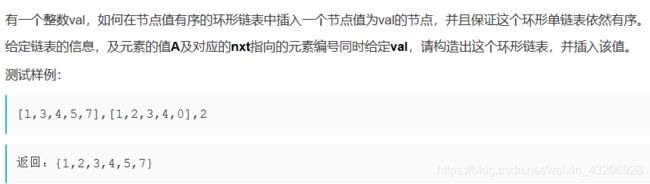
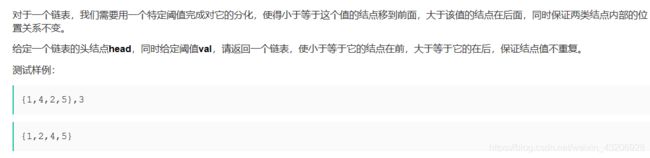
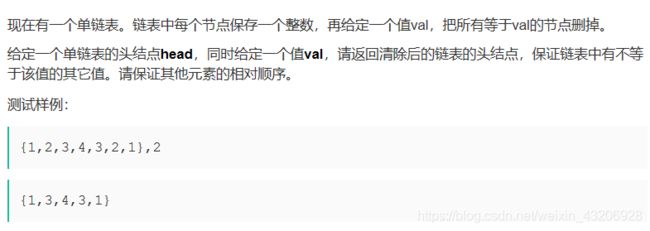
链表题目总结
文章目录
- 一、链表插值练习
- 二、访问单个节点的删除练习题
- 三、链表的分化练习题
- 四、打印两个链表的公共值
- 五、链表的k逆序练习题
- 六、链表指定值清除
- 七、链表的回文结构
- 八、链表中倒数第k个结点
- 九、复杂链表的复制练习
- 十、链表判环练习
- 十一、无环链表相交问题
- 十二、有环单链表相交问题
- 十三、单链表相交问题
一、链表插值练习
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class InsertValue {
public ListNode insert(int[] A, int[] nxt, int val) {
// write code here
//如果A为空的情况
if(A == null){
return new ListNode(val);
}
//构建链表
ListNode head = new ListNode(A[0]);//头节点
ListNode cur = head;
for(int i = 0;i<A.length-1;i++){
ListNode node = new ListNode(A[nxt[i]]);
cur.next = node;
//node.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
//将值等于val的节点加入到链表中
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode next = head.next;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
if(head.val >= val){
newNode.next = head;
//cur.next = newNode;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
while(next!=null){
if(next.val >= val){
pre.next = newNode;
newNode.next = next;
return head;
}else{
pre = next;
next = next.next;
}
}
newNode.next = next;
pre.next = newNode;
return head;
}
}二、访问单个节点的删除练习题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Remove {
public ListNode removeNode(ListNode pNode, int delVal) {
// write code here
if(pNode==null){
return null;
}
if(pNode.val == delVal){
return pNode.next;
}
ListNode pre = pNode;
ListNode cur = pNode.next; //被删除的节点
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == delVal){
pre.next = cur.next;
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return pNode;
}
}三、链表的分化练习题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Divide {
public ListNode listDivide(ListNode head, int val) {
// write code here
ListNode sh = null;
ListNode st = null;
ListNode bh = null;
ListNode bt = null;
ListNode next = null;
while(head != null){
next = head.next;
head.next = null;
if(head.val <= val){
if(sh == null){
sh = head;
st = head;
}else{
st.next = head;
st = head;
}
}else{
if(bh == null){
bh = head;
bt = head;
}else{
bt.next = head;
bt = head;
}
}
head = next;
}
//small and equal reconnect
if(st != null){
st.next = bh;
}
return sh != null ? sh : bh;
}
}四、打印两个链表的公共值
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Common {
public int[] findCommonParts(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// write code here
ArrayList<Integer> arrlist = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
ListNode nodeA = headA;
ListNode nodeB = headB;
while(nodeA != null && nodeB != null){
if(nodeA.val < nodeB.val){
nodeA = nodeA.next;
}else if(nodeB.val < nodeA.val){
nodeB = nodeB.next;
}else{
arrlist.add(nodeA.val);
nodeA = nodeA.next;
nodeB = nodeB.next;
}
}
int[] arr = new int[arrlist.size()];
for(i=0;i<arrlist.size();i++){
arr[i] = arrlist.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
}五、链表的k逆序练习题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class KInverse {
public ListNode inverse(ListNode head, int k) {
// write code here
if(k < 2){
return head;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int count = 0;
ListNode temp = head;
ListNode newhead = head;
while(temp != null){
stack.push(temp.val);
count++;
temp = temp.next;
if(count == k){
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
newhead.val = stack.pop();
newhead = newhead.next;
}
count=0;
}
}
return head;
}
}六、链表指定值清除
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class ClearValue {
public ListNode clear(ListNode head, int val) {
// write code here
if(head==null){
return head;
}
while(head!=null){
if(head.val != val){
break;
}
head = head.next;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == val){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}七、链表的回文结构
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Palindrome {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode pHead) {
// write code here
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null){
return true;
}
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = pHead;
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = pHead;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val != stack.pop().val){
return false;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return true;
}
}思路2:使用快慢指针
在这里插入代码片八、链表中倒数第k个结点
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
//得到总长度
int length = 0;
ListNode temp = head;
if(temp == null){
return null;
}
while(temp != null){
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
if(k<=0 || k>length){
return null;
}
ListNode temp2 = head;
for(int i=0;i<length-k;i++){
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
return temp2;
}
}九、复杂链表的复制练习
import java.util.HashMap;
/*
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
{
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
HashMap<RandomListNode,RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
while(cur != null){
map.put(cur,new RandomListNode(cur.label));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = pHead;
while(cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(pHead);
}
}十、链表判环练习
- 每次遍历到一个节点,先查一下这个节点在hashset中存不存在,如果不存在,就添加到hashset中,如果存在,说明当前节点为入环节点
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class ChkLoop {
public int chkLoop(ListNode head, int adjust) {
// write code here
ListNode cur = head;
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while(cur != null){
if(set.contains(cur)){
return cur.val;
}
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}思路二:不用哈希表,使用快慢指针
- 准备两个指针,一个是快指针,一个是慢指针
- 快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果快指针在走的时候,遇到空,直接返回无环
- 如果有环,快指针和慢指针一定会在环上相遇
- 相遇的时刻,快指针回到开头,然后快指针由一次走两步,变为一次走一步,快指针和慢指针一定会在第一个入环节点处相遇
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class ChkLoop {
public int chkLoop(ListNode head, int adjust) {
// write code here
if(head == null || head.next==null || head.next.next==null){
return -1;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast.val;
}
}
return -1;
}
}十一、无环链表相交问题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class CheckIntersect {
public boolean chkIntersect(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// write code here
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return false;
}
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(curA.next != null){
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB != null){
curB = curB.next;
}
if(curA == curB){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}十二、有环单链表相交问题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class ChkIntersection {
public boolean chkInter(ListNode head1, ListNode head2, int adjust0, int adjust1) {
// write code here
if(head1 == null || head2 == null){
return false;
}
//找到两个有环单链表的入环节点
ListNode loop1 = nodeLoop(head1);
ListNode loop2 = nodeLoop(head2);
if(loop1==null || loop2==null){
return false;
}
if(loop1 == loop2){
return true;
}
ListNode cur = loop1.next;
while(cur != loop1){
if(cur == loop2){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
public ListNode nodeLoop(ListNode head){
if(head==null || head.next==null || head.next.next == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
fast = head;
while(fast!= slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
}
}十三、单链表相交问题
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class ChkIntersection {
public boolean chkInter(ListNode head1, ListNode head2, int adjust0, int adjust1) {
// write code here
if(head1 == null || head2 == null){
return false;
}
ListNode loop1 = isLoop(head1);
ListNode loop2 = isLoop(head2);
if(loop1 == null && loop2 != null || loop1 != null && loop2 == null){
return false;
}else if(loop1 == null && loop2 == null){
//判断两个无环是否相交
boolean nonloop = isLinked(head1,head2);
return nonloop;
}else{
//判断两个有环是否相交
boolean flag = isLinkedLoop(head1,loop1,head2,loop2);
return flag;
}
}
//判断两个有环链表是否相交
public boolean isLinkedLoop(ListNode head1,ListNode loop1,ListNode head2,ListNode loop2){
if(loop1 == loop2){
return true;
}
ListNode cur = loop1.next;
while(cur != loop1){
if(cur == loop2){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//判断两个无环链表是否相交
public boolean isLinked(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){
ListNode cur1 = head1;
ListNode cur2 = head2;
while(cur1.next!=null){
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2.next != null){
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if(cur1 == cur2){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断链表是否有环
public ListNode isLoop(ListNode head){
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
}
}