Vrep 中的运动规划1(主要是基于RRT算法)
声明:本文摘自其它参考资料之内容,会在文末声明,绝无冒犯之意,只为一时复习之方便,侵权必删!
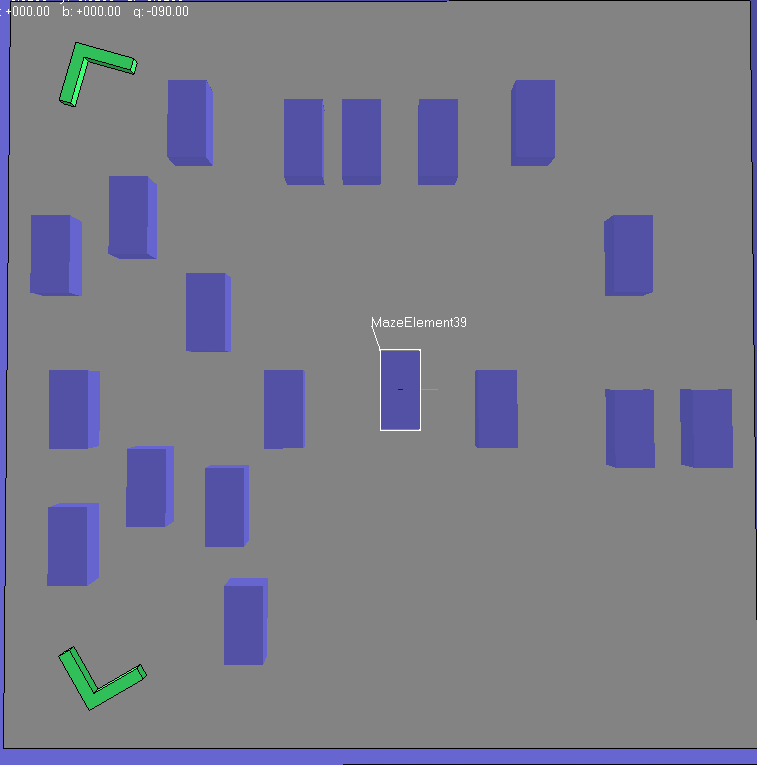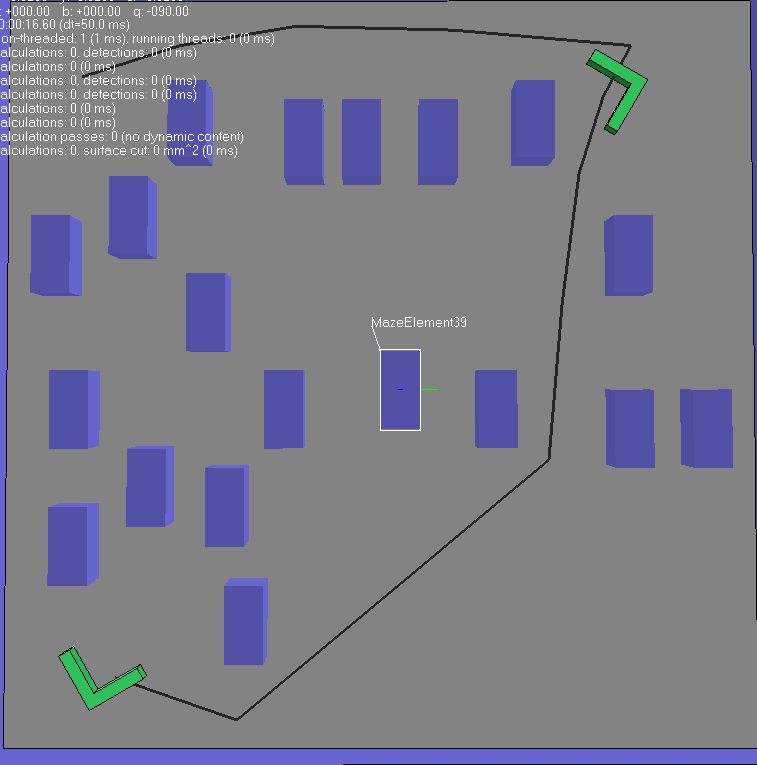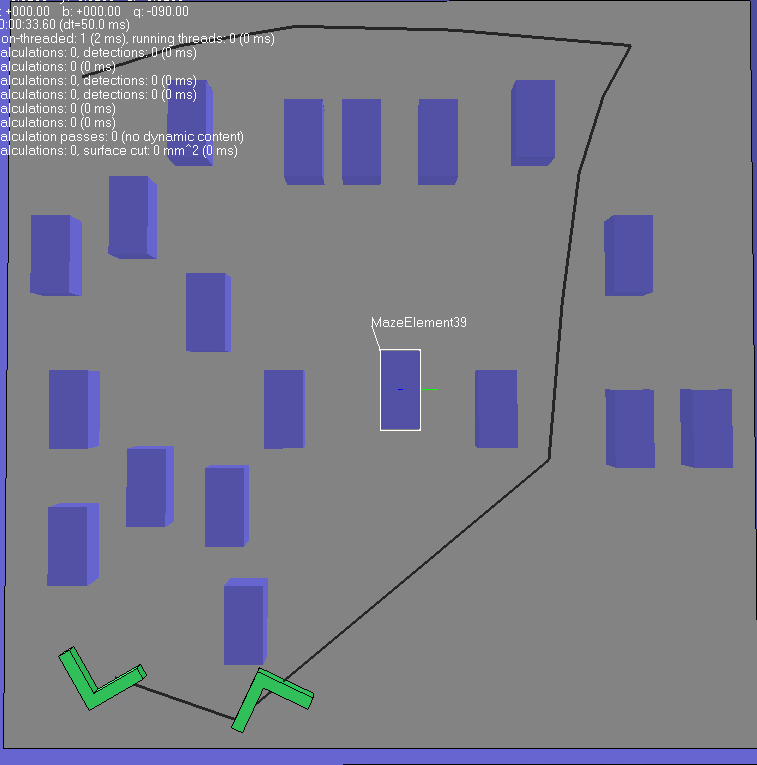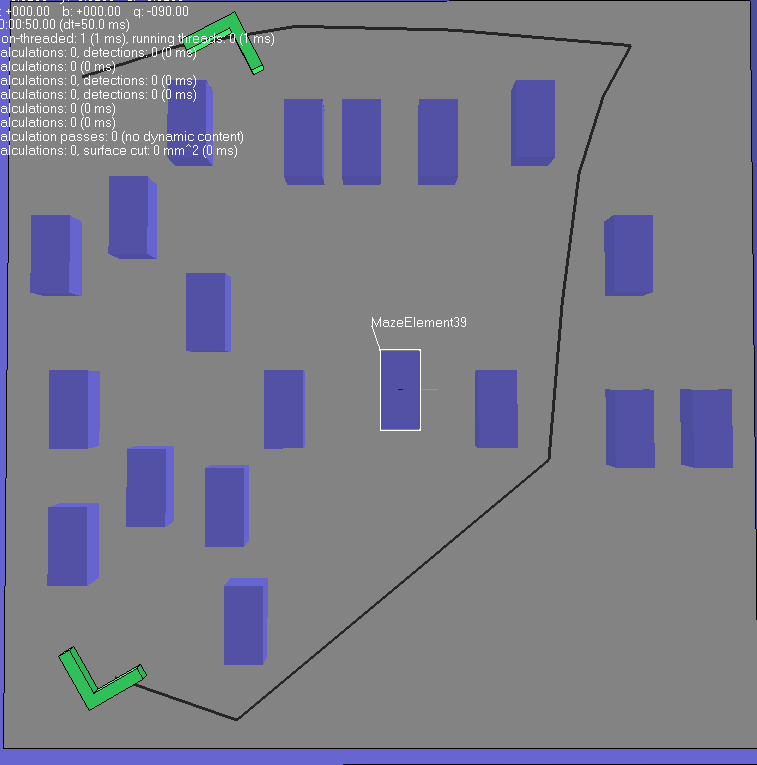
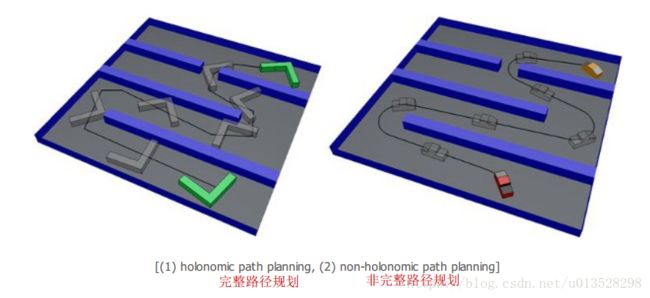
1.算法效果
(1)第一种情况
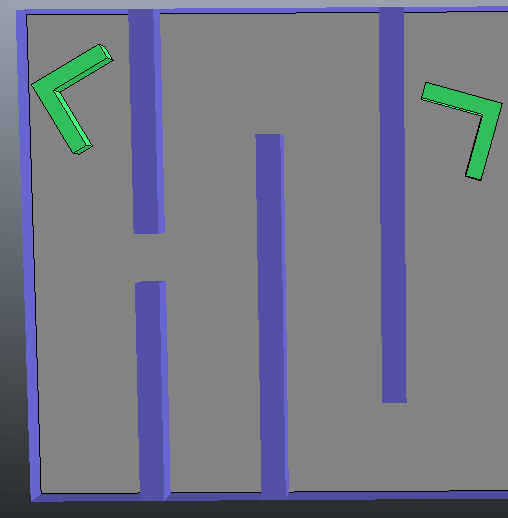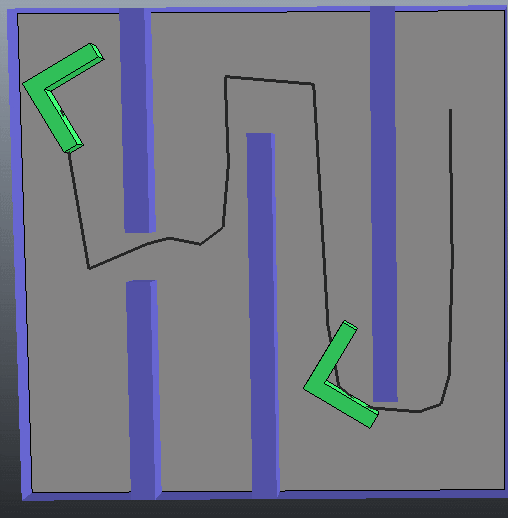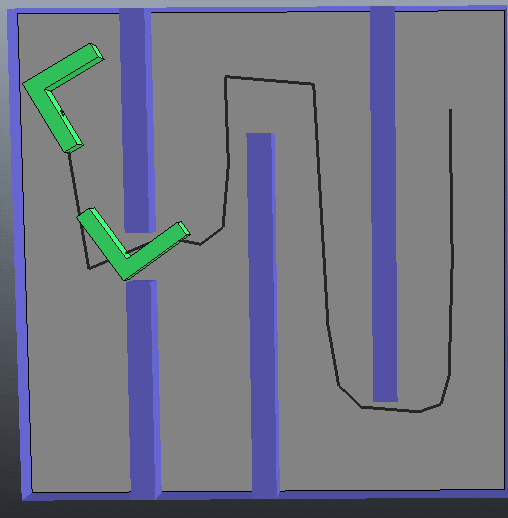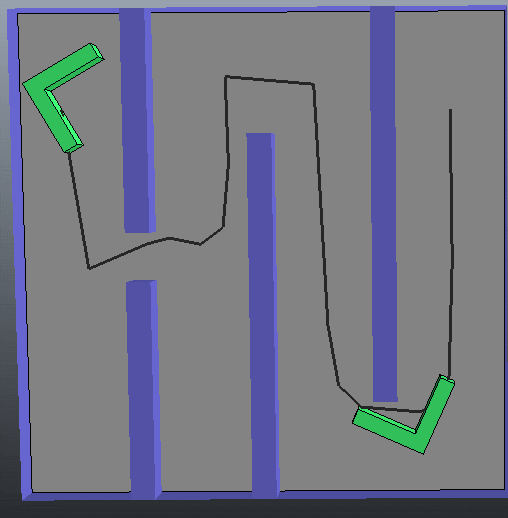
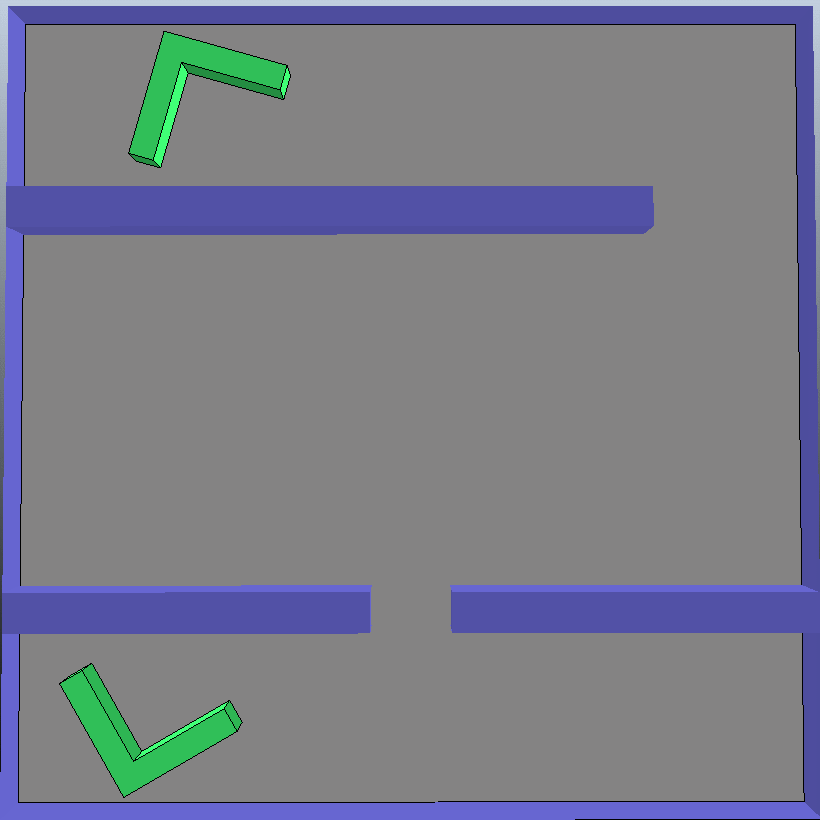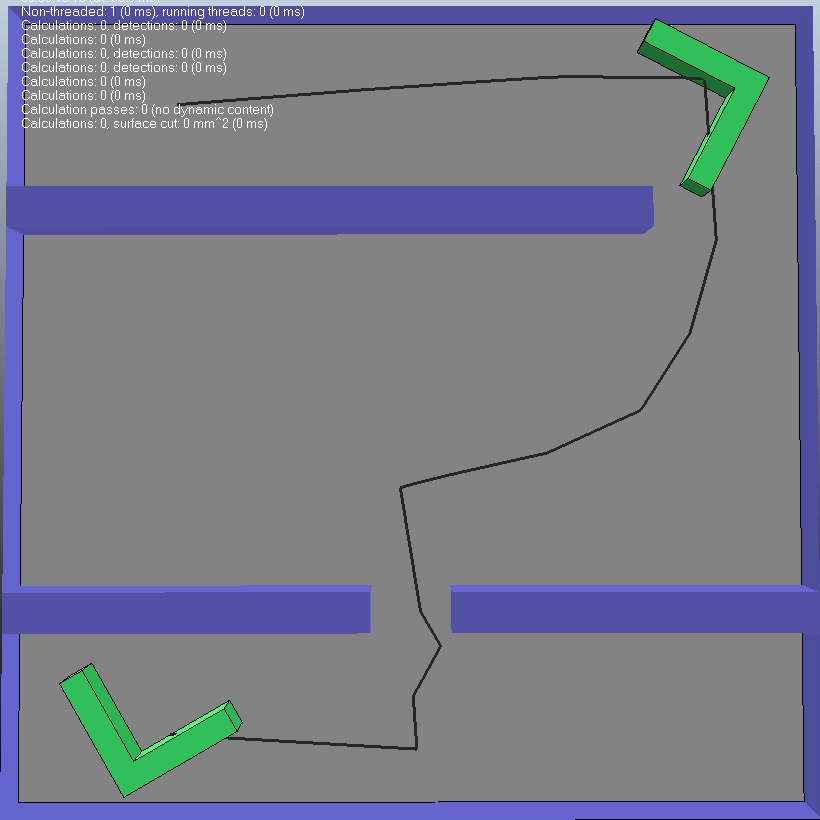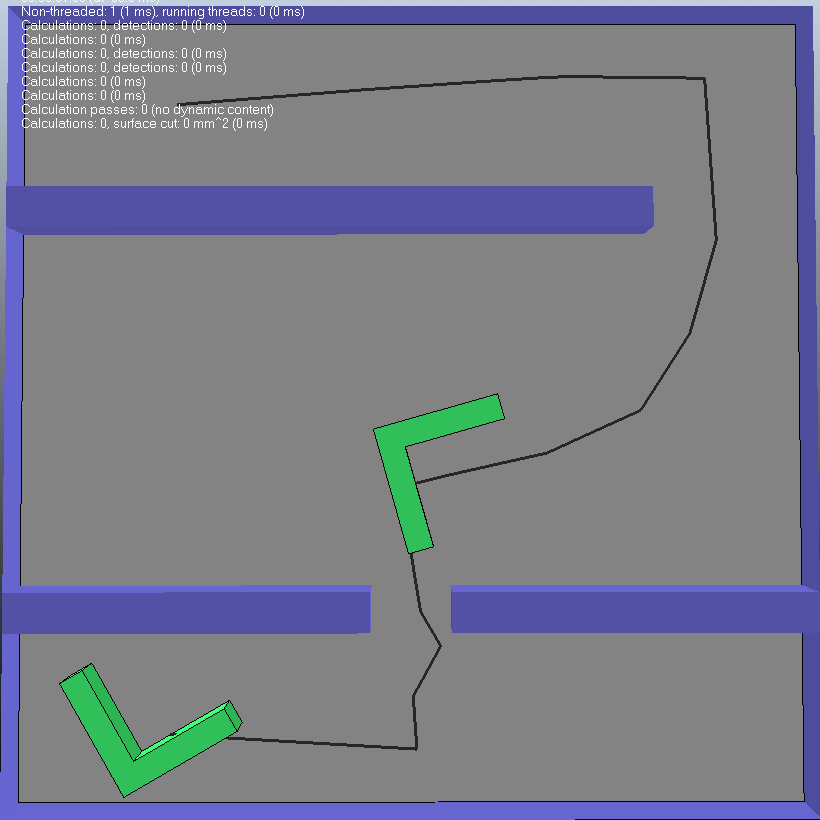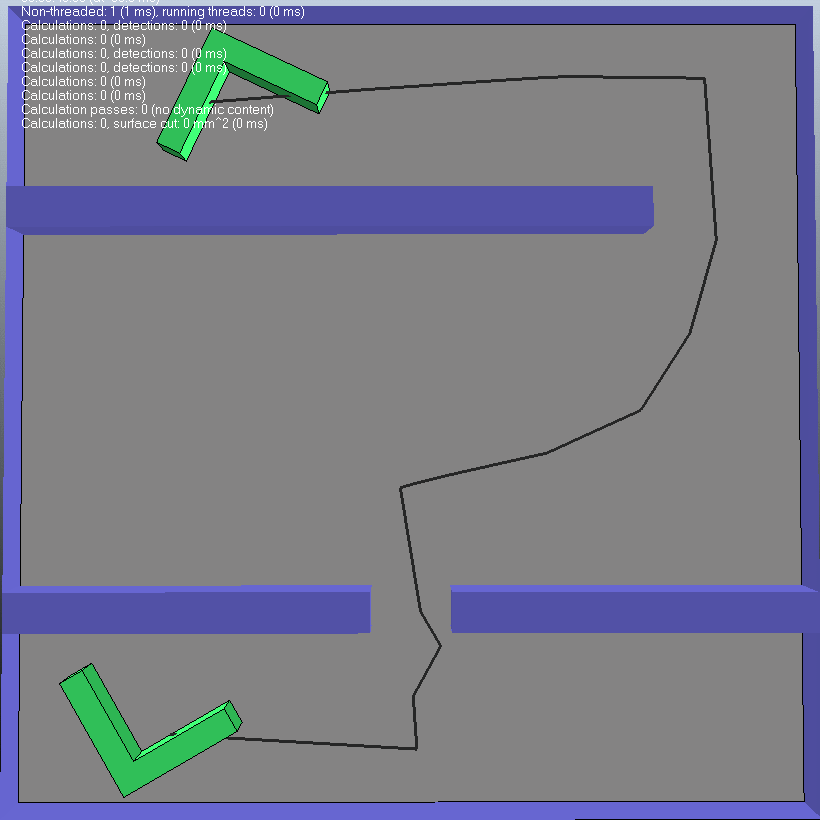
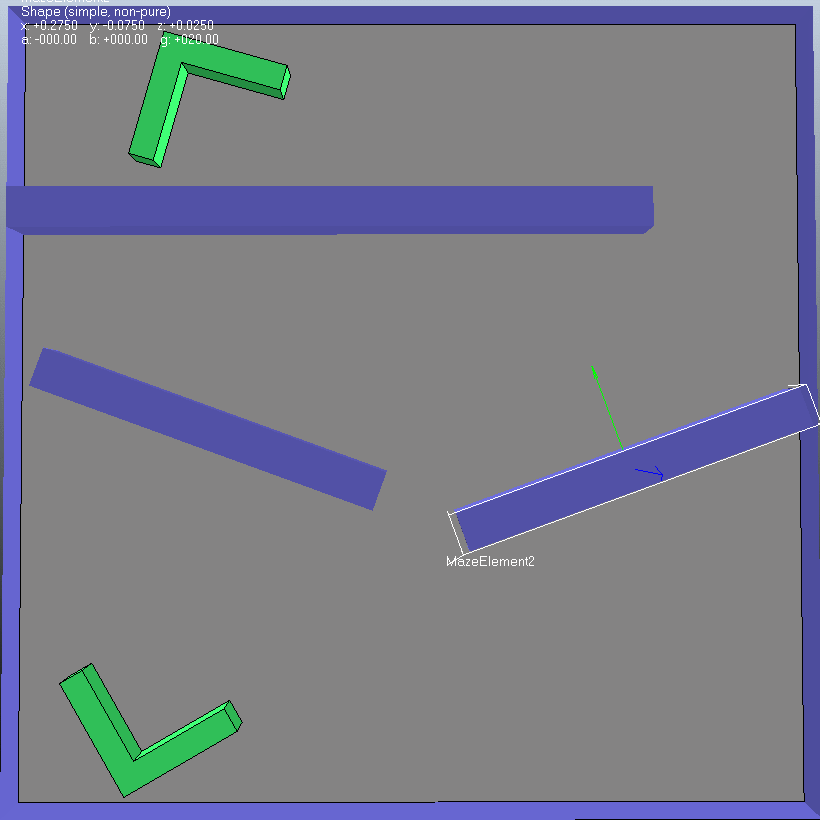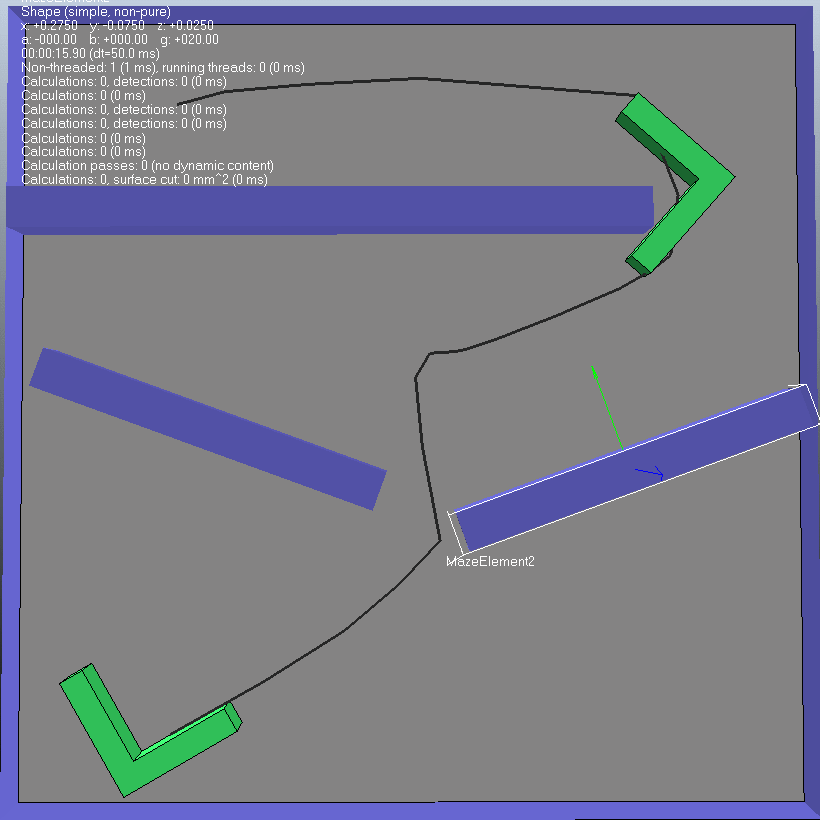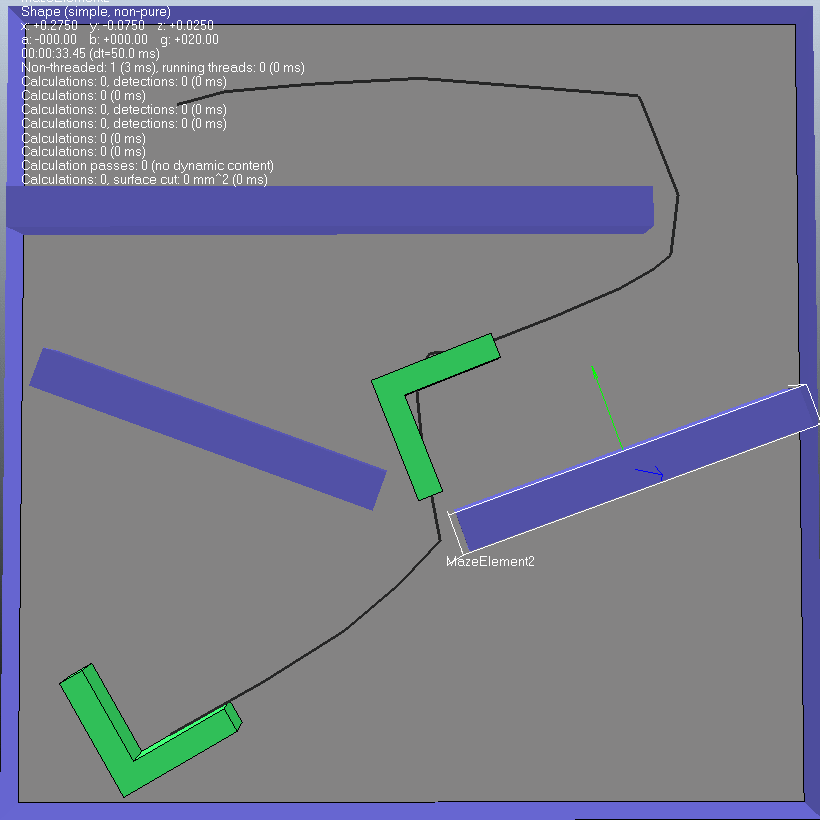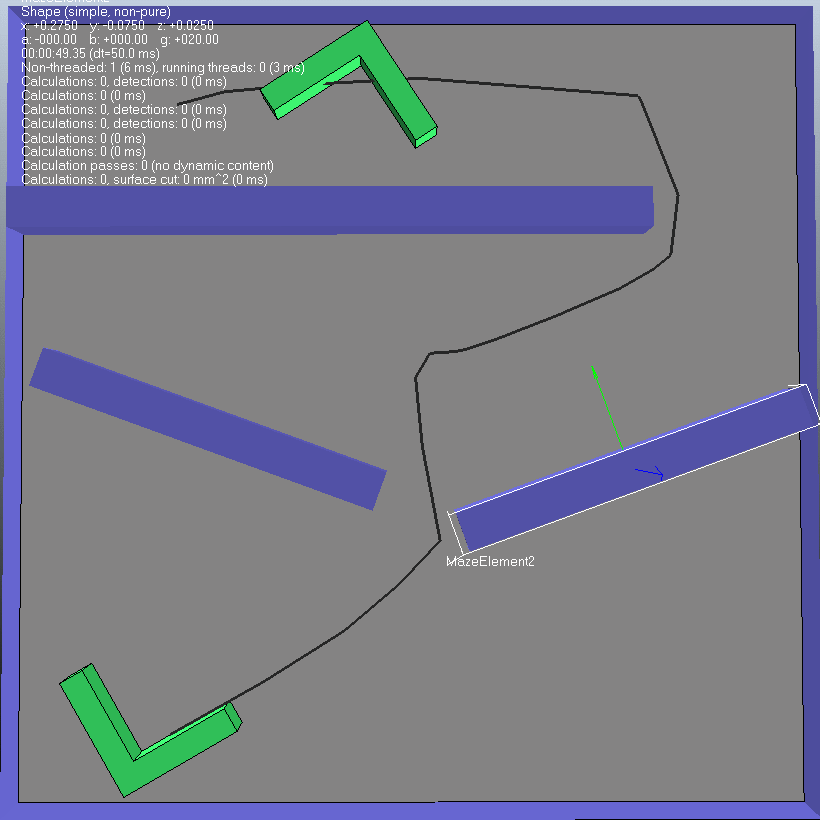
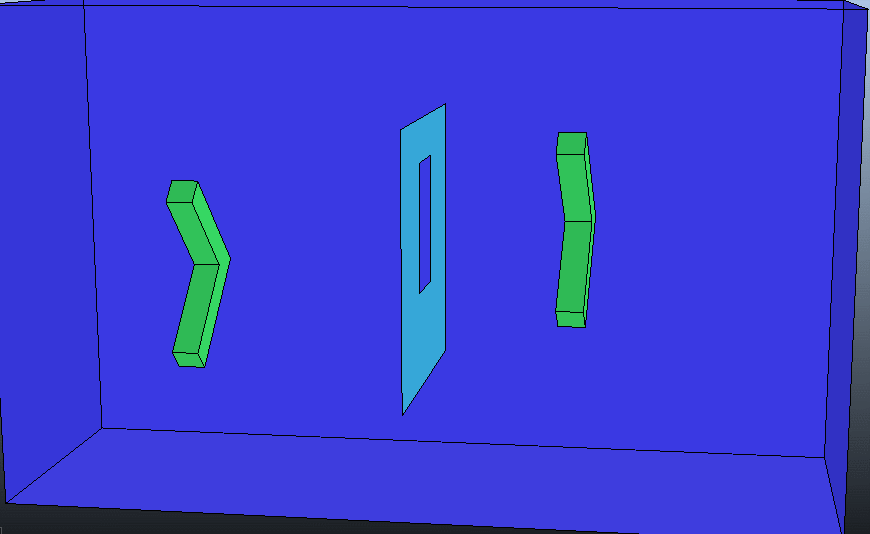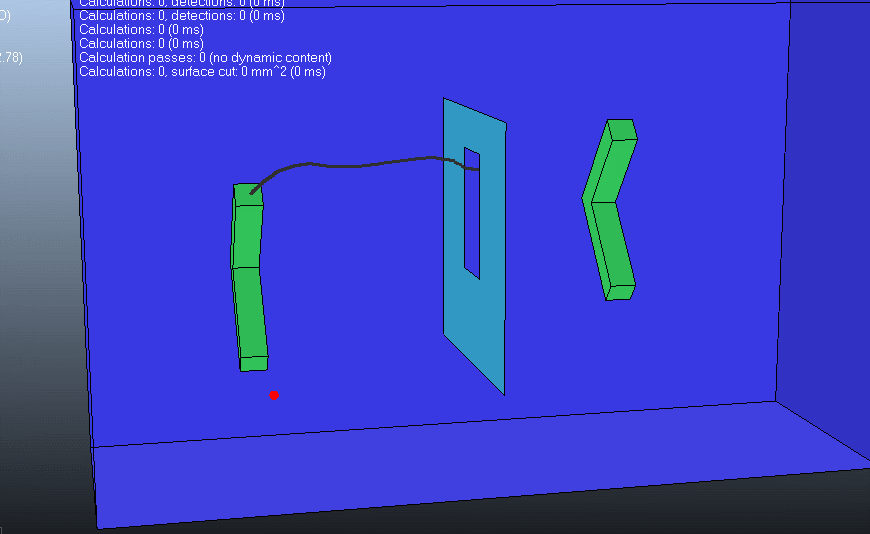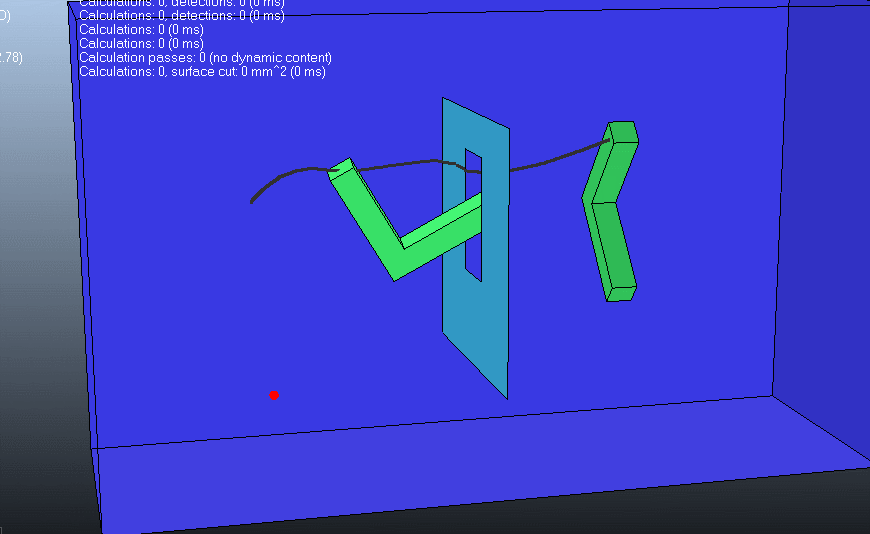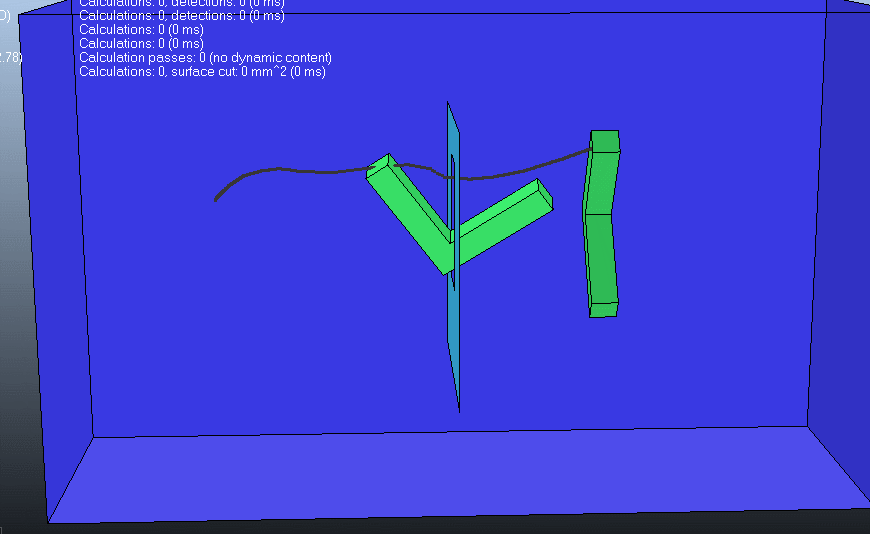
(2) 第二种情况 从图中可以看出来,开始时规划路径需要几秒钟。
(3)第三种情况可以看出 此种情况似乎是计较简单的,规划路径所需要的时间很短
(4)第四种情况
(5)三维空间中的路径规划
2.path planning 示例
3.path planning
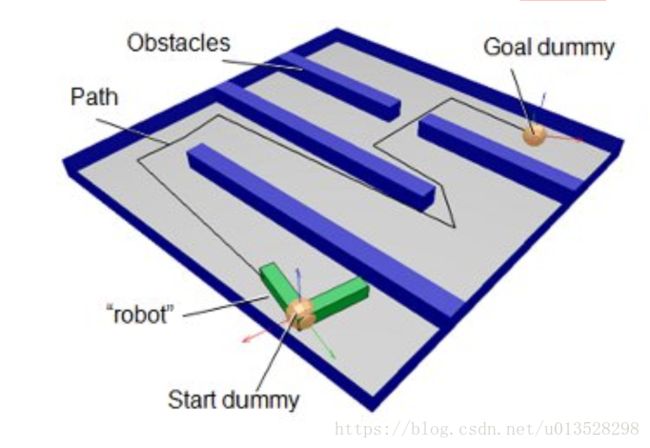
一个路径 规划任务通常有以下几个需要考虑的事项:
A path planning task usually takes several input values or parameters:
- a collidable or measurable robot entity: this entity represents the device that should avoid obstacles and is referred to hereafter as robot.
- a start dummy: the start dummy represents the initial configuration of the robot. The robot entity should be built on top of the start dummy. Make sure that the center of the robot approximately matches the position of the start dummy.
- a goal dummy: the goal dummy represents the desired configuration of the robot. The path planning algorithms will try to move the start dummy towards the goal dummy while avoiding collisions between the robot and obstacle.
- a collidable or measurable obstacle entity: this entity represents the obstacles that the robot should avoid. It is referred to hereafter as obstacle.
- a path: the path acts as a container for a trajectory calculated by the path planning algorithm.
A path linking the start configuration to the goal configuration can be specified (or restricted to be) in a
configuration space with a specific number of dimensions (e.g. the X, Y configuration space). Moreover
additional constraints are usually needed that make the task more complicated (e.g. keeping a certain
distance threshold to the obstacles, or moving only in one direction).
下图包含了以上列举的五个元素:
visualizePath=function(path)
if not _lineContainer then
_lineContainer=sim.addDrawingObject(sim.drawing_lines,3,0,-1,99999,{0.2,0.2,0.2})
end
sim.addDrawingObjectItem(_lineContainer,nil)
if path then
local pc=#path/3
for i=1,pc-1,1 do
lineDat={path[(i-1)*3+1],path[(i-1)*3+2],initPos[3],path[i*3+1],path[i*3+2],initPos[3]}
sim.addDrawingObjectItem(_lineContainer,lineDat)
end
end
end
function sysCall_threadmain()
robotHandle=sim.getObjectHandle('StartConfiguration')
targetHandle=sim.getObjectHandle('GoalConfiguration')
initPos=sim.getObjectPosition(robotHandle,-1)
initOrient=sim.getObjectOrientation(robotHandle,-1)
t=simOMPL.createTask('t')
ss={simOMPL.createStateSpace('2d',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.pose2d,robotHandle,{-0.5,-0.5},{0.5,0.5},1)}
simOMPL.setStateSpace(t,ss)
simOMPL.setAlgorithm(t,simOMPL.Algorithm.RRTConnect)
simOMPL.setCollisionPairs(t,{sim.getObjectHandle('L_start'),sim.handle_all})
startpos=sim.getObjectPosition(robotHandle,-1)
startorient=sim.getObjectOrientation(robotHandle,-1)
startpose={startpos[1],startpos[2],startorient[3]}
simOMPL.setStartState(t,startpose)
goalpos=sim.getObjectPosition(targetHandle,-1)
goalorient=sim.getObjectOrientation(targetHandle,-1)
goalpose={goalpos[1],goalpos[2],goalorient[3]}
simOMPL.setGoalState(t,goalpose)
r,path=simOMPL.compute(t,4,-1,800)
while path do
visualizePath(path)
-- Simply jump through the path points, no interpolation here:
for i=1,#path-3,3 do
pos={path[i],path[i+1],initPos[3]}
orient={initOrient[1],initOrient[2],path[i+2]}
sim.setObjectPosition(robotHandle,-1,pos)
sim.setObjectOrientation(robotHandle,-1,orient)
sim.switchThread()
end
end
end介绍一个比较重要的函数:
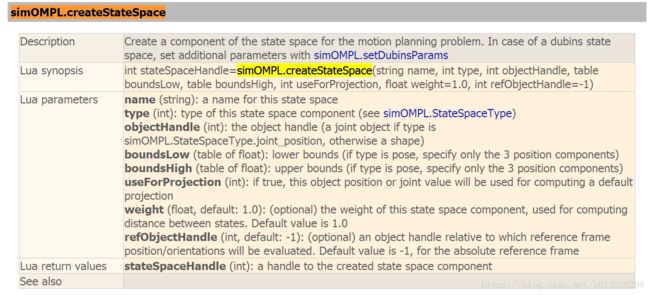
1.函数simExtOMPL_createStateSpace的参数type表示创建的状态空间的类型。type的值可以为:
sim_ompl_statespacetype_position2d:二维平面内的移动(X,Y方向移动)sim_ompl_statespacetype_pose2d:二维平面内的移动加转动(X,Y方向移动和绕Z轴的转动)
sim_ompl_statespacetype_position3d:三维空间内的移动(X,Y,Z方向上的移动)
sim_ompl_statespacetype_pose3d:三维空间内的移动加转动(X,Y,Z方向上的移动和绕X,Y,Z轴的转动)
sim_ompl_statespacetype_joint_position:关节空间内的运动
上面的例子中“机器人”可以进行在平面上移动和转动,因此参数选为sim_ompl_statespacetype_pose2d
2.指定好路径规划任务的configuration space非常重要
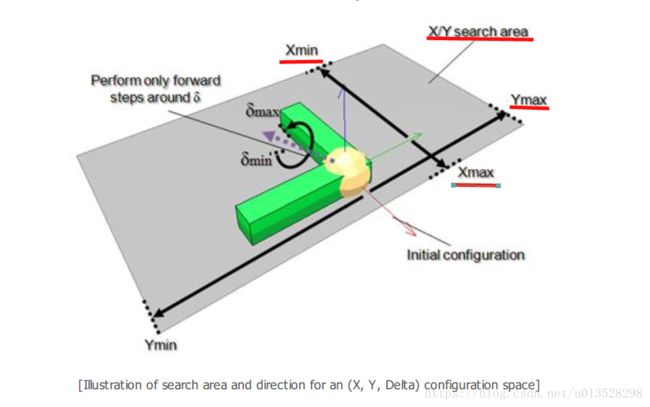
In addition to being able to specify the configuration space for a path planning task, the user is also able to
specify the area and direction in which the search has to be performed:
ss={simOMPL.createStateSpace('2d',simOMPL.StateSpaceType.pose2d,robotHandle,{-0.5,-0.5},{0.5,0.5},1)}在3DoFHolonomicPathPlanning这个例子中,搜索的面积是1x1(单位:平方米)。
{-0.5,-0.5}是搜索的下限{Xmin,Ymin}。{0.5,0.5}是搜索的上限{Xmax,Ymax}
适当的限制搜索的面积十分重要,有助于减少计算时间。
It is important to appropriately limit the search area in order to: (1) reduce calculation times, and (2) make
the path planning task realizable. Following figure illustrates the effect of the search direction:
如下图所示,指定搜索方向为X的正方向或者X的正负方向,搜索算法的搜索面积将不同。
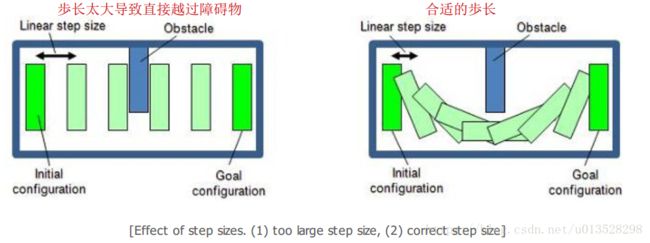
3.选择合适的歩长
适当增大歩长可以降低运算量,但是过大可能会导致直接越过障碍物,现实的物理世界中表现为,机器人直接和障碍物相撞。
合适的歩长就可以避开障碍物,如下图所示:
4.使用的算法:RRTConnect
RRTConnect( The basic idea is to grow two RRTs, one from the start and one from the goal, and attempt to connect them.)
( 以下内容参考博客RRT路径规划算法,目前没有深刻的理解,今后有深刻的理解的时候再自行记录一番)
基本的RRT每次搜索都只有从初始状态点生长的快速扩展随机树来搜索整个状态空间,如果从初始状态点和目标状态点同时生长两棵快速扩展随机树来搜索状态空间,效率会更高。为此,基于双向扩展平衡的连结型双树RRT算法,即RRT_Connect算法被提出。
使用matlab实现的RRTconnnect算法
5. 代码简易分析
代码分析,查看自己的Notepad++里的代码解析。
参考:
1.RRT路径规划算法-冬木远景
2.Path planning
3.V-rep学习笔记:机器人路径规划1 - 冬木远景 - 博客园