乐鑫科技数字芯片2020
(1)序列发生器,产生周期性的"0010110111"序列
module xlgen (clk,rst,Q);
input clk ;
input rst ;
output Q ;
reg Q ;
reg [9:0] Q_r ;
always @( posedge clk or posedge rst)
begin
if (rst == 1)
begin
Q <= 1'b0;
Q_r <= 10'b0010110111;
end
else
begin
Q <= Q_r[9];
Q_r <= Q_r<<1;//左移
Q_r[0] <=Q;//循环
end
end
endmodule(2)饮料售卖机
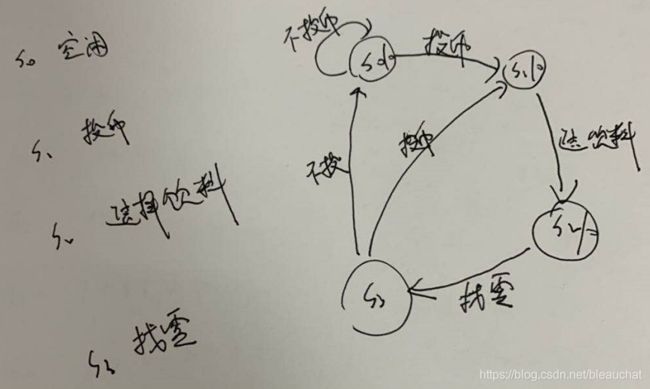
首先画出FSM,第一步定义状态机的输入输出和状态,要记住每次只能投入一个硬币:
输入有三个:a和b,其中a为投入5分的硬币,b为投入10分的硬币,c为选择的饮料类型,c为0选择饮料B,为1选择饮料A;
输出有三个:x,y,z,其中x为输出5分的饮料B,y为输出10分的饮料,z为找零5分;
去抖动模块:
module qu_dou ( clk ,rst , a ,b );
input clk ;
input rst ;
input a ;
output reg b ;
reg [31:0] cnt ;
//reg clkout ;
always @ ( posedge clk or negedge rst )
begin
if ( rst == 1'b0 )
begin
cnt <= 0 ;
b <= 0;
end
else
begin
if ( a==1'b1 )
begin
if ( cnt >= 32'd3000000 )
b <= 1 ;
else
cnt <= cnt + 1'b1 ;
end
else
begin
b <= 1'b0 ;
cnt <= 0 ;
end
end
end
endmodulemodule machine(clk,rst,a,b,c,x,y,z);
input clk,rst;
input a,b;
input [1:0] c;//01为5分饮料,10为10分饮料
output reg x,y,z;
parameter s0=2'b00,s1=2'b01,s2=2'b10,s3=2'b11;
reg [1:0] cs,ns;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(~rst)
cs <= s0;
else
cs <= ns;
end
reg [1:0] coin_in;
reg [1:0] drink_in;
always @(*)
begin
if(~rst)
ns = s0;
coin_in = 0;
drink_in = 0;
else
begin
case(cs)
s0:begin
if({a,b} == 2'b01)//投入10分硬币
begin
ns = s1;
coin_in = 2'b10;
end
else if({a,b} == 2'b10)
begin
ns = s1;
coin_in = 2'b01;
end
else
ns = s0;
end
endcase
s1:begin
if(c == 2'10)//选择10分的饮料
begin
drink_in = 2'b10;
ns = s2;
end
else if(c == 2'b01)
begin
drink_in = 2'b01;
ns = s2;
end
else
ns = s0;
end
s2:begin
if(coin_in == 2'b10 || coin_in = 2'b01)
ns = s3;
else
ns = s0;
end
s3:begin
if({a,b} == 2'b01)//投入10分硬币
begin
ns = s1;
coin_in = 2'b10;
end
else if({a,b} == 2'b10)
begin
ns = s1;
coin_in = 2'b01;
end
else
ns = s0;
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(~rst)
begin
{x,y,z}=3'd0;
end
else if(cs == s3)
begin
if(coin_in = 2'b10 && drink_in = 2'b10)
{x,y,z}=3'b010;
else if(coin_in = 2'b10 && drink_in = 2'b01)
{x,y,z}=3'b101;
else if(coin_in = 2'b01 && drink_in = 2'b01)
{x,y,z}=3'b100;
else if(coin_in = 2'b10 && drink_in = 2'b10)
{x,y,z}=3'b001;
else
{x,y,z}=3'd0;
end
end
endmodule
题目要求:将一个串行执行的C语言算法转化为单拍完成的并行可综合verilog
C语言源码如下:
unsignedcharcal_table_high_first(unsignedcharvalue)
{
unsigned char i ;
unsigned char checksum = value ;
for (i=8;i>0;--i)
{
if (check_sum& 0x80)
{
check_sum = (check_sum<<1) ^ 0x31;
}
else
{
check_sum = (check_sum << 1);
}
}
return check_sum;算法C语言实现:
#include
int main(){
unsignedchar cal_table_high_first(unsignedchar value);
unsignedchar data;
for (unsignedchar i = 0; i < 16;++i)
{
data= cal_table_high_first(i);
printf("value =0x%0x:check_sum=0x%0x \n", i, data);
}
getchar();
}
unsignedchar cal_table_high_first(unsignedchar value)
{
unsignedchar i;
unsigned char check_sum = value;
for (i = 8; i > 0;--i)
{
if (check_sum &0x80)
{
check_sum= (check_sum << 1) ^ 0x31;
}
else
{
check_sum= (check_sum << 1);
}
}
return check_sum;
} 该算法逻辑如下:
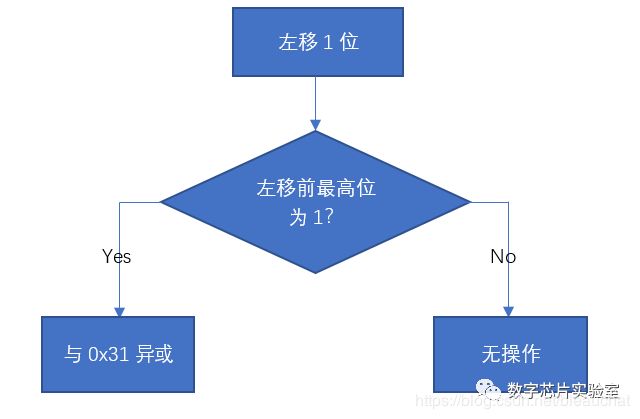
输入一个8bit的数,首先判断最高位是否为1,如果为1则左移一位,并且和8‘b00110001异或;如果最高位不为1则左移一位。此过程执行8次
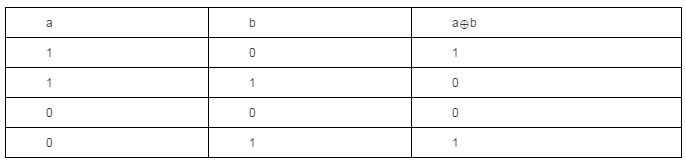
此时我们来看一下异或操作的真值表
我们可以看出:任何数与0异或都等于它本身,即0^x=x。所以我们可以把算法流程变换为:
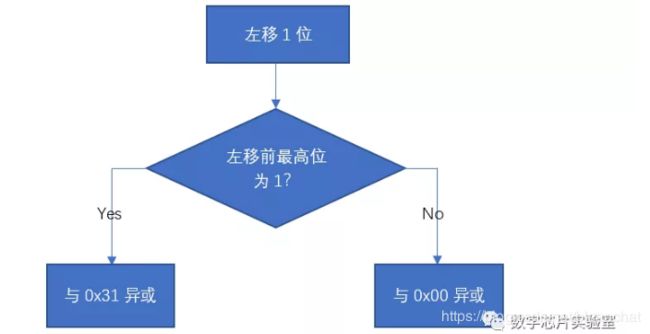
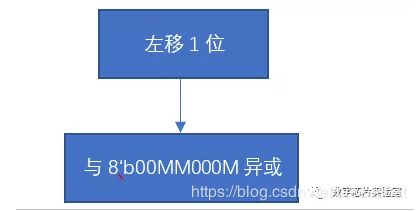
8'h31 = 8'b00110001, 8'h00 = 8'b00000000,设左移前最高位为M,可以将判断左移前最高位是否为1的过程省略,直接与8'b00MM000M异或,此时流程图可以简化为:
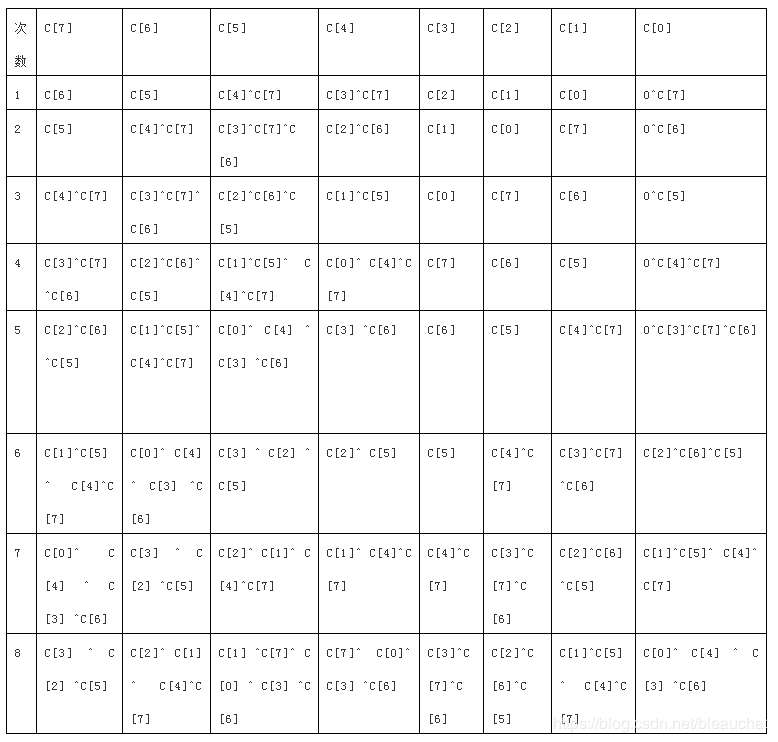
由此,我们可以将循环解开,设输入为一个8bit数C[7:0],下面为解循环过程:
根据上述结果,可以用verilog描述:
module loop1(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0] check_sum,
output reg [7:0] check_sum_o
);
//reg [7:0] check_sum_o;
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
begin
check_sum_o<= 8'h0;
end
else
begin
check_sum_o[7]<= check_sum[3]^check_sum[2]^check_sum[5];
check_sum_o[6]<= check_sum[2]^check_sum[1]^check_sum[4]^check_sum[7];
check_sum_o[5]<= check_sum[1]^check_sum[7]^check_sum[0]^check_sum[3]^check_sum[6];
check_sum_o[4]<= check_sum[7]^check_sum[0]^check_sum[3]^check_sum[6];
check_sum_o[3]<= check_sum[3]^check_sum[7]^check_sum[6];
check_sum_o[2]<= check_sum[2]^check_sum[6]^check_sum[5];
check_sum_o[1]<= check_sum[1]^check_sum[5]^check_sum[4]^check_sum[7];
check_sum_o[0]<= check_sum[0]^check_sum[4]^check_sum[3]^check_sum[6];
end
endmodule驱动4x4矩阵键盘的思路
图1 4x4矩阵键盘的SCH(箭头表示输入输出方向)
如图所示,将ROW[3:0]设为输入,COL[3:0]设为输出。如果没有任何键被按下,则ROW[3:0]一直被上拉为高电平。只有当有键被按下,且COL[3:0]中有低电平输出,ROW[3:0]中才有可能有低电平输入,也可说是被动地输入
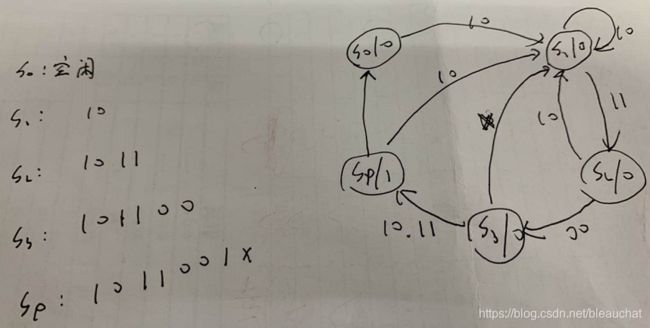
请实现对(1011001)2的序列检测功能,模块每拍并行输入2bit,且顺序为高位先输入,当检测到序列,输出一拍高电平脉冲。请用Verilog描述该模块
相当于检测10 11 00 1x,状态转换图
module sequence_check_2bit(clk,rst,seq_in,out_pulse);
input clk,rst;
input [1:0] seq_in;
output reg out_pulse;
parameter s0=3'b000,s1=3'b001,s2=3'b010,s3=3'b011,s4=3'b100;
reg [1:0] cs,ns;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(~rst)
begin
cs <= 0;
ns <= 0;
end
else
begin
cs <= ns;
end
end
always @(*)
begin
if(rst)
ns = s0;
else
begin
case(cs)
s0:begin
if(seq_in == 2'b10)
ns = s1;
else
ns = s0;
end
s1:begin
if(seq_in == 2'b10)
ns = s1;
else if(seq_in == 2'b11)
ns = s2;
else
ns = s0;
end
s2:begin
if(seq_in == 2'b00)
ns = s3;
else if(seq_in == 2'b10)
ns = s1;
else
ns = s0;
end
s3:begin
if(seq_in == 2'b10 || seq_in == 2'b11)
ns = s4;
else
ns = s0;
end
s4:begin
if(seq_in == 2'b10)
ns = s1;
else
ns = s0;
end
default: ns = s0;
endcase
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)
begin
if(~rst)
out_pulse <= 0;
else
out_pulse <=(cs == s4)?1'b1:1'b0;
end
endmodule