74BCFF', alpha=0.5)
ax.hist(l_in[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=the_range, color='#FF9359')
ax_bn.hist(l_in_bn[i].data.numpy().ravel(), bins=10, range=the_range, color='#74BCFF')
for a in [ax_pa, ax, ax_pa_bn, ax_bn]:
a.set_yticks(())
a.set_xticks(())
ax_pa_bn.set_xticks(p_range)
ax_bn.set_xticks(the_range)
axs[0, 0].set_ylabel('PreAct')
axs[1, 0].set_ylabel('BN PreAct')
axs[2, 0].set_ylabel('Act')
axs[3, 0].set_ylabel('BN Act')
plt.pause(0.01)
if __name__ == "__main__":
f, axs = plt.subplots(4, N_HIDDEN + 1, figsize=(10, 5))
plt.ion()
plt.show()
# 训练
losses = [[], []] # 记录两个网络的误差
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
print('Epoch: ', epoch)
layer_inputs, pre_acts = [], []
for net, l in zip(nets, losses):
net.eval() # 脱离训练模式,用于输出当前的参数
pred, layer_input, pre_act = net(test_x)
l.append(loss_func(pred, test_y).data.item())
layer_inputs.append(layer_input)
pre_acts.append(pre_act)
net.train() # 重新进入训练模式
plot_histogram(*layer_inputs, *pre_acts) # 数据可视化
for step, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
for net, opt in zip(nets, opts): # 为每个网络进行训练
pred, _, _ = net(b_x)
loss = loss_func(pred, b_y)
opt.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
opt.step() # 更新网络
plt.ioff()
# 显示训练误差
plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(losses[0], c='#FF9359', lw=3, label='Original')
plt.plot(losses[1], c='#74BCFF', lw=3, label='Batch Normalization')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('test loss')
plt.ylim((0, 2000))
plt.legend(loc='best')
# set net to eval mode to freeze the parameters in batch normalization layers
[net.eval() for net in nets] # set eval mode to fix moving_mean and moving_var
preds = [net(test_x)[0] for net in nets]
plt.figure(3)
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), preds[0].data.numpy(), c='#FF9359', lw=4, label='Original')
plt.plot(test_x.data.numpy(), preds[1].data.numpy(), c='#74BCFF', lw=4, label='Batch Normalization')
plt.scatter(test_x.data.numpy(), test_y.data.numpy(), c='r', s=50, alpha=0.2, label='train')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
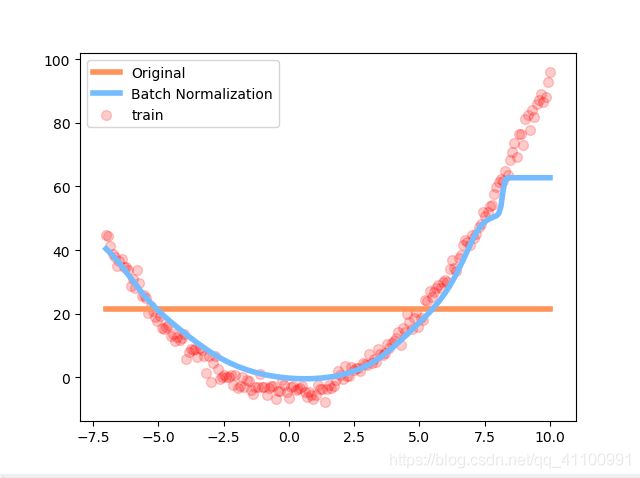
效果
可以看到没有进行批标准化的到后面两层层已经无法激活函数了
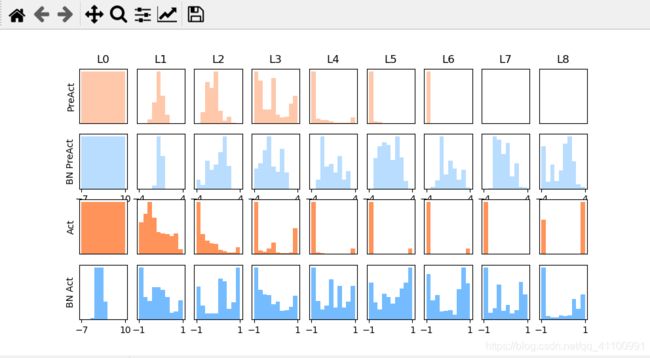
而下图可以看到,经过批标准化的神经网络依然在拟合训练数据,而没有经过批标准化的神经网络已经成一条直线了,不再工作了。