NIO Channel和Buffer
前言
Java NIO 由以下几个核心部分组成:
- Buffer
- Channel
- Selector
传统的IO操作面向数据流,意味着每次从流中读一个或多个字节,直至完成,数据没有被缓存在任何地方。NIO操作面向缓冲区,数据从Channel读取到Buffer缓冲区,随后在Buffer中处理数据。本文着重介绍Channel和Buffer的概念以及在文件读写方面的应用和内部实现原理。
Buffer
A buffer is a linear, finite sequence of elements of a specific primitive type.
一块缓存区,内部使用字节数组存储数据,并维护几个特殊变量,实现数据的反复利用。
- mark:初始值为-1,用于备份当前的position
- position:初始值为0。position表示当前可以写入或读取数据的位置。当写入或读取一个数据后, position向前移动到下一个位置。
- limit:
写模式下,limit表示最多能往Buffer里写多少数据,等于capacity值。
读模式下,limit表示最多可以读取多少数据。 - capacity:缓存数组大小
mark():把当前的position赋值给mark
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}reset():把mark值还原给position
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}clear():一旦读完Buffer中的数据,需要让Buffer准备好再次被写入,clear会恢复状态值,但不会擦除数据。
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}flip():Buffer有两种模式,写模式和读模式,flip后Buffer从写模式变成读模式。
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}rewind():重置position为0,从头读写数据。
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
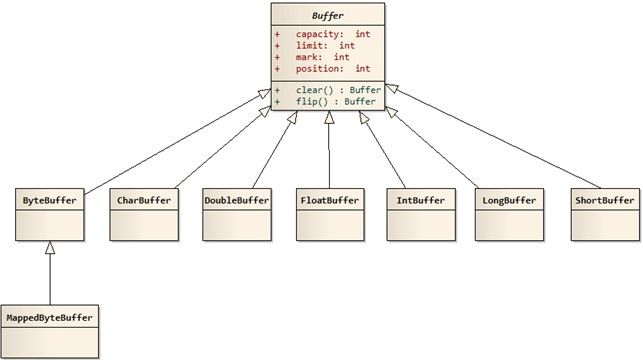
}目前Buffer的实现类有以下几种:
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- MappedByteBuffer
其中MappedByteBuffer实现比较特殊,感兴趣的可以看看 深入浅出MappedByteBuffer
ByteBuffer
A byte buffer,extend from Buffer
ByteBuffer的实现类包括HeapByteBuffer和DirectByteBuffer两种。
-
HeapByteBuffer
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) { if (capacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity); } HeapByteBuffer(int cap, int lim) { super(-1, 0, lim, cap, new byte[cap], 0); }HeapByteBuffer通过初始化字节数组hd,在虚拟机堆上申请内存空间。
-
DirectByteBuffer
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) { return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity); } DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { super(-1, 0, cap, cap); boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned(); int ps = Bits.pageSize(); long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0)); Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap); long base = 0; try { base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size); } catch (OutOfMemoryError x) { Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap); throw x; } unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0); if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) { // Round up to page boundary address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1)); } else { address = base; } cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap)); att = null; }DirectByteBuffer通过unsafe.allocateMemory在物理内存中申请地址空间(非jvm堆内存),并在ByteBuffer的address变量中维护指向该内存的地址。
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0)方法把新申请的内存数据清零。
Channel
A channel represents an open connection to an entity such as a hardware device, a file, a network socket, or a program component that is capable of performing one or more distinct I/O operations, for example reading or writing.
又称“通道”,NIO把它支持的I/O对象抽象为Channel,类似于原I/O中的流(Stream),但有所区别:
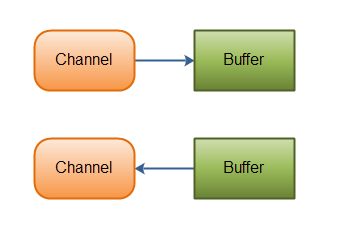
- 流是单向的,通道是双向的,可读可写。
- 流读写是阻塞的,通道可以异步读写。
- 流中的数据可以选择性的先读到缓存中,通道的数据总是要先读到一个缓存中,或从缓存中写入,如下所示:
目前已知Channel的实现类有:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
FileChannel
A channel for reading, writing, mapping, and manipulating a file.
一个用来写、读、映射和操作文件的通道。
FileChannel的read、write和map通过其实现类FileChannelImpl实现。
-
read实现
public int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (!readable) throw new NonReadableChannelException(); synchronized (positionLock) { int n = 0; int ti = -1; try { begin(); ti = threads.add(); if (!isOpen()) return 0; do { n = IOUtil.read(fd, dst, -1, nd); } while ((n == IOStatus.INTERRUPTED) && isOpen()); return IOStatus.normalize(n); } finally { threads.remove(ti); end(n > 0); assert IOStatus.check(n); } } }FileChannelImpl的read方法通过IOUtil的read实现:
static int read(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer dst, long position, NativeDispatcher nd) IOException { if (dst.isReadOnly()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Read-only buffer"); if (dst instanceof DirectBuffer) return readIntoNativeBuffer(fd, dst, position, nd); // Substitute a native buffer ByteBuffer bb = Util.getTemporaryDirectBuffer(dst.remaining()); try { int n = readIntoNativeBuffer(fd, bb, position, nd); bb.flip(); if (n > 0) dst.put(bb); return n; } finally { Util.offerFirstTemporaryDirectBuffer(bb); } }通过上述实现可以看出,基于channel的文件数据读取步骤如下:
1、申请一块和缓存同大小的DirectByteBuffer bb。
2、读取数据到缓存bb,底层由NativeDispatcher的read实现。
3、把bb的数据读取到dst(用户定义的缓存,在jvm中分配内存)。
read方法导致数据复制了两次。 -
write实现
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException { ensureOpen(); if (!writable) throw new NonWritableChannelException(); synchronized (positionLock) { int n = 0; int ti = -1; try { begin(); ti = threads.add(); if (!isOpen()) return 0; do { n = IOUtil.write(fd, src, -1, nd); } while ((n == IOStatus.INTERRUPTED) && isOpen()); return IOStatus.normalize(n); } finally { threads.remove(ti); end(n > 0); assert IOStatus.check(n); } } }和read实现一样,FileChannelImpl的write方法通过IOUtil的write实现:
static int write(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer src, long position, NativeDispatcher nd) throws IOException { if (src instanceof DirectBuffer) return writeFromNativeBuffer(fd, src, position, nd); // Substitute a native buffer int pos = src.position(); int lim = src.limit(); assert (pos <= lim); int rem = (pos <= lim ? lim - pos : 0); ByteBuffer bb = Util.getTemporaryDirectBuffer(rem); try { bb.put(src); bb.flip(); // Do not update src until we see how many bytes were written src.position(pos); int n = writeFromNativeBuffer(fd, bb, position, nd); if (n > 0) { // now update src src.position(pos + n); } return n; } finally { Util.offerFirstTemporaryDirectBuffer(bb); } }通过上述实现可以看出,基于channel的文件数据写入步骤如下:
1、申请一块DirectByteBuffer,bb大小为byteBuffer中的limit - position。
2、复制byteBuffer中的数据到bb中。
3、把数据从bb中写入到文件,底层由NativeDispatcher的write实现,具体如下:private static int writeFromNativeBuffer(FileDescriptor fd, ByteBuffer bb, long position, NativeDispatcher nd) throws IOException { int pos = bb.position(); int lim = bb.limit(); assert (pos <= lim); int rem = (pos <= lim ? lim - pos : 0); int written = 0; if (rem == 0) return 0; if (position != -1) { written = nd.pwrite(fd, ((DirectBuffer)bb).address() + pos, rem, position); } else { written = nd.write(fd, ((DirectBuffer)bb).address() + pos, rem); } if (written > 0) bb.position(pos + written); return written; }write方法也导致了数据复制了两次
Channel和Buffer示例
File file = new RandomAccessFile("data.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
while (bytesRead != -1) {
System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead);
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.print((char) buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear();
bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
}
file.close();注意buffer.flip() 的调用,首先将数据写入到buffer,然后变成读模式,再从buffer中读取数据。