Hotspot 偏向锁BiasedLocking 源码解析
目录
1、定义
2、init
3、init方法补充说明
4、revoke_bias
5、bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint
6、revoke_and_rebias
7、VM_RevokeBias / VM_BulkRevokeBias
8、revoke_at_safepoint / revoke
9、preserve_marks / restore_marks
10、MacroAssembler::biased_locking_enter / biased_locking_exit
之前的博客中已经讲解了synchronized关键字的底层实现,其中涉及偏向锁的逻辑都封装在BiasedLocking中,本篇博客就详细探讨该类的实现。
1、定义
BiasedLocking的定义位于hotspot\src\share\vm\runtime\biasedLocking.hpp中,该类定义的属性和方法都是静态的,其中属性只有一个,如下图:
BiasedLockingCounters的定义在同一个文件中,就是一个保存各项跟偏向锁有关的统计数据的数据结构,如下图:
这些统计数据主要是为了打印日志使用,如果PrintBiasedLockingStatistics为true就会打印该数据结构中的数据,默认为false。参考获取_total_entry_count内存地址的total_entry_count_addr方法的调用链,如下:
其中MacroAssembler::fast_lock和对应的MacroAssembler::fast_unlock是C2即时编译器使用的加锁和解锁的方法。
除此之外,还有一个比较关键的枚举Condition,用来描述当前偏向锁的状态,其定义如下:
NOT_BIASED表示该对象没有持有偏向锁,BIAS_REVOKED表示该对象的偏向锁已经被撤销了,即其对象头已经恢复成默认的不开启偏向锁时的状态,BIAS_REVOKED_AND_REBIASED表示当前线程重新获取了该偏向锁。
2、init
init方法用于初始化BiasedLocking,该方法是在JVM启动时调用的,其调用链如下:
其实现如下:
void BiasedLocking::init() {
if (UseBiasedLocking) {
//UseBiasedLocking默认为true,表示是否使用偏向锁
if (BiasedLockingStartupDelay > 0) {
//BiasedLockingStartupDelay表示BiasedLocking初始化时的延时,默认为4000,避免在JVM启动时初始化,可加快JVM的启动
EnableBiasedLockingTask* task = new EnableBiasedLockingTask(BiasedLockingStartupDelay);
task->enroll();
} else {
VM_EnableBiasedLocking op(false);
VMThread::execute(&op);
}
}
}EnableBiasedLockingTask中执行任务的实现task方法跟else分支基本一样,如下:
就构造函数的参数不同,一个是false,一个是true,该参数决定了VM_EnableBiasedLocking的执行模式,其实现如下:
class VM_EnableBiasedLocking: public VM_Operation {
private:
bool _is_cheap_allocated;
public:
VM_EnableBiasedLocking(bool is_cheap_allocated) { _is_cheap_allocated = is_cheap_allocated; }
VMOp_Type type() const { return VMOp_EnableBiasedLocking; }
Mode evaluation_mode() const { return _is_cheap_allocated ? _async_safepoint : _safepoint; }
bool is_cheap_allocated() const { return _is_cheap_allocated; }
void doit() {
//将所有通过SystemDictionary加载过的类的对象头标记成其支持偏向
SystemDictionary::classes_do(enable_biased_locking);
//_biased_locking_enabled是一个静态static变量
_biased_locking_enabled = true;
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("Biased locking enabled");
}
}
bool allow_nested_vm_operations() const { return false; }
};
static void enable_biased_locking(Klass* k) {
//prototype_header表示该Klass对应oop的初始对象头
k->set_prototype_header(markOopDesc::biased_locking_prototype());
}
static markOop biased_locking_prototype() {
//biased_lock_pattern表示该对象支持偏向锁
return markOop( biased_lock_pattern );
}
void SystemDictionary::classes_do(void f(Klass*)) {
dictionary()->classes_do(f);
}
void Dictionary::classes_do(void f(Klass*)) {
for (int index = 0; index < table_size(); index++) {
for (DictionaryEntry* probe = bucket(index);
probe != NULL;
probe = probe->next()) {
Klass* k = probe->klass();
if (probe->loader_data() == InstanceKlass::cast(k)->class_loader_data()) {
f(k);
}
}
}
}3、init方法补充说明
理解init方法的逻辑需要知道以下几点:
1)、Klass的prototype_header的用途,其调用链如下:
其中must_be开头的三个方法用于判断该对象头是否需要保存下来,oopDesc::init_mark用于初始化对象头,将其设置为对应Klass的prototype_header,prototype_header_offset方法返回prototype_header的偏移量,主要给解释器和编译器生成Stub使用,同样用于获取Klass的prototype_header将其作为一个新创建对象的对象头,其调用链如下:
2) 枚举biased_lock_pattern的含义
biased_lock_pattern仅仅只是表示JVM已经开启了偏向锁,当前对象支持偏向锁,具体是否持有偏向锁需要通过biased_locker方法来判断,其实现如下:
即判断用来存储持有当前对象偏向锁的线程指针是否为空,为空则表示该对象的偏向锁未被其他线程占有,不为空则表示已经被其他线程占用了。
与biased_locking_prototype方法相对的就是prototype方法,该方法返回默认的即不开启偏向锁时的对象头,其实现如下:
no_hash_in_place和no_lock_in_place都是枚举值,其定义如下:
no_hash_in_place表示未初始化hash码,unlocked_value表示当前对象没有持有任何锁,也不支持偏向锁,此时对象头的状态就是neutral,参考 is_neutral方法的实现,如下:
3) Dictionary::classes_do
Dictionary::classes_do用于遍历所有已加载的Klass,那这个Klass是哪来的了?参考与之对应的add_klass方法实现,如下:
void Dictionary::add_klass(Symbol* class_name, ClassLoaderData* loader_data,
KlassHandle obj) {
assert_locked_or_safepoint(SystemDictionary_lock);
assert(obj() != NULL, "adding NULL obj");
assert(obj()->name() == class_name, "sanity check on name");
assert(loader_data != NULL, "Must be non-NULL");
//计算hash值,Dictionary用于保存DictionaryEntry的数据结构跟Java中的HashMap是一样的
unsigned int hash = compute_hash(class_name, loader_data);
//计算保存该Klass的数组索引
int index = hash_to_index(hash);
//创建一个新的key-value键值对对象
DictionaryEntry* entry = new_entry(hash, obj(), loader_data);
//将其加入到数组中
add_entry(index, entry);
}该方法的调用链如下:
其最上层的调用方法resolve_or_null和resolve_array_class_or_null都是用来解析常量池中的Class类型的符号引用,当某个类执行某个方法时,会判断该方法字节码所用到的符号引用是否解析完成,如果未解析则调用上述resolve方法完成解析,即会加载该类,创建对应的Klass,创建完成后就会调用add_klass方法将创建的Klass加入到Dictionary中管理。可参考《Hotspot 类加载、链接和初始化 C++源码解析》。
4)静态属性_biased_locking_enabled
_biased_locking_enabled默认为false,如果UseBiasedLocking为true,则在init方法中会将其置为true,其调用链如下:
enable方法直接返回该属性,如下:
update_dictionary方法中的调用如下:
在调用add_class方法前会先执行上述逻辑,跟上面的enable_biased_locking方法一样,即将_biased_locking_enabled置为true以后会保证后面新加载的Klass的prototype_header都是biased_locking_prototype,而在此之前已加载的Klass已经通过init方法做了同样处理,如此就可以保证后续新创建的锁对象oop都可以支持偏向锁,但是之前已经创建的锁对象oop则不支持偏向锁。
4、revoke_bias
revoke_bias的返回值只有两种NOT_BIASED和BIAS_REVOKED,前者表示目标对象没有偏向锁,后者表示已经成功撤销了该对象的偏向锁,即该方法就是用于撤销偏向锁。该方法的参数is_bulk无实际意义,只用于判断是否打印日志;参数allow_rebias用于判断是否彻底撤销偏向锁,如果为true将只是清除偏向锁中的线程指针,将其变成一个匿名的即没有被其他线程占用的偏向锁;如果为false则将其恢复成无锁状态。在撤销偏向锁时,如果是匿名偏向锁或者持有该锁的线程已经退出了或者持有该锁的线程中没有对应的BasicObjectLock(即占用该锁的方法或者代码块已经执行完了)则按照参数allow_rebias撤销偏向锁;如果有某个线程正在持有该偏向锁,无论是否当前线程,都需要将其持有的偏向锁膨胀成轻量级锁,且需要考虑锁嵌套的情形。
static BiasedLocking::Condition revoke_bias(oop obj, bool allow_rebias, bool is_bulk, JavaThread* requesting_thread) {
markOop mark = obj->mark();
if (!mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
//如果未加锁
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
ResourceMark rm;
tty->print_cr(" (Skipping revocation of object of type %s because it's no longer biased)",
obj->klass()->external_name());
}
return BiasedLocking::NOT_BIASED;
}
uint age = mark->age();
markOop biased_prototype = markOopDesc::biased_locking_prototype()->set_age(age);
markOop unbiased_prototype = markOopDesc::prototype()->set_age(age);
if (TraceBiasedLocking && (Verbose || !is_bulk)) {
ResourceMark rm;
tty->print_cr("Revoking bias of object " INTPTR_FORMAT " , mark " INTPTR_FORMAT " , type %s , prototype header " INTPTR_FORMAT " , allow rebias %d , requesting thread " INTPTR_FORMAT,
p2i((void *)obj), (intptr_t) mark, obj->klass()->external_name(), (intptr_t) obj->klass()->prototype_header(), (allow_rebias ? 1 : 0), (intptr_t) requesting_thread);
}
JavaThread* biased_thread = mark->biased_locker();
if (biased_thread == NULL) {
//如果是匿名偏向锁
if (!allow_rebias) {
//将其变成无锁状态
obj->set_mark(unbiased_prototype);
}
if (TraceBiasedLocking && (Verbose || !is_bulk)) {
tty->print_cr(" Revoked bias of anonymously-biased object");
}
return BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED;
}
//biased_thread不为空
bool thread_is_alive = false;
if (requesting_thread == biased_thread) {
//如果当前线程就是占有偏向锁的线程
thread_is_alive = true;
} else {
for (JavaThread* cur_thread = Threads::first(); cur_thread != NULL; cur_thread = cur_thread->next()) {
if (cur_thread == biased_thread) {
//遍历所有的线程,如果找到了占用偏向锁的线程
thread_is_alive = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!thread_is_alive) {
//如果占用偏向锁的线程退出了
if (allow_rebias) {
//如果允许使用偏向锁,则设置为匿名偏向锁,注意此时的对象头中线程指针没了
obj->set_mark(biased_prototype);
} else {
//如果不允许使用偏向锁,置为无锁状态
obj->set_mark(unbiased_prototype);
}
if (TraceBiasedLocking && (Verbose || !is_bulk)) {
tty->print_cr(" Revoked bias of object biased toward dead thread");
}
//返回偏向锁被撤销了
return BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED;
}
//如果拥有偏向锁的线程还是存活的
//获取该线程的所有MonitorInfo,MonitorInfo是对BasicObjectLock的一层包装而已
//返回的MonitorInfo数组中最近分配的在前面
GrowableArray* cached_monitor_info = get_or_compute_monitor_info(biased_thread);
BasicLock* highest_lock = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < cached_monitor_info->length(); i++) {
MonitorInfo* mon_info = cached_monitor_info->at(i);
if (mon_info->owner() == obj) {
if (TraceBiasedLocking && Verbose) {
tty->print_cr(" mon_info->owner (" PTR_FORMAT ") == obj (" PTR_FORMAT ")",
p2i((void *) mon_info->owner()),
p2i((void *) obj));
}
//找到关联的BasicObjectLock,注意此处找到了跟目标obj关联的BasicObjectLock后并不会终止遍历而是继续遍历
//因为存在锁嵌套的情形,这里继续遍历找到最外层的BasicObjectLock
markOop mark = markOopDesc::encode((BasicLock*) NULL);
highest_lock = mon_info->lock();
//修改displaced_header属性,实际就是将其置为NULL
highest_lock->set_displaced_header(mark);
} else {
if (TraceBiasedLocking && Verbose) {
tty->print_cr(" mon_info->owner (" PTR_FORMAT ") != obj (" PTR_FORMAT ")",
p2i((void *) mon_info->owner()),
p2i((void *) obj));
}
}
}
if (highest_lock != NULL) {
//修改displaced_header,撤销原对象头中包含的偏向锁
highest_lock->set_displaced_header(unbiased_prototype);
//修改对象头让其指向highest_lock,实际就是将其膨胀成轻量级锁
obj->release_set_mark(markOopDesc::encode(highest_lock));
assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "illegal mark state: stack lock used bias bit");
if (TraceBiasedLocking && (Verbose || !is_bulk)) {
tty->print_cr(" Revoked bias of currently-locked object");
}
} else {
//没有关联的BasicObjectLock,说明该线程实际已经释放了偏向锁
if (TraceBiasedLocking && (Verbose || !is_bulk)) {
tty->print_cr(" Revoked bias of currently-unlocked object");
}
if (allow_rebias) {
//设置成匿名偏向锁
obj->set_mark(biased_prototype);
} else {
//设置成无锁状态
obj->set_mark(unbiased_prototype);
}
}
return BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED;
}
static GrowableArray* get_or_compute_monitor_info(JavaThread* thread) {
//获取目标线程的cached_monitor_info属性
GrowableArray* info = thread->cached_monitor_info();
if (info != NULL) {
//如果不为空说明之前已经调用过get_or_compute_monitor_info方法,直接返回
return info;
}
//info为null,创建一个新的
info = new GrowableArray();
if (thread->has_last_Java_frame()) {
//如果包含Java栈帧
RegisterMap rm(thread);
//遍历所有的Java栈帧
for (javaVFrame* vf = thread->last_java_vframe(&rm); vf != NULL; vf = vf->java_sender()) {
//monitors方法中返回的MonitorInfo的顺序是最先分配的BasicObjectLock在前面
GrowableArray *monitors = vf->monitors();
if (monitors != NULL) {
int len = monitors->length();
//遍历Java栈帧中的MonitorInfo,注意此处是倒序遍历的,即最先遍历最近分配的BasicObjectLock
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
MonitorInfo* mon_info = monitors->at(i);
//如果该MonitorInfo已经被淘汰
if (mon_info->eliminated()) continue;
oop owner = mon_info->owner();
if (owner != NULL) {
//owner不为空,即是非空闲的BasicObjectLock,则加入到info中
info->append(mon_info);
}
}
}
}
}
//info中最近分配的BasicObjectLock在数组前面
thread->set_cached_monitor_info(info);
return info;
}
static markOop encode(BasicLock* lock) {
return (markOop) lock;
}
inline void oopDesc::release_set_mark(markOop m) {
OrderAccess::release_store_ptr(&_mark, m);
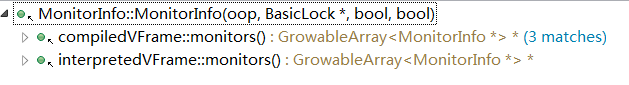
} 上述代码中涉及的MonitorInfo是一个用来保存BasicObjectLock重要属性的数据结构,其定义如下:
其构造函数的调用链如下:
以interpretedVFrame::monitors的实现为例说明,如下:
该方法会遍历当前调用栈帧中包含的所有BasicObjectLock,利用该对象构造一个MonitorInfo实例然后放入数组中,注意其是从高地址往低地址遍历,即先遍历最早分配的BasicObjectLock,参考previous_monitor_in_interpreter_frame方法的实现,如下:
5、bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint
该方法用于批量的撤销或者重新偏向,批量是指会对某个oop对应的Klass的所有作为锁对象的位于调用栈帧上的oop,撤销就是将该Klass的所有作为锁对象oop的对象头都置为无锁状态,同时把prototype_header也置为无锁状态,即该Klass新创建的作为锁对象的oop不再支持偏向锁;重新偏向时,如果prototype_header支持偏向锁,则将prototype_header中的epoch加1,并且同样的将该Klass的所有作为锁对象的oop的epoch加1,注意此时除目标对象o以外的其他锁对象的锁状态不变,只是增加epoch而已;此时如果attempt_rebias_of_object为true,则目标对象的偏向锁会先被置为匿名偏向锁,再置为偏向请求线程的偏向锁,如果为false则置为无锁状态。注意该方法只能在安全点下执行,其返回值只有BIAS_REVOKED和BIAS_REVOKED_AND_REBIASED两种。
static BiasedLocking::Condition bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint(oop o,
bool bulk_rebias,
bool attempt_rebias_of_object,
JavaThread* requesting_thread) {
assert(SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must be done at safepoint");
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("* Beginning bulk revocation (kind == %s) because of object "
INTPTR_FORMAT " , mark " INTPTR_FORMAT " , type %s",
(bulk_rebias ? "rebias" : "revoke"),
p2i((void *) o), (intptr_t) o->mark(), o->klass()->external_name());
}
jlong cur_time = os::javaTimeMillis();
//更新批量撤销的时间
o->klass()->set_last_biased_lock_bulk_revocation_time(cur_time);
Klass* k_o = o->klass();
Klass* klass = k_o;
if (bulk_rebias) {
//如果批量重新偏向
if (klass->prototype_header()->has_bias_pattern()) {
int prev_epoch = klass->prototype_header()->bias_epoch();
//增加prototype_header中的bias_epoch
klass->set_prototype_header(klass->prototype_header()->incr_bias_epoch());
int cur_epoch = klass->prototype_header()->bias_epoch();
// 遍历所有的Java线程
for (JavaThread* thr = Threads::first(); thr != NULL; thr = thr->next()) {
//获取该线程的所有调用栈帧包含的BasicObjectLock
GrowableArray* cached_monitor_info = get_or_compute_monitor_info(thr);
for (int i = 0; i < cached_monitor_info->length(); i++) {
MonitorInfo* mon_info = cached_monitor_info->at(i);
oop owner = mon_info->owner();
markOop mark = owner->mark();
//如果BasicObjectLock关联的obj的kass跟目标对象的klass一致
if ((owner->klass() == k_o) && mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
//修改关联obj的epoch,确保跟prototype_header保持一致,注意此时偏向锁并未撤销
assert(mark->bias_epoch() == prev_epoch || mark->bias_epoch() == cur_epoch, "error in bias epoch adjustment");
owner->set_mark(mark->set_bias_epoch(cur_epoch));
}
}
}
}
//撤销目标对象的偏向锁
revoke_bias(o, attempt_rebias_of_object && klass->prototype_header()->has_bias_pattern(), true, requesting_thread);
} else {
//如果批量撤销
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
ResourceMark rm;
tty->print_cr("* Disabling biased locking for type %s", klass->external_name());
}
//将prototype_header恢复成默认的无锁状态
klass->set_prototype_header(markOopDesc::prototype());
//遍历所有Java线程持有的所有BasicObjectLock
for (JavaThread* thr = Threads::first(); thr != NULL; thr = thr->next()) {
GrowableArray* cached_monitor_info = get_or_compute_monitor_info(thr);
for (int i = 0; i < cached_monitor_info->length(); i++) {
MonitorInfo* mon_info = cached_monitor_info->at(i);
oop owner = mon_info->owner();
markOop mark = owner->mark();
//如果关联obj的klass和目标obj的klass一致
if ((owner->klass() == k_o) && mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
//撤销偏向锁,将其膨胀成轻量级锁,因为这些偏向锁都是正在使用中的
revoke_bias(owner, false, true, requesting_thread);
}
}
}
//撤销偏向锁,上面的遍历其实就会完成对应o的偏向锁撤销
revoke_bias(o, false, true, requesting_thread);
}
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("* Ending bulk revocation");
}
BiasedLocking::Condition status_code = BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED;
if (attempt_rebias_of_object && //只有attempt_rebias_of_object和bulk_rebias都为true时后面两个条件才可能成立
o->mark()->has_bias_pattern() &&
klass->prototype_header()->has_bias_pattern()) {
//重置偏向锁
markOop new_mark = markOopDesc::encode(requesting_thread, o->mark()->age(),
klass->prototype_header()->bias_epoch());
o->set_mark(new_mark);
status_code = BiasedLocking::BIAS_REVOKED_AND_REBIASED;
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr(" Rebiased object toward thread " INTPTR_FORMAT, (intptr_t) requesting_thread);
}
}
//最后的结果要么o撤销了偏向锁,要么o重新设置了偏向锁
assert(!o->mark()->has_bias_pattern() ||
(attempt_rebias_of_object && (o->mark()->biased_locker() == requesting_thread)),
"bug in bulk bias revocation");
return status_code;
}
markOop incr_bias_epoch() {
return set_bias_epoch((1 + bias_epoch()) & epoch_mask);
} 6、revoke_and_rebias
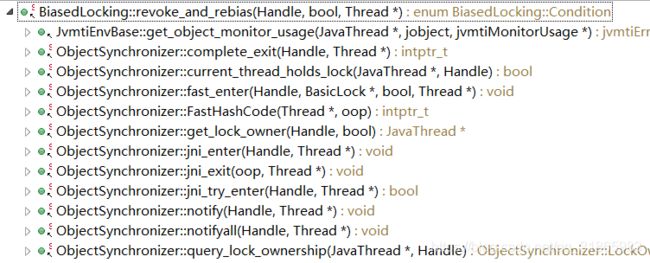
此方法的逻辑不是很复杂,但是有很多的条件判断,要想知道其背后的用意,需要清楚revoke_and_rebias的调用场景,其调用链如下:
其中fast_enter用于实现synchronized关键字,其调用时attempt_rebias为true;FastHashCode用于获取对象头中的hash码,其调用时attempt_rebias为false;jni开头的三个调用方法用于实现JNI和Unsafe类中的监视器锁获取和释放,其调用时attempt_rebias为false;wait,nofity,notifyall三个方法用于实现Object的本地方法,其调用时attempt_rebias为false,其他的几处调用attempt_rebias也都是为false。
BiasedLocking::Condition BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(Handle obj, bool attempt_rebias, TRAPS) {
assert(!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must not be called while at safepoint");
//非fast_enter的调用可能会走if或者else if分支,此时attempt_rebias都是false,即这种情形下都是撤销偏向锁
markOop mark = obj->mark();
if (mark->is_biased_anonymously() && !attempt_rebias) {
//如果obj的偏向锁未被占有且不需要获取偏向锁,则尝试将其恢复成默认的
markOop biased_value = mark;
//将对象的分代年龄写入初始对象头中
markOop unbiased_prototype = markOopDesc::prototype()->set_age(mark->age());
//原子的修改对象头,将其恢复成无锁状态
markOop res_mark = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(unbiased_prototype, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
if (res_mark == biased_value) {
//修改成功
return BIAS_REVOKED;
}
} else if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
//如果obj的偏向锁已经被占用了或者attempt_rebias为true
Klass* k = obj->klass();
//prototype_header变更只能在安全点下,变更时会将位于栈上的该klass的所有锁对象oop都做同样的变更
//如果某个锁对象oop不在当时的调用栈帧中,则可能出现不一致
markOop prototype_header = k->prototype_header();
if (!prototype_header->has_bias_pattern()) {
//如果prototype_header中没有偏向锁标识
markOop biased_value = mark;
//将当前对象的对象头原子的修改成prototype_header,将其恢复成无锁状态
markOop res_mark = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(prototype_header, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
assert(!(*(obj->mark_addr()))->has_bias_pattern(), "even if we raced, should still be revoked");
return BIAS_REVOKED;
} else if (prototype_header->bias_epoch() != mark->bias_epoch()) {
//如果两个对象头的epoch的值不等,说明更新prototype_header的epoch值时该对象不在任何Java线程栈帧中,即该对象的偏向锁实际已经释放了
if (attempt_rebias) {
//如果需要重新偏向
assert(THREAD->is_Java_thread(), "");
markOop biased_value = mark;
//生成一个新的偏向锁对象头,让当前线程占用该偏向锁
markOop rebiased_prototype = markOopDesc::encode((JavaThread*) THREAD, mark->age(), prototype_header->bias_epoch());
markOop res_mark = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(rebiased_prototype, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
if (res_mark == biased_value) {
//如果修改成功
return BIAS_REVOKED_AND_REBIASED;
}
} else {
//attempt_rebias为false,则将对象头恢复成无锁状态
markOop biased_value = mark;
markOop unbiased_prototype = markOopDesc::prototype()->set_age(mark->age());
markOop res_mark = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(unbiased_prototype, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
if (res_mark == biased_value) {
//修改成功
return BIAS_REVOKED;
}
}
}
}
//进入此逻辑的有以下几种情形:目标对象处于无锁状态;目标对象有偏向锁,其Klass的prototype_header也有偏向锁,且两者epoch一致。
//如果是并发抢占偏向锁,则抢占失败的线程会进入此逻辑,通过VM_RevokeBias将偏向锁膨胀成轻量级锁,
HeuristicsResult heuristics = update_heuristics(obj(), attempt_rebias);
if (heuristics == HR_NOT_BIASED) {
//返回没有偏向锁
return NOT_BIASED;
} else if (heuristics == HR_SINGLE_REVOKE) {
Klass *k = obj->klass();
markOop prototype_header = k->prototype_header();
if (mark->biased_locker() == THREAD &&
prototype_header->bias_epoch() == mark->bias_epoch()) {
//如果目标对象的偏向锁被当前线程占有
ResourceMark rm;
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("Revoking bias by walking my own stack:");
}
/将偏向锁膨胀成轻量级锁或者撤销
BiasedLocking::Condition cond = revoke_bias(obj(), false, false, (JavaThread*) THREAD);
//将cached_monitor_info置为NULL,revoke_bias方法会设置该属性
((JavaThread*) THREAD)->set_cached_monitor_info(NULL);
assert(cond == BIAS_REVOKED, "why not?");
return cond;
} else {
//如果占用偏向锁的不是当前线程,底层也是调用revoke_bias,撤销偏向锁或者将其膨胀成轻量级锁
//因为是修改其他线程占用的obj,为了安全需要在安全点下执行,借此暂停持有该偏向锁的线程,注意这个任务并不是立即执行,而是有一个短暂的延时
VM_RevokeBias revoke(&obj, (JavaThread*) THREAD);
VMThread::execute(&revoke);
return revoke.status_code();
}
}
assert((heuristics == HR_BULK_REVOKE) ||
(heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS), "?");
//执行批量撤销或者重偏向,底层调用bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint
//同一个Klass的多个锁对象oop累计调用update_heuristics超过一定次数就会返回HR_BULK_REBIAS,通过VM_BulkRevokeBias将Klass和对应的多个位于调用栈帧中的锁对象oop的epoch值增加,这样没有为调用栈帧中也是该Klass的锁对象oop就会被用于重新获取偏向锁,减少update_heuristics的调用
//如果调用更加频繁,则返回HR_BULK_REVOKE,将该Klass的prototype_header和对应的多个位于调用栈帧中的锁对象oop恢复成无锁状态,因为频繁的执行此逻辑说明当前的并发调用场景已经不适用于偏向锁了
VM_BulkRevokeBias bulk_revoke(&obj, (JavaThread*) THREAD,
(heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS),
attempt_rebias);
VMThread::execute(&bulk_revoke);
return bulk_revoke.status_code();
}
//目前对象的偏向锁是否被占有了
bool is_biased_anonymously() const {
return (has_bias_pattern() && (biased_locker() == NULL));
}
//获取epoch值
int bias_epoch() const {
assert(has_bias_pattern(), "should not call this otherwise");
return (mask_bits(value(), epoch_mask_in_place) >> epoch_shift);
}
//重新生成一个偏向锁对象头
static markOop encode(JavaThread* thread, uint age, int bias_epoch) {
intptr_t tmp = (intptr_t) thread;
assert(UseBiasedLocking && ((tmp & (epoch_mask_in_place | age_mask_in_place | biased_lock_mask_in_place)) == 0), "misaligned JavaThread pointer");
assert(age <= max_age, "age too large");
assert(bias_epoch <= max_bias_epoch, "bias epoch too large");
//全部用或运算
return (markOop) (tmp | (bias_epoch << epoch_shift) | (age << age_shift) | biased_lock_pattern);
}
//HeuristicsResult是一个枚举
static HeuristicsResult update_heuristics(oop o, bool allow_rebias) {
markOop mark = o->mark();
if (!mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
//返回没有偏向锁
return HR_NOT_BIASED;
}
Klass* k = o->klass();
jlong cur_time = os::javaTimeMillis();
//获取上一次偏向锁被批量撤销的时间
jlong last_bulk_revocation_time = k->last_biased_lock_bulk_revocation_time();
//获取偏向锁被撤销的次数
int revocation_count = k->biased_lock_revocation_count();
//BiasedLockingBulkRebiasThreshold的默认值是20
//BiasedLockingBulkRevokeThreshold的默认值是40
//BiasedLockingDecayTime的默认值是25000,单位毫秒
if ((revocation_count >= BiasedLockingBulkRebiasThreshold) &&
(revocation_count < BiasedLockingBulkRevokeThreshold) &&
(last_bulk_revocation_time != 0) &&
(cur_time - last_bulk_revocation_time >= BiasedLockingDecayTime)) {
//将其重置为0,即在BiasedLockingDecayTime内,如果
//无论如何都是先触发HR_BULK_REBIAS,触发完了以后如果频繁的调用update_heuristics会导致revocation_count达到BiasedLockingBulkRevokeThreshold,触发HR_BULK_REVOKE
//如果调用不频繁,则不会触发HR_BULK_REVOKE
k->set_biased_lock_revocation_count(0);
revocation_count = 0;
}
if (revocation_count <= BiasedLockingBulkRevokeThreshold) {
//增加计数器
revocation_count = k->atomic_incr_biased_lock_revocation_count();
}
if (revocation_count == BiasedLockingBulkRevokeThreshold) {
return HR_BULK_REVOKE;
}
if (revocation_count == BiasedLockingBulkRebiasThreshold) {
return HR_BULK_REBIAS;
}
return HR_SINGLE_REVOKE;
}7、VM_RevokeBias / VM_BulkRevokeBias
VM_RevokeBias用于撤销偏向锁,支持单个对象或者一组对象,VM_BulkRevokeBias继承自VM_RevokeBias,只能用于单个对象,其底层都是revoke_bias和bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint方法,因为这两方法需要遍历线程栈帧中包含的BasicObjectLock,为了保证遍历的过程中栈帧包含的BasicObjectLock不变,所以必须在安全点下执行。其实现如下:
class VM_RevokeBias : public VM_Operation {
protected:
Handle* _obj; //被撤销偏向锁的单个对象
GrowableArray* _objs; //被撤销偏向锁的对象数组
JavaThread* _requesting_thread; //请求线程
BiasedLocking::Condition _status_code; //执行结果
public:
//两种构造函数,对应两种用法
VM_RevokeBias(Handle* obj, JavaThread* requesting_thread)
: _obj(obj)
, _objs(NULL)
, _requesting_thread(requesting_thread)
, _status_code(BiasedLocking::NOT_BIASED) {}
VM_RevokeBias(GrowableArray* objs, JavaThread* requesting_thread)
: _obj(NULL)
, _objs(objs)
, _requesting_thread(requesting_thread)
, _status_code(BiasedLocking::NOT_BIASED) {}
virtual VMOp_Type type() const { return VMOp_RevokeBias; }
virtual bool doit_prologue() {
// 检查是否包含带有偏向锁的对象,如果有返回true,如果没有则返回false,避免触发安全点同步
if (_obj != NULL) {
markOop mark = (*_obj)()->mark();
if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
return true;
}
} else {
//遍历数组中所有对象
for ( int i = 0 ; i < _objs->length(); i++ ) {
markOop mark = (_objs->at(i))()->mark();
if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
virtual void doit() {
if (_obj != NULL) {
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("Revoking bias with potentially per-thread safepoint:");
}
//调用revoke_bias撤销偏向锁
_status_code = revoke_bias((*_obj)(), false, false, _requesting_thread);
//清除所有线程的cached_monitor_info
clean_up_cached_monitor_info();
return;
} else {
if (TraceBiasedLocking) {
tty->print_cr("Revoking bias with global safepoint:");
}
//批量撤销,底层调用bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint
BiasedLocking::revoke_at_safepoint(_objs);
}
}
BiasedLocking::Condition status_code() const {
return _status_code;
}
};
bool has_bias_pattern() const {
return (mask_bits(value(), biased_lock_mask_in_place) == biased_lock_pattern);
}
static void clean_up_cached_monitor_info() {
//将所有线程的cached_monitor_info置为NULL
for (JavaThread* thr = Threads::first(); thr != NULL; thr = thr->next()) {
thr->set_cached_monitor_info(NULL);
}
}
class VM_BulkRevokeBias : public VM_RevokeBias {
private:
bool _bulk_rebias;
bool _attempt_rebias_of_object;
public:
VM_BulkRevokeBias(Handle* obj, JavaThread* requesting_thread,
bool bulk_rebias,
bool attempt_rebias_of_object)
: VM_RevokeBias(obj, requesting_thread)
, _bulk_rebias(bulk_rebias)
, _attempt_rebias_of_object(attempt_rebias_of_object) {}
virtual VMOp_Type type() const { return VMOp_BulkRevokeBias; }
virtual bool doit_prologue() { return true; }
virtual void doit() {
_status_code = bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint((*_obj)(), _bulk_rebias, _attempt_rebias_of_object, _requesting_thread);
clean_up_cached_monitor_info();
}
};
8、revoke_at_safepoint / revoke
该方法有个重载方法,一个处理单个对象,一个处理一组对象,其处理逻辑一样,前者适用于单个对象,后者适用于一组对象
void BiasedLocking::revoke_at_safepoint(Handle h_obj) {
assert(SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must only be called while at safepoint");
oop obj = h_obj();
HeuristicsResult heuristics = update_heuristics(obj, false);
if (heuristics == HR_SINGLE_REVOKE) {
revoke_bias(obj, false, false, NULL);
} else if ((heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS) ||
(heuristics == HR_BULK_REVOKE)) {
bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint(obj, (heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS), false, NULL);
}
clean_up_cached_monitor_info();
}
void BiasedLocking::revoke_at_safepoint(GrowableArray* objs) {
assert(SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must only be called while at safepoint");
int len = objs->length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
oop obj = (objs->at(i))();
HeuristicsResult heuristics = update_heuristics(obj, false);
if (heuristics == HR_SINGLE_REVOKE) {
revoke_bias(obj, false, false, NULL);
} else if ((heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS) ||
(heuristics == HR_BULK_REVOKE)) {
bulk_revoke_or_rebias_at_safepoint(obj, (heuristics == HR_BULK_REBIAS), false, NULL);
}
}
clean_up_cached_monitor_info();
}
void BiasedLocking::revoke(GrowableArray* objs) {
assert(!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must not be called while at safepoint");
if (objs->length() == 0) {
return;
}
//最终也是调用revoke_at_safepoint方法
VM_RevokeBias revoke(objs, JavaThread::current());
VMThread::execute(&revoke);
}
9、preserve_marks / restore_marks
preserve_marks方法在GC开始前将所有持有偏向锁的对象和对象头放入对应Stack中,然后在GC结束后恢复其对象头。
void BiasedLocking::preserve_marks() {
if (!UseBiasedLocking)
return;
//必须在安全点调用
assert(SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must only be called while at safepoint");
assert(_preserved_oop_stack == NULL, "double initialization");
assert(_preserved_mark_stack == NULL, "double initialization");
_preserved_mark_stack = new (ResourceObj::C_HEAP, mtInternal) GrowableArray(10, true);
_preserved_oop_stack = new (ResourceObj::C_HEAP, mtInternal) GrowableArray(10, true);
ResourceMark rm;
Thread* cur = Thread::current();
//遍历所有的JavaThread
for (JavaThread* thread = Threads::first(); thread != NULL; thread = thread->next()) {
if (thread->has_last_Java_frame()) {
RegisterMap rm(thread);
//遍历所有的java栈帧
for (javaVFrame* vf = thread->last_java_vframe(&rm); vf != NULL; vf = vf->java_sender()) {
//获取当前栈帧中包含的所有MonitorInfo
GrowableArray *monitors = vf->monitors();
if (monitors != NULL) {
int len = monitors->length();
//遍历所有的MonitorInfo
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
MonitorInfo* mon_info = monitors->at(i);
if (mon_info->owner_is_scalar_replaced()) continue;
oop owner = mon_info->owner();
if (owner != NULL) {
markOop mark = owner->mark();
//如果其持有偏向锁,将对象和对象头分别保存到对应的Stack中
if (mark->has_bias_pattern()) {
_preserved_oop_stack->push(Handle(cur, owner));
_preserved_mark_stack->push(mark);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void BiasedLocking::restore_marks() {
if (!UseBiasedLocking)
return;
assert(_preserved_oop_stack != NULL, "double free");
assert(_preserved_mark_stack != NULL, "double free");
//恢复Stack中保存的对象的对象头
int len = _preserved_oop_stack->length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Handle owner = _preserved_oop_stack->at(i);
markOop mark = _preserved_mark_stack->at(i);
owner->set_mark(mark);
}
//释放掉Stack占用的内存
delete _preserved_oop_stack;
_preserved_oop_stack = NULL;
delete _preserved_mark_stack;
_preserved_mark_stack = NULL;
} 10、MacroAssembler::biased_locking_enter / biased_locking_exit
biased_locking_enter用于获取偏向锁,如果该对象的锁已经膨胀成轻量级锁或者重量级锁,则直接返回;如果还是当前线程持有该对象的偏向锁且该对象的对象头中的epoch和该对象的klass的prototype_header中的epoch一致,则跳转到加锁完成标签,即该对象的加锁完成;如果该对象的klass的prototype_header已经没有偏向锁标识了,则需要将目标对象的对象头恢复成默认的无锁状态,然后跳转到slow_path;如果该对象的klass的prototype_header中的epoch发生改变了,则重新设置目标对象的偏向锁对象头,跳转到slow_path标签;如果klass的prototype_header没有改变,是一个新的线程请求该对象的偏向锁,则将当前线程的线程指针写入目标对象的偏向锁对象头中,跳转到slow_path标签。
biased_locking_exit只是校验目标对象的偏向锁标识是否存在,如果存在说明未向上膨胀,则直接跳转到解锁完成标签,即该对象的解锁完成,如果不存在则直接返回。
void MacroAssembler::biased_locking_exit(Register obj_reg, Register temp_reg, Label& done) {
assert(UseBiasedLocking, "why call this otherwise?");
//获取obj的对象头
movptr(temp_reg, Address(obj_reg, oopDesc::mark_offset_in_bytes()));
//将其进行and运算,biased_lock_mask_in_place就是7,二进制111
andptr(temp_reg, markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place);
//判断and后的结果是否是5即101
cmpptr(temp_reg, markOopDesc::biased_lock_pattern);
//如果是则跳转到done,如果是表明未发生锁膨胀
jcc(Assembler::equal, done);
}
int MacroAssembler::biased_locking_enter(Register lock_reg,
Register obj_reg,
Register swap_reg,
Register tmp_reg,
bool swap_reg_contains_mark,
Label& done,
Label* slow_case,
BiasedLockingCounters* counters) {
assert(UseBiasedLocking, "why call this otherwise?");
assert(swap_reg == rax, "swap_reg must be rax for cmpxchgq");
LP64_ONLY( assert(tmp_reg != noreg, "tmp_reg must be supplied"); )
bool need_tmp_reg = false;
if (tmp_reg == noreg) {
//如果tmp_reg不存在,临时使用lock_reg
need_tmp_reg = true;
tmp_reg = lock_reg;
assert_different_registers(lock_reg, obj_reg, swap_reg);
} else {
assert_different_registers(lock_reg, obj_reg, swap_reg, tmp_reg);
}
assert(markOopDesc::age_shift == markOopDesc::lock_bits + markOopDesc::biased_lock_bits, "biased locking makes assumptions about bit layout");
//obj的对象头地址
Address mark_addr (obj_reg, oopDesc::mark_offset_in_bytes());
//BasicLock中保存对象头的地址
Address saved_mark_addr(lock_reg, 0);
if (PrintBiasedLockingStatistics && counters == NULL) {
counters = BiasedLocking::counters();
}
Label cas_label;
int null_check_offset = -1;
if (!swap_reg_contains_mark) {
null_check_offset = offset();
//将对象头放入swap_reg即rax中
movptr(swap_reg, mark_addr);
}
if (need_tmp_reg) {
//将lock_reg中保存的BasicLock地址压入栈帧,从而可以利用lock_reg执行其他的运算
push(tmp_reg);
}
//将swap_reg中的对象头拷贝到tmp_reg
movptr(tmp_reg, swap_reg);
//执行and运算,biased_lock_mask_in_place就是111
andptr(tmp_reg, markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place);
//判断结果是否是biased_lock_pattern
cmpptr(tmp_reg, markOopDesc::biased_lock_pattern);
if (need_tmp_reg) {
//将栈顶的BasicLock地址pop出来放到lock_reg中
pop(tmp_reg);
}
//如果不等于,说明该对象的锁已经变成轻量级锁或者重量级锁,则跳转到cas_label
jcc(Assembler::notEqual, cas_label);
//如果等于,说明该对象的锁还是偏向锁,判断持有偏向锁的线程是否是当前线程
if (need_tmp_reg) {
//重新将tmp_reg中的BasicLock地址压入栈顶
push(tmp_reg);
}
if (swap_reg_contains_mark) {
null_check_offset = offset();
}
//获取obj对应klass的prototype_header,将其拷贝到tmp_reg中
load_prototype_header(tmp_reg, obj_reg);
//将r15_thread中保存的当前thread指针和prototype_header进行or运算,结果保存在tmp_reg
orptr(tmp_reg, r15_thread);
//与obj的对象头做异或运算,将结果保存到tmp_reg,如果两者的thead指针和epoch一样则这些位置为0,prototype_header中没有age,这4位是1
xorptr(tmp_reg, swap_reg);
Register header_reg = tmp_reg;
//进行and运算,相当于将header_reg中表示age的4位置为0
andptr(header_reg, ~((int) markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place));
if (need_tmp_reg) {
pop(tmp_reg);
}
if (counters != NULL) {
cond_inc32(Assembler::zero,
ExternalAddress((address) counters->biased_lock_entry_count_addr()));
}
//将swap_reg即rax与header_reg比较
//判断header_reg的结果是为0,如果是则还是当前线程持有的偏向锁
jcc(Assembler::equal, done);
//如果不等于,说明有一个新的线程请求获取偏向锁或者prototype_header发生变更了
Label try_revoke_bias;
Label try_rebias;
testptr(header_reg, markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place);
//如果prototype header的最后三位中有一位是1,说明prototype_header中已经没有偏向锁了,
//则跳转到try_revoke_bias,撤销偏向锁,恢复成默认的对象头
jccb(Assembler::notZero, try_revoke_bias);
//最后三位还是0,说明obj还是可以用于偏向锁
testptr(header_reg, markOopDesc::epoch_mask_in_place);
//如果epoch位上不是0,说明prototype_header中的epoch和obj的对象头中包含的epoch不一致,prototype_header中的epoch发生改变了
//则跳转到try_rebias
jccb(Assembler::notZero, try_rebias);
//epoch相同,说明就是当前线程与obj对象头中包含的线程指针不一样或者obj对象头中的线程指针为空
//将对象头进行and运算,即去掉obj对象中包含的线程指针
andptr(swap_reg,
markOopDesc::biased_lock_mask_in_place | markOopDesc::age_mask_in_place | markOopDesc::epoch_mask_in_place);
if (need_tmp_reg) {
push(tmp_reg);
}
//将其拷贝到tmp_reg,然后跟当前线程指针做or运算
movptr(tmp_reg, swap_reg);
//将线程指针写入tmp_reg
orptr(tmp_reg, r15_thread);
if (os::is_MP()) {
lock();
}
//将obj对象头与swap_reg中已经去掉线程指针的对象头比较,如果相等则把tmp_reg写入对象头,占用偏向锁成功,否则把新的对象头写入swap_reg中
cmpxchgptr(tmp_reg, mark_addr); // compare tmp_reg and swap_reg
if (need_tmp_reg) {
pop(tmp_reg);
}
if (counters != NULL) {
//增加计数器
cond_inc32(Assembler::zero,
ExternalAddress((address) counters->anonymously_biased_lock_entry_count_addr()));
}
if (slow_case != NULL) {
//如果不等则跳转到slow_case
jcc(Assembler::notZero, *slow_case);
}
jmp(done);
bind(try_rebias);
if (need_tmp_reg) {
push(tmp_reg);
}
//重新加载prototype_header
load_prototype_header(tmp_reg, obj_reg);
//跟当前线程指针做or运算,确保新的对象头跟prototype_header中的epoch值一致
orptr(tmp_reg, r15_thread);
if (os::is_MP()) {
lock(); //lock指令让cmpxchgptr变成一个原子操作
}
//将obj对象头同swap_reg中的对象头比较,如果相等将运算结果写入对象头,即占用偏向锁成功,如果不等将新的对象头放入swap_reg中
cmpxchgptr(tmp_reg, mark_addr); // compare tmp_reg and swap_reg
if (need_tmp_reg) {
pop(tmp_reg);
}
if (counters != NULL) {
//更新计数器
cond_inc32(Assembler::zero,
ExternalAddress((address) counters->rebiased_lock_entry_count_addr()));
}
if (slow_case != NULL) {
//如果不等于,说明抢占偏向锁失败,则跳转到slow_case,尝试锁膨胀
jcc(Assembler::notZero, *slow_case);
}
jmp(done);
bind(try_revoke_bias);
if (need_tmp_reg) {
push(tmp_reg);
}
//重新加载prototype_header
load_prototype_header(tmp_reg, obj_reg);
if (os::is_MP()) {
lock();//lock指令前缀让cmpxchgptr变成一个原子操作
}
//将obj对象头同swap_reg中的对象头比较,如果相等将prototype_header写入对象头,如果不等将新的对象头写入swap_reg中,多线程线下只有一个线程
//判断相等,其他的都是不等
//此时对象头已经恢复成无锁状态,如果是多线程请求会则触发锁膨胀
cmpxchgptr(tmp_reg, mark_addr);
if (need_tmp_reg) {
pop(tmp_reg);
}
if (counters != NULL) {
//增加计数器
cond_inc32(Assembler::zero,
ExternalAddress((address) counters->revoked_lock_entry_count_addr()));
}
bind(cas_label);
return null_check_offset;
}
void MacroAssembler::load_prototype_header(Register dst, Register src) {
load_klass(dst, src);
movptr(dst, Address(dst, Klass::prototype_header_offset()));
}