迷宫问题(二)------复杂迷宫
所需知识
结构体
递归
❀思路分析
1.跟上篇比较区别在于,多通路,同出口,同入口,如何在已经找到了一个出口的情况下,如何返回来找另外一条最短路径,还是用赋值法。
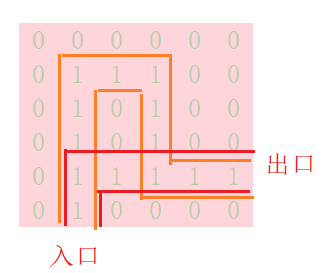
2.探路的顺序是上左右下。
从入口开始,通路的条件为,下一位置值为1或值大于当前位置的值,
赋值依次加1
每次走位置,都调用一次函数,形成递归
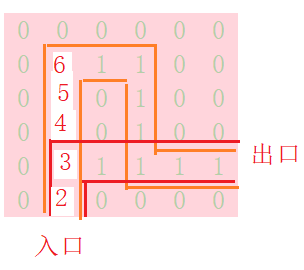
向上走为最高优先级,走不通后向右走,然后向下

当前位置进入死胡同,走不通,存储路径的栈弹出该错误位置。并递归到上一层,上一个节点,依此类推。退回到有其他通路可走的节点,再进入该下一位置的函数,进行递归。
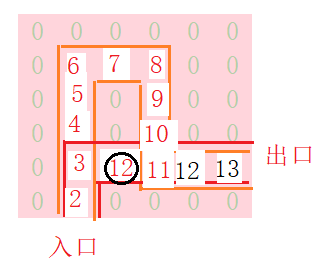
到达出口后,将栈s中保存的这条有效路径保存到栈Path。然后再进行。该出口处函数走不通,将会退回到上一个还有其他通路的节点
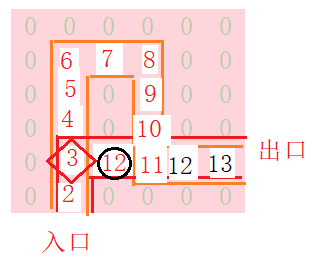
只有节点3位置处右侧有第一次未走过的路径(11到左侧12与3到自己的右侧虽然未同一节点,但路线不同),且12>3满足通路条件,开始探路
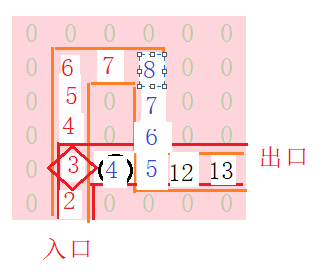
走到该位置后发现,下一个位置的7<当前位置的8,死路,回退,同时出栈,这些错误位置,递归退到上一个有其他通路的路口。
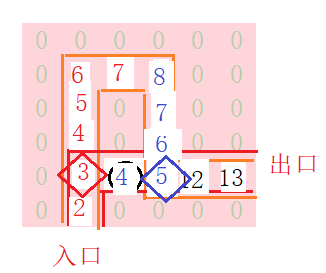
当前位置5还有右出口。
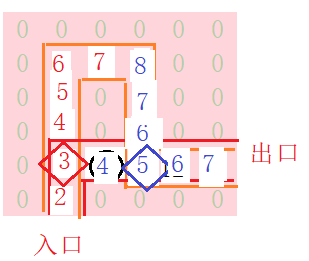
再一次来到出口,与刚才存进去的栈Path里存的路径相比较,若比之小,则进行替换。
而后继续程序,出口位置再不可走。递归返回,直到2都没有再有其他未走通路的节点。返回到入口,程序结束。
具体实现
//maze.h
#define __MAZE_H__
#ifdef __MAZE_H__
#define ROW 6 //行,纵坐标
#define COL 6 //列,横坐标
#include //打印
#include //maze.c
#include "Maze.h"
//初始化栈
void InitStack(Stack * s)
{
assert(s);
s->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void PushStack(Stack * s, int x, int y)
{
assert(s);
if (40 == s->top)
{
perror("PushStack error\n");
return;
}
s->Sta[s->top].x = x;
s->Sta[s->top].y = y;
s->top++;
}
//出栈
void PopStack(Stack *s)
{
if (s->top == 0)
{
perror("PopStack error\n");
return;
}
assert(s);
s->top--;
}
//取栈顶元素
Point StackTop(Stack * s)
{
if (s->top == 0)
{
perror("StackTop error \n");
return ;
}
return (s->Sta[s->top - 1]);
}
//打印栈
void PrintStack(Stack * s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s->top; i++)
{
printf(" x=%d ,y = %d \n", s->Sta[i].x, s->Sta[i].y);
}
printf("\n");
}
//清空栈
void EmptyStack(Stack * s)
{
s->top = 0;
}
//把栈s里的内容全部赋值给Path
void s_Path(Stack * s, Stack * Path)
{
int tmp = s->top;
while (tmp)
{
tmp--;
Path->Sta[tmp] = s->Sta[tmp];
}
Path->top = s->top;
}
//测试栈
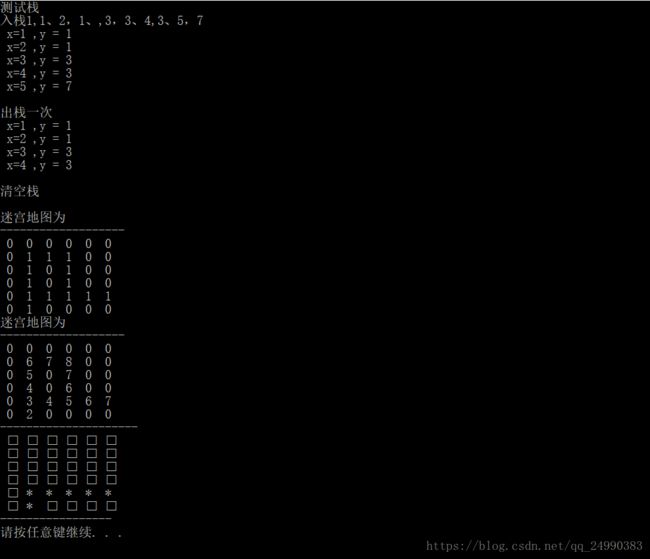
void testStack(Stack * s)
{
printf("测试栈\n");
InitStack(s);
printf("入栈1,1、2,1、,3,3、4,3、5,7\n");
PushStack(s, 1, 1);
PushStack(s, 2, 1);
PushStack(s, 3, 3);
PushStack(s, 4, 3);
PushStack(s, 5, 7);
PrintStack(s);
PopStack(s);
printf("出栈一次\n");
PrintStack(s);
EmptyStack(s);
printf("清空栈\n");
PrintStack(s);
}
void InitMaze(Map * maze)
{
int col = 0, row = 0;
if (maze == NULL)//非法传参,按理这里为Map类型的指针
{
return;
}
//0 0 0 0 0 0
//1 1 1 1 0 0
//0 0 0 1 0 0
//0 1 1 1 1 1
//0 0 1 0 0 0
//0 0 0 0 0 0
//初始化一个数组
DataType arr[ROW][COL] = {
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
//把该数组的值传递给迷宫
for (row = 0; row < ROW; row++)
{
for (col = 0; col < COL; col++)
{
maze->map[row][col] = arr[row][col];
}
}
}
void PrintMap(Map *maze)
{
int col = 0, row = 0;
printf("迷宫地图为\n-------------------\n");
for (row = 0; row < ROW; row++)
{
for (col = 0; col < COL; col++)
{
printf(" %d ", maze->map[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//检测当前节点是否有通路,优先次序为上左右下,入栈
int Pass(Map * maze,Point cur,Point next)
{
if ((cur.x>ROW-1)||(cur.y>COL-1)||(next.x>ROW-1)||(next.y>COL-1))
{
return 0;
}
if ((maze->map[next.x][next.y] == 1)||(maze ->map [next.x][next.y]>maze->map [cur.x][cur.y]))
return 1;
return 0;
}
//检测是否走出迷宫
int YesPass(Map * maze, Point pos)
{
if (pos.x == 0 || pos.y == 0 || pos.x == ROW - 1 || pos.y == COL - 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
//通过迷宫地图和入口找出口
void FindExit(Map * maze, Point cur,Point entry, Stack * s,Stack * Path)
{
Point next = cur;
//探路走起来,先赋值,再走路
//若为入口,先赋值2
if ((0 == s->top) && (entry.x == cur.x) && (entry.y == cur.y))
{
maze->map[cur.x][cur.y] = 2;
PushStack(s, cur.x, cur.y);
}
//若找到了出口进行标记
if (YesPass(maze, cur)&&((entry.x != cur.x)||(entry.y != cur.y)))
{
if (Path->top == 0)
{
s_Path(s,Path);
}
if (s->top < Path->top)
{
s_Path(s, Path);
}
}
//上通路
next.x = cur.x-1;
next.y = next.y;
if (Pass(maze,cur, next))
{
maze->map[next.x][next.y] = maze->map[cur.x][cur.y] + 1;
PushStack(s, next.x, next.y);
FindExit(maze, next, entry, s, Path);
}
//左通路
next.x = cur.x;
next.y = cur.y-1;
if (Pass(maze,cur, next))
{
maze->map[next.x][next.y] = maze->map[cur.x][cur.y] + 1;
PushStack(s, next.x, next.y);
FindExit(maze, next, entry, s, Path);
}
//右通路
next.x = cur.x;
next.y = cur.y+1;
if (Pass(maze, cur,next))
{
maze->map[next.x][next.y] = maze->map[cur.x][cur.y] + 1;
PushStack(s, next.x, next.y);
FindExit(maze, next, entry, s, Path);
}
//下通路
next.x = cur.x + 1;
next.y = cur.y;
if (Pass(maze,cur, next))
{
maze->map[next.x][next.y] = maze->map[cur.x][cur.y] + 1;
PushStack(s, next.x, next.y);
FindExit(maze, next, entry, s, Path);
}
PopStack(s);
}
//显示路线
void PrintPath(Map * maze,Stack * Path)
{
char arr[ROW][COL];
while (Path->top)
{
maze->map[StackTop(Path).x][StackTop(Path).y] = 20;
arr[StackTop(Path).x][StackTop(Path).y] = '*';
PopStack(Path);
}
printf("---------------------\n");
for (int row = 0; row < ROW; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < COL; col++)
{
if (maze->map[row][col] != 20)
{
maze->map[row][col] = 0;
arr[row][col] = 1;
}
printf(" %c ", arr[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}//源.c
#include "Maze.h"
int main()
{
//给定入口
Point e;
e.x = 5;
e.y = 1;
//定义迷宫
Map maze;
//定义栈存放路径
Stack s;
//定义栈存放最短路径
Stack Path;
//初始化两个栈
InitStack(&Path);
testStack(&s);
//初始化迷宫
InitMaze(&maze);
//打印迷宫
PrintMap(&maze);
//通过迷宫和入口找出口
FindExit(&maze,e, e, &s,&Path);
//打印当前栈中保存的路径
//PrintStack(&Path);
//打印因为探路而改变的迷宫
PrintMap(&maze);
//显示路线
PrintPath(&maze,&Path);
printf("-----------------\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}