【驱动代码移植高通平台之二十三】高通平台i2c设备驱动
原理图分析
假如该器件连接到GPIO18和GPIO19,查阅MSM8917的手册知道连接的i2c控制器为5
i2c控制器的配置
根据80-NU767-1 H文档进行配置
1 kernel里配置
i2c_5: i2c@7af5000 { /* BLSP2 QUP1 */
compatible = "qcom,i2c-msm-v2";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg-names = "qup_phys_addr";
reg = <0x7af5000 0x600>;
interrupt-names = "qup_irq";
interrupts = <0 299 0>;
qcom,clk-freq-out = <400000>;
qcom,clk-freq-in = <19200000>;
clock-names = "iface_clk", "core_clk";
clocks = <&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_ahb_clk>,
<&clock_gcc clk_gcc_blsp2_qup1_i2c_apps_clk>;
pinctrl-names = "i2c_active", "i2c_sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c_5_active>;
pinctrl-1 = <&i2c_5_sleep>;
qcom,noise-rjct-scl = <0>;
qcom,noise-rjct-sda = <0>;
qcom,master-id = <84>;
dmas = <&dma_blsp2 4 64 0x20000020 0x20>,
<&dma_blsp2 5 32 0x20000020 0x20>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
};
2 trustzone里添加权限
设备驱动程序的编写
查询手册作为i2c slave的地址,寄存器,以及寄存器的读写时序
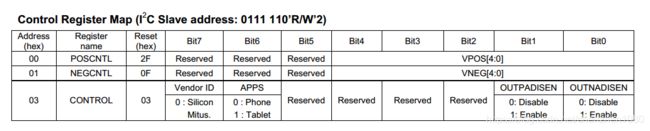
查询手册可知 该款器件的i2c地址为0x3E,该器件比较简单只有三个寄存器(只是为了验证i2c驱动程序的框架,忽略具体寄存器的含义)
a 设备注册的方式
1 通过i2c_new_device的方法
2 通过设备树
&i2c_5 {
......
sm5109@3E {
compatible = "sm,sm5109";
reg = <0x3E>;
};
.......
};
b 构造i2c_driver结构体,填充其中的函数(probe,remove,id_table,driver里的of_match_table)
c.调用i2c_add_driver注册驱动程序
d.编写i2c对寄存器的读写函数:构造i2c_msg结构体,然后调用i2c_transfer
最后就是具体逻辑的编写
参考程序
设备注册的方式
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define TAG "sm5109 "
static int sm5109_i2c_read(struct i2c_client *client, char *writebuf,
int writelen, char *readbuf, int readlen)
{
int ret;
if (writelen > 0) {
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = writebuf,
},
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = I2C_M_RD,
.len = readlen,
.buf = readbuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 2);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s: i2c read error.\n",
__func__);
} else {
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = I2C_M_RD,
.len = readlen,
.buf = readbuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 1);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s:i2c read error.\n", __func__);
}
return ret;
}
static int sm5109_i2c_write(struct i2c_client *client, char *writebuf,
int writelen)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = writebuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 1);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s: i2c write error.\n", __func__);
return ret;
}
static int sm5109_write_reg(struct i2c_client *client, u8 addr, const u8 val)
{
u8 buf[2] = {0};
buf[0] = addr;
buf[1] = val;
return sm5109_i2c_write(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
static int sm5109_read_reg(struct i2c_client *client, u8 addr, u8 *val)
{
return sm5109_i2c_read(client, &addr, 1, val, 1);
}
static int sm5109_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
u8 addr;
u8 val;
addr=0;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 0 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=1;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 1 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=3;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 3 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=3;
val=3;
sm5109_write_reg(client, addr , val);
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
static int sm5109_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
static const struct i2c_device_id sm5109_id[] = {
{"sm5109", 0},
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, sm5109_id);
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static struct of_device_id sm5109_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "sm,sm5109",},
{ },
};
#else
#define ft5x06_match_table NULL
#endif
static struct i2c_driver sm5109_driver = {
.probe = sm5109_probe,
.remove = sm5109_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "sm5109",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = sm5109_match_table,
},
.id_table = sm5109_id,
};
static struct i2c_client *clt;
static int __init sm5109_init(void)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adap = i2c_get_adapter(5);
struct i2c_board_info info = {
.type = "sm5109",
.addr = 0x3E,
};
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
clt = i2c_new_device(adap, &info);
if (!clt) {
printk(TAG"failed to i2c_new_device\n");
}
return i2c_add_driver(&sm5109_driver);
}
module_init(sm5109_init);
static void __exit sm5109_exit(void)
{
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
i2c_unregister_device(clt);
i2c_del_driver(&sm5109_driver);
}
module_exit(sm5109_exit);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("sm5109 driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
通过设备树的参考代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define TAG "sm5109 "
static int sm5109_i2c_read(struct i2c_client *client, char *writebuf,
int writelen, char *readbuf, int readlen)
{
int ret;
if (writelen > 0) {
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = writebuf,
},
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = I2C_M_RD,
.len = readlen,
.buf = readbuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 2);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s: i2c read error.\n",
__func__);
} else {
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = I2C_M_RD,
.len = readlen,
.buf = readbuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 1);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s:i2c read error.\n", __func__);
}
return ret;
}
static int sm5109_i2c_write(struct i2c_client *client, char *writebuf,
int writelen)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = client->addr,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = writebuf,
},
};
ret = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msgs, 1);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&client->dev, "%s: i2c write error.\n", __func__);
return ret;
}
static int sm5109_write_reg(struct i2c_client *client, u8 addr, const u8 val)
{
u8 buf[2] = {0};
buf[0] = addr;
buf[1] = val;
return sm5109_i2c_write(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
static int sm5109_read_reg(struct i2c_client *client, u8 addr, u8 *val)
{
return sm5109_i2c_read(client, &addr, 1, val, 1);
}
static int sm5109_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
u8 addr;
u8 val;
addr=0;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 0 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=1;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 1 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=3;
sm5109_read_reg(client, addr , &val);
printk(TAG"addr 3 is 0x%x\n", val);
addr=3;
val=3;
sm5109_write_reg(client, addr , val);
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
static int sm5109_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
static const struct i2c_device_id sm5109_id[] = {
{"sm5109", 0},
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, sm5109_id);
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
static struct of_device_id sm5109_match_table[] = {
{ .compatible = "sm,sm5109",},
{ },
};
#else
#define ft5x06_match_table NULL
#endif
static struct i2c_driver sm5109_driver = {
.probe = sm5109_probe,
.remove = sm5109_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "sm5109",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = sm5109_match_table,
},
.id_table = sm5109_id,
};
static int __init sm5109_init(void)
{
return i2c_add_driver(&sm5109_driver);
}
module_init(sm5109_init);
static void __exit sm5109_exit(void)
{
printk(TAG"%s\n", __func__);
i2c_del_driver(&sm5109_driver);
}
module_exit(sm5109_exit);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("sm5109 driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
i2c用户空间测试程序
构造i2c_msg和i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data
然后使用ioctl系统调用发送给内核
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static uint16_t slave_address;
static uint8_t reg_addr;
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(*a))
/* i2c_test [path] [slave_addr] r reg_addr length
* i2c_test [path] [slave_addr] w reg_addr value
*/
static int do_i2c_write(int fd, char *writebuf, int writelen)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = slave_address,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = (void *)writebuf,
},
};
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data msgset = {
.msgs = msgs,
.nmsgs = ARRAY_SIZE(msgs),
};
ret = ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &msgset);
return ret;
}
static int do_i2c_read(int fd, char *writebuf,
int writelen, char *readbuf, int readlen)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_msg msgs[] = {
{
.addr = slave_address,
.flags = 0,
.len = writelen,
.buf = (void *)writebuf,
},
{
.addr = slave_address,
.flags = I2C_M_RD,
.len = readlen,
.buf = (void *)readbuf,
}
};
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data msgset = {
.msgs = msgs,
.nmsgs = ARRAY_SIZE(msgs),
};
ret = ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, &msgset);
return ret;
}
void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("%s [path] [slave_addr] r reg_addr\n", file);
printf("%s [path] [slave_addr] r reg_addr length\n", file);
printf("%s [path] [slave_addr] w reg_addr value\n", file);
printf("Example:\n");
printf("%s /dev/i2c-5 0x3E r 3 1\n", file);
printf("this command means that the adapter is 5, the slave address is 0x3E, read red 3 and read length is 1\n");
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char value;
char wbuf[2];
char* devname;
int i,length = 0;
if ((argc != 5) && (argc != 6))
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
devname = malloc(100);
strcpy(devname,argv[1]);
fd = open(devname, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can't open %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
} else {
printf("open %s success!\n", devname);
}
slave_address = strtoul(argv[2], NULL, 0);
if ((strcmp(argv[3], "r")==0)||(strcmp(argv[3], "0")==0))
{
if(argc == 5) {
reg_addr = strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 0);
do_i2c_read(fd, ®_addr, 1, &value, 1);
printf("reg 0x%x value is 0x%x\n", reg_addr, value);
} else if (argc == 6) {
reg_addr = strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 0);
length = strtoul(argv[5], NULL, 0);
for(i = 0 ; i < length; i++) {
do_i2c_read(fd, ®_addr, 1, &value, 1);
printf("0x%02x 0x%02x\n", reg_addr, value);
reg_addr++;
}
}
} else if ((strcmp(argv[3], "w")==0)||(strcmp(argv[3], "1")==0) && argc == 6)
{
reg_addr = strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 0);
value = strtoul(argv[5], NULL, 0);
wbuf[0] = reg_addr;
wbuf[1] = value;
do_i2c_write(fd, &wbuf, 2);
printf("write reg 0x%x value is 0x%x\n", reg_addr, value);
} else
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
free(devname);
return 0;
}
假如编译出来的文件名为i2c_test
./i2c_test /dev/i2c-5 0x3E r 3 1
表明适配器是i2c5,设备地址是0x3E,r表示读,3表示寄存器地址,1表示读取的长度为1
./i2c_test /dev/i2c-5 0x3E r 0 3
寄存器地址为0,连续读取3个地址寄存器的数据
./i2c_test /dev/i2c-5 0x3E w 1 0x2F
w表示写,往地址为1的寄存器写0x2F