参考:
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UBwCpsK7kbPfmI4_PiJJCA
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hJJUbb6aLbxmNl3k91M7UQ
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/1a8837872ed0
今天说一说加解密,我们先了解一下相关的概念:
- 不可逆加密
- 可逆加密
从加密方式来说,加密分为可逆和不可逆加密,而可逆加密有具体分为:
- 算法加密
- 对称加密算法
- 非对称加密算法
我们分别说说他们的区别和特性。
1.不可逆加密
不可逆加密算法的特征是加密过程中不需要使用密钥,输入明文后由系统直接经过加密算法处理成密文,这种加密后的数据是无法被解密的,只有重新输入明文,并再次经过同样不可逆的加密算法处理,得到相同的加密密文并被系统重新识别后,才能真正解密。
如信息摘要(Message Digest)和安全散列(Secure Hash)算法属于此类,常见的算法包括 MD5、SHA1、PBKDF2、bcrypt 等。
特点:
ok,那我们演示如何使用MD5和SHA进行加解密
// MD5加密
private static String toMd5(String str) {
// 实例化一个指定摘要算法为MD5的MessageDigest对象
MessageDigest algorithm;
try {
algorithm = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
// 重置摘要以供再次使用
algorithm.reset();
// 使用bytes更新摘要
algorithm.update(str.getBytes());
// 使用指定的byte数组对摘要进行最后更新,然后完成摘要计算
return toHexString(algorithm.digest(), "");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// SHA加密
private static String toSHA(String str) {
// 实例化一个指定摘要算法为SHA的MessageDigest对象
MessageDigest algorithm;
try {
algorithm = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA");
// 重置摘要以供再次使用
algorithm.reset();
// 使用bytes更新摘要
algorithm.update(str.getBytes());
// 使用指定的byte数组对摘要进行最后更新,然后完成摘要计算
return toHexString(algorithm.digest(), "");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 将字符串中的每个字符转换为十六进制
private static String toHexString(byte[] bytes, String separtor) {
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hexString.append("0");
}
hexString.append(hex).append(separtor);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
2.可逆加密
2.1算法加密
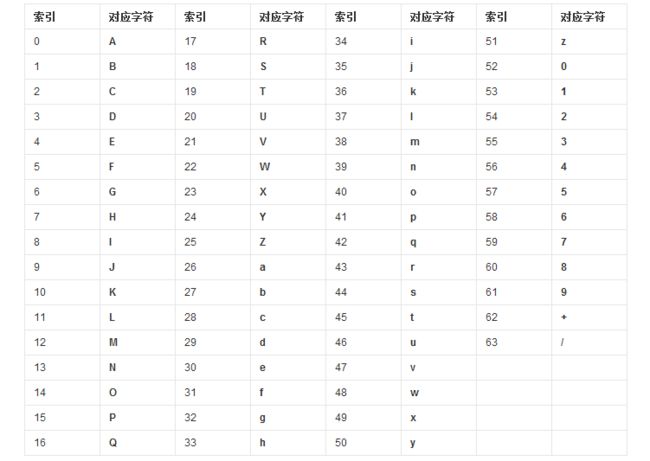
基于算法的加密算法,也被称为古典加密算法,如 HTTP 认证中的 base64,是一种基于64个基本字符,加密后的内容只包含这64个字符,加密后长度会变大。它是最简单的一种算法,一般用于加密URL.
下图为Base64编码表
Base64加解密相关代码
需要引入包:android.util.Base64切记是android自带的
// Base64加密
private static String encode(String str) {
byte[] encodeBytes = Base64.getEncoder().encode(str.getBytes());
return new String(encodeBytes);
}
// Base64解密
private static String decode(String str) {
byte[] decodeBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(str.getBytes());
return new String(decodeBytes);
}
2.2对称加密
对称加密:加密和解密的密钥一样。常见的对称加密算法有 DES、3DES、AES。这三者的关系可以理解为迭代和替代。3DES是对DES的发展,AES是为了替代DES.
DES加解密相关代码
public class DESUtil {
// 初始化向量
private static byte[] iv = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 1, 2, '*' };
// DES加密
// encryptText为原文
// encryptKey为密匙
private static String encryptDES(String encryptText, String encryptKey)
throws Exception {
// 实例化IvParameterSpec对象,使用指定的初始化向量
IvParameterSpec spec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
// 实例化SecretKeySpec类,根据字节数组来构造SecretKeySpec
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(encryptKey.getBytes(), "DES");
// 创建密码器
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
// 用密码初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, spec);
// 执行加密操作
byte[] encryptData = cipher.doFinal(encryptText.getBytes());
// 返回加密后的数据
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptData);
}
// 解密
private static String decryptDES(String decryptString, String decryptKey)
throws Exception {
// 先使用Base64解密
byte[] base64byte = Base64.getDecoder().decode(decryptString);
// 实例化IvParameterSpec对象,使用指定的初始化向量
IvParameterSpec spec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
// 实例化SecretKeySpec类,根据字节数组来构造SecretKeySpec
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(decryptKey.getBytes(), "DES");
// 创建密码器
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
// 用密码初始化Cipher对象
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, spec);
// 获取解密后的数据
byte decryptedData[] = cipher.doFinal(base64byte);
// 将解密后数据转换为字符串输出
return new String(decryptedData);
}
}
AES加解密相关代码
public class AESUtil {
// 采用对称分组密码体制,密钥长度的最少支持为128、192、256
String key = "abcdefghijklmnop";
// 初始化向量参数,AES 为16bytes. DES 为8bytes, 16*8=128
String initVector = "0000000000000000";
IvParameterSpec iv;
SecretKeySpec skeySpec;
Cipher cipher;
private static class HOLDER {
private static AESUtil instance = new AESUtil();
}
public static AESUtil getInstance() {
return HOLDER.instance;
}
private AESUtil() {
try {
iv = new IvParameterSpec(initVector.getBytes("UTF-8"));
skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes("UTF-8"), "AES");
// 这是CBC模式
// cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5PADDING");
// 默认就是ECB模式
cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5PADDING");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String encrypt(String value) {
try {
// CBC模式需要传入向量,ECB模式不需要
// cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(value.getBytes());
return Base64.encodeToString(encrypted, Base64.DEFAULT);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public String decrypt(String encrypted) {
try {
// CBC模式需要传入向量,ECB模式不需要
// cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
byte[] original = cipher.doFinal(Base64.decode(encrypted, Base64.DEFAULT));
return new String(original);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
2.3非对称加密
非对称加密:加密和解密的密钥不同,通常是公钥加密私钥解密,当然也可以私钥加密公钥解密,公钥通常用来对内容加密,而私钥既可以解密也可以用来确定是否是对应的公钥加的密,防止他人用错误的公钥进行加密。
非对称加密中另外两个重要的概念是公钥和私钥。公钥对外公开,任何人均可持有和使用;私钥自行保管,其安全性是通信安危的关键。常见的算法有 RSA、DH(Diffie-Hellman)、椭圆曲线算法(Elliptic curve cryptography,ECC)。
私钥和公钥的作用一般分为两种:
公钥加密,私钥解密,主要用于通信;
私钥加密(签名),公钥解密(验证),主要用于数字签名。
RSA算法相关代码
public class RSAUtil {
public static final String RSA = "RSA";
public static final String ECB_PKCS1_PADDING = "RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding";
// 秘钥默认长度
public static final int DEFAULT_KEY_SIZE = 2048;
// 当要加密的内容超过bufferSize,则采用partSplit进行分块加密
public static final byte[] DEFAULT_SPLIT = "#PART#".getBytes();
// 当前秘钥支持加密的最大字节数
public static final int DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE = (DEFAULT_KEY_SIZE / 8) - 11;
// 随机生成RSA密钥对,密钥长度,范围:512~2048
public static KeyPair generateRSAKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(RSA);
kpg.initialize(keyLength);
return kpg.genKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 私钥加密
* @param data 待加密数据
* @param privateKey 密钥
* @return byte[] 加密数据
*/
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
// 得到私钥
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PrivateKey keyPrivate = kf.generatePrivate(keySpec);
// 数据加密
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keyPrivate);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 使用私钥进行解密
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] encrypted, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
// 得到私钥
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PrivateKey keyPrivate = kf.generatePrivate(keySpec);
// 解密数据
Cipher cp = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cp.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keyPrivate);
byte[] arr = cp.doFinal(encrypted);
return arr;
}
// 用公钥对字符串进行加密
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
// 得到公钥
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PublicKey keyPublic = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
// 加密数据
Cipher cp = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cp.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keyPublic);
return cp.doFinal(data);
}
/**
* 公钥解密
* @param data 待解密数据
* @param publicKey 密钥
* @return byte[] 解密数据
*/
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
// 得到公钥
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PublicKey keyPublic = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
// 数据解密
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keyPublic);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
// 以下开始分段解密
// 使用私钥分段解密
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(byte[] encrypted, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
int splitLen = DEFAULT_SPLIT.length;
if (splitLen <= 0) {
return decryptByPrivateKey(encrypted, privateKey);
}
int dataLen = encrypted.length;
List allBytes = new ArrayList(1024);
int latestStartIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
byte bt = encrypted[i];
boolean isMatchSplit = false;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
// 到data的最后了
byte[] part = new byte[dataLen - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPrivateKey(part, privateKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
} else if (bt == DEFAULT_SPLIT[0]) {
// 这个是以split[0]开头
if (splitLen > 1) {
if (i + splitLen < dataLen) {
// 没有超出data的范围
for (int j = 1; j < splitLen; j++) {
if (DEFAULT_SPLIT[j] != encrypted[i + j]) {
break;
}
if (j == splitLen - 1) {
// 验证到split的最后一位,都没有break,则表明已经确认是split段
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
}
} else {
// split只有一位,则已经匹配了
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
if (isMatchSplit) {
byte[] part = new byte[i - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPrivateKey(part, privateKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
// 私钥分段加密
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(byte[] data, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
int dataLen = data.length;
if (dataLen <= DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE) {
return encryptByPrivateKey(data, privateKey);
}
List allBytes = new ArrayList(2048);
int bufIndex = 0;
int subDataLoop = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
buf[bufIndex] = data[i];
if (++bufIndex == DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE || i == dataLen - 1) {
subDataLoop++;
if (subDataLoop != 1) {
for (byte b : DEFAULT_SPLIT) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
}
byte[] encryptBytes = encryptByPrivateKey(buf, privateKey);
for (byte b : encryptBytes) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
bufIndex = 0;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
buf = null;
} else {
buf = new byte[Math.min(DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE, dataLen - i - 1)];
}
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
// 用公钥对字符串进行分段加密
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
int dataLen = data.length;
if (dataLen <= DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE) {
return encryptByPublicKey(data, publicKey);
}
List allBytes = new ArrayList(2048);
int bufIndex = 0;
int subDataLoop = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
buf[bufIndex] = data[i];
if (++bufIndex == DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE || i == dataLen - 1) {
subDataLoop++;
if (subDataLoop != 1) {
for (byte b : DEFAULT_SPLIT) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
}
byte[] encryptBytes = encryptByPublicKey(buf, publicKey);
for (byte b : encryptBytes) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
bufIndex = 0;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
buf = null;
} else {
buf = new byte[Math.min(DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE, dataLen - i - 1)];
}
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
// 公钥分段解密
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(byte[] encrypted, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
int splitLen = DEFAULT_SPLIT.length;
if (splitLen <= 0) {
return decryptByPublicKey(encrypted, publicKey);
}
int dataLen = encrypted.length;
List allBytes = new ArrayList(1024);
int latestStartIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
byte bt = encrypted[i];
boolean isMatchSplit = false;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
// 到data的最后了
byte[] part = new byte[dataLen - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPublicKey(part, publicKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
} else if (bt == DEFAULT_SPLIT[0]) {
// 这个是以split[0]开头
if (splitLen > 1) {
if (i + splitLen < dataLen) {
// 没有超出data的范围
for (int j = 1; j < splitLen; j++) {
if (DEFAULT_SPLIT[j] != encrypted[i + j]) {
break;
}
if (j == splitLen - 1) {
// 验证到split的最后一位,都没有break,则表明已经确认是split段
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
}
} else {
// split只有一位,则已经匹配了
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
if (isMatchSplit) {
byte[] part = new byte[i - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPublicKey(part, publicKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
}
3.数字签名
数字签名的出现一个很重要的作用是解决私钥加密文件过大,耗时过长。同样公钥解密的过程中也很耗时。
数字签名我们来举一个例子:
第一步:.故事主人公A要给B发送一个文件,他首先用哈希算法对文件进行加密得到哈希值,称之为摘要,取名HashA。
第二步:对生成的哈希值进行私钥加密,称之为数字签名。
第三步:A将数字签名和文件一起发送给B。
第四步:B对数字签名进行公钥解密得到Hash值即摘要,如果成功表示来自A。
第五步:B和A一样对正文进行摘要得到Hash值,取名HashB,对比同A的HaahA.如果一致表示文件没有被篡改。
总结:数字签名可以保证文件的来源(即文件来自于B)和完整性.
4.数字证书
说到数字证书,我们还需要拿上面的例子,说明一下数字签名的局限性。我们都知道公钥通常是公开的保存在本地的,如果此时有个C,在B的本地将A的公钥替换为自己的公钥,同时用自己的私钥加密数据传递给B,这样B是没有办法辨别的。
为了解决这个问题,我们引入了CA认证,也就是A拿着自己的公钥去CA中心做认证,证书中心用自己的私钥,对A的公钥和一些相关信息一起加密,生成"数字证书"(Digital Certificate)。然后将之前的数字签名,正文内容,数字证书一起发送给B。
B这边怎么做呢?B用CA给的公钥先解密数字证书得到A的公钥(注意之前公钥可能保存在B的本地中,现在改为网络传输了),然后用A的公钥解密数字签名,在解密的正文和传递的正文作比较。
说了这么多,CA是什么呢?
CA证书就是电子商务认证授权机构,也称为电子商务认证中心,是负责发放和管理数字证书的权威机构,并作为电子商务交易中受信任的第三方,承担公钥体系中公钥的合法性检验的责任。
证书的内容包括:电子签证机关的信息、公钥用户信息、公钥、权威机构的签字和有效期等等。目前,证书的格式和验证方法普遍遵循X.509 国际标准。
所以说CA具有可靠性,也就是说CA生成的数字证书也具有可靠性,如果数字证书被中途篡改,是无法被CA的公钥解密的要是有多个人要给B发邮件,难道B要保存1万份不同的CA公钥吗?
答案:不需要,CA认证中心给可以给B一份“根证书”,里面存储CA公钥来验证所有CA分中心颁发的数字证书。CA中心是分叉树结构,类似于公安部->省公安厅->市级派出所,不管A从哪个CA分支机构申请的证书,B只要预存根证书就可以验证下级证书可靠性。
关于加解密,主要内容就这么多。