HandlerThread
HandlerThread是什么
HandlerThread继承自Thread,因此HandlerThread其实就是一个线程。
线程开启时也就是run方法运行起来后,线程同时创建一个含有消息队列的looper,并对外提供自己这个对象的get方法,这就是和普通的Thread不一样的地方。可用于多个耗时任务要串行执行。
使用流程
1.实例对象,参数为线程名
HandlerThread handlerThread = new HandlerThread("handlerThread");2.启动线程
handlerThread.start();3.实例主线程的Handler,参数为HandlerThread内部的一个looper.
Handler handler = new Handler(handlerThread.getLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};4.使用工作线程Handler向工作线程的消息队列发送消息:
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = “2”
message.obj = "骚风"
mHandler.sendMessage(message);5.结束线程,即停止线程的消息循环
mHandlerThread.quit();IntentService就是由HandlerThread实现的
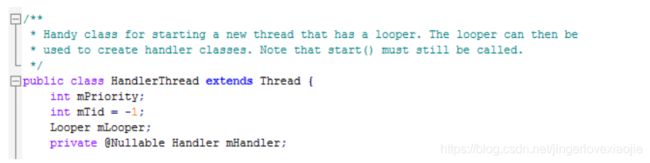
Android为了方便对Thread和Handler进行封装,也就是HandlerThread。HandlerThread继承自Thread,说白了就是Thread加上一个Looper。源码:
可以看到其本身便持有一个Looper对象。
之前学习的时候有两个疑问:
1. HandlerThread为什么start完了之后不会退出?
一般我们都是在某个方法里(如onCreate)调用start方法来启动HandlerThread:
mWorkThread = new HandlerThread("workThread");
mWorkThread.start();那岂不是在调用完start方法之后就退出了?那这有什么意义,如果是一个普通的线程:
Thread thread = new Thread();
thread.start();在调用完start()方法之后肯定会退出的。
查看HandlerThread源码:
@Override
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare();
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();
mTid = -1;
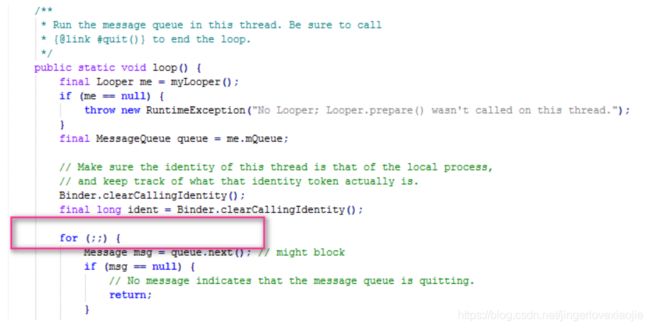
}当调用完start()方法后系统会自动调用run()方法,run方法里有一个 Looper.loop();
可以看到这个looper方法里有一个死循环,它也是跑在run方法里的,所以HandlerThread在start()完了之后不会立即退出。
2. Handler里的handlerMessage()方法究竟运行于哪个线程?
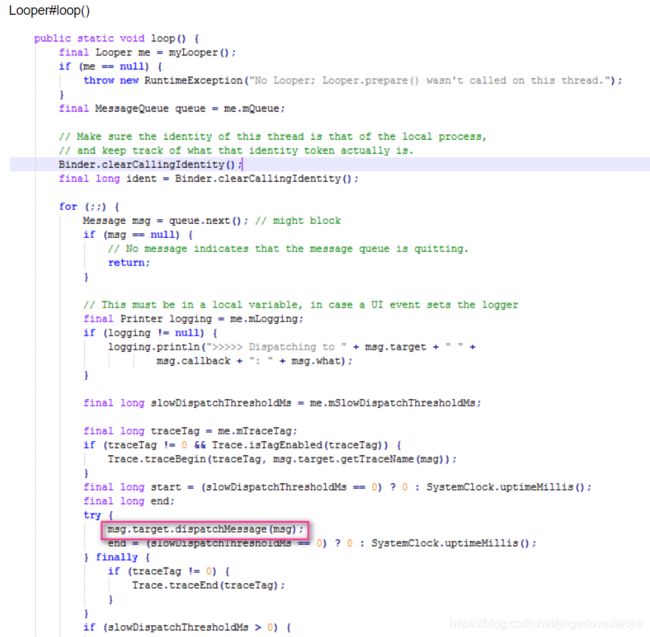
handlerMessage()方法究竟运行于哪个线程,得看这个方法在哪个线程里被调用,之前分析过handlerMessage是在Looper的loop()方法里辗转被调用的。
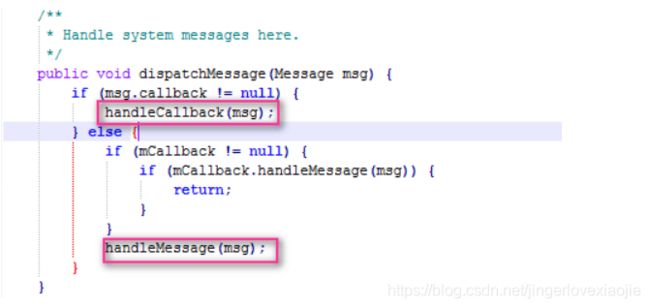
Handler#dispatchMessage()
那其实可以这样说,Looper.loop()方法跑在哪个线程,handlerMessage就跑在哪个线程。
对于自定义的Thread+Looper方式:
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// process incoming messages here
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}很明显,handlerMessage()方法跑在子线程。
对于HandlerThread方式:
HandlerThread#run()
@Override
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare();
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();
mTid = -1;
}也是跑在子线程。
对于mHandler = new Handler()方式:
虽然未传Looper, 但默认使用的是主线程的Looper, 所以此时handlerMessage跑在主线程。
参考链接https://www.cnblogs.com/yongdaimi/p/11571166.html