计算机视觉——全景图像拼接
文章目录
- 1. RANSAC
- 1.1 概述
- 1.2 示例
- 1.3 原理
- 1.4 算法步骤
- 2. 实验结果与分析
- 2.1 固定点拼接
- 2.1.1 远景
- 2.1.2 结果
- 2.1.2 分析
- 2.2 同一场景
- 2.2.1 室内近景
- 2.2.2 结果
- 2.2.3 分析
- 3. 实现代码
- 4. 问题与解决
- 4.1 `ValueError: did not meet fit acceptance criteria
- 4.2 拼接图片模糊
- 5. 总结
1. RANSAC
1.1 概述
RANSAC 是“RANdom SAmple Consensus”(随机一致性采样)的缩写。该方法是用来找到正确模型来拟合带有噪声数据的迭代方法。给定一个模型,例如点集之间的单应性矩阵,RANSAC 基本的思想是,数据中包含正确的点和噪声点,合理的模型应该能够在描述正确数据点的同时摒弃噪声点。
1.2 示例
一个简单的例子是从一组观测数据中找出合适的2维直线。假设观测数据中包含局内点和局外点,其中局内点近似的被直线所通过,而局外点远离于直线。简单的最小二乘法不能找到适应于局内点的直线,原因是最小二乘法尽量去适应包括局外点在内的所有点。相反,RANSAC能得出一个仅仅用局内点计算出模型,并且概率还足够高。但是,RANSAC并不能保证结果一定正确,为了保证算法有足够高的合理概率,我们必须小心的选择算法的参数。

1.3 原理
OpenCV中滤除误匹配对采用RANSAC算法寻找一个最佳单应性矩阵H,矩阵大小为3×3。RANSAC目的是找到最优的参数矩阵使得满足该矩阵的数据点个数最多,通常令h33=1h33=1来归一化矩阵。由于单应性矩阵有8个未知参数,至少需要8个线性方程求解,对应到点位置信息上,一组点对可以列出两个方程,则至少包含4组匹配点对。

其中(x,y)表示目标图像角点位置,(x’,y’)为场景图像角点位置,s为尺度参数。
RANSAC算法从匹配数据集中随机抽出4个样本并保证这4个样本之间不共线,计算出单应性矩阵,然后利用这个模型测试所有数据,并计算满足这个模型数据点的个数与投影误差(即代价函数),若此模型为最优模型,则对应的代价函数最小。
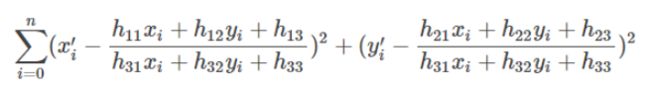
1.4 算法步骤
1. 随机从数据集中随机抽出4个样本数据 (此4个样本之间不能共线),计算出变换矩阵H,记为模型M;
2. 计算数据集中所有数据与模型M的投影误差,若误差小于阈值,加入内点集 I ;
3. 如果当前内点集 I 元素个数大于最优内点集 I_best , 则更新 I_best = I,同时更新迭代次数k ;
4. 如果迭代次数大于k,则退出 ; 否则迭代次数加1,并重复上述步骤;
2. 实验结果与分析
2.1 固定点拼接
2.1.1 远景
2.1.2 结果
2.1.2 分析
- 第一次是直接用原图拼接的,每个图片的大小在5.0MB左右,运行时间非常久但是效果看起来大约是还可以的,左侧看起来毕竟自然,但是右侧有一条非常明显的分界线。我发现算法进行拼接的顺序应是从右往左排,所以图片的顺序也应5该是从右往左。
- 在室外场景的拼接没有出现跟室内一样的重影现象,但是出现了新的问题就是拼接分界线。而最左边的图片出现了扭曲是因为APAP算法对每个小格左单应性变换,从单个小ge看是没有特征的,所以出现了扭曲。
2.2 同一场景
2.2.1 室内近景
2.2.2 结果
2.2.3 分析
- 室内的近景图片进行拼接的话可以看出:出现了重影问题,两个花盆两个桌子,所拍摄的桌子与相机之间隔着一个花盆,所以在移动拍摄角度的时候物体和目标之间与相机的偏差产生了变化,从而导致重影现象。我觉得是因为拍摄距离太近导致全景拼接时图片需要过分拉伸所以近景图片拼接效果不如远景好,近景图片产生的重影问题可以通过最大流最小割。
3. 实现代码
from pylab import *
from numpy import *
from PIL import Image
# If you have PCV installed, these imports should work
from PCV.geometry import homography, warp
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
"""
This is the panorama example from section 3.3.
"""
# set paths to data folder
featname = ['E:/python/picture/a' + str(i + 1) + '.sift' for i in range(5)]
imname = ['E:/python/picture/a' + str(i + 1) + '.jpg' for i in range(5)]
# extract features and match
l = {}
d = {}
for i in range(5):
sift.process_image(imname[i], featname[i])
l[i], d[i] = sift.read_features_from_file(featname[i])
matches = {}
for i in range(4):
matches[i] = sift.match(d[i + 1], d[i])
# visualize the matches (Figure 3-11 in the book)
for i in range(4):
im1 = array(Image.open(imname[i]))
im2 = array(Image.open(imname[i + 1]))
figure()
sift.plot_matches(im2, im1, l[i + 1], l[i], matches[i], show_below=True)
# function to convert the matches to hom. points
def convert_points(j):
ndx = matches[j].nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l[j + 1][ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[j][i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l[j][ndx2, :2].T)
# switch x and y - TODO this should move elsewhere
fp = vstack([fp[1], fp[0], fp[2]])
tp = vstack([tp[1], tp[0], tp[2]])
return fp, tp
# estimate the homographies
model = homography.RansacModel()
fp, tp = convert_points(1)
H_12 = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)[0] # im 1 to 2
fp, tp = convert_points(0)
H_01 = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)[0] # im 0 to 1
tp, fp = convert_points(2) # NB: reverse order
H_32 = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)[0] # im 3 to 2
tp, fp = convert_points(3) # NB: reverse order
H_43 = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)[0] # im 4 to 3
# warp the images
delta = 2000 # for padding and translation
im1 = array(Image.open(imname[1]), "uint8")
im2 = array(Image.open(imname[2]), "uint8")
im_12 = warp.panorama(H_12, im1, im2, delta, delta)
im1 = array(Image.open(imname[0]), "f")
im_02 = warp.panorama(dot(H_12, H_01), im1, im_12, delta, delta)
im1 = array(Image.open(imname[3]), "f")
im_32 = warp.panorama(H_32, im1, im_02, delta, delta)
im1 = array(Image.open(imname[4]), "f")
im_42 = warp.panorama(dot(H_32, H_43), im1, im_32, delta, 2 * delta)
figure()
imshow(array(im_42, "uint8"))
axis('off')
savefig("example5.png", dpi=300)
show()
4. 问题与解决
4.1 `ValueError: did not meet fit acceptance criteria
具体问题如下:
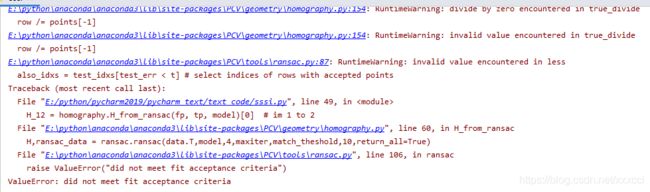
解决方法:这是因为拍摄的图片落差比较大,需要重新拍摄一组图片。
4.2 拼接图片模糊
跟图片像素大小有关,如果图片太小会导致拼接结果如同马赛克:

解决方法:将图片像素调大。
5. 总结
- 对比室内室外的拼接图片,各有各的问题,但是图片都是有点扭曲的。室外的出现明显拼接分界线我觉得是因为图片的曝光度即亮度不太一样,右边图片明显更暗一点所以看起来非常明显。
- 室内拼接场景不是很理想,试了几组图片都是一样的效果,除了算法本身的一点问题以外,可能跟我拍摄角度也有一定问题,可以尝试把镜头拉远一点。









