Java IO流之BufferedWriter和BufferedReader分析
简介
BufferedWriter和BufferedReader分别是字符缓冲输出流和字符缓冲输入流,为底层字符流提供了缓冲的功能,底层字符流读取字符或者写入字符时,会频繁与硬盘进行交互,导致读取效率很低.缓冲流的作用就是硬盘中的数据读取到内存,再从内存中一次性读取多个数据.提高了读取的速度.根据jdk的api文档介绍,缓冲流的推荐使用方式.
- BufferedReader用来包装开销比较高的底层字符流(如FileReader或者是InputStreamReader).底层字符流每次调用read()或者readLine()都是先从文件中读取字节,然后转化成字符返回,造成读取效率低.使用缓冲流包装例如BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("foo.txt"));将会提升读取读取的速度.
- BufferedWriter()同样是用于包装开销比较高的底层字符输出流(FileWriter或者是InputStreamWriter).例如BufferedWriter out=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("foo.txt")).相比于底层字符流写到文件速度有很大提升.
BufferedWriter介绍
1.构造方法
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) {}
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) {}- 创建一个指定了底层字符输出流,缓冲区的大小为默认的8192个字符的缓冲字符输出流.
- 创建一个指定了底层字符输出流,缓冲区大小为sz个字符的缓冲字符输出流.
2.内部变量
private Writer out;
private char cb[];
private int nChars, nextChar;
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
private String lineSeparator;- out---表示的是底层字符输出流.
- cb---缓冲字符输出流中缓冲区,即为字符数组.
- nChar---缓冲区大小.
- nextChar---缓冲区中下一个读取字符的索引.
- defaultCharBufferSize---创建的默认缓冲区的大小为8192个字符.
- lineSeparator---换行符,会在创建缓冲字符输出流时进行赋值.
3.内部方法
private void ensureOpen(){}
public void write(int c){}
public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len){}
public void write(String s, int off, int len){}
public void newLine() {}
public void flush(){}
public void close() {}- ensureOpen()---确保底层字符输出流没有关闭.
- wirte(int c)---将一个字符写到字符缓冲输出流中.
- write(char cbuf[],int off, int len)---将字符数组cbuf中off位置开始,len个字符写到缓冲区中.
- write(String s, int off, int len)---将字符串s中off位置开始,len个字符写到缓冲区中.
- newLine()---将一个换行符写到字符缓冲输出流中.(每个平台的换行符是不一样).
- flush()---刷新缓冲区,将缓冲区数据写出.
- close()---关闭流,释放相关资源.
BufferedReader介绍
1.构造方法
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {}
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {}- 有参构造方法,创建一个指定了底层字符输入流,和缓冲区大小为sz的字符缓冲输入流.
- 有参构造方法,创建一个指定了底层 字符输入流,缓冲区大小为默认的8192个字符的字符缓冲输入流.
2.内部变量
private Reader in;
private char cb[];
private int nChars, nextChar;
private static final int INVALIDATED = -2;
private static final int UNMARKED = -1;
private int markedChar = UNMARKED;
private int readAheadLimit = 0;
private boolean skipLF = false;
private boolean markedSkipLF = false;
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
private static int defaultExpectedLineLength = 80;- in---底层字符输入流.
- cb---字符缓冲输入流中缓冲区,即为字符数组.
- nChars---缓冲区中有效字符数, nextChars---缓冲区中读取下一个字符的索引位置.
- INVALIDATED---用于表示缓冲区中标记失效.
- UNMARKED---缓冲区中标记位置初始化为-1,表示的是没有标记.
- markChar---表示的是标记位置,此值会保存调用mark()时缓冲区中当前读取字符位置.
- readAheadLimit---用于标记之后,在标记任然有效的情况下,可读取字符的最大值,超过此值,标记将会失效.
- skipLF---是否跳过换行符.
- markedSkipLF---标记情况下,是否跳过换行符.
- defaultCharBufferSize---字符缓冲输入流中缓冲区的大小为8192个字符
- defaultExpectedLineLength---默认的一行的字符数为80个字符.
3.内部方法
private void ensureOpen()
private void fill()
public int read()
public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len)
public String readLine()
public long skip(long n)
public boolean ready()
public boolean markSupported()
public void mark(int readAheadLimit)
public void reset()
public void close()
public Stream lines() - ensureOpen()---确保底层字符输入流没有关闭.
- fill()---填充方法,缓冲区没有可读取数据时会调用此方法,从底层字符输入流中读取数据填充到缓冲区,根据缓冲区是否存在标记,填充对应的区域.
- read()---从缓冲区读取一个字符.
- read(char cbuf[],int off,int len)---从缓冲区中读取len个字符到字符数组cbuf中,位置从off开始.
- readLine---从缓冲区中读取一行数据.传入是否忽略换行符.
- skip(long n)---跳过n个字符.
- ready()---此流是否准备读取.
- markSuported()---缓冲区是否支持标记.
- mark(int readAheadLimit)---标记当前位置.调用reset()方法时会将当前位置重置到标记的位置.
- reset()---调用此方法,会将当前位置重置到最后一次调用mark()标记的位置.
- close()---关闭流,释放相关资源.
- lines()---jdk1.8中新添加的方法,按照系统换行符,迭代每一个行的内容.得到是缓冲区中所有的字符的流.
案例
public class BufferedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
testBufferedWriter();
testBufferedReader();
}
//a test of BufferedWriter
private static void testBufferedWriter() throws IOException{
char[] cbuf = new char[] {'h','e','l','l','o','w','o','r','l','d'};
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\java.txt"));
bw.write("1234567890");
bw.write(cbuf, 0, 8);
bw.write('z');
bw.newLine(); //调用newline相当于write('\n')('\n'是系统换行符)
bw.write("bufferedDemo", 2, 5);
bw.close();
}
//a test of BufferedReader
private static void testBufferedReader() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\java.txt"));
int read = br.read();
System.out.println("单个字符------"+(char)read);
char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
br.read(cbuf, 0, 10);
System.out.println("字符数组----------"+new String(cbuf));
if(br.markSupported()) {
br.mark(100);
}
String readLine = br.readLine(); //调用readLine()读取的是下一个读取字符位置到换行符之前所有的字符.
System.out.println("读取一行-----------"+readLine);
br.reset();
System.out.println("调用reset()方法-------------"+(char)br.read());
br.skip(5);
System.out.println("跳过5个字符位置-------------"+(char)br.read());
br.close();
}
}运行结果:
testBufferedWriter运行结果:
1234567890helloworz
ffere
testBufferedReader运行结果:
单个字符------1
字符数组----------234567890h
读取一行-----------elloworz
调用reset()方法-------------e
跳过5个字符位置-------------r
源码分析
1.BufferedWriter源码
public class BufferedWriter extends Writer {
//底层字符输出流
private Writer out;
//缓冲区为字符数组cb
private char cb[];
//nChars是缓冲区的大小.
//nextChar是缓冲区中下一个要读取字符的位置索引.
private int nChars, nextChar;
//缓冲区默认的大小为了8192个字符
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
//换行符,在创建缓冲字符输出流时赋值
private String lineSeparator;
//创建一个底层字符输出流为out,缓冲区大小为默认的8192个字符的缓冲字符输出流.
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) {
this(out, defaultCharBufferSize);
}
//创建一个底层字符输出流为out,缓冲区大小为sz的缓冲字符出输出流.
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) {
super(out);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.out = out;
cb = new char[sz];
nChars = sz;
nextChar = 0;
//获取系统的分行符
lineSeparator = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction("line.separator"));
}
//确保底层字符输出流没有关闭
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (out == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
//刷新缓冲区中,将缓冲区数据写到底层字符输出流中.
void flushBuffer() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (nextChar == 0)
return;
//将缓冲区中的字符写到底层字符输出流中.
out.write(cb, 0, nextChar);
nextChar = 0;
}
}
//将单个字符c写到缓冲区中.
public void write(int c) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
//缓冲区没有剩余位置,刷新缓冲区,再将字符c写到缓冲区.
if (nextChar >= nChars)
flushBuffer();
cb[nextChar++] = (char) c;
}
}
//取a和b中的较小值
private int min(int a, int b) {
if (a < b) return a;
return b;
}
//将字符数组cbuf中off位置开始,最多len个字符写到缓冲区
//缓冲区大小与要写入字符数比较.
//a.要写入字符数多于缓冲区大小,需要先刷新缓冲区,然后写入
//b.要写入字符数少于缓冲区大小,需要先判断剩余可写入的字符数,实际写入缓冲区的字符数要看缓冲区剩余位置.
public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if ((off < 0) || (off > cbuf.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > cbuf.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return;
}
//如果要写入缓冲区的数据长度大于缓冲区的大小.
if (len >= nChars) {
//刷新缓冲区.直接将字符数组cbuf里面数据写到底层字符输出流.
flushBuffer();
out.write(cbuf, off, len);
return;
}
//如要写入缓冲区的数据长度小于缓冲区的大小
int b = off, t = off + len;
while (b < t) {
//剩余可写入字符长度和要写入字符的长度取较小的值.
int d = min(nChars - nextChar, t - b);
//将字符数组cbuf中b位置开始,复制d个字符到缓冲区cb中nextChar位置开始.
System.arraycopy(cbuf, b, cb, nextChar, d);
b += d;
nextChar += d;
//缓冲区没有剩余位置,刷新缓冲区.
if (nextChar >= nChars)
flushBuffer();
}
}
}
//将字符串s中,off位置开始,len个字符写到缓冲区.len为负数时,不会有字符写到缓冲区.
public void write(String s, int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
int b = off, t = off + len;
while (b < t) {
//剩余可写入字符 长度与要写入的长度取两者最小值.
int d = min(nChars - nextChar, t - b);
//将字符串s中b开始到b+d之间的字符写到缓冲区cb中,从nextChar位置开始
s.getChars(b, b + d, cb, nextChar);
b += d;
nextChar += d;
//没有剩余位置,刷新缓冲区
if (nextChar >= nChars)
flushBuffer();
}
}
}
//写入一个换行符,换行符是系统定义的,不一定是单一'\n'符号.
public void newLine() throws IOException {
write(lineSeparator);
}
//刷新流,调用此方法会将缓冲区字符强制写出
public void flush() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
flushBuffer();
out.flush();
}
}
//关闭流,释放相关资源
@SuppressWarnings("try")
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (out == null) {
return;
}
try (Writer w = out) {
flushBuffer();
} finally {
out = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}2.BufferedReader源码
public class BufferedReader extends Reader {
//底层字符输入流
private Reader in;
//字符缓冲输入流中的缓冲区
private char cb[];
//nchars表示的是缓冲区的里面有效字符数.
//nextChar表示缓冲区中下一个读取字符的索引.
private int nChars, nextChar;
//表示标记失效
private static final int INVALIDATED = -2;
//没有标记
private static final int UNMARKED = -1;
//缓冲区中标记的位置初始化设置为-1.
private int markedChar = UNMARKED;
//用于标记之后,任需保留标记的情况下,从缓冲区可读取字符的最大值,超过此限制,标记将会失效.
private int readAheadLimit = 0;
//是否跳过换行符(lf,line feed)
private boolean skipLF = false;
//标记的情况下,是否跳过换行符.
private boolean markedSkipLF = false;
//缓冲区默认的大小为8192个字符.
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
//默认的每行字符的大小为80个字符.
private static int defaultExpectedLineLength = 80;
//有参构造方法,创建的是一个指定了缓冲区大小sz的字符缓冲输入流.
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {
super(in);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.in = in;
cb = new char[sz];
//初始化,下一个可读取的字符和有效字符数都为0
nextChar = nChars = 0;
}
//有参构造方法,创建的是缓冲区大小为默认的8192个字符的字符缓冲输入流.
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {
this(in, defaultCharBufferSize);
}
//用于确保底层字符输入流没有关闭.
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (in == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
//填充缓冲区,共存在四种情况.
//1.没有标记的情况下,从底层字符输入流读取数据将填充缓冲区中0-buffer.length之间位置.
//2.有标记的情况下,用于标记失效的限制值,此值与标记长度(下一个读取字符的位置-标记的位置,即标记位置开始读取的字符数)作比较.
//a.如果从标记位置开始读取字符超过限制值readAheadLimit,标记将会失效.从底层字符输入流读取数据将填充缓冲区中0-buffer.length位置.
//b.如果从标记位置开始读取的字符没有超过限制值readAheadLimit,
//第一种,readAheadLimitbuffer.length(缓冲区大小)情况下,仍会保留标记位置之后的字符.
private void fill() throws IOException {
int dst;
//没有标记,调用fill()方法,将填充缓冲区中0-cb.length之间的位置.
if (markedChar <= UNMARKED) {
dst = 0;
} else {
//delta表示标记之后读取的字符,是读取下一个字符位置与标记位置markedChar的差值.
int delta = nextChar - markedChar;
//超过限制值readAheadLimit,标记失效,调用fill()方法,将填充缓冲区中0-cb.length之间的位置.
if (delta >= readAheadLimit) {
markedChar = INVALIDATED;
readAheadLimit = 0;
dst = 0;
} else {
//如果限制值小于cb.length值,保留标记之后的字符.
if (readAheadLimit <= cb.length) {
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, cb, 0, delta);
markedChar = 0;
//调用fill()将会填充缓冲区中delta-cb.length之间位置.
dst = delta;
} else {
//限制值readAheadLimit超过了cb.length值,缓冲区扩容成readAheadLimit大小
char ncb[] = new char[readAheadLimit];
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, ncb, 0, delta);
cb = ncb;
markedChar = 0;
dst = delta;
}
//标记没有失效的情况下,会保存标记之后字符.
//所以下一个要读取字符的位置nextChar和有效字符数nChars都赋值delta.
nextChar = nChars = delta;
}
}
int n;
do {
//从底层字符输入流中读取数据,填充缓冲区
n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst);
} while (n == 0);
if (n > 0) {
nChars = dst + n;
nextChar = dst;
}
}
//读取单个字符,字符十进制范围是0-65535之间(十六进制0x00-0xffff),返回-1表示已达到文件末尾.
public int read() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
//确保底层字符输入流没有关闭
ensureOpen();
for (;;) {
//缓冲区中没有剩余位置,调用fill()方法填充缓冲区.
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
fill();
//调用fill()填充后,数据未更新,返回-1.
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
//skipLF为true情况下,跳过换行符
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
continue;
}
}
return cb[nextChar++];
}
}
}
//从缓冲区中读取最多len个字符到cbuf字符数组中,off是字符数组cbuf开始位置.
//要读取的字符长度len,剩余可读取的字符长度n,
//a.如果剩余字符数多于要读取的字符len,那么实际可读取的字符长度为len
//b.如果剩余字符数少于要读取的字符长度len,那么实际只能读取剩余的字符数.
private int read1(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
//如果读取字符长度超过缓冲区cb.length大小,并且没有标记和跳过换行符情况下,直接从底层输入流中读取len个字符
if (len >= cb.length && markedChar <= UNMARKED && !skipLF) {
return in.read(cbuf, off, len);
}
//是否调用fill()进行填充
fill();
}
//填充如果没有可读取的字符,返回-1.
if (nextChar >= nChars) return -1;
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
//跳过换行符'\n',继续读取
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
//如果没有剩余可读取的字符,调用fill()方法填充.
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
//填充后缓冲区的数据没有变化,表明文件到达末尾,返回-1
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
}
//取要读取字符的长度len与剩余可读取字符的长度中较小值,
int n = Math.min(len, nChars - nextChar);
System.arraycopy(cb, nextChar, cbuf, off, n);
nextChar += n;
return n;
}
//将缓冲区中的数据最多len个字符读取到cbuf字符数组中,off是cbuf开始位置.
public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if ((off < 0) || (off > cbuf.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > cbuf.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
//调用read1()方法读取字符
int n = read1(cbuf, off, len);
//n<=0,没有读取到字符.
if (n <= 0) return n;
//读取的字符len超过了n个字符
while ((n < len) && in.ready()) {
int n1 = read1(cbuf, off + n, len - n);
if (n1 <= 0) break;
n += n1;
}
return n;
}
}
//读取文本的一行数据,一行结束标志是换行符('\n'),回车符号('\r')或者是回车+换行符
//此方法读取一行的内容时,读取的是实际是下一个读取字符的位置到换行符之间的所有字符.
String readLine(boolean ignoreLF) throws IOException {
StringBuffer s = null;
int startChar;
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
//ignoreLF,表示下个'\n'将会被跳过
boolean omitLF = ignoreLF || skipLF;
bufferLoop:
for (;;) {
//缓冲区没有剩余可读字符,调用fill()填充
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
//填充后数据没有变化,说明已到达文件末尾,直接返回
if (nextChar >= nChars) { /* EOF */
if (s != null && s.length() > 0)
return s.toString();
else
return null;
}
boolean eol = false;
char c = 0;
int i;
//可以跳过字符'\n',并且下一个读取的字符就是'\n',nextChar++,即从下一行可以读取
if (omitLF && (cb[nextChar] == '\n'))
nextChar++;
skipLF = false;
omitLF = false;
charLoop:
//从nextChar(下一个读取字节的位置)到换行符(一行结束)之间还有多少个字符
//i的最终值就是nextChar+换行符之前可读字符数
for (i = nextChar; i < nChars; i++) {
c = cb[i];
if ((c == '\n') || (c == '\r')) {
eol = true;
//跳出此循环
break charLoop;
}
}
//缓冲区中从nextChar位置开始读取字符
startChar = nextChar;
//即下一次读取的位置是从i位置开始,将i赋值给nextChar,下面有nextChar++,即跳过换行符.
nextChar = i;
if (eol) {
String str;
if (s == null) {
//将缓冲区中startChar位置开始,到换行符之前所有的字符转换成字符串.
str = new String(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
} else {
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
str = s.toString();
}
//跳过换行符
nextChar++;
if (c == '\r') {
skipLF = true;
}
return str;
}
if (s == null)
s = new StringBuffer(defaultExpectedLineLength);
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
}
}
}
//读取文本的一行数据,行结束标志是换行符('\n'),回车符号('\r')或者是回车+换行符
public String readLine() throws IOException {
return readLine(false);
}
//跳过n个字符,返回跳过的字符数
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
if (n < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("skip value is negative");
}
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
long r = n;
while (r > 0) {
//没有可读取的字符,调用fill()进行填充
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
//填充完之后数据没有变化,说明文件已经到达末尾
if (nextChar >= nChars) /* EOF */
break;
//跳过换行符
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
}
}
//有效字符数-下一个可读字符位置=剩余可读取字符d
long d = nChars - nextChar;
//如果跳过的字符数r小于等于剩余可读取字符d,将下一个读取字符位置加r
if (r <= d) {
nextChar += r;
r = 0;
break;
}
//如果跳过字符数r大于剩余可取字符d,那么最多跳过字符只能是剩余可读取字符d.
//将下一个读取字符位置置为nchars(有效字符末尾)
else {
r -= d;
nextChar = nChars;
}
}
return n - r;
}
}
//缓冲区有剩余可读取的字符,或者底层字符流准备可读,返回true.
public boolean ready() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
//跳过换行符
if (skipLF) {
//如果没有剩余可读取的字符.调用fill()填充缓冲区
if (nextChar >= nChars && in.ready()) {
fill();
}
//有剩余可读取的字符,跳过'\n'
if (nextChar < nChars) {
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n')
nextChar++;
skipLF = false;
}
}
//返回缓冲区中是否有剩余的字符,或者底层字符输入流可读
return (nextChar < nChars) || in.ready();
}
}
//是否支持标记
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
//标记当前位置,调用reset()方法将会重置到当前位置.
//readAheadLimit表示的是保留标记的情况下,可读取字符的上限值.超过此值,调用reset()将会失败.
//readAheadLimit超过缓冲区大小时,缓冲区将会扩容.
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException {
if (readAheadLimit < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Read-ahead limit < 0");
}
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
this.readAheadLimit = readAheadLimit;
markedChar = nextChar;
markedSkipLF = skipLF;
}
}
//调用reset()方法,将会将当前重置到最后一次调用mark()标记的位置
public void reset() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (markedChar < 0)
throw new IOException((markedChar == INVALIDATED)
? "Mark invalid"
: "Stream not marked");
nextChar = markedChar;
skipLF = markedSkipLF;
}
}
//关闭流,释放相关资源
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (in == null)
return;
try {
in.close();
} finally {
in = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}
//jdk1.8中新添加的方法,按照系统换行符,迭代每一个行的内容.得到是缓冲区中所有的字符的流.
public Stream lines() {
Iterator iter = new Iterator() {
String nextLine = null;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (nextLine != null) {
return true;
} else {
try {
nextLine = readLine();
return (nextLine != null);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new UncheckedIOException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public String next() {
if (nextLine != null || hasNext()) {
String line = nextLine;
nextLine = null;
return line;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
};
return StreamSupport.stream(Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(
iter, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL), false);
}
} 对于BufferedReader流fill()方法,缓冲区中没有可读取的字符时,将会调用此方法填充缓冲区.总结分析以下几种情况:
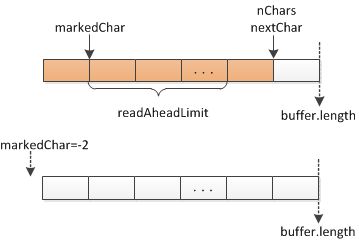
先了解一下一些重要变量的含义:
- markedChar标记当前位置,将缓冲区中当前位置保存到markedChar中,其中markedChar=-1表示没有标记,markedChar=-2表示标记失效.
- nChars是缓冲区中有效字符数.nextChar是缓冲区中下一个要读取字符的索引位置.
- readAheadLimit是标记之后,在标记有效情况下,可读取的字符数最大值,超过此值标记将会失效.
1.没有标记的情况下,从底层字符输入流读取数据将填充缓冲区中0~buffer.length之间位置.
2.有标记的情况下,用于标记失效的限制值,此值与标记长度(下一个读取字符的位置-标记的位置,即标记位置开始读取的字符数)作比较.
a.如果从标记位置开始读取字符超过限制值readAheadLimit,标记将会失效.从底层字符输入流读取数据将填充缓冲区中0~buffer.length位置.(如下,nextChar-markedChar超过readAheadLimit,标记会失效).
b.如果从标记位置开始读取的字符没有超过限制值readAheadLimit. 关于BufferedWriter流中有写入单个字符,字符串以及字符数组等方法,源码不难分析.而BufferedReader流中读取有读取单个字节,读取到字符数组,读取一行数据等方法,此外还有标记mark()和重置方法reset().作为缓冲字符流,提供的主要功能还是对底层字符流进行缓冲.提高读取文件的效率.
第一种,readAheadLimit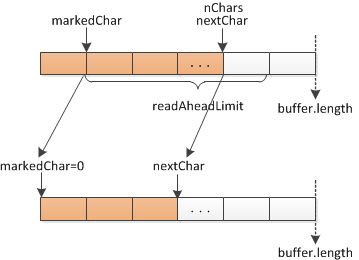
第二种,readAheadLimit>buffer.length(缓冲区大小)情况下,会将缓冲进行扩容到readAheadLimit大小,且会保留标记位置之后的字符.(如下,将会扩容到readAheadLimit,仍旧会保存markedChar到nextChars之间的字符.下次填充从nextChar位置开始)总结