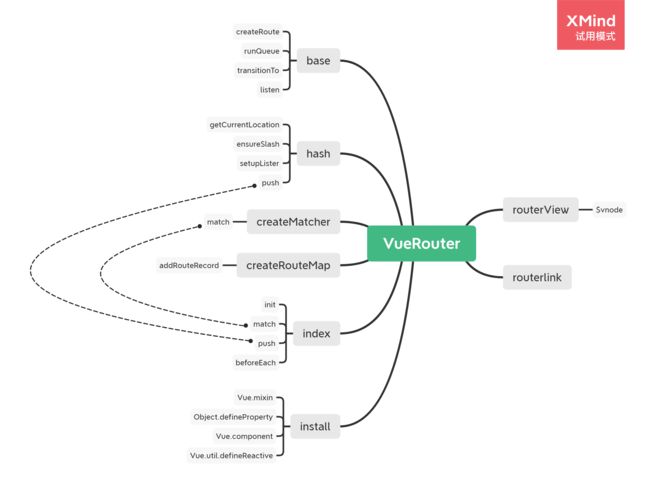
Vue-Router提供了俩个组件 `router-link` `router-view`, 提供了俩个原型上的属性`$route` `$router` ,我现在跟着源码来把它实现一下
开始
先看平时使用的 `Vue-Router` ,引入`Router` , `Vue.use` 注册插件。直接从这里开始入手
使用场景
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from "../vue-router" import routes from './routes' Vue.use(Router) let router = new Router({ routes })
index
先看`vue-router.js`文件,先生成一个`VueRouter`类,然后导入`install`方法,因为`Vue-Router`的`install`方法比`Vuex`复杂一些,所以将`install`单独作为一个文件。
import install from './install'; class VueRouter { constructor(options) { } } VueRouter.install = install; export default VueRouter
Vue.use()
来先看 `Vue.use()`的源码中的一部分,这里面判断注册的插件里的`install`是不是一个函数,有就执行插件里的`install`函数。或者判断插件本身是不是一个函数,有就执行插件本身。这里本质上是没有区别,有没有`install`都可以。而`VueRouter`使用了`install`,目的是为了将`install`作为入口函数,方便封装,同时也将`install`和其他代码分开。
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') { plugin.install.apply(plugin, args) } else if (typeof plugin === 'function') { plugin.apply(null, args) }
install
上述已经将`vue-router`的类构建好,现在`VueRouter`实例已经有了,然后执行`vue.use()`,然后会执行`VueRouter`类里的`install`函数,那来看`install.js`。
install里使用了`Vue.mixin`,混入代码,下面代码是在当前组件生命周期`beforeCreate`里混入代码,代码逻辑是判断当前组件是否为根组件,如果是则将`_routerRoot`作为键放入当前组件中,值为`Vue`实例。再将`_router`作为键放入当前组件中,值为`VueRouter`实例。然后执行初始化操作。
如果不为当前组件不是根组件,则该组件为根组件的子组件。将`_routerRoot`作为键放入当前组件中,值为父组件的`_routerRoot`,从父亲身上获取.
`$route`和`$router`是利用`Object.definePropert`代理`_routerRoot`里的`_router`和`_route`,访问到的。
接着注册全局组件`router-view`和`router-link`
import RouterView from '../components/router-view' import RouterLink from '../components/router-link' const install = (_Vue, s) => { _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate() { if (this.$options.router) { // 判断是不是根组件 this._routerRoot = this; // 把vue实例放在当前组件的——routerRoot属性上 this._router = this.$options.router // 这里直接获取根实例 this._router.init(this); // 初始化 _Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current) // 将属性_route成为响应式属性 } else { this._routerRoot = this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot // 这里的是从父亲最顶层获取Router实例 } } }) Object.defineProperty(_Vue.prototype, '$route', { // 代理$route get() { return this._routerRoot._route } }) Object.defineProperty(_Vue.prototype, '$router', { // 代理$router get() { return this._routerRoot._router } }) _Vue.component('router-view', RouterView) // 注册组件router-view _Vue.component('router-link', RouterLink) // 注册组件router-view } export default install
init
vue-router 默认 hash 模式 —— 使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。
然后回到`VueRouter`类中,此时多了个`init`函数。目前做的路由方式是`hash`方式,还有另外俩种方式,`history`,`abstract`。因为有三种方式,所以`Vue-Router`做了一个父类`base`执行同样的逻辑,子类三种方式继承父类`base`,再独自执行自己方式的代码。
通过`new HashHistory` 获取 `history`实例,初始化`init`执行`history`实例对应函数。将目光放到`history`实例上,这些函数来自于`base.js`和`hash.js`。
import install from './install'; class VueRouter { constructor(options) { this.history = new HashHistory(this); } init(app) { const history = this.history; const setupHashLister = () => { history.setupLister(); // hash的跳转 } history.transitionTo( history.getCurrentLocation(), setupHashLister ) history.listen((route) => { app._route = route }) } } VueRouter.install = install; export default VueRouter
base.js
先看构造函数`construcror`,将`router`作为键放在自身实例上,值为`VueRouter`实例,`curent`为当前导航正要离开的路由,也就是路由守卫的参数里的`from`
1.`transitionTo()`为跳转后立即执行的函数,传入当前路径和回调函数,`r`为`$route`,是扁平化后的配置,也就是即将要进入的目标 路由对象
2.`cb`是`History`的`listen()`函数,将`$route`放入当前组件上供用户使用。
3.`callback`是执行`HashHistory`的`setupHashLister()`函数,是给当前`window`添加监听事件`onhashChange`,`onhashChange`后续通过`hash`变化执行`transitionTo`进行更新。
4.最后将`r`赋值给`current`,更新路由信息。
class History { constructor(router) { this.router = router; this.current = createRoute(null, { path: '/' }) } transitionTo(location, callback) { let r = this.router.match(location) if (location == this.current.path && r.matched.length == this.current.matched.length) { // 防止重复跳转 return } this.cb && this.cb(r); callback && callback(); this.current = r; } listen(cb) { this.cb = cb; } }
hash.js
`hash`方式的函数就简单介绍一下,看构造函数`constructor`,跟父类一样赋值`router`。执行`ensureSlash`函数,因为`hash`相比其他函数,一进入页面就会多个#。所以就初始化的时候处理一下。`getCurrentLocation`函数是获取当前路径的,`push`是`hash`方式的跳转,`setupLister`函数是刚刚所述的监听函数`hashchange`。
import Histroy from './base'; function ensureSlash() { if (window.location.hash) { return } window.location.hash = '/'; } class HashHistory extends Histroy { constructor(router) { super(); this.router = router; ensureSlash(); } getCurrentLocation() { return window.location.hash.slice(1); } push(location){ this.transitionTo(location,()=>{ window.location.hash = location }) } setupLister() { window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => { this.transitionTo(window.location.hash.slice(1)); }) } } export default HashHistory
扁平化
刚刚`base.js`里执行的`this.router.match(location)`以及`createRoute()`,都是需要建立在扁平化配置基础之上的。
平时配置的路由是这样的,需要将配置进行扁平化,才能用得上。
[ { path: '/', name: 'home', component: Home }, { path: '/about', name: 'about', component: About, children: [ { path: 'add', name: 'add', component: Add }, { path: 'bull', name: 'bull', component: Bull } ] } ]
扁平化后是这样的
/: {path: "/", component: {…}, parnent: undefined}
/about: {path: "about", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
/about/add: {path: "add", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
/about/bull: {path: "bull", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
接着看扁平化函数createMatcher以及createRouteMap
createMatcher
`createMatcher`返回一个`match`函数,`match`方法是匹配路径,根据路径拿扁平化对象里的配置,然后执行`createRoute`方法,将其转化为`route`,返回。`pathMap`由`createRouteMap`生成
import createRouteMap from './create-route-map' import { createRoute } from './history/base'; export default function createMatcher(routes) { let { pathList, pathMap } = createRouteMap(routes); function match(location) { console.log(pathMap) let record = pathMap[location]; return createRoute(record,{ path: location }) } return { match } }
createRouteMap
将`routes`配置传入`createRouteMap`中,遍历`routes`,进行扁平化操作
`pathMap`以路径为键名,值为一个对象包裹着路径,组件,父组件。
将路径匹配上父组件的路径和自身的路径
如果有子组件就进行递归,全部转为扁平化返回。
export default function createRouteMap(routes, oldPathList, oldpathMap) { let pathList = oldPathList || []; let pathMap = oldpathMap || Object.create(null); routes.forEach(route => { addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap); }) return { pathList, pathMap } } function addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap,parnent) { let path = parnent ? `${parnent.path}/${route.path}`: route.path; let record = { path: route.path, component: route.component, parnent } if (!pathMap[path]) { pathList.push(path); pathMap[path] = record; } if(route.children){ route.children.forEach(route=>{ addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap,record) }) } }
createRoute
`createRoute`是生成`$route`的函数,传入参数为扁平化配置,路径。将`res`作为空数组,如果传进来的扁平化配置有值,则进行`while`循环,将自己从数组头部插入,取出父组件再从头部插入,如此反复,得到一个含着层次关系的数组。将`loaction`和数组包裹为对象返回。
export function createRoute(record, location) { let res = []; if (record) { while (record) { res.unshift(record) record = record.parnent } } return { ...location, matched: res } }
router-view
然后在来看看`routerview`
是一个函数式组件,
返回`render`方法
进行`while`循环,遍历出嵌套的`routerview`
用`depth`作为深度,也是`matched`的`index`.
每遍历一次,就在`$vnode.data.rouView` 改为`true`,将深度加1
返回对应的组件即可
export default { name:'routerView', functional: true, render(h,{parent,data}) { let route = parent.$route let depth = 0; while (parent) { if (parent.$vnode && parent.$vnode.data.routeView) { depth++; } parent = parent.$parent; } data.routeView = true; let record = route.matched[depth]; if (!record) { return h(); } return h(record.component, data); } }
router-link
再来看看`routerlink`
没什么东西就返回一个`a`标签,用插槽把对应的文本显示出来,在添加的跳转事件
调用`$router`的`push`方法,也就是`Router`类上的`push`
export default { name: 'routerLink', props: { to: { type: String, required: true }, tag: { type: String, default: 'a' } }, methods: { handler(to) { this.$router.push(to) // 路由跳转 } }, render() { return this.handler.bind(this,this.to)}>{this.$slots.default[0].text} } }
vuerouter草稿:https://juejin.im/post/6862215979745673224