Android之Fresco框架(二)--ImagePipeline基本内容和配置
先附上官网的介绍:
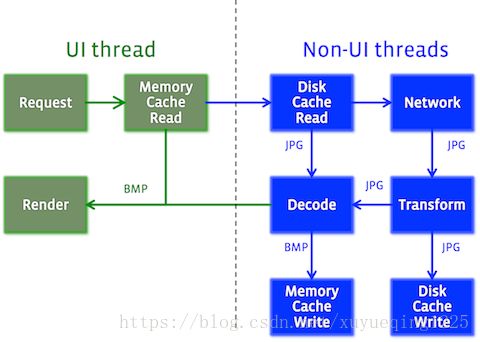
Image pipeline 负责完成加载图像,变成Android设备可呈现的形式所要做的每个事情。
大致流程如下:
- 检查内存缓存,如有,返回
- 后台线程开始后续工作
- 检查是否在未解码内存缓存中。如有,解码,变换,返回,然后缓存到内存缓存中。
- 检查是否在磁盘缓存中,如果有,变换,返回。缓存到未解码缓存和内存缓存中。
- 从网络或者本地加载。加载完成后,解码,变换,返回。存到各个缓存中。
从上面的讲述可以看出,ImagePipiline中主要有三个缓存,一个是DiskCache,一个是未解码Bitmap缓存,还有一个是已解码的Bitmap缓存。下面通过源码观察下这些缓存及缓存算法如何实现,以及如果对图片进行缓存和读取。
ImagePipelineFactory
这里采用了工厂模式来进行实现,通过在ImagePipelineFactory对各种信息进行配置和初始化。在Fresco.initialize()方法中就对ImagePipelineFactroy进行了初始化:
if (imagePipelineConfig == null) {
ImagePipelineFactory.initialize(context);
} else {
ImagePipelineFactory.initialize(imagePipelineConfig);
}这里可以看到,我们在初始化的时候是可以传入一个imagePipelineConfig的,这也是方便我们对ImagePipelineFactory进行自定义。我们先看一下imagePipelineConfig中定义了那些配置信息:
//对Bitmap的信息进行配置,主要是决定每个pixel用多个byte存储以及颜色的存储
private final Bitmap.Config mBitmapConfig;
//已解码的Bitmap缓存策略信息
private final Supplier mBitmapMemoryCacheParamsSupplier;
//存储缓存修剪策略的信息,在不同Android系统中,缓存需要进行相应的修剪,用于未解码的Bitmap缓存中
private final CountingMemoryCache.CacheTrimStrategy mBitmapMemoryCacheTrimStrategy;
//缓存文件生成的CacheKey策略
private final CacheKeyFactory mCacheKeyFactory;
private final Context mContext;
private final boolean mDownsampleEnabled;
//DiskCache工厂,用于获得DiskCache实例
private final FileCacheFactory mFileCacheFactory;
//未解码的Bitmap缓存策略信息
private final Supplier mEncodedMemoryCacheParamsSupplier;
//获取线程池,为CPU绑定操作提供一个线程池,为IO绑定操作提供另一个线程池。
private final ExecutorSupplier mExecutorSupplier;
//图片缓存操作的跟踪接口,会组合到MemoryCache中,可以方便我们监听图片缓存操作,默认无任何操作
private final ImageCacheStatsTracker mImageCacheStatsTracker;
//图片解码,对图片进行解码生成一个实现了Closeable的image实例,方便用于释放资源
@Nullable private final ImageDecoder mImageDecoder;
//默认返回true
private final Supplier mIsPrefetchEnabledSupplier;
//DiskCache配置信息
private final DiskCacheConfig mMainDiskCacheConfig;
//观察者模式,保存其他注册的类,用于通知系统内存事件,不自行定义的话默认没有任何操作
private final MemoryTrimmableRegistry mMemoryTrimmableRegistry;
//定义pipeline使用的network fetcher,默认使用HttpURLConnection类
private final NetworkFetcher mNetworkFetcher;
//用于平台优化的Bitmap工厂
@Nullable private final PlatformBitmapFactory mPlatformBitmapFactory;
//创建各种pool的工厂
private final PoolFactory mPoolFactory;
//渐进式JPEG配置
private final ProgressiveJpegConfig mProgressiveJpegConfig;
//ImageRequest的监听器
private final Set mRequestListeners;
//是否允许缩放和旋转
private final boolean mResizeAndRotateEnabledForNetwork;
//对小图缓存的配置,默认和DiskCache配置信息相同
private final DiskCacheConfig mSmallImageDiskCacheConfig;
//ImageDecoder的信息配置
@Nullable private final ImageDecoderConfig mImageDecoderConfig;
//对处于experimental state的ImagePipelineConfig的其他元素进行封装,不建议从默认值进行修改
private final ImagePipelineExperiments mImagePipelineExperimens;
可以看到里面配置了三级缓存,图片网络请求,图片解码相关的信息,我们可以对这些信息进行自定义。这个我们后面再说。先来看一下这些信息是怎么应用到ImagePipelineFactory中。首先先来看一下ImagePipelineFactory中又包含了哪些信息:
//single instance模式
private static ImagePipelineFactory sInstance = null;
//一旦从已解码的Bitmap缓存中读取失败,将图片的其他请求操作交付到新的线程(防止UI线程阻塞)
private final ThreadHandoffProducerQueue mThreadHandoffProducerQueue;
private final ImagePipelineConfig mConfig;
//利用LRU算法对缓存元素的管理,查找,写入,根据trim()方法实现不同策略的回收
private CountingMemoryCache mBitmapCountingMemoryCache;
//组合了CountingMemetyCache和ImageCacheStatsTracker(监听接口)
private MemoryCache mBitmapMemoryCache;
private CountingMemoryCache mEncodedCountingMemoryCache;
private MemoryCache mEncodedMemoryCache;
//在BufferedDiskCache中存储了一个StagingArea用于存储写入缓存的值,以便可以高速并行的get返回
private BufferedDiskCache mMainBufferedDiskCache;
//DiskStrorageCache,采用synchroinzed方式实现文件的读写
private FileCache mMainFileCache;
//将EncodeImage转为CloseableImage
private ImageDecoder mImageDecoder;
//ImagePipeline实例
private ImagePipeline mImagePipeline;
//Producer工厂
private ProducerFactory mProducerFactory;
//PruducerSequence工厂
private ProducerSequenceFactory mProducerSequenceFactory;
//小图磁盘缓存的配置信息
private BufferedDiskCache mSmallImageBufferedDiskCache;
private FileCache mSmallImageFileCache;
/*
下面几个暂时不知道用途
*/
private MediaVariationsIndex mMediaVariationsIndex;
//为平台优化的位图工厂
private PlatformBitmapFactory mPlatformBitmapFactory;
private PlatformDecoder mPlatformDecoder;
//图像的动画效果
private AnimatedFactory mAnimatedFactory; 在这些配置信息中,除了最后几个之外,其他的可以大致分为这两种:用于设置三级缓存的相关信息,用于图像请求的管道化实现的Producer和ProducerSequence信息。其中第二部分等到下一篇文章再来讲。这里先看以下三级缓存的配置。
在ImagePipelineFactory中,以上变量的初始化都是采用的懒加载,所以ImagePipelineFactory不是线程安全的。这里为啥可以不用线程安全呢,这个我们待会再看。我们先看看一下三级缓存:
Decoded Bitmap Cache:
public CountingMemoryCache getBitmapCountingMemoryCache() {
if (mBitmapCountingMemoryCache == null) {
mBitmapCountingMemoryCache =
BitmapCountingMemoryCacheFactory.get(
mConfig.getBitmapMemoryCacheParamsSupplier(),
mConfig.getMemoryTrimmableRegistry(),
getPlatformBitmapFactory(),
mConfig.getExperiments().isExternalCreatedBitmapLogEnabled(),
mConfig.getBitmapMemoryCacheTrimStrategy());
}
return mBitmapCountingMemoryCache;
}
public MemoryCache getBitmapMemoryCache() {
if (mBitmapMemoryCache == null) {
mBitmapMemoryCache =
BitmapMemoryCacheFactory.get(
getBitmapCountingMemoryCache(),
mConfig.getImageCacheStatsTracker());
}
return mBitmapMemoryCache;
}
Encoded Bitmap Cache:
public CountingMemoryCache getEncodedCountingMemoryCache() {
if (mEncodedCountingMemoryCache == null) {
mEncodedCountingMemoryCache =
EncodedCountingMemoryCacheFactory.get(
mConfig.getEncodedMemoryCacheParamsSupplier(),
mConfig.getMemoryTrimmableRegistry(),
getPlatformBitmapFactory());
}
return mEncodedCountingMemoryCache;
}
public MemoryCache getEncodedMemoryCache() {
if (mEncodedMemoryCache == null) {
mEncodedMemoryCache =
EncodedMemoryCacheFactory.get(
getEncodedCountingMemoryCache(),
mConfig.getImageCacheStatsTracker());
}
return mEncodedMemoryCache;
} 基本上是一毛一样的代码,这里面主要涉及到CountingMemoryCache类和MemoryCache类,大致看一下这两个的源码
CountingMemoryCache
// How often the cache checks for a new cache configuration.
@VisibleForTesting
static final long PARAMS_INTERCHECK_INTERVAL_MS = TimeUnit.MINUTES.toMillis(5);
// Contains the items that are not being used by any client and are hence viable for eviction.
@GuardedBy("this")
@VisibleForTesting
final CountingLruMap> mExclusiveEntries;
// Contains all the cached items including the exclusively owned ones.
@GuardedBy("this")
@VisibleForTesting
final CountingLruMap> mCachedEntries;
@GuardedBy("this")
@VisibleForTesting
final Map mOtherEntries = new WeakHashMap<>();
private final ValueDescriptor mValueDescriptor;
private final CacheTrimStrategy mCacheTrimStrategy;
// Cache size constraints.
private final Supplier mMemoryCacheParamsSupplier;
@GuardedBy("this")
protected MemoryCacheParams mMemoryCacheParams;
@GuardedBy("this")
private long mLastCacheParamsCheck;
public CountingMemoryCache(
ValueDescriptor valueDescriptor,
CacheTrimStrategy cacheTrimStrategy,
Supplier memoryCacheParamsSupplier,
PlatformBitmapFactory platformBitmapFactory,
boolean isExternalCreatedBitmapLogEnabled) {
mValueDescriptor = valueDescriptor;
mExclusiveEntries = new CountingLruMap<>(wrapValueDescriptor(valueDescriptor));
mCachedEntries = new CountingLruMap<>(wrapValueDescriptor(valueDescriptor));
mCacheTrimStrategy = cacheTrimStrategy;
//自定义参数
mMemoryCacheParamsSupplier = memoryCacheParamsSupplier;
mMemoryCacheParams = mMemoryCacheParamsSupplier.get();
mLastCacheParamsCheck = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (isExternalCreatedBitmapLogEnabled) {
platformBitmapFactory.setCreationListener(
new PlatformBitmapFactory.BitmapCreationObserver() {
@Override
public void onBitmapCreated(
Bitmap bitmap,
Object callerContext) {
mOtherEntries.put(bitmap, callerContext);
}
});
}
} 在这里我们看到了CountingLruMap,它里面组合了一个LinkedHashMap实例,通过采用LRU算法来对图片进行管理。关于LRU算法LinkedHashMap的内容就不在这里说了。当Cache中内存紧张时,需要对内存进行裁剪,这个是在trim()方法中实现的:
/** Trims the cache according to the specified trimming strategy and the given trim type. */
@Override
public void trim(MemoryTrimType trimType) {
ArrayList> oldEntries;
final double trimRatio = mCacheTrimStrategy.getTrimRatio(trimType);
synchronized (this) {
int targetCacheSize = (int) (mCachedEntries.getSizeInBytes() * (1 - trimRatio));
int targetEvictionQueueSize = Math.max(0, targetCacheSize - getInUseSizeInBytes());
//删除掉mExclusiveEntries的内容直到item数量和总大小都满足要求
oldEntries = trimExclusivelyOwnedEntries(Integer.MAX_VALUE, targetEvictionQueueSize);
makeOrphans(oldEntries);
}
//关闭资源
maybeClose(oldEntries);
maybeNotifyExclusiveEntryRemoval(oldEntries);
//判读是否需要更新参数
maybeUpdateCacheParams();
//判断是否需要继续删除mExclusiveEntries中的内容
maybeEvictEntries();
} 我们再看一下maybeEvictEntries()方法:
private void maybeEvictEntries() {
ArrayList> oldEntries;
synchronized (this) {
int maxCount = Math.min(
mMemoryCacheParams.maxEvictionQueueEntries,
mMemoryCacheParams.maxCacheEntries - getInUseCount());
int maxSize = Math.min(
mMemoryCacheParams.maxEvictionQueueSize,
mMemoryCacheParams.maxCacheSize - getInUseSizeInBytes());
oldEntries = trimExclusivelyOwnedEntries(maxCount, maxSize);
makeOrphans(oldEntries);
}
maybeClose(oldEntries);
maybeNotifyExclusiveEntryRemoval(oldEntries);
} 可以看出,我们判断是否要对内存进行删减,是取决于我们配置的MemoryCacheParams参数的,所以我们可以自定义mMemoryCacheParams参数来改变我们的缓存配置。
MemoryCache
MemoryCache实例是由BitmapMemoryCacheFactory.get()获得的,生成的是一个InstrumentedMemoryCache实例,它所实现的,就是一个简单的将CountingMemoryCache和监听接口的组合
public class InstrumentedMemoryCache implements MemoryCache {
//CountingMemoryCache实例
private final MemoryCache mDelegate;
//Tracker
private final MemoryCacheTracker mTracker;
public InstrumentedMemoryCache(MemoryCache delegate, MemoryCacheTracker tracker) {
mDelegate = delegate;
mTracker = tracker;
}
@Override
public CloseableReference get(K key) {
CloseableReference result = mDelegate.get(key);
if (result == null) {
mTracker.onCacheMiss();
} else {
mTracker.onCacheHit(key);
}
return result;
}
@Override
public CloseableReference cache(K key, CloseableReference value) {
mTracker.onCachePut();
return mDelegate.cache(key, value);
}
@Override
public int removeAll(Predicate predicate) {
return mDelegate.removeAll(predicate);
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Predicate predicate) {
return mDelegate.contains(predicate);
}
} 接下来再看一下ImagePipelineFactory中对磁盘缓存的配置:
磁盘缓存
public BufferedDiskCache getMainBufferedDiskCache() {
if (mMainBufferedDiskCache == null) {
mMainBufferedDiskCache =
new BufferedDiskCache(
getMainFileCache(),
mConfig.getPoolFactory().getPooledByteBufferFactory(),
mConfig.getPoolFactory().getPooledByteStreams(),
mConfig.getExecutorSupplier().forLocalStorageRead(),
mConfig.getExecutorSupplier().forLocalStorageWrite(),
mConfig.getImageCacheStatsTracker());
}
return mMainBufferedDiskCache;
}
public FileCache getMainFileCache() {
if (mMainFileCache == null) {
DiskCacheConfig diskCacheConfig = mConfig.getMainDiskCacheConfig();
mMainFileCache = mConfig.getFileCacheFactory().get(diskCacheConfig);
}
return mMainFileCache;
}
前面说到FileCache涉及到的是底层的文件读写,而BufferedDiskCache是有一个对当前写入文件的缓存。我们也来大致看一下它们的源码:
FileCache
在工厂中真正的实现类是DiskStorageCache,代码实在太多,挑一些来看。首先是对存储空间参数的设置,DiskStorageCache有一个内部类Params用于对参数进行设置,在初始化的时候再将这些值赋给DiskStorageCache中相应参数:
public static class Params {
public final long mCacheSizeLimitMinimum;
public final long mLowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit;
public final long mDefaultCacheSizeLimit;
public Params(
long cacheSizeLimitMinimum,
long lowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit,
long defaultCacheSizeLimit) {
mCacheSizeLimitMinimum = cacheSizeLimitMinimum;
mLowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit = lowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit;
mDefaultCacheSizeLimit = defaultCacheSizeLimit;
}
}
public DiskStorageCache(
DiskStorage diskStorage,
EntryEvictionComparatorSupplier entryEvictionComparatorSupplier,
Params params,
CacheEventListener cacheEventListener,
CacheErrorLogger cacheErrorLogger,
@Nullable DiskTrimmableRegistry diskTrimmableRegistry,
final Context context,
final Executor executorForBackgrountInit,
boolean indexPopulateAtStartupEnabled) {
this.mLowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit = params.mLowDiskSpaceCacheSizeLimit;
this.mDefaultCacheSizeLimit = params.mDefaultCacheSizeLimit;
this.mCacheSizeLimit = params.mDefaultCacheSizeLimit;
this.mStatFsHelper = StatFsHelper.getInstance();
...
}DiskStorageCache的实例化是在DiskStorageCacheFactory实现的,在里面利用DiskCacheConfig的信息对params的信息进行配置:
public static DiskStorageCache buildDiskStorageCache(
DiskCacheConfig diskCacheConfig,
DiskStorage diskStorage,
Executor executorForBackgroundInit) {
DiskStorageCache.Params params = new DiskStorageCache.Params(
diskCacheConfig.getMinimumSizeLimit(),
diskCacheConfig.getLowDiskSpaceSizeLimit(),
diskCacheConfig.getDefaultSizeLimit());
return new DiskStorageCache(
diskStorage,
diskCacheConfig.getEntryEvictionComparatorSupplier(),
params,
diskCacheConfig.getCacheEventListener(),
diskCacheConfig.getCacheErrorLogger(),
diskCacheConfig.getDiskTrimmableRegistry(),
diskCacheConfig.getContext(),
executorForBackgroundInit,
diskCacheConfig.getIndexPopulateAtStartupEnabled());
}所以我们如果想要对磁盘的存储空间等信息进行自定义,只需要设置DiskCacheConfig里面的相关信息就好了。还有就是如果我们需要对磁盘缓存设置监听器也是在DiskCacheConfig里面设置我们自定义的CacheEventListener。
再看一下DiskStorageCache里面的读内存和写内存操作:
/**
* Retrieves the file corresponding to the mKey, if it is in the cache. Also
* touches the item, thus changing its LRU timestamp. If the file is not
* present in the file cache, returns null.
*
* This should NOT be called on the UI thread.
*
* @param key the mKey to check
* @return The resource if present in cache, otherwise null
*/
@Override
public BinaryResource getResource(final CacheKey key) {
String resourceId = null;
SettableCacheEvent cacheEvent = SettableCacheEvent.obtain()
.setCacheKey(key);
try {
synchronized (mLock) {
BinaryResource resource = null;
List resourceIds = CacheKeyUtil.getResourceIds(key);
for (int i = 0; i < resourceIds.size(); i++) {
resourceId = resourceIds.get(i);
cacheEvent.setResourceId(resourceId);
resource = mStorage.getResource(resourceId, key);
if (resource != null) {
break;
}
}
if (resource == null) {
mCacheEventListener.onMiss(cacheEvent);
mResourceIndex.remove(resourceId);
} else {
mCacheEventListener.onHit(cacheEvent);
mResourceIndex.add(resourceId);
}
return resource;
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
mCacheErrorLogger.logError(
CacheErrorLogger.CacheErrorCategory.GENERIC_IO,
TAG,
"getResource",
ioe);
cacheEvent.setException(ioe);
mCacheEventListener.onReadException(cacheEvent);
return null;
} finally {
cacheEvent.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public BinaryResource insert(CacheKey key, WriterCallback callback) throws IOException {
// Write to a temp file, then move it into place. This allows more parallelism
// when writing files.
SettableCacheEvent cacheEvent = SettableCacheEvent.obtain()
.setCacheKey(key);
mCacheEventListener.onWriteAttempt(cacheEvent);
String resourceId;
synchronized (mLock) {
// for multiple resource ids associated with the same image, we only write one file
resourceId = CacheKeyUtil.getFirstResourceId(key);
}
cacheEvent.setResourceId(resourceId);
try {
// getting the file is synchronized
DiskStorage.Inserter inserter = startInsert(resourceId, key);
try {
inserter.writeData(callback, key);
// Committing the file is synchronized
BinaryResource resource = endInsert(inserter, key, resourceId);
cacheEvent.setItemSize(resource.size())
.setCacheSize(mCacheStats.getSize());
mCacheEventListener.onWriteSuccess(cacheEvent);
return resource;
} finally {
if (!inserter.cleanUp()) {
FLog.e(TAG, "Failed to delete temp file");
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
cacheEvent.setException(ioe);
mCacheEventListener.onWriteException(cacheEvent);
FLog.e(TAG, "Failed inserting a file into the cache", ioe);
throw ioe;
} finally {
cacheEvent.recycle();
}
}
/**
* Creates a temp file for writing outside the session lock
*/
private DiskStorage.Inserter startInsert(
final String resourceId,
final CacheKey key)
throws IOException {
//判读是否需要清除内存
maybeEvictFilesInCacheDir();
return mStorage.insert(resourceId, key);
}
/**
* Commits the provided temp file to the cache, renaming it to match
* the cache's hashing convention.
*/
private BinaryResource endInsert(
final DiskStorage.Inserter inserter,
final CacheKey key,
String resourceId) throws IOException {
synchronized (mLock) {
BinaryResource resource = inserter.commit(key);
mResourceIndex.add(resourceId);
mCacheStats.increment(resource.size(), 1);
return resource;
}
}
BufferedDiskCache
BufferedDiskCache主要有两个线程池(读和写)用于操作数据(因为磁盘读写操作不能直接在主线程中执行),还有一个StagingArea(Map)用于存储当前正在写入缓存的值,方便我们的更快的读取。
private final FileCache mFileCache;
private final PooledByteBufferFactory mPooledByteBufferFactory;
private final PooledByteStreams mPooledByteStreams;
private final Executor mReadExecutor;
private final Executor mWriteExecutor;
private final StagingArea mStagingArea;
private final ImageCacheStatsTracker mImageCacheStatsTracker;
public BufferedDiskCache(
FileCache fileCache,
PooledByteBufferFactory pooledByteBufferFactory,
PooledByteStreams pooledByteStreams,
Executor readExecutor,
Executor writeExecutor,
ImageCacheStatsTracker imageCacheStatsTracker) {
mFileCache = fileCache;
mPooledByteBufferFactory = pooledByteBufferFactory;
mPooledByteStreams = pooledByteStreams;
mReadExecutor = readExecutor;
mWriteExecutor = writeExecutor;
mImageCacheStatsTracker = imageCacheStatsTracker;
mStagingArea = StagingArea.getInstance();
}我们也是主要看BufferedDiskCache的get/put方法:
获取图片:
//判断mStagingArea中是否能够匹配到
public Task get(CacheKey key, AtomicBoolean isCancelled) {
final EncodedImage pinnedImage = mStagingArea.get(key);
if (pinnedImage != null) {
return foundPinnedImage(key, pinnedImage);
}
return getAsync(key, isCancelled);
}
//在线程池中进行对磁盘数据的读取
private Task getAsync(final CacheKey key, final AtomicBoolean isCancelled) {
try {
return Task.call(
new Callable() {
@Override
public EncodedImage call()
throws Exception {
if (isCancelled.get()) {
throw new CancellationException();
}
EncodedImage result = mStagingArea.get(key);
if (result != null) {
FLog.v(TAG, "Found image for %s in staging area", key.getUriString());
mImageCacheStatsTracker.onStagingAreaHit(key);
} else {
FLog.v(TAG, "Did not find image for %s in staging area", key.getUriString());
mImageCacheStatsTracker.onStagingAreaMiss();
try {
final PooledByteBuffer buffer = readFromDiskCache(key);
CloseableReference ref = CloseableReference.of(buffer);
try {
result = new EncodedImage(ref);
} finally {
CloseableReference.closeSafely(ref);
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
return null;
}
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
FLog.v(TAG, "Host thread was interrupted, decreasing reference count");
if (result != null) {
result.close();
}
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
return result;
}
}
},
mReadExecutor);
} catch (Exception exception) {
// Log failure
// TODO: 3697790
FLog.w(
TAG,
exception,
"Failed to schedule disk-cache read for %s",
key.getUriString());
return Task.forError(exception);
}
}
//从磁盘中读数据
private PooledByteBuffer readFromDiskCache(final CacheKey key) throws IOException {
try {
FLog.v(TAG, "Disk cache read for %s", key.getUriString());
final BinaryResource diskCacheResource = mFileCache.getResource(key);
if (diskCacheResource == null) {
FLog.v(TAG, "Disk cache miss for %s", key.getUriString());
mImageCacheStatsTracker.onDiskCacheMiss();
return null;
} else {
FLog.v(TAG, "Found entry in disk cache for %s", key.getUriString());
mImageCacheStatsTracker.onDiskCacheHit();
}
PooledByteBuffer byteBuffer;
final InputStream is = diskCacheResource.openStream();
try {
byteBuffer = mPooledByteBufferFactory.newByteBuffer(is, (int) diskCacheResource.size());
} finally {
is.close();
}
FLog.v(TAG, "Successful read from disk cache for %s", key.getUriString());
return byteBuffer;
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// TODO: 3697790 log failures
// TODO: 5258772 - uncomment line below
// mFileCache.remove(key);
FLog.w(TAG, ioe, "Exception reading from cache for %s", key.getUriString());
mImageCacheStatsTracker.onDiskCacheGetFail();
throw ioe;
}
}
图片写入:
//在线程池中执行写操作
public void put(
final CacheKey key,
EncodedImage encodedImage) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(key);
Preconditions.checkArgument(EncodedImage.isValid(encodedImage));
// Store encodedImage in staging area
mStagingArea.put(key, encodedImage);
// Write to disk cache. This will be executed on background thread, so increment the ref count.
// When this write completes (with success/failure), then we will bump down the ref count
// again.
final EncodedImage finalEncodedImage = EncodedImage.cloneOrNull(encodedImage);
try {
mWriteExecutor.execute(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
writeToDiskCache(key, finalEncodedImage);
} finally {
mStagingArea.remove(key, finalEncodedImage);
EncodedImage.closeSafely(finalEncodedImage);
}
}
});
} catch (Exception exception) {
// We failed to enqueue cache write. Log failure and decrement ref count
// TODO: 3697790
FLog.w(
TAG,
exception,
"Failed to schedule disk-cache write for %s",
key.getUriString());
mStagingArea.remove(key, encodedImage);
EncodedImage.closeSafely(finalEncodedImage);
}
}
//写入到磁盘中
private void writeToDiskCache(
final CacheKey key,
final EncodedImage encodedImage) {
FLog.v(TAG, "About to write to disk-cache for key %s", key.getUriString());
try {
mFileCache.insert(
key, new WriterCallback() {
@Override
public void write(OutputStream os) throws IOException {
mPooledByteStreams.copy(encodedImage.getInputStream(), os);
}
}
);
FLog.v(TAG, "Successful disk-cache write for key %s", key.getUriString());
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// Log failure
// TODO: 3697790
FLog.w(TAG, ioe, "Failed to write to disk-cache for key %s", key.getUriString());
}
}Ok,到这里三级缓存基本就讲完了,虽然讲的有点粗略...
ImagePipeline
最后再看一下ImagePipelineFactory中对ImagePipeline的实例化:
public ImagePipeline getImagePipeline() {
if (mImagePipeline == null) {
mImagePipeline =
new ImagePipeline(
getProducerSequenceFactory(),
mConfig.getRequestListeners(),
mConfig.getIsPrefetchEnabledSupplier(),
getBitmapMemoryCache(),
getEncodedMemoryCache(),
getMainBufferedDiskCache(),
getSmallImageBufferedDiskCache(),
mConfig.getCacheKeyFactory(),
mThreadHandoffProducerQueue,
Suppliers.of(false));
}
return mImagePipeline;
}首先可以看到,在实例化的过程中,会对ImagePipelineFactory中其他的变量也调用相应的实例化方法,那这里就可以看下前面提到的一个问题了,为什么ImagePipelineFactory中可以不用线程安全?
我们先回到Fresco.initialize()中:
public static void initialize(
Context context,
@Nullable ImagePipelineConfig imagePipelineConfig,
@Nullable DraweeConfig draweeConfig) {
if (sIsInitialized) {
FLog.w(
TAG,
"Fresco has already been initialized! `Fresco.initialize(...)` should only be called " +
"1 single time to avoid memory leaks!");
} else {
sIsInitialized = true;
}
try {
SoLoader.init(context, 0);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not initialize SoLoader", e);
}
// we should always use the application context to avoid memory leaks
context = context.getApplicationContext();
if (imagePipelineConfig == null) {
ImagePipelineFactory.initialize(context);
} else {
ImagePipelineFactory.initialize(imagePipelineConfig);
}
initializeDrawee(context, draweeConfig);
}在方法最后调用了initializeDrawee(context, draweeConfig),看下代码:
private static void initializeDrawee(
Context context,
@Nullable DraweeConfig draweeConfig) {
sDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier =
new PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier(context, draweeConfig);
SimpleDraweeView.initialize(sDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier);
}这里new了一个PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier,我们看一下它的源码:
private final Context mContext;
private final ImagePipeline mImagePipeline;
private final PipelineDraweeControllerFactory mPipelineDraweeControllerFactory;
private final Set mBoundControllerListeners;
public PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier(
Context context,
@Nullable DraweeConfig draweeConfig) {
this(context, ImagePipelineFactory.getInstance(), draweeConfig);
}
public PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier(
Context context,
ImagePipelineFactory imagePipelineFactory,
@Nullable DraweeConfig draweeConfig) {
this(context, imagePipelineFactory, null, draweeConfig);
}
public PipelineDraweeControllerBuilderSupplier(
Context context,
ImagePipelineFactory imagePipelineFactory,
Set boundControllerListeners,
@Nullable DraweeConfig draweeConfig) {
mContext = context;
//获取ImagePipelineFactory中的ImagePipeline实例
mImagePipeline = imagePipelineFactory.getImagePipeline();
if (draweeConfig != null && draweeConfig.getPipelineDraweeControllerFactory() != null) {
mPipelineDraweeControllerFactory = draweeConfig.getPipelineDraweeControllerFactory();
} else {
mPipelineDraweeControllerFactory = new PipelineDraweeControllerFactory();
}
mPipelineDraweeControllerFactory.init(
context.getResources(),
DeferredReleaser.getInstance(),
imagePipelineFactory.getAnimatedDrawableFactory(context),
UiThreadImmediateExecutorService.getInstance(),
mImagePipeline.getBitmapMemoryCache(),
draweeConfig != null
? draweeConfig.getCustomDrawableFactories()
: null,
draweeConfig != null
? draweeConfig.getDebugOverlayEnabledSupplier()
: null);
mBoundControllerListeners = boundControllerListeners;
} 所以其实在Fresco.initialize()的时候,就已经初始化了ImagePipeline实例,而且通常情况下我们只会从imagePipelineFactory中获取它,所以其实ImagePipelineFactory中的变量都是在Fresco.initialize()的时候就初始化了,而ImagePipelineFactory中并没有对这些变量的setter方法,所以我们就可以不用考虑线程安全的事情了。
ImagePipelineConfig自定义配置
最后给一个ImagePipelineConfig的配置,写得比较简单,等以后用Fresco多了之后再来做一些修改吧。
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.util.Log;
import com.facebook.cache.common.CacheEvent;
import com.facebook.cache.common.CacheEventListener;
import com.facebook.cache.disk.DiskCacheConfig;
import com.facebook.common.internal.Supplier;
import com.facebook.common.util.ByteConstants;
import com.facebook.imagepipeline.backends.okhttp3.OkHttpImagePipelineConfigFactory;
import com.facebook.imagepipeline.cache.ImageCacheStatsTracker;
import com.facebook.imagepipeline.cache.MemoryCacheParams;
import com.facebook.imagepipeline.core.ImagePipelineConfig;
import com.facebook.imagepipeline.listener.RequestListener;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
public class FrescoConfig {
public static final String DISK_CACHR_TAG = "DiskCache";
public static final String REQUEST_TAG = "MyRequest";
public static final String CACHE_TRACKER_TAG = "MyImageCacheStatsTracker";
public static final int MAX_DISK_SIZE = 20*ByteConstants.MB;
public static final int MAX_DISK_SIZE_ON_LOW_DISK_SPACE = 10*ByteConstants.MB;
public static final int MAX_DISK_SIZE_ON_VERY_LOW_DISK_SPACE = 5*ByteConstants.MB;
public static final String FRESCO_CACHE_DIR = "fresco_cache";
private static ImagePipelineConfig imagePipelineConfig;
public static ImagePipelineConfig getImagePipelineConfig(final Context context){
if(imagePipelineConfig == null) {
File fileDir = context.getApplicationContext().getCacheDir();
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
fileDir = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath());
}
//MemoryCache参数配置
Supplier supplier = new MyMemoryCacheParamsSupplier((ActivityManager)context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE));
//对FileCache中内存操作的监听
CacheEventListener cacheEventListener = new MyCacheEventListener(DISK_CACHR_TAG);
//磁盘内存配置
DiskCacheConfig diskCacheConfig = DiskCacheConfig.newBuilder(context)
.setBaseDirectoryName(FRESCO_CACHE_DIR)
.setBaseDirectoryPath(fileDir)
.setMaxCacheSize(MAX_DISK_SIZE)
.setMaxCacheSizeOnLowDiskSpace(MAX_DISK_SIZE_ON_LOW_DISK_SPACE)
.setMaxCacheSizeOnVeryLowDiskSpace(MAX_DISK_SIZE_ON_VERY_LOW_DISK_SPACE)
.setCacheEventListener(cacheEventListener)
.build();
//对request操作的各个状态进行监听(开始,结束,成功,失败等)
Set requestListeners = new HashSet<>();
requestListeners.add(new MyRequestListener(REQUEST_TAG));
//监听各个缓存(MemoryCache,BufferDiskCache)查找情况
ImageCacheStatsTracker imageCacheStatsTracker = new MyImageCacheStatsTracker(CACHE_TRACKER_TAG);
//将网络请求设置为okhttp,取消连接失败之后的重试
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder().retryOnConnectionFailure(false).build();
imagePipelineConfig = OkHttpImagePipelineConfigFactory.newBuilder(context,okHttpClient)
.setBitmapMemoryCacheParamsSupplier(supplier)
.setRequestListeners(requestListeners)
.setMainDiskCacheConfig(diskCacheConfig)
.setImageCacheStatsTracker(imageCacheStatsTracker)
.build();
}
return imagePipelineConfig;
}
} public class MyMemoryCacheParamsSupplier implements Supplier {
//最大缓存数量
private static final int MAX_CACHE_ENTRIES = 64;
private static final int MAX_CACHE_ASHM_ENTRIES = 128;
private static final int MAX_CACHE_EVICTION_ENTRIES = 32;
private final ActivityManager mActivityManager;
public MyMemoryCacheParamsSupplier(ActivityManager activityManager) {
mActivityManager = activityManager;
}
@Override
public MemoryCacheParams get() {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
return new MemoryCacheParams(getMaxCacheSize(), //最大总图片缓存空间
MAX_CACHE_ENTRIES, //最大总图片缓存数量
getMaxCacheSize()/2, //准备清除的总图片最大空间
MAX_CACHE_EVICTION_ENTRIES, //准备清除的总图片最大数量
getMaxCacheSize()/2); //单个图片最大大小
} else {
return new MemoryCacheParams(
getMaxCacheSize(),
MAX_CACHE_ASHM_ENTRIES,
Integer.MAX_VALUE,
Integer.MAX_VALUE,
Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
//获取最大缓存大小
private int getMaxCacheSize() {
final int maxMemory =
Math.min(mActivityManager.getMemoryClass() * ByteConstants.MB, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
if (maxMemory < 32 * ByteConstants.MB) {
return 4 * ByteConstants.MB;
} else if (maxMemory < 64 * ByteConstants.MB) {
return 6 * ByteConstants.MB;
} else {
return maxMemory / 4;
}
}
} 里面监听类的实现代码就不贴了,就只是简单相应接口。
在代码中我们用OkHttp代替了原来的请求。这个的话需要在gradle中添加相应的依赖:
compile "com.facebook.fresco:imagepipeline-okhttp3:0.12.0+"在Fresco初始化的时候调用:
Fresco.initialize(this,getImagePipelineConfig(this));