Python 显示图像的直方图
http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/p/5096790.html
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/7600666
reshape和flatten函数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Spyder Editor
Python version 3.5
This is a temporary script file.
"""
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
vec=np.arange(15)
print (vec)如果我们要把这个一维数组,变成一个3*5二维矩阵,我们可以使用reshape来实现
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Spyder Editor
Python version 3
This is a temporary script file.
"""
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
vec=np.arange(15)
mat= vec.reshape(3,5)
print (mat)[ 5 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13 14]]
现在如果我们返过来,知道一个二维矩阵,要变成一个一维数组,就不能用reshape了,只能用flatten. 我们来看两者的区别
a1=mat.reshape(1,-1) #-1表示为任意,让系统自动计算
print (a1)
a2=mat.flatten()
print (a2)[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]
可以看出,用reshape进行变换,实际上变换后还是二维数组,两个方括号,因此只能用flatten.
我们要对图像求直方图,就需要先把图像矩阵进行flatten操作,使之变为一维数组,然后再进行统计。
一、画灰度图直方图
绘图都可以调用matplotlib.pyplot库来进行,其中的hist函数可以直接绘制直方图。
调用方式:
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(arr, bins=50, normed=1, facecolor='green', alpha=0.75)n, bins, patches = plt.hist(arr, bins=50, normed=1, facecolor='green', alpha=0.75)
hist的参数非常多,但常用的就这五个,只有第一个是必须的,后面四个可选
arr: 需要计算直方图的一维数组
bins: 直方图的柱数,可选项,默认为10
normed: 是否将得到的直方图向量归一化。默认为0
facecolor: 直方图颜色
alpha: 透明度
返回值 :
n: 直方图向量,是否归一化由参数设定
bins: 返回各个bin的区间范围
patches: 返回每个bin里面包含的数据,是一个list
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=np.array(Image.open('d:/pic/lena.jpg').convert('L'))
plt.figure("lena")
arr=img.flatten()
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(arr, bins=256, normed=1, facecolor='green', alpha=0.75)
plt.show()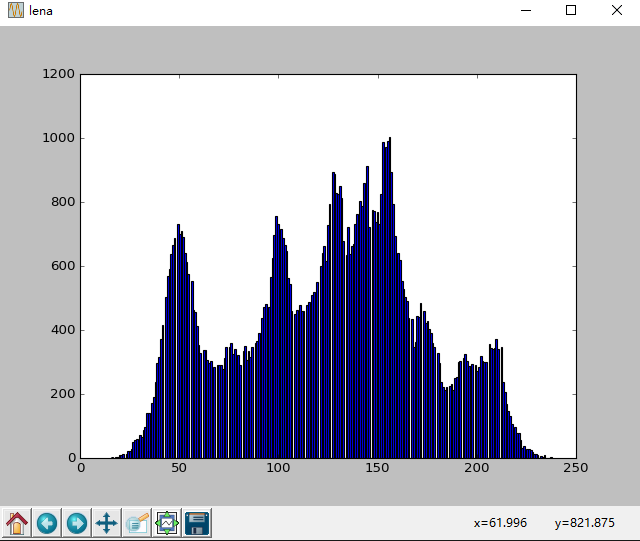
(用spyder没有这种效果,用ubuntu可以)
二、彩色图片直方图
实际上是和灰度直方图一样的,只是分别画出三通道的直方图,然后叠加在一起。
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
src=Image.open('d:/ex.jpg')
r,g,b=src.split()
plt.figure("lena")
ar=np.array(r).flatten()
plt.hist(ar, bins=256, normed=1,facecolor='r',edgecolor='r',hold=1)
ag=np.array(g).flatten()
plt.hist(ag, bins=256, normed=1, facecolor='g',edgecolor='g',hold=1)
ab=np.array(b).flatten()
plt.hist(ab, bins=256, normed=1, facecolor='b',edgecolor='b')
plt.show()
三 opencv画直方图
//绘制灰度直方图
int main( )
{
Mat src,gray;
src=imread("baboon.jpg");
cvtColor(src,gray,CV_RGB2GRAY);
int bins = 256;
int hist_size[] = {bins};
float range[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { range};
MatND hist;
int channels[] = {0};
calcHist( &gray, 1, channels, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist, 1, hist_size, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
double max_val;
minMaxLoc(hist, 0, &max_val, 0, 0);
int scale = 2;
int hist_height=256;
Mat hist_img = Mat::zeros(hist_height,bins*scale, CV_8UC3);
for(int i=0;i(i);
int intensity = cvRound(bin_val*hist_height/max_val); //要绘制的高度
rectangle(hist_img,Point(i*scale,hist_height-1),
Point((i+1)*scale - 1, hist_height - intensity),
CV_RGB(255,255,255));
}
imshow( "Source", src );
imshow( "Gray Histogram", hist_img );
waitKey(10000000000);
return 0;
} 绘制三维直方图
//绘制RGB三色分量直方图
int main( )
{
Mat src;
src=imread("baboon.jpg");
int bins = 256;
int hist_size[] = {bins};
float range[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { range};
MatND hist_r,hist_g,hist_b;
int channels_r[] = {0};
calcHist( &src, 1, channels_r, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist_r, 1, hist_size, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
int channels_g[] = {1};
calcHist( &src, 1, channels_g, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist_g, 1, hist_size, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
int channels_b[] = {2};
calcHist( &src, 1, channels_b, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist_b, 1, hist_size, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
double max_val_r,max_val_g,max_val_b;
minMaxLoc(hist_r, 0, &max_val_r, 0, 0);
minMaxLoc(hist_g, 0, &max_val_g, 0, 0);
minMaxLoc(hist_b, 0, &max_val_b, 0, 0);
int scale = 1;
int hist_height=256;
Mat hist_img = Mat::zeros(hist_height,bins*3, CV_8UC3);
for(int i=0;i(i);
float bin_val_g = hist_g.at(i);
float bin_val_b = hist_b.at(i);
int intensity_r = cvRound(bin_val_r*hist_height/max_val_r); //要绘制的高度
int intensity_g = cvRound(bin_val_g*hist_height/max_val_g); //要绘制的高度
int intensity_b = cvRound(bin_val_b*hist_height/max_val_b); //要绘制的高度
rectangle(hist_img,Point(i*scale,hist_height-1),
Point((i+1)*scale - 1, hist_height - intensity_r),
CV_RGB(255,0,0));
rectangle(hist_img,Point((i+bins)*scale,hist_height-1),
Point((i+bins+1)*scale - 1, hist_height - intensity_g),
CV_RGB(0,255,0));
rectangle(hist_img,Point((i+bins*2)*scale,hist_height-1),
Point((i+bins*2+1)*scale - 1, hist_height - intensity_b),
CV_RGB(0,0,255));
}
imshow( "Source", src );
imshow( "RGB Histogram", hist_img );
waitKey(10000000000);
return 0;
}
//绘制H-S二维直方图
int main( )
{
Mat src,hsv;
src=imread("baboon.jpg");
cvtColor(src, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Quantize the hue to 30 levels
// and the saturation to 32 levels
int hbins = 256, sbins = 180;
int histSize[] = {hbins, sbins};
// hue varies from 0 to 179, see cvtColor
float hranges[] = { 0, 180 };
// saturation varies from 0 (black-gray-white) to
// 255 (pure spectrum color)
float sranges[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { hranges, sranges };
MatND hist;
// we compute the histogram from the 0-th and 1-st channels
int channels[] = {0, 1};
calcHist( &hsv, 1, channels, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist, 2, histSize, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
double maxVal=0;
minMaxLoc(hist, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0);
int scale = 2;
Mat histImg = Mat::zeros(sbins*scale, hbins*scale, CV_8UC3);
for( int h = 0; h < hbins; h++ )
for( int s = 0; s < sbins; s++ )
{
float binVal = hist.at(h, s);
int intensity = cvRound(binVal*255/maxVal);
rectangle( histImg, Point(h*scale, s*scale),
Point( (h+1)*scale - 1, (s+1)*scale - 1),
Scalar::all(intensity),
CV_FILLED );
}
namedWindow( "Source", 1 );
imshow( "Source", src );
namedWindow( "H-S Histogram", 1 );
imshow( "H-S Histogram", histImg );
waitKey(10000000000);
return 0;
}