Android自定义View——多边形网格属性图
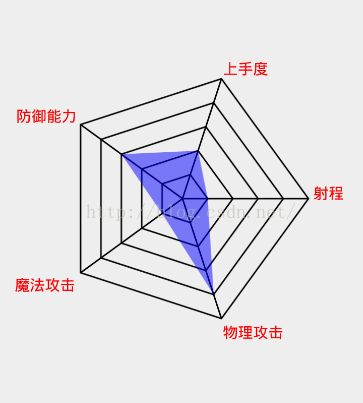
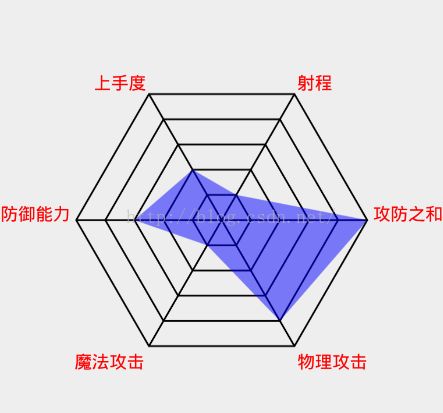
效果展示
实现步骤
1、初始化变量
//-------------我们必须给的模拟数据-------------
//n边形
private int n = 5;
//文字
private String[] text = new String[]{"物理攻击", "魔法攻击", "防御能力", "上手度", "射程"};
//区域等级,值不能超过n边形的个数
private int[] area = new int[]{4, 1, 3, 2, 1};
//-------------View相关-------------
//View自身的宽和高
private int mHeight;
private int mWidth;
//-------------画笔相关-------------
//边框的画笔
private Paint borderPaint;
//文字的画笔
private Paint textPaint;
//区域的画笔
private Paint areaPaint;
//-------------多边形相关-------------
//n边形个数
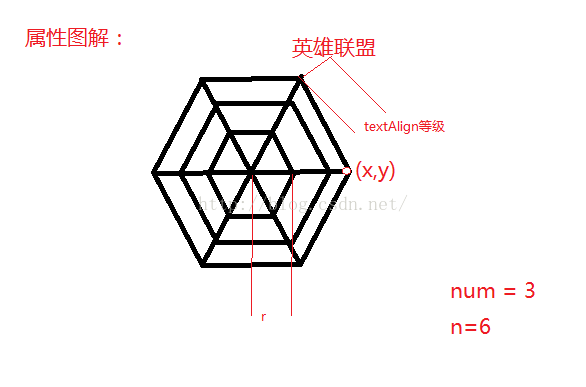
private int num = 5;
//两个多边形之间的半径
private int r = 50;
//n边形顶点坐标
private float x, y;
//n边形角度
private float angle = (float) ((2 * Math.PI) / n);
//文字与边框的边距等级,值越大边距越小
private int textAlign = 5;
//-------------颜色相关-------------
//边框颜色
private int mColor = 0xFF000000;
//文字颜色
private int textColor = 0xFFFF0000;
//区域颜色
private int areaColor = 0x800000ff;2、属性图解
3、如果想切换到5、6、7边形等等,则必须修改下面几条数据
//-------------我们必须给的模拟数据-------------
//n边形
private int n = 5;
//文字
private String[] text = new String[]{"物理攻击", "魔法攻击", "防御能力", "上手度", "射程"};
//区域等级,值不能超过n边形的个数
private int[] area = new int[]{4, 1, 3, 2, 1};4、获取宽和高
public MyPolygonView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyPolygonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyPolygonView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}5、绘制图形
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//初始化画笔
initPaint();
//画布移到中心点
canvas.translate(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
//画n边形
drawPolygon(canvas);
//画n边形的中点到顶点的线
drawLine(canvas);
//画文字
drawText(canvas);
//画蓝色区域
drawArea(canvas);
} /**
* 初始化画笔
*/
private void initPaint() {
//边框画笔
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
borderPaint.setColor(mColor);
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
//文字画笔
textPaint = new Paint();
textPaint.setTextSize(30);
textPaint.setColor(textColor);
textPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
//区域画笔
areaPaint = new Paint();
areaPaint.setColor(areaColor);
areaPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
areaPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL_AND_STROKE);
}
/**
* 绘制多边形
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawPolygon(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = new Path();
//n边形数目
for (int j = 1; j <= num; j++) {
float r = j * this.r;
path.reset();
//画n边形
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
x = (float) (Math.cos(i * angle) * r);
y = (float) (Math.sin(i * angle) * r);
if (i == 1) {
path.moveTo(x, y);
} else {
path.lineTo(x, y);
}
}
//关闭当前轮廓。如果当前点不等于第一个点的轮廓,一条线段是自动添加的
path.close();
canvas.drawPath(path, borderPaint);
}
}
/**
* 画多边形线段
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawLine(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = new Path();
float r = num * this.r;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
path.reset();
x = (float) (Math.cos(i * angle) * r);
y = (float) (Math.sin(i * angle) * r);
path.lineTo(x, y);
canvas.drawPath(path, borderPaint);
}
}
/**
* 画文字
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawText(Canvas canvas) {
float r = num * this.r;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
//测量文字的宽高
Rect rect = new Rect();
textPaint.getTextBounds(text[i - 1], 0, text[i - 1].length(), rect);
float textWidth = rect.width();
float textHeight = rect.height();
x = (float) (Math.cos(i * angle) * r);
y = (float) (Math.sin(i * angle) * r);
//位置微调
if (x < 0) {
x = x - textWidth;
}
if (y > 25) {
y = y + textHeight;
}
//调文字与边框的边距
float LastX = x + x / num / textAlign;
float LastY = y + y / num / textAlign;
canvas.drawText(text[i - 1], LastX, LastY, textPaint);
}
}
/**
* 画区域
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawArea(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = new Path();
for (int i= 1; i<= n; i++) {
float r = area[i - 1] * this.r;
x = (float) (Math.cos(i * angle) * r);
y = (float) (Math.sin(i * angle) * r);
if (i == 1) {
path.moveTo(x, y);
} else {
path.lineTo(x, y);
}
}
//关闭当前轮廓。如果当前点不等于第一个点的轮廓,一条线段是自动添加的
path.close();
canvas.drawPath(path, areaPaint);
}原理分析
1、开始画画前:我们要把画笔准备好,这里看代码就能明白意思了,接着把整个View的图纸的重心点定位到我们整个View宽高的中点,这样开始画画的(0,0)点就在这个View的中点了。
2、画n边形:第一层循环是画出n边形的数目,第二层循环才是画n边形的步骤,我们讲解第二层循环。首先通过角度(angle)可以找出我们n边形的顶点,用到了高中知识。接着让Path移到(path.moveTo)某一顶点开始,然后连接下一个顶点(path.lineTo)作为直线,最后用(path.close)会自动把最后一条边自动合上。记住,画完一个n边形后记得(path.reset),让path的起点回到(0,0)。
3、画n边形到顶点之间的直线:这个不难理解,这里就不多讲了。
4、画红色文字:这里的实现方法大家都可以自己实现,放在哪里看你个人的爱好,如果有更好的方法请留言,谢谢。这里我用的方法就是先测量出每个字符串的宽高,只要想办法将字符串的某个顶点移到n边形的顶点重合,并不占用网格位置,接着全部向外扩散就行了。
5、画区域:根据绘制了多边形可以理解这个绘制区域,只是将其r改为区域所需要的值即可,这里不过多介绍。
源码下载