《面试准备》Mysql数据库简单操作
环境:ubuntu16.04
Mysql搭建:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/
一、数据库及表操作:
1、数据库配置修改位置 :
vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf修改datadir位置:
[mysqld]
pid-file = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
socket = /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
datadir = /var/lib/mysql
log-error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
# By default we only accept connections from localhost
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
2、连接数据库
mysql -u root -p3、创建/删除用户
mysql -u root -p #进入root下的mysql
create user 'name'@'localhost' identified by 'passwd'; #localhost表示本机访问
create user 'name'@'localhost'; #可以不要密码
create user 'name'@'%' identified by 'passwd'; #%表示可以远程访问
drop user 'name'@'%'; #删除user
4、给新建用户权限
mysql -u root -p #进入root下的mysql
create database example; #创建一个数据库example
grant all privileges on 'example'.* to 'name'@'%' #把example权限给新建用户(新建用户是不能创建database的)
flush privileges #立即更新5、在新的用户上建立数据库
mysql -u create_name -p #进入root下的mysql
use example; #用example数据库(由root用户授权)
drop example; #删除数据库6、在数据库中创建/删除表
use example; #用example数据库建表
create table 表名 ( #创建表
属性名 数据类型 [完整约束条件],
属性名 数据类型 [完整约束条件],
...
...
属性名 数据类型 [完整约束条件]
);
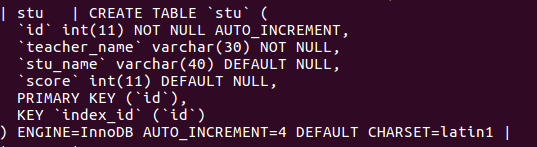
create table stu( #example
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null
);
desc stu; #查看表结构
drop table stu; #删除表约束条件(constraint)说明:
PRIMARY KEY: 标识该属性为该表的主键,可以唯一的标识对应的元组(唯一unique,非空not null,便于查询)
FOREIGN KEY: 标识该属性为该表的外键,是与之联系某表的主键
NOT NULL: 标识该属性不能为空
UNIQUE: 标识该属性的值是唯一的,不可重复
AUTO_INCREMENT 标识该属性的值是自动增加,这是MySQL的SQL语句的特色(配合主键用)
DEFAULT: 如果添加语句为空,为该属性设置默认值
7、修改表的属性
alter table stu add teacher_name varchar(20) not null after id; #添加表
alter table stu modify name varchar(80) after id; #修改表中name的属性
alter table stu change name stu_name varchar(20); #改变表中name的名字及属性
alter table stu drop teacher_name; #删除表
desc stu; #查看表结构
二、索引操作
1、为什么使用索引
数据库的索引跟书的目录一样,,主要是为了提高表中检索数据的速度,由于数据存储在数据库表中,所以索引就是创建在数据库表对象上,由表中的一个字段或多个字段生成的键组成,这些键存储在数据结构(B-树或哈希表)。所以索引的存储类型分为B型树索引和哈希索引。
2、索引的优缺点
优点;索引能帮助我们快速查询数据,提高查询速度。
缺点:建立索引需要占据存储空间,维护索引需要时间成本,因此对于不经常查询或者拥有很多重复值的字段不适合用索引,而对于频繁需要查询的字段,或者有父子关系(主外键)的联合查询适合用索引。
3、索引的原理
以空间换时间,建立索引之后,会将索引的KEY值放在一个BTree上,这个方式是一种n分法,btree适合在磁盘上动态查找表,每次以索引进行查找的时候,会根据key值进行搜索,logn级别的。
4、6种索引
索引的操作分为创建索引、修改索引、删除索引,Mysql支持6种索引:普通索引,唯一索引,全文索引,单、双列索引,空间索引。
(1)普通索引
普通索引在创建时,不附加任何限制条件,也就是说可以创建在任何数据类型的字段上。
#创建普通索引方法1:
create table stu(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
index index_id(id) #在id字段上创建索引
);
#创建普通索引方法2:
alter table stu add index index_id(id);
#创建普通索引方法3:
create index index_id on stu(id);
测试:
(2)唯一索引
所谓唯一索引就是在创建索引时,限制索引的值必须是唯一的,这样可以更快速的查询某条记录。
#创建唯一索引方法1:
create table stu(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
unique index index_id(id) #在id字段上创建唯一索引
);
#创建唯一索引方法2:
alter table stu add unique index index_id(id);
#创建唯一索引方法3:
create unique index index_id on stu(id);(3)全文索引
全文索引主要关注在数据类型为char、varchar、text数据类型上,
#创建全文索引方法1:
create table stu(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
fulltext index index_name(name) #在name字段上创建全文索引
);
#创建全文索引方法2:
alter table stu add fulltext index index_name(name);
#创建全文索引方法3:
create fulltext index index_id on stu(name);(4)多列索引
在创建索引时,所关联的不是一个字段,而是多个字段(普通索引的增加版本)。
#创建多列索引方法1:
create table stu(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
index index_id_name(id,name) #在name字段上创建多列索引
);
#创建多列索引方法2:
alter table stu add index index_id_name(id,name);
#创建多列索引方法3:
create index index_id_name on stu(id,name);5、删除索引
drop index index_id on stu;三、数据操作
1、插入数据
(1)insert into命令方式
insert into stu(id,name) values(1,'xxx'); #插入一条数据
insert into stu(id,name) #插入多条数据
values(1,'xxx'),
values(2,'xxxx'),
values(3,'xxxxx'),
values(4,'xxxxxx');
select * from stu; #显示表内容(2)txx文件方式
load data infile 'txt path' into table stu; #注意txt内容中两个值之间默认为一个tab键
load data infile 'txt path' into table stu fields terminated ','; #也可以为','
select * from stu; #显示表内容导入txt文档遇到的错误:
ERROR 1290 (HY000): The MySQL server is running with the --secure-file-priv option so it cannot exec错误原因:只能在规定的目录下才能导入,我们需要通过下面命令查看 secure-file-priv 当前的值是什么,进入mysql,执行:
show variables like '%secure%';我们可以看到secure_file_priv的值为/var/lib/mysql-files/
那么我们把导入的路径改为上面的值就可以了
2、更新数据
update stu
set id=1
where name='xxx';
update stu
set name='xxx'
where id>1;3、删除数据
delect from stu
where name='xxxx';四、单表记录查询
1、简单的数据记录查询
select * from stu; #显示所有信息
select name from stu; #显示部分信息
select distinct name from stu; #去重显示
select id*2 from stu; #使用四则运算
select concat(id,'名字为',name) from stu; #设置显示格式2、条件数据记录查询 (where condition)
select name from stu where name='xxxxxx'; #条件显示
select name from stu where id>2; #条件显示
Mysql支持的比较运算符:
> :大于
< :小于
= :等于
!= :不等于
>= :大于等于
<= :小于等于
Mysql支持的逻辑运算符:
AND(&&)) :逻辑与
OR(||) :逻辑或
XOR :逻辑异或
NOT(!) :逻辑非
用关键字查询:
select name from stu where id between 1 and 3; #范围查询
select name from stu where id in (2,4); #集合查询
select id from stu where name is null; #空值查询
select id from stu where name like 'x%'; #模糊查询(x开头的都将查询到)
select id from stu where name like '_x%'; #模糊查询(第二个为x的都将查询到)
select id from stu where name not like '_x%'; #模糊查询(第二个不为x的都将查询到)
3、顺序数据记录查询 (order by)
alter table stu add score int; #添加得分
update stu #更新得分
set score=99
where id>1&&id<2;
update stu
set score=87
where id>3;
select name from stu order by score desc; #根据得分降序排列名字
select name from stu order by score asc; #根据得分升序排列名字(默认升序)
select name from stu order by score limit 1; #根据得分升序排列名字(显示1条记录)
select name from stu order by score limit 1,2; #根据得分升序排列名字(显示1至2条记录)4、统计函数和分组数据记录查询 (group by)
(1)统计函数:count(),avg(),sum(),max(),min();
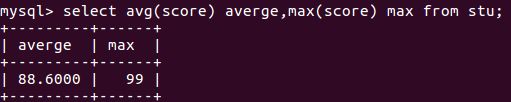
select avg(score) average from stu; #计算得分平均值,average为计算结果
select avg(score) average,max(score) max from stu; #同时计算得分平均值和最大值(2)分组数据查询(group by)
【注】分组所依据的字段上的值一定具有重复性,否则无意义,也就是把字段重复的分为一组;
select * from stu group by score;#查询以分数为分组的姓名、数量信息
select score group_concat(name) names,count(name) number
from stu
group by score;在执行group by遇到错误:
ERROR 1055 (42000): Expression #1 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and
contains nonaggregated column 'example.stu.id' which is not functionally dependent
on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible withsql_mode=only_full_group_by
解决:
select version(),
@@sql_mode;SET sql_mode=(SELECT REPLACE(@@sql_mode,'ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY',''));未完。。。。。。