自定义控件View之onMeasure调用时机源码分析
终于建了一个自己个人小站:https://huangtianyu.gitee.io,以后优先更新小站博客,欢迎进站,O(∩_∩)O~~
先上测试代码:
MainActivity.java
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.e("hty", "before setContextView");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.e("hty", "after setContextView");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.e("hty", "onResume");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.e("hty", "onDestroy");
}
}import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView extends View {
Paint paint;
public MyView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
Log.e("hty","view constructor");
paint = new Paint();
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
paint.setTextSize(20);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
Log.e("hty","view onMeasure");
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
Log.e("hty","view onLayout");
}
String str = "这里是测试";
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Log.e("hty","view onDraw");
canvas.drawText(str, getWidth()/2-paint.measureText(str)/2,getHeight()/2, paint);
}
}

从Log输出可以看出在一个View的绘制过程中,onMeasure是被多次调用了的。下面通过源码来一步步分析 onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)函数,尤其是传过来的两个参数到底是从哪里来的。
首先看下MainActivity里面的setContentView,进入该函数后,其对应的代码如下:
Activity.java
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}
PhoneWindow.java
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor();//这里生成了mDecor,它是所有应用窗口的根View 。
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);//这里就生成了mContentParent,这个generateLayout会根据设定的style来布局显示的界面
// Set up decor part of UI to ignore fitsSystemWindows if appropriate.
mDecor.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows();
....
}
}
PhoneWindow.java
protected DecorView generateDecor() {
return new DecorView(getContext(), -1);
}PhoneWindow.java
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
// Apply data from current theme.
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();//获取窗口的style
。。。。
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE);//看到没,你在xml里面设置的FEATURE_NO_TITLE,在这里生效了
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) {
// Don't allow an action bar if there is no title.
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
。。。。
final Context context = getContext();
。。。。
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = getAttributes();
if (!hasSoftInputMode()) {
params.softInputMode = a.getInt(
R.styleable.Window_windowSoftInputMode,
params.softInputMode);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_backgroundDimEnabled,
mIsFloating)) {
/* All dialogs should have the window dimmed */
if ((getForcedWindowFlags()&WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DIM_BEHIND) == 0) {
params.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DIM_BEHIND;
}
if (!haveDimAmount()) {
params.dimAmount = a.getFloat(
android.R.styleable.Window_backgroundDimAmount, 0.5f);
}
}
。。。。
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
。。。。
View in = mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);//这里把给定的布局加载出来,然后加到decor中
decor.addView(in, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) in;
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);//看到没这个ID_ANDROID_CONTENT,也就是一个窗口的根布局
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
。。。。
mDecor.finishChanging();
return contentParent;
}
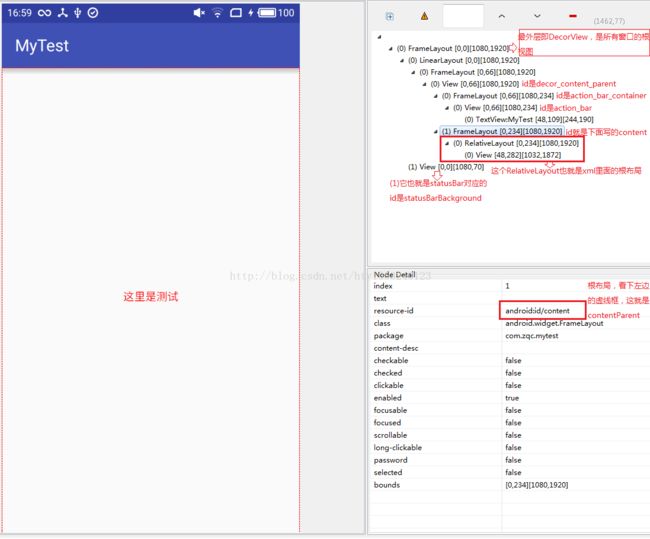
图上标的很详细,在最外层是一个FramLayout,其实也就是DecorView,是所有窗口的根布局,在该根布局下有一个(0)LinearLayout和一个(1)View,这个(1)View就是状态栏,(0)LinearLayout里面有个FrameLayout,在里面的多个View有固定的id,在图中已经标明,所有在一个Activity通过findViewById获取的ID_ANDROID_CONTENT就是
(0)FrameLayout->(0)LinearLayout->(0)FrameLayout->(1)FrameLayout对应的View。
要知道onMeasure两个参数到底是从哪里来的,还得再找下View是如何绘制的,上一篇文章有分析。View的绘制从ViewRootImpl的performTraversals()函数开始,下面进入该方法中具体分析下。
ViewRootImpl.java
private void performTraversals() {
// cache mView since it is used so much below...
final View host = mView;
。。。。
mIsInTraversal = true;
mWillDrawSoon = true;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
boolean newSurface = false;
boolean surfaceChanged = false;
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
int desiredWindowWidth;
int desiredWindowHeight;
final int viewVisibility = getHostVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
|| mNewSurfaceNeeded;
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = null;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged) {
mWindowAttributesChanged = false;
surfaceChanged = true;
params = lp;
}
。。。。
Rect frame = mWinFrame;
if (mFirst) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
if (lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR_PANEL
|| lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
// NOTE -- system code, won't try to do compat mode.
Point size = new Point();
mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
} else {
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
}
。。。。
} else {
desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
if (desiredWindowWidth != mWidth || desiredWindowHeight != mHeight) {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(TAG,
"View " + host + " resized to: " + frame);
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
if (viewVisibilityChanged) {
mAttachInfo.mWindowVisibility = viewVisibility;
host.dispatchWindowVisibilityChanged(viewVisibility);
if (viewVisibility != View.VISIBLE || mNewSurfaceNeeded) {
destroyHardwareResources();
}
if (viewVisibility == View.GONE) {
// After making a window gone, we will count it as being
// shown for the first time the next time it gets focus.
mHasHadWindowFocus = false;
}
}
。。。。
boolean layoutRequested = mLayoutRequested && (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw);
if (layoutRequested) {
final Resources res = mView.getContext().getResources();
if (mFirst) {
// make sure touch mode code executes by setting cached value
// to opposite of the added touch mode.
mAttachInfo.mInTouchMode = !mAddedTouchMode;
ensureTouchModeLocally(mAddedTouchMode);
} else {
。。。。
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
|| lp.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
if (lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR_PANEL
|| lp.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
// NOTE -- system code, won't try to do compat mode.
Point size = new Point();
mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
} else {
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics = res.getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
}
}
}
// Ask host how big it wants to be
windowSizeMayChange |= measureHierarchy(host, lp, res,
desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
}
。。。。
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth()
|| mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight() || contentInsetsChanged) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);//获取
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);//看这里,看这里
// Implementation of weights from WindowManager.LayoutParams
// We just grow the dimensions as needed and re-measure if
// needs be
int width = host.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = host.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean measureAgain = false;
if (lp.horizontalWeight > 0.0f) {
width += (int) ((mWidth - width) * lp.horizontalWeight);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (lp.verticalWeight > 0.0f) {
height += (int) ((mHeight - height) * lp.verticalWeight);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (measureAgain) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG,
"And hey let's measure once more: width=" + width
+ " height=" + height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);//看这里,看这里
}
layoutRequested = true;
}
}
}
。。。。
mIsInTraversal = false;
}
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}看下如下两行代码
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);//获取
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);ViewRootImpl.java
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
这里应该很好理解了,其中调用了MeasureSpec类中的方法,关于MeasureSpec类网上资料很多,该类中用一个int值的两部分分别表示Mode和具体的尺寸。其中最高两位表示
Mode,而最低的30位表示具体的尺寸值,这里计算完之后就进入了View的measure函数中,代码如下:
View.java
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ||
widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec ||
heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
int cacheIndex = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ? -1 :
mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}FrameLayout.java
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}ViewGroup.java
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}View.java
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}至此分析结束,所以说一个View的大小是由自己和父类两者共同决定的。