计算机视觉(二)——图像特征对比(Harris角点和Sift)
图像特征对比——对Sift原理的理解
这次试验是在python的环境下使用sift,即尺度不变特征变换,来进行实验,对比两张图像的特征点匹配,后面也会涉及到关于Harris角点与Sift的效果对比。
SIFT算法在解决特征匹配的问题上被称为是过去的十年来最为成功的图像局部描述子之一。SIFT算法之所以如此成功、流行,其稳定性扮演至关重要的角色。与Harris角点相比,SIFT算法在图像的尺度、旋转、亮度都展现出它自身强大的稳定性。网络上关于SIFT的具体步骤有许多专业文章,对SIFT有着更为详细解读。链接:SIFT特征详解。有兴趣的读者可以去阅读
SIFT算法实现步骤
SIFT实现可以大致分为四步
- 尺度空间的极值检测
极值检测也可以说是在整个尺度空间中找到特征点,也可以成为兴趣点。这些点都具有不会因为光照、尺度、旋转等因素的改变而消失的特点。这样才能在两张尺度不同,光照不同,角度不同的图片中有自己的特征点。 - 特征点定位
特征点的定位在SIFT常用到高斯金字塔和DoG高斯差分金字塔,高斯金字塔通过对图像的平滑处理和对图像的降采样,形成一个类似金字塔的图像堆积,不同高度上图像的大小不同。DoG中局部极值点可以组成特征点,所以在DoG中通过对比像素点和所有与之相邻的点比较(这是一个立体的对比,所以需要对比其它26个点) - 特征方向赋值
对关键点的方向采用梯度直方图统计。以关键点为原点,在特定区域之中像素点的关键方向的分布情况来确定主方向。 - 特征点描述
在特征点周围划分22的区域,在22中的一个区域中在划分22个区域就有共44个区域的分布。给这每一块的区域中再划分22个区域,并把其每个区域的方向直方图累加,作为一个8个方向向量的信息。而这样就作为关键点的描述,共有44*8=128维向量表征。
SIFT算法和Harris算法的具体实现
Harris算法实现代码:
#encoding:utf-8
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
from PCV.tools.imtools import imresize
"""
This is the Harris point matching example in Figure 2-2.
"""
# Figure 2-2上面的图
#im1 = array(Image.open("../data/crans_1_small.jpg").convert("L"))
#im2= array(Image.open("../data/crans_2_small.jpg").convert("L"))
# Figure 2-2下面的图
im1 = array(Image.open("E:/Py_code/photo/7.jpg").convert("L"))
im2 = array(Image.open("E:/Py_code/photo/8.jpg").convert("L"))
# resize加快匹配速度
im1 = imresize(im1, (im1.shape[1]//2, im1.shape[0]//2))
im2 = imresize(im2, (im2.shape[1]//2, im2.shape[0]//2))
wid = 5
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d1 = harris.get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid+1)
d2 = harris.get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
print('starting matching')
matches = harris.match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
harris.plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
实现结果:

在结果中,我们可以看到Harris角点对比的效果在这种图像角度发生变化的图像中不理想,很大的原因是因为Harris角点对比对于旋转角度拍摄的图像没有相应的功能去识别。Harris的算法效率也不高,这样的两张图片大小都在300k之下,程序需要跑出结果需要几分钟。
SIFT算法代码实现:
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
# im1f = '../data/sf_view1.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/sf_view2.jpg'
im1f = 'E:/Py_code/photo/3.jpg'
im2f = 'E:/Py_code/photo/4.jpg'
# im1f = '../data/climbing_1_small.jpg'
# im2f = '../data/climbing_2_small.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
#matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print ('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
实现结果:

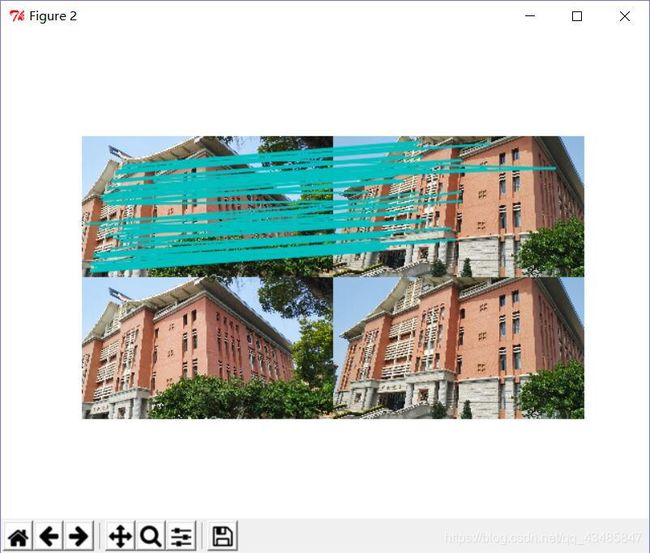
在上面的对比结果中可以看出,即使图像拍照的角度有很大的区别,SIFT依然可以有很好的对比匹配的效果,这就是SIFT能被称为过去十年来最成功的图像局部描述子的原因。相对Harris的效率相比,SIFT的效率有大的提升,程序的运行很快。
匹配地理标记图像
实现代码:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
""" This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10.
To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py."""
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "E:/Py_code/photo/z" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "E:/Py_code/photo/z/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('E:/Py_code/photo/result/path.png')
实现结果:


图一是匹配地理标记图像的连线结果。关于连线这么紧密的问题,我认为是在大多数的图片中,都有拍摄到建筑的某个部分。单独的那两张图片,是我在中山纪念馆的正侧面拍摄,所以有许多相同特征。
实现过程遇到的一些问题
在实验中,需要我们在原来配置好的环境中添加新模块。SIFT需要我们下载VLFeat,下载链接:VLFeat下载。建议下载vlfeat-0.9.20-bin.tar.gz这个。因为我之前下载21的,出现问题。换到20就解决了。下载之后打开文件,打开bin文件,根据自己的windows的版本选择。我是64的,复制win64这个文件夹。粘贴到你项目的目录下。

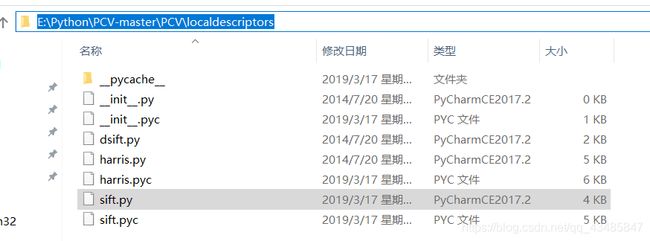
之后在文件中找到sift.py文件,将cmmd中改为如图所示。

这样在运行sift对比就不会有报错情况出现了。
在匹配地理标记图像时候,需要我们装pydot的模块。这个模块需要装GraphViz和pydot,GraphViz下载地址:GraphViz。我们下载后缀为.msi的文件,下载安装。在电脑的环境变换path中加入GraphViz目录下的bin文件路径。我在cmd中写入pip install pydot代码中的import pydot不报错了,但是出现了如图所示的错误。
我参考这位博主的文章解决“dot” not found in path报错。使用Anaconda的命令行,输入
conda install pydot-ng
conda install graphviz
就解决了问题。

