Spark-TimeSeries使用方法
1.spark里面的库是没有时间序列算法的,但是国外有人已经写好了相应的算法。其github网址是:https://github.com/sryza/spark-timeseries
但基本国内没有太多的资料,所以自己想写一个造福一下后来者。
2.github项目里面的Time-Series Data格式:
(1)假如有如下的数据格式:
其中timestamp很显然是时间,key我们可以看成是不同公司所测到的一些数据,value就是测到的一些真实数据。
(2)TimeSeriesRDD
要把上面所讲述的数据转换成TimeSeriesRDD格式,其实例如下:

3.时间序列中的模型。
(1)由于本人用的是该sparkts版本的0.3.0,运行在spark1.6中,其有拥有的时间序列模型不多,有如下:
Arima、ARGARCH、EWMA、GARCH、RegressionARIMA
(2)在项目中现在已经更新到了0.4.0,其运行spark版本为2.0以上,如果在1.6以上运行的话则会报错。
相比于0.3.0时间序列模型,0.4.0版本更新了一个算法:holtwinters(这个算法添加上了季节性因素)
4.实例
(1)时间序列的训练数据:

其中time为时间,data为数据。
其图形如下所示:

(2)相比于TimeSeriesRDD格式是少了一个key的格式,所以我在这里先在自己的代码增加一个key的列名。
val timeDataKeyDf=hiveDataDf.withColumn(hiveColumnName(0)+"Key",hiveDataDf(hiveColumnName(1))*0)
.select(hiveColumnName(0),hiveColumnName(0)+"Key",hiveColumnName(1))其中hiveDataDf是读出来的dataframe,然后增加了一列
(3)把数据转换成TimeSeriesRDD使,然后建立Arima或者HoltWinters模型,之后进行预测。可到如下图:
Arima的预测图:
HoltWinters的预测图:
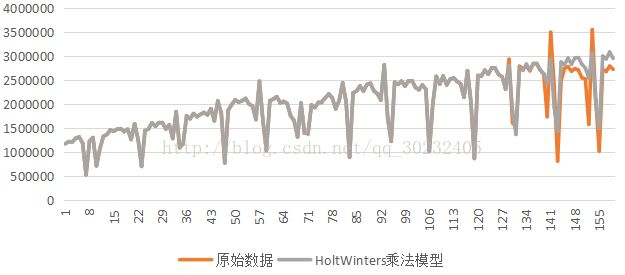
我们从这两个图形上可以看出来,Arima模型没有针对实际的季节性部分来进行预测,所以预测效果比HoltWinters要差。
(4)代码:(详细的项目地址可以看我的csdn_code项目:其地址为:https://code.csdn.net/qq_30232405/spark-timeseries/tree/master)
1)TimeSeriesTrain
package kingpoint.timeSeries.local
import java.sql.Timestamp
import java.time.{ZoneId, ZonedDateTime}
import com.cloudera.sparkts._
import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._
import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame, Row, SQLContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* 时间序列模型time-series的建立
* Created by llq on 2017/4/17.
*/
object TimeSeriesTrain {
/**
* 把数据中的“time”列转换成固定时间格式:ZonedDateTime(such as 2007-12-03T10:15:30+01:00 Europe/Paris.)
* @param timeDataKeyDf
* @param sqlContext
* @param hiveColumnName
* @return zonedDateDataDf
*/
def timeChangeToDate(timeDataKeyDf:DataFrame,sqlContext: SQLContext,hiveColumnName:List[String],startTime:String,sc:SparkContext): DataFrame ={
var rowRDD:RDD[Row]=sc.parallelize(Seq(Row(""),Row("")))
//具体到月份
if(startTime.length==6){
rowRDD=timeDataKeyDf.rdd.map{row=>
row match{
case Row(time,key,data)=>{
val dt = ZonedDateTime.of(time.toString.substring(0,4).toInt,time.toString.substring(4).toInt,1,0,0,0,0,ZoneId.systemDefault())
Row(Timestamp.from(dt.toInstant), key.toString, data.toString.toDouble)
}
}
}
}else if(startTime.length==8){
//具体到日
rowRDD=timeDataKeyDf.rdd.map{row=>
row match{
case Row(time,key,data)=>{
val dt = ZonedDateTime.of(time.toString.substring(0,4).toInt,time.toString.substring(4,6).toInt,time.toString.substring(6).toInt,0,0,0,0,ZoneId.systemDefault())
Row(Timestamp.from(dt.toInstant), key.toString, data.toString.toDouble)
}
}
}
}
//根据模式字符串生成模式,转化成dataframe格式
val field=Seq(
StructField(hiveColumnName(0), TimestampType, true),
StructField(hiveColumnName(0)+"Key", StringType, true),
StructField(hiveColumnName(1), DoubleType, true)
)
val schema=StructType(field)
val zonedDateDataDf=sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD,schema)
return zonedDateDataDf
}
/**
* 总方法调用
* @param args
*/
def main(args: Array[String]) {
/*****环境设置*****/
//shield the unnecessary log in terminal
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
//set the environment
System.setProperty("hadoop.home.dir", "D:\\ideaIU\\hadoop-2.2.0-x64-bin\\")
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("kingpoint.timeSeries.local.TimeSeriesTrain").setMaster("local[4]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext=new SQLContext(sc)
/*****参数设置*****/
//hive中的数据库名字.数据表名
val databaseTableName="time_series.jxt_electric_month"
//选择模型(holtwinters或者是arima)
val modelName="holtwinters"
//选择要hive的数据表中要处理的time和data列名(输入表中用于训练的列名,必须前面是时间,后面是data)
val hiveColumnName=List("time","data")
//日期的开始和结束,格式为“yyyyMM”或者为“yyyyMMdd”
val startTime="200305"
val endTime="201412"
//预测后面N个值
val predictedN=19
//存放的表名字
val outputTableName="timeseries_outputdate"
//只有holtWinters才有的参数
//季节性参数(12或者4)
val period=12
//holtWinters选择模型:additive(加法模型)、Multiplicative(乘法模型)
val holtWintersModelType="Multiplicative"
/*****读取数据和创建训练数据*****/
// //read the data form the hive
// val hiveDataDf=hiveContext.sql("select * from "+databaseTableName)
// .select(hiveColumnName.head,hiveColumnName.tail:_*)
val hiveDataDf=sqlContext.load("com.databricks.spark.csv",Map("path" -> "src/main/resources/data/timeSeriesDate.csv", "header" -> "true"))
.select(hiveColumnName.head,hiveColumnName.tail:_*)
//In hiveDataDF:increase a new column.This column's name is hiveColumnName(0)+"Key",it's value is 0.
//The reason is:The string column labeling which string key the observation belongs to.
val timeDataKeyDf=hiveDataDf.withColumn(hiveColumnName(0)+"Key",hiveDataDf(hiveColumnName(1))*0)
.select(hiveColumnName(0),hiveColumnName(0)+"Key",hiveColumnName(1))
val zonedDateDataDf=timeChangeToDate(timeDataKeyDf,sqlContext,hiveColumnName,startTime,sc)
/**
* 创建数据中时间的跨度(Create an daily DateTimeIndex):开始日期+结束日期+递增数
* 日期的格式要与数据库中time数据的格式一样
*/
//参数初始化
val zone = ZoneId.systemDefault()
var dtIndex:UniformDateTimeIndex=DateTimeIndex.uniformFromInterval(
ZonedDateTime.of(2003, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, zone),
ZonedDateTime.of(2004, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, zone),
new MonthFrequency(1))
//具体到月份
if(startTime.length==6) {
dtIndex = DateTimeIndex.uniformFromInterval(
ZonedDateTime.of(startTime.substring(0, 4).toInt, startTime.substring(4).toInt, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, zone),
ZonedDateTime.of(endTime.substring(0, 4).toInt, endTime.substring(4).toInt, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, zone),
new MonthFrequency(1))
}else if(startTime.length==8){
//具体到日,则把dtIndex覆盖了
dtIndex = DateTimeIndex.uniformFromInterval(
ZonedDateTime.of(startTime.substring(0,4).toInt,startTime.substring(4,6).toInt,startTime.substring(6).toInt,0,0,0,0,zone),
ZonedDateTime.of(endTime.substring(0,4).toInt,endTime.substring(4,6).toInt,endTime.substring(6).toInt,0,0,0,0,zone),
new DayFrequency(1))
}
//创建训练数据TimeSeriesRDD(key,DenseVector(series))
val trainTsrdd = TimeSeriesRDD.timeSeriesRDDFromObservations(dtIndex, zonedDateDataDf,
hiveColumnName(0), hiveColumnName(0)+"Key", hiveColumnName(1))
/*****建立Modle对象*****/
val timeSeriesModel=new TimeSeriesModel(predictedN,outputTableName)
var forecastValue:RDD[String]=sc.parallelize(Seq(""))
//选择模型
modelName match{
case "arima"=>{
//创建和训练arima模型
forecastValue=timeSeriesModel.arimaModelTrain(trainTsrdd)
}
case "holtwinters"=>{
//创建和训练HoltWinters模型(季节性模型)
forecastValue=timeSeriesModel.holtWintersModelTrain(trainTsrdd,period,holtWintersModelType)
}
case _=>throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Currently only supports 'ariam' and 'holtwinters")
}
//合并实际值和预测值,并加上日期,形成dataframe(Date,Data),并保存
timeSeriesModel.actualForcastDateSaveInHive(trainTsrdd,forecastValue,modelName,predictedN,startTime,endTime,sc,hiveColumnName,sqlContext)
}
}
2)TimeSeriesModel
package kingpoint.timeSeries.local
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.{Calendar, Properties}
import com.cloudera.sparkts.TimeSeriesRDD
import com.cloudera.sparkts.models.ARIMA
import kingpoint.timeSeries.HoltWinters
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StringType, StructField, StructType}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SQLContext, SaveMode}
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
/**
* 时间序列模型
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/19.
*/
class TimeSeriesModel {
//预测后面N个值
private var predictedN=1
//存放的表名字
private var outputTableName="timeseries_output"
def this(predictedN:Int,outputTableName:String){
this()
this.predictedN=predictedN
this.outputTableName=outputTableName
}
/**
* Arima模型:
* 输出其p,d,q参数
* 输出其预测的predictedN个值
* @param trainTsrdd
*/
def arimaModelTrain(trainTsrdd:TimeSeriesRDD[String]): RDD[String] ={
/***参数设置******/
val predictedN=this.predictedN
/***创建arima模型***/
//创建和训练arima模型.其RDD格式为(ArimaModel,Vector)
val arimaAndVectorRdd=trainTsrdd.map{line=>
line match {
case (key,denseVector)=>
(ARIMA.autoFit(denseVector),denseVector)
}
}
//参数输出:p,d,q的实际值和其系数值
val coefficients=arimaAndVectorRdd.map{line=>
line match{
case (arimaModel,denseVector)=>{
(arimaModel.coefficients.mkString(","),
(arimaModel.p,
arimaModel.d,
arimaModel.q))
}
}
}
coefficients.collect().map{_ match{
case (coefficients,(p,d,q))=>
println("coefficients:"+coefficients+"=>"+"(p="+p+",d="+d+",q="+q+")")
}}
/***预测出后N个的值*****/
val forecast = arimaAndVectorRdd.map{row=>
row match{
case (arimaModel,denseVector)=>{
arimaModel.forecast(denseVector, predictedN)
}
}
}
val forecastValue=forecast.map(_.toArray.mkString(","))
//取出预测值
val preditcedValueRdd=forecastValue.map{parts=>
val partArray=parts.split(",")
for(i<- partArray.length-predictedN until partArray.length) yield partArray(i)
}.map(_.toArray.mkString(","))
preditcedValueRdd.collect().map{row=>
println("forecast of next "+predictedN+" observations: "+row)
}
return preditcedValueRdd
}
/**
*实现HoltWinters模型
* @param trainTsrdd
*/
def holtWintersModelTrain(trainTsrdd:TimeSeriesRDD[String],period:Int,holtWintersModelType:String): RDD[String] ={
/***参数设置******/
//往后预测多少个值
val predictedN=this.predictedN
/***创建HoltWinters模型***/
//创建和训练HoltWinters模型.其RDD格式为(HoltWintersModel,Vector)
val holtWintersAndVectorRdd=trainTsrdd.map{line=>
line match {
case (key,denseVector)=>
(HoltWinters.fitModel(denseVector,period,holtWintersModelType),denseVector)
}
}
/***预测出后N个的值*****/
//构成N个预测值向量,之后导入到holtWinters的forcast方法中
val predictedArrayBuffer=new ArrayBuffer[Double]()
var i=0
while(i
row match{
case (holtWintersModel,denseVector)=>{
holtWintersModel.forecast(denseVector, predictedVectors)
}
}
}
val forecastValue=forecast.map(_.toArray.mkString(","))
forecastValue.collect().map{row=>
println("HoltWinters forecast of next "+predictedN+" observations: "+row)
}
return forecastValue
}
/**
* 批量生成日期(具体到月份的),用来保存
* @param predictedN
* @param startTime
* @param endTime
*/
def productStartDatePredictDate(predictedN:Int,startTime:String,endTime:String): ArrayBuffer[String] ={
//形成开始start到预测predicted的日期
var dateArrayBuffer=new ArrayBuffer[String]()
val dateFormat= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMM");
val cal1 = Calendar.getInstance()
val cal2 = Calendar.getInstance()
//设置训练数据中开始和结束日期
cal1.set(startTime.substring(0,4).toInt,startTime.substring(4).toInt,0)
cal2.set(endTime.substring(0,4).toInt,endTime.substring(4).toInt,0)
//开始日期和预测日期的月份差
val monthDiff = (cal2.getTime.getYear() - cal1.getTime.getYear()) * 12 +( cal2.getTime.getMonth() - cal1.getTime.getMonth())+predictedN
var iMonth=0
while(iMonth<=monthDiff){
//日期加1个月
cal1.add(Calendar.MONTH, iMonth)
//保存日期
dateArrayBuffer+=dateFormat.format(cal1.getTime)
cal1.set(startTime.substring(0,4).toInt,startTime.substring(4).toInt,0)
iMonth=iMonth+1
}
return dateArrayBuffer
}
/**
* 批量生成日期(具体到日的),用来保存
* @param predictedN
* @param startTime
* @param endTime
*/
def productStartDayPredictDay(predictedN:Int,startTime:String,endTime:String): ArrayBuffer[String] ={
//形成开始start到预测predicted的日期
var dayArrayBuffer=new ArrayBuffer[String]()
val dateFormat= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
val cal1 = Calendar.getInstance()
val cal2 = Calendar.getInstance()
//设置训练数据中开始和结束日期
cal1.set(startTime.substring(0,4).toInt,startTime.substring(4,6).toInt-1,startTime.substring(6).toInt)
cal2.set(endTime.substring(0,4).toInt,endTime.substring(4,6).toInt-1,endTime.substring(6).toInt)
//开始日期和预测日期的月份差
val dayDiff = (cal2.getTimeInMillis-cal1.getTimeInMillis)/ (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24)+predictedN
var iDay=0
while(iDay<=dayDiff){
//日期加1天
cal1.add(Calendar.DATE, iDay)
//保存日期
dayArrayBuffer+=dateFormat.format(cal1.getTime)
cal1.set(startTime.substring(0,4).toInt,startTime.substring(4,6).toInt-1,startTime.substring(6).toInt)
iDay=iDay+1
}
return dayArrayBuffer
}
/**
* 合并实际值和预测值,并加上日期,形成dataframe(Date,Data)
* 并保存在hive中
* @param trainTsrdd 从hive中读取的数据
* @param forecastValue 预测出来的数据(分为arima和holtwinters预测的)
* @param modelName 选择哪个模型名字(arima和holtwinters)
* @param predictedN 预测多少个值
* @param startTime 开始日期
* @param endTime 结束日期
* @param sc
* @param hiveColumnName 选择的列名字
* @param sqlContext
*/
def actualForcastDateSaveInHive(trainTsrdd:TimeSeriesRDD[String],forecastValue:RDD[String],modelName:String,predictedN:Int,startTime:String,endTime:String,sc:SparkContext,hiveColumnName:List[String],sqlContext:SQLContext): Unit ={
//在真实值后面追加预测值
val actualAndForcastArray=trainTsrdd.map{line=>
line match {
case (key,denseVector)=>
denseVector.toArray.mkString(",")
}
}.union(forecastValue).collect()
val actualAndForcastSting=(actualAndForcastArray(0).toString+","+actualAndForcastArray(1).toString).split(",").map(data=>(data))
val actualAndForcastRdd=sc.parallelize(actualAndForcastSting)
//获取日期,并转换成rdd
var dateArray:ArrayBuffer[String]=new ArrayBuffer[String]()
if(startTime.length==6){
dateArray=productStartDatePredictDate(predictedN,startTime,endTime)
}else if(startTime.length==8){
dateArray=productStartDayPredictDay(predictedN,startTime,endTime)
}
val dateRdd=sc.parallelize(dateArray.toArray.mkString(",").split(",").map(date=>(date)))
//合并日期和数据值,形成RDD[Row]
val dateDataRdd=dateRdd.zip(actualAndForcastRdd).map{
_ match {
case (date,data)=>Row(date,data)
}
}
//把dateData转换成dataframe
val schemaString=hiveColumnName.mkString(" ")
val schema=StructType(schemaString.split(" ")
.map(fieldName=>StructField(fieldName,StringType,true)))
val dateDataDf=sqlContext.createDataFrame(dateDataRdd,schema)
//加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
//设置用户名和密码
val prop = new Properties()
prop.setProperty("user","root")
prop.setProperty("password","86914381")
var sqlCommand=""
//命名表格名字
dateDataDf.registerTempTable("dateDataDf")
//编写sql语句
sqlCommand="select * from dateDataDf"
// 调用DataFrameWriter将数据写入mysql(表可以不存在)
sqlContext.sql(sqlCommand).write.mode(SaveMode.Append).jdbc("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydata",outputTableName,prop)
}
}
3)HoltWinters
/**
* Copyright (c) 2015, Cloudera, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
*
* Cloudera, Inc. licenses this file to you under the Apache License,
* Version 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use this file except in
* compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* This software is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
* CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for
* the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the
* License.
*/
//package com.cloudera.sparkts.models
package kingpoint.timeSeries
import org.apache.commons.math3.analysis.MultivariateFunction
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg._
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.MaxIter
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.nonlinear.scalar.ObjectiveFunction
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.MaxEval
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.SimpleBounds
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.nonlinear.scalar.noderiv.BOBYQAOptimizer
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.InitialGuess
import org.apache.commons.math3.optim.nonlinear.scalar.GoalType
/**
* Triple exponential smoothing takes into account seasonal changes as well as trends.
* Seasonality is defined to be the tendency of time-series data to exhibit behavior that repeats
* itself every L periods, much like any harmonic function.
*
* The Holt-Winters method is a popular and effective approach to forecasting seasonal time series
*
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exponential_smoothing#Triple_exponential_smoothing
* for more information on Triple Exponential Smoothing
* See https://www.otexts.org/fpp/7/5 and
* https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/stats/html/HoltWinters.html
* for more information on Holt Winter Method.
*/
object HoltWinters {
/**
* Fit HoltWinter model to a given time series. Holt Winter Model has three parameters
* level, trend and season component of time series.
* We use BOBYQA optimizer which is used to calculate minimum of a function with
* bounded constraints and without using derivatives.
* See http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/na/NA_papers/NA2009_06.pdf for more details.
*
* @param ts Time Series for which we want to fit HoltWinter Model
* @param period Seasonality of data i.e period of time before behavior begins to repeat itself
* @param modelType Two variations differ in the nature of the seasonal component.
* Additive method is preferred when seasonal variations are roughly constant through the series,
* Multiplicative method is preferred when the seasonal variations are changing
* proportional to the level of the series.
* @param method: Currently only BOBYQA is supported.
*/
def fitModel(ts: Vector, period: Int, modelType: String = "additive", method: String = "BOBYQA")
: HoltWintersModel = {
method match {
case "BOBYQA" => fitModelWithBOBYQA(ts, period, modelType)
case _ => throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Currently only supports 'BOBYQA'")
}
}
def fitModelWithBOBYQA(ts: Vector, period: Int, modelType:String): HoltWintersModel = {
val optimizer = new BOBYQAOptimizer(7)
val objectiveFunction = new ObjectiveFunction(new MultivariateFunction() {
def value(params: Array[Double]): Double = {
new HoltWintersModel(modelType, period, params(0), params(1), params(2)).sse(ts)
}
})
// The starting guesses in R's stats:HoltWinters
val initGuess = new InitialGuess(Array(0.3, 0.1, 0.1))
val maxIter = new MaxIter(30000)
val maxEval = new MaxEval(30000)
val goal = GoalType.MINIMIZE
val bounds = new SimpleBounds(Array(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), Array(1.0, 1.0, 1.0))
val optimal = optimizer.optimize(objectiveFunction, goal, bounds,initGuess, maxIter, maxEval)
val params = optimal.getPoint
new HoltWintersModel(modelType, period, params(0), params(1), params(2))
}
}
class HoltWintersModel(
val modelType: String,
val period: Int,
val alpha: Double,
val beta: Double,
val gamma: Double) extends TimeSeriesModel {
if (!modelType.equalsIgnoreCase("additive") && !modelType.equalsIgnoreCase("multiplicative")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid model type: " + modelType)
}
val additive = modelType.equalsIgnoreCase("additive")
/**
* Calculates sum of squared errors, used to estimate the alpha and beta parameters
*
* @param ts A time series for which we want to calculate the SSE, given the current parameters
* @return SSE
*/
def sse(ts: Vector): Double = {
val n = ts.size
val smoothed = new DenseVector(Array.fill(n)(0.0))
addTimeDependentEffects(ts, smoothed)
var error = 0.0
var sqrErrors = 0.0
// We predict only from period by using the first period - 1 elements.
for(i <- period to (n - 1)) {
error = ts(i) - smoothed(i)
sqrErrors += error * error
}
sqrErrors
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
def removeTimeDependentEffects(ts: Vector, dest: Vector = null): Vector = {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("not yet implemented")
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
def addTimeDependentEffects(ts: Vector, dest: Vector): Vector = {
val destArr = dest.toArray
val fitted = getHoltWintersComponents(ts)._1
for (i <- 0 to (dest.size - 1)) {
destArr(i) = fitted(i)
}
dest
}
/**
* Final prediction Value is sum of level trend and season
* But in R's stats:HoltWinters additional weight is given for trend
*
* @param ts
* @param dest
*/
def forecast(ts: Vector, dest: Vector): Vector = {
val destArr = dest.toArray
val (_, level, trend, season) = getHoltWintersComponents(ts)
val n = ts.size
val finalLevel = level(n - period)
val finalTrend = trend(n - period)
val finalSeason = new Array[Double](period)
for (i <- 0 until period) {
finalSeason(i) = season(i + n - period)
}
for (i <- 0 until dest.size) {
destArr(i) = if (additive) {
(finalLevel + (i + 1) * finalTrend) + finalSeason(i % period)
} else {
(finalLevel + (i + 1) * finalTrend) * finalSeason(i % period)
}
}
dest
}
/**
* Start from the intial parameters and then iterate to find the final parameters
* using the equations of HoltWinter Method.
* See https://www.otexts.org/fpp/7/5 and
* https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/stats/html/HoltWinters.html
* for more information on Holt Winter Method equations.
*
* @param ts A time series for which we want the HoltWinter parameters level,trend and season.
* @return (level trend season). Final vectors of level trend and season are returned.
*/
def getHoltWintersComponents(ts: Vector): (Vector, Vector, Vector, Vector) = {
val n = ts.size
require(n >= 2, "Requires length of at least 2")
val dest = new Array[Double](n)
val level = new Array[Double](n)
val trend = new Array[Double](n)
val season = new Array[Double](n)
val (initLevel, initTrend, initSeason) = initHoltWinters(ts)
level(0) = initLevel
trend(0) = initTrend
for (i <- 0 until initSeason.size){
season(i) = initSeason(i)
}
for (i <- 0 to (n - period - 1)) {
dest(i + period) = level(i) + trend(i)
// Add the seasonal factor for additive and multiply for multiplicative model.
if (additive) {
dest(i + period) += season(i)
} else {
dest(i + period) *= season(i)
}
val levelWeight = if (additive) {
ts(i + period) - season(i)
} else {
ts(i + period) / season(i)
}
level(i + 1) = alpha * levelWeight + (1 - alpha) * (level(i) + trend(i))
trend(i + 1) = beta * (level(i + 1) - level(i)) + (1 - beta) * trend(i)
val seasonWeight = if (additive) {
ts(i + period) - level(i + 1)
} else {
ts(i + period) / level(i + 1)
}
season(i + period) = gamma * seasonWeight + (1 - gamma) * season(i)
}
(Vectors.dense(dest), Vectors.dense(level), Vectors.dense(trend), Vectors.dense(season))
}
def getKernel(): (Array[Double]) = {
if (period % 2 == 0){
val kernel = Array.fill(period + 1)(1.0 / period)
kernel(0) = 0.5 / period
kernel(period) = 0.5 / period
kernel
} else {
Array.fill(period)(1.0 / period)
}
}
/**
* Function to calculate the Weighted moving average/convolution using above kernel/weights
* for input data.
* See http://robjhyndman.com/papers/movingaverage.pdf for more information
* @param inData Series on which you want to do moving average
* @param kernel Weight vector for weighted moving average
*/
def convolve(inData: Array[Double], kernel: Array[Double]): (Array[Double]) = {
val kernelSize = kernel.size
val dataSize = inData.size
val outData = new Array[Double](dataSize - kernelSize + 1)
var end = 0
while (end <= (dataSize - kernelSize)) {
var sum = 0.0
for (i <- 0 until kernelSize) {
sum += kernel(i) * inData(end + i)
}
outData(end) = sum
end += 1
}
outData
}
/**
* Function to get the initial level, trend and season using method suggested in
* http://robjhyndman.com/hyndsight/hw-initialization/
* @param ts
*/
def initHoltWinters(ts: Vector): (Double, Double, Array[Double]) = {
val arrTs = ts.toArray
// Decompose a window of time series into level trend and seasonal using convolution
val kernel = getKernel()
val kernelSize = kernel.size
val trend = convolve(arrTs.take(period * 2), kernel)
// Remove the trend from time series. Subtract for additive and divide for multiplicative
val n = (kernelSize -1) / 2
val removeTrend = arrTs.take(period * 2).zip(
Array.fill(n)(0.0) ++ trend ++ Array.fill(n)(0.0)).map{
case (a, t) =>
if (t != 0){
if (additive) {
(a - t)
} else {
(a / t)
}
} else{
0
}
}
// seasonal mean is sum of mean of all season values of that period
val seasonalMean = removeTrend.splitAt(period).zipped.map { case (prevx, x) =>
if (prevx == 0 || x == 0) (x + prevx) else (x + prevx) / 2
}
val meanOfFigures = seasonalMean.sum / period
// The seasonal mean is then centered and removed to get season.
// Subtract for additive and divide for multiplicative.
val initSeason = if (additive) {
seasonalMean.map(_ - meanOfFigures )
} else {
seasonalMean.map(_ / meanOfFigures )
}
// Do Simple Linear Regression to find the initial level and trend
val indices = 1 to trend.size
val xbar = (indices.sum: Double) / indices.size
val ybar = trend.sum / trend.size
val xxbar = indices.map( x => (x - xbar) * (x - xbar) ).sum
val xybar = indices.zip(trend).map {
case (x, y) => (x - xbar) * (y - ybar)
}.sum
val initTrend = xybar / xxbar
val initLevel = ybar - (initTrend * xbar)
(initLevel, initTrend, initSeason)
}
}

