剑指offer面试题11-20
#11二进制中1的个数
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
思想:
//定义一个标志位flag,依次将flag向左移位,然后与数组的数字进行按位&
//如果按位与的结果为1则说明输入数的二进制位的值为1
//直到移位到最左端(int 32位)
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
unsigned int flag=1;
int count=0;
while(flag)
{
if(n&flag)
count++;
flag=flag<<1;
}
return count;
}
};
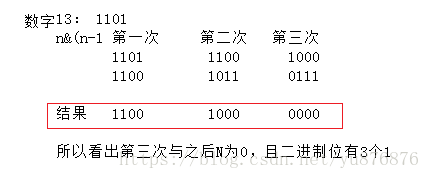
思想:
n&(n-1),第一次按位&后,输入数字的二进制位从右向左少了一个1
直到n的值小于零则循环结束.
class Solution {
public:
static int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count=0;
while(n!=0) //当n不为0时,说明有二进制位为1
{
count++;
n=n&(n-1); //按位与一次二进制少一个1
}
return count;
}
};
#12数的整数次方
给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
class Solution {
public:
double Power(double base, int exponent) {
double result=1;
if(base==0)
return 0;
else if(exponent==0)
{
return 1;
}
else if(exponent<0)
{
for(int i=1;i<=(-exponent);i++)
{
result*=base;
}
return 1/result;
}
else
{
for(int i=1;i<=exponent;i++)
{
result*=base;
}
return result;
}
}
};
#13调整数组顺序使得奇数位于偶数前面
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
思想:定义两个vector,
将第一次遍历出奇数插入到vector
将第二次遍历出偶数插入到vector
然后将vector的值拷贝到数组中
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector &array) {
//定义一个vector,第一次遍历将奇数插入,第二次遍历将偶数插入
//然后将vector的值赋值给数组
vector result;
for(int i=0;i #14链表倒数第K个结点
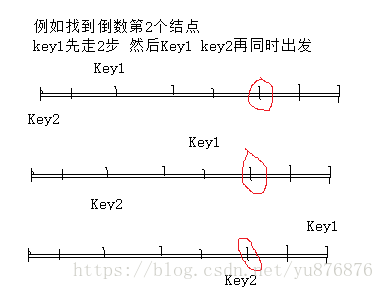
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
思想:指针1先走K步,指针2再出发,注意K的合法性检验
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k) {
while(pListHead==NULL||k==0)
return NULL;
ListNode* key1=pListHead;
ListNode* key2=NULL;
for(int i=1;inext!=NULL)
key1=key1->next;
else
return NULL;
}
key2=pListHead;
while(key1->next!=NULL)
//key1,key2同时出发,当key1走到结尾则此时key2的位置就是倒数第K个结点
{
key1=key1->next;
key2=key2->next;
}
return key2;
}
};
#15链表的反转
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
思想:
定义一个新链表, 定义一个栈
将旧链表中的结点值入栈,然后将栈中值出栈,插入到新链表中。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
//借助栈实现,
//将链表结点插入栈中,将栈中结点插入新结点中
std::stack st;
if(pHead==nullptr||pHead->next==nullptr)
return pHead;
ListNode* cur=pHead;
while(cur->next!=nullptr) //入栈
{
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->next;
}
ListNode* newhead=cur;
while(!st.empty()) //出栈
{
cur->next=st.top();
cur=cur->next;
st.pop();
}
cur->next=nullptr; //下一个置空
return newhead;
}
};
#16合并两个排序链表
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
思想:
//定义一个新头结点
//比较两个链表结点大小,比较小的结点插入到新头结点中
//递归比较剩下的结点值大小
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2)
//定义一个新的头结点
//比较两个结点的值,较小值插入新头节点(递归插入)
{
if(pHead1==NULL)
return pHead2;
if(pHead2==NULL)
return pHead1;
ListNode* head;
if(pHead1->valval)
{
head=pHead1;
pHead1->next=Merge(pHead1->next,pHead2);
}
else
{
head=pHead2;
pHead2->next=Merge(pHead1,pHead2->next);
}
return head;
}
};
#17树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思想:
//合法性检验
//选择那个两个结点进行比较
//在Tree1中查找Tree2的结点
//如果Tree2为空说明找到了找完了,如果Tree1为空说明没找到
//如果Tree1和Tree2根结点相同再递归访问左右子树
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubtree(TreeNode *Tree1, TreeNode *Tree2){
if(Tree2==NULL) return true;
if(Tree1==NULL && Tree2!=NULL) return false;
if(Tree2->val == Tree1->val){
bool lTree = isSubtree(Tree1->left, Tree2->left);
bool rTree = isSubtree(Tree1->right, Tree2->right);
return lTree && rTree;
}else return false;
}
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2)
{
if(pRoot1 == NULL || pRoot2 == NULL) return false;
return isSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) || HasSubtree(pRoot1->left, pRoot2)|| HasSubtree(pRoot1->right, pRoot2);
}
};
#18二叉树的镜像
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
思想:
//合法性检验
//定义一个指针,交换根结点左右孩子的地址
//递归遍历根结点的左右孩子结点
class Solution {
public:
void Mirror(TreeNode *pRoot) {
//合法性检验
if(pRoot==NULL)
return ;
TreeNode* tmp; //交换左右结点的地址
tmp=pRoot->left;
pRoot->left=pRoot->right;
pRoot->right=tmp;
Mirror(pRoot->left);//递归遍历左子树(其实是右子树)
Mirror(pRoot->right);//递归遍历右子树(其实是左子树)
return ;
}
};
#19顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
思想:
//合法性检验
//定义数组存储序列
//定义上下左右四种边界值,作为循环条件
//判断循环条件(从左到右,从上到下,从右到左,从下到上)
class Solution {
public:
vector printMatrix(vector > mat) {
int row=mat.size();
int col=mat[0].size();
vector ret; //定义一个数组存储
if(row==0||col==0) //合法性检验
return ret;
int left=0;
int right=col-1;
int top=0;
int bottom=row-1;
while(left<=right&&top<=bottom) //循环条件
{
//从左到右插入
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++) ret.push_back(mat[top][i]);
//从上到下插入
for(int i=top+1;i<=bottom;i++) ret.push_back(mat[i][right]);
//从右到左插入
for(int i=right-1;i>=left&&toptop&&left #20包含min函数的栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
思想
栈 3,4,2,5,1
栈 3, 4 ,3 ,2,2,5,2,1,1
//入栈之前先判断如果小于栈顶元素插入两次
//判断如果大于栈顶元素,先插入该元素,再插入旧栈顶元素
//出栈时出栈两次即可
思想2
栈 3,4,2,5,1
辅助栈 3,3,2,2,1
//重新定义一个栈,入栈前先比较如果小于栈顶元素插入到新栈中,再入栈
//如果当前值大于栈顶元素,则入栈然后,将栈顶元素入到新栈
//出栈时辅助栈也出栈,保证辅助栈顶为最小值
class Solution {
public:
stack datast,minst;
void push(int value) {
datast.push(value);
if(minst.empty())
minst.push(value);
else
int min=minst.top(); //入栈时入较小值
value<=min? minst.push(value):minst.push(min);
}
void pop() { //出栈时两个栈都出栈操作
minst.pop();
datast.pop();
}
int top() { //正常栈的栈顶元素
return datast.top();
}
int min() { //最小栈的栈顶元素为最小值
return minst.top();
}
};