4.推荐系统之Hive
一.Hive简介
1.1什么是Hive
- Hive 由 Facebook 实现并开源,是基于 Hadoop 的一个数据仓库工具,可以将结构化的数据映射为一张数据库表,并提供 HQL(Hive SQL)查询功能,底层数据是存储在 HDFS 上。
- Hive 本质: 将 SQL 语句转换为 MapReduce 任务运行,使不熟悉 MapReduce 的用户很方便地利用 HQL 处理和计算 HDFS 上的结构化的数据,是一款基于 HDFS 的 MapReduce 计算框架
- 主要用途:用来做离线数据分析,比直接用 MapReduce 开发效率更高。
为什么使用Hive:
- 直接使用 Hadoop MapReduce 处理数据所面临的问题:
- 人员学习成本太高
- MapReduce 实现复杂查询逻辑开发难度太大
- 使用 Hive
- 操作接口采用类 SQL 语法,提供快速开发的能力
- 避免了去写 MapReduce,减少开发人员的学习成本
- 功能扩展很方便
1.2 Hive架构
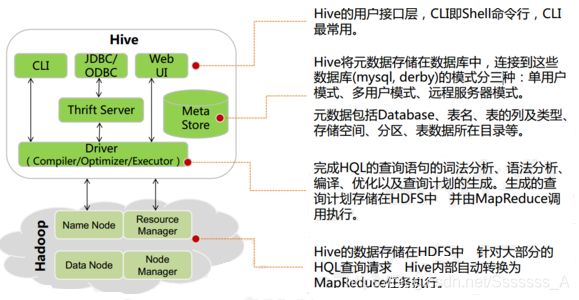
1.2.1 Hive架构图
1.2.2 Hive组件
- 用户接口:包括 CLI、JDBC/ODBC、WebGUI。
- CLI(command line interface)为 shell 命令行
- JDBC/ODBC 是 Hive 的 JAVA 实现,与传统数据库JDBC 类似
- WebGUI 是通过浏览器访问 Hive。
- HiveServer2基于Thrift, 允许远程客户端使用多种编程语言如Java、Python向Hive提交请求
- 元数据存储:通常是存储在关系数据库如 mysql/derby 中。
- Hive 将元数据存储在数据库中。
- Hive 中的元数据包括
- 表的名字
- 表的列
- 分区及其属性
- 表的属性(是否为外部表等)
- 表的数据所在目录等。
- 解释器、编译器、优化器、执行器:完成 HQL 查询语句从词法分析、语法分析、编译、优化以及查询计划的生成。生成的查询计划存储在 HDFS 中,并在随后由 MapReduce 调用执行
1.2.3 Hive与Hadoop的关系
Hive 利用 HDFS 存储数据,利用 MapReduce 查询分析数据。
Hive是数据仓库工具,没有集群的概念,如果想提交Hive作业只需要在hadoop集群 Master节点上装Hive就可以了
1.3 Hive与传统数据库对比
-
hive用于海量数据的离线数据分析
Hive 关系型数据库 ANSI SQL 不完全支持 支持 更新 INSERT OVERWRITE\INTO TABLE UPDATE\INSERT|DELETE 事务 不支持 支持 模式 读模式 写模式 查询语言 HQL SQL 数据存储 HDFS Raw Device or Local FS 执行 MapReduce Executor 执行延迟 高 低 子查询 只能在From子句中 完全支持 处理数据规模 大 小 可扩展性 高 低 索引 0.8版本后加入位图索引 有复杂的索引 -
Hive支持的数据类型
- 原子数据类型
- TINYINT SMALLINT INT BIGINT BOOLEAN FLOAT DOUBLE STRING BINARY TIMESTAMP DECIMAL CHAR VARCHAR DATE
- 复杂数据类型
- ARRAY
- MAP
- STRUCT
- 原子数据类型
-
hive中表的类型
- 托管表 (managed table) (内部表)
- 外部表
1.4 Hive数据模型
- ive 中所有的数据都存储在 HDFS 中,没有专门的数据存储格式
- 在创建表时指定数据中的分隔符,Hive 就可以映射成功,解析数据。
- Hive 中包含以下数据模型:
- db:在 hdfs 中表现为 hive.metastore.warehouse.dir 目录下一个文件夹
- table:在 hdfs 中表现所属 db 目录下一个文件夹
- external table:数据存放位置可以在 HDFS 任意指定路径
- partition:在 hdfs 中表现为 table 目录下的子目录
- bucket:在 hdfs 中表现为同一个表目录下根据 hash 散列之后的多个文件
二.Hive基本操作
2.1 Hive HQL基本操作
-
创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE test; -
显示所有数据库
SHOW DATABASES; -
创建表
CREATE TABLE student(classNo string, stuNo string, score int) row format delimited fields terminated by ',';- row format delimited fields terminated by ‘,’ 指定了字段的分隔符为逗号,所以load数据的时候,load的文本也要为逗号,否则加载后为NULL。hive只支持单个字符的分隔符,hive默认的分隔符是\001
-
将数据load到表中
-
在本地文件系统创建一个如下的文本文件:/home/hadoop/tmp/student.txt
C01,N0101,82 C01,N0102,59 C01,N0103,65 C02,N0201,81 C02,N0202,82 C02,N0203,79 C03,N0301,56 C03,N0302,92 C03,N0306,72 -
load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/tmp/student.txt'overwrite into table student; -
这个命令将student.txt文件复制到hive的warehouse目录中,这个目录由hive.metastore.warehouse.dir配置项设置,默认值为/user/hive/warehouse。Overwrite选项将导致Hive事先删除student目录下所有的文件, 并将文件内容映射到表中。 Hive不会对student.txt做任何格式处理,因为Hive本身并不强调数据的存储格式。
-
-
查询表中的数据,跟SQL类似
hive>select * from student; -
分组查询group by和统计count
hive>select classNo,count(score) from student where score>=60 group by classNo;从执行结果可以看出 hive把查询的结果变成了MapReduce作业通过hadoop执行
2.2 Hive的内部表和外部表
| 内部表 | 外部表 | |
|---|---|---|
| 概念 | 创建表时无external修饰 | 创建表时被external修饰 |
| 数据管理 | 由Hive自身管理 | 由HDFS管理 |
| 数据保存位置 | Hive.metastore.warehouse.dir | hdfs中任意位置 |
| 删除时影响 | 直接删除元数据(metastore)及存储数据 | 仅会删除元数据,HDFS上的数据不会被删除 |
| 表结构修改时的影响 | 修改会将修改直接同步给元数据 | 表结构和分区进行修改,则需要修复 |
2.3分区表
-
什么是分区表
- 随着表的不断增大,对于新纪录的增加,查找,删除等(DML)的维护也更加困难。对于数据库中的超大型表,可以通过把它的数据分成若干个小表,从而简化数据库的管理活动,对于每一个简化后的小表,我们称为一个单个的分区。
- hive中分区表实际就是对应hdfs文件系统上独立的文件夹,该文件夹内的文件是该分区所有数据文件。
- 分区可以理解为分类,通过分类把不同类型的数据放到不同的目录下。
- 分类的标准就是分区字段,可以一个,也可以多个。
- 分区表的意义在于优化查询。查询时尽量利用分区字段。如果不使用分区字段,就会全部扫描。
-
创建分区表
tom,4300 jerry,12000 mike,13000 jake,11000 rob,10000
create table employee (name string,salary bigint) partitioned by (date1 string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile;
-
查看表的分区
show partitions employee; -
添加分区
alter table employee add if not exists partition(date1='2018-12-01'); -
加载数据到分区
load data local inpath '/root/tmp/employee.txt' into table employee partition(date1='2018-12-01'); -
如果重复加载同名文件,不会报错,会自动创建一个*_copy_1.txt文件
-
外部分区表即使有分区的目录结构,也必须要通过hql添加分区,才能看到相应的数据
hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hive/warehouse/employee/date1=2018-12-04 hadoop fs -copyFromLocal /tmp/employee.txt /user/hive/warehouse/test.db/employee/date1=2018-12-04/employee.txt-
此时查看表中数据发现数据并没有变化, 需要通过hql添加分区
alter table employee add if not exists partition(date1='2018-12-04'); -
此时再次查看才能看到新加入的数据
-
-
总结
- 利用分区表方式减少查询时需要扫描的数据量
- 分区字段不是表中的列, 数据文件中没有对应的列
- 分区仅仅是一个目录名
- 查看数据时, hive会自动添加分区列
- 支持多级分区, 多级子目录
- 利用分区表方式减少查询时需要扫描的数据量
2.4动态分区
-
在写入数据时自动创建分区(包括目录结构)
-
创建表
create table employee2 (name string,salary bigint) partitioned by (date1 string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile; -
导入数据
insert into table employee2 partition(date1) select name,salary,date1 from employee; -
使用动态分区需要设置参数
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;
三.Hive函数
3.1内置运算符
在hive有四种类型的运算符:
- 关系运算符
- 算术运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 复杂运算
3.2内置函数
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+UDF
- 简单函数: 日期函数 字符串函数 类型转换
- 统计函数: sum avg distinct
- 集合函数
- 分析函数
- show functions; 显示所有函数
- desc function 函数名;
- desc function extended 函数名
3.3 Hive自定义函数和Transform
3.3.1 UDF
当 Hive 提供的内置函数无法满足你的业务处理需要时,此时就可以考虑使用用户自定义函数(UDF:user-defined function)。
it is possible to plug in your own custom mappers and reducers
A UDF is basically only a transformation done by a mapper meaning that each row should be mapped to exactly one row. A UDAF on the other hand allows us to transform a group of rows into one or more rows, meaning that we can reduce the number of input rows to a single output row by some custom aggregation.
UDF:就是做一个mapper,对每一条输入数据,映射为一条输出数据。
UDAF:就是一个reducer,把一组输入数据映射为一条(或多条)输出数据。
一个脚本至于是做mapper还是做reducer,又或者是做udf还是做udaf,取决于我们把它放在什么样的hive操作符中。放在select中的基本就是udf,放在distribute by和cluster by中的就是reducer。
We can control if the script is run in a mapper or reducer step by the way we formulate our HiveQL query.
The statements DISTRIBUTE BY and CLUSTER BY allow us to indicate that we want to actually perform an aggregation.
User-Defined Functions (UDFs) for transformations and even aggregations which are therefore called User-Defined Aggregation Functions (UDAFs)
3.3.2 UDF使用示例
-
在hdfs中创建 /user/hive/lib目录
hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hive/lib -
把 hive目录下 lib/hive-contrib-hive-contrib-1.1.0-cdh5.7.0.jar 放到hdfs中
hadoop fs -put hive-contrib-1.1.0-cdh5.7.0.jar /user/hive/lib/ -
把集群中jar包的位置添加到hive中
hive> add jar hdfs:///user/hive/lib/hive-contrib-1.1.0-cdh5.7.0.jar; -
在hive中创建临时UDF
hive> CREATE TEMPORARY FUNCTION row_sequence as 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.udf.UDFRowSequence' -
在之前的案例中使用临时自定义函数(函数功能: 添加自增长的行号)
Select row_sequence(),* from employee; -
创建非临时自定义函数
CREATE FUNCTION row_sequence as 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.contrib.udf.UDFRowSequence' using jar 'hdfs:///user/hive/lib/hive-contrib-1.1.0-cdh5.7.0.jar';
3.3.3 Python UDF
-
准备案例环境
-
创建表
CREATE table u(fname STRING,lname STRING); -
向表中插入数据
insert into table u2 values('George','washington'); insert into table u2 values('George','bush'); insert into table u2 values('Bill','clinton'); insert into table u2 values('Bill','gates');
-
-
编写map风格脚本
import sys for line in sys.stdin: line = line.strip() fname , lname = line.split('\t') l_name = lname.upper() print '\t'.join([fname, str(l_name)]) -
通过hdfs向hive中add file
-
加载文件到hdfs
hadoop fs -put udf.py /user/hive/lib/ -
hive从hdfs中加载python脚本
ADD FILE hdfs:///user/hive/lib/udf.py; ADD FILE /root/tmp/udf1.py;
-
-
Transform
SELECT TRANSFORM(fname, lname) USING 'python udf1.py' AS (fname, l_name) FROM u;
四.Hive综合案例
4.1内容推荐数据处理
- 需求
- 根据用户行为以及文章标签筛选出用户最感兴趣(阅读最多的)标签
4.2相关数据
- user_id article_id event_time
11,101,2018-12-01 06:01:10
22,102,2018-12-01 07:28:12
33,103,2018-12-01 07:50:14
11,104,2018-12-01 09:08:12
22,103,2018-12-01 13:37:12
33,102,2018-12-02 07:09:12
11,101,2018-12-02 18:42:12
35,105,2018-12-03 09:21:12
22,104,2018-12-03 16:42:12
77,103,2018-12-03 18:31:12
99,102,2018-12-04 00:04:12
33,101,2018-12-04 19:10:12
11,101,2018-12-05 09:07:12
35,102,2018-12-05 11:00:12
22,103,2018-12-05 12:11:12
77,104,2018-12-05 18:02:02
99,105,2018-12-05 20:09:11
-
文章数据
artical_id,artical_url,artical_keywords 101,http://www.itcast.cn/1.html,kw8|kw1 102,http://www.itcast.cn/2.html,kw6|kw3 103,http://www.itcast.cn/3.html,kw7 104,http://www.itcast.cn/4.html,kw5|kw1|kw4|kw9 105,http://www.itcast.cn/5.html,
4.3处理步骤
-
数据上传hdfs
hadoop fs -mkdir /tmp/demo hadoop fs -mkdir /tmp/demo/user_action -
创建外部表
-
用户行为表
drop table if exists user_actions; CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE user_actions( user_id STRING, article_id STRING, time_stamp STRING ) ROW FORMAT delimited fields terminated by ',' LOCATION '/tmp/demo/user_action'; -
文章表
drop table if exists articles; CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE articles( article_id STRING, url STRING, key_words array<STRING> ) ROW FORMAT delimited fields terminated by ',' COLLECTION ITEMS terminated BY '|' LOCATION '/tmp/demo/article_keywords'; /* key_words array数组的数据类型 COLLECTION ITEMS terminated BY '|' 数组的元素之间用'|'分割 */ -
查看数据
select * from user_actions; select * from articles; -
分组查询每个用户的浏览记录
-
collect_set/collect_list作用:
- 将group by中的某列转为一个数组返回
- collect_list不去重而collect_set去重
-
collect_set
select user_id,collect_set(article_id) from user_actions group by user_id;select user_id,collect_list(article_id) from user_actions group by user_id; -
sort_array: 对数组排序
select user_id,sort_array(collect_list(article_id)) as contents from user_actions group by user_id;11 ["101","101","101","104"] 22 ["102","103","103","104"] 33 ["101","102","103"] 35 ["102","105"] 77 ["103","104"] 99 ["102","105"]
-
-
查看每一篇文章的关键字 lateral view explode
-
explode函数 将array 拆分
select explode(key_words) from articles; -
lateral view 和 explode 配合使用,将一行数据拆分成多行数据,在此基础上可以对拆分的数据进行聚合
select article_id,kw from articles lateral view explode(key_words) t as kw;101 kw8 101 kw1 102 kw6 102 kw3 103 kw7 104 kw5 104 kw1 104 kw4 104 kw9select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw;101 kw8 101 kw1 102 kw6 102 kw3 103 kw7 104 kw5 104 kw1 104 kw4 104 kw9 105 NULL #含有outer
-
-
4.4获取结果
-
根据文章id找到用户查看文章的关键字
-
原始数据
101 http://www.itcast.cn/1.html ["kw8","kw1"] 102 http://www.itcast.cn/2.html ["kw6","kw3"] 103 http://www.itcast.cn/3.html ["kw7"] 104 http://www.itcast.cn/4.html ["kw5","kw1","kw4","kw9"] 105 http://www.itcast.cn/5.html []
select a.user_id, b.kw from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) order by a.user_id;11 kw1 11 kw8 11 kw5 11 kw1 11 kw4 11 kw1 11 kw9 11 kw8 11 kw1 11 kw8 22 kw1 22 kw7 22 kw9 22 kw4 22 kw5 22 kw7 22 kw3 22 kw6 33 kw8 33 kw1 33 kw3 33 kw6 33 kw7 35 NULL 35 kw6 35 kw3 77 kw9 77 kw1 77 kw7 77 kw4 77 kw5 99 kw3 99 kw6 99 NULL -
-
根据文章id找到用户查看文章的关键字并统计频率
select a.user_id, b.kw,count(1) as weight from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) group by a.user_id,b.kw order by a.user_id,weight desc;11 kw1 4 11 kw8 3 11 kw5 1 11 kw9 1 11 kw4 1 22 kw7 2 22 kw9 1 22 kw1 1 22 kw3 1 22 kw4 1 22 kw5 1 22 kw6 1 33 kw3 1 33 kw8 1 33 kw7 1 33 kw6 1 33 kw1 1 35 NULL 1 35 kw3 1 35 kw6 1 77 kw1 1 77 kw4 1 77 kw5 1 77 kw7 1 77 kw9 1 99 NULL 1 99 kw3 1 99 kw6 1 -
CONCAT: CONCAT(str1,str2,…)
返回结果为连接参数产生的字符串。如有任何一个参数为NULL ,则返回值为 NULL。
select concat(user_id,article_id) from user_actions;CONCAT_WS:
使用语法为:CONCAT_WS(separator,str1,str2,…)
CONCAT_WS() 代表 CONCAT With Separator ,是CONCAT()的特殊形式。第一个参数是其它参数的分隔符。分隔符的位置放在要连接的两个字符串之间。分隔符可以是一个字符串,也可以是其它参数。如果分隔符为 NULL,则结果为 NULL。
select concat_ws(':',user_id,article_id) from user_actions;
4.5处理分析结果
-
将用户查看的关键字和频率合并成 key:value形式并按用户聚合
select a.user_id, concat_ws(':',b.kw,cast (count(1) as string)) as kw_w from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) group by a.user_id,b.kw;11 kw1:4 11 kw4:1 11 kw5:1 11 kw8:3 11 kw9:1 22 kw1:1 22 kw3:1 22 kw4:1 22 kw5:1 22 kw6:1 22 kw7:2 22 kw9:1 33 kw1:1 33 kw3:1 33 kw6:1 33 kw7:1 33 kw8:1 35 1 35 kw3:1 35 kw6:1 77 kw1:1 77 kw4:1 77 kw5:1 77 kw7:1 77 kw9:1 99 1 99 kw3:1 99 kw6:1 -
将用户查看的关键字和频率合并成 key:value形式并按用户聚合
select cc.user_id,concat_ws(',',collect_set(cc.kw_w)) from( select a.user_id, concat_ws(':',b.kw,cast (count(1) as string)) as kw_w from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) group by a.user_id,b.kw ) as cc group by cc.user_id;11 kw1:4,kw4:1,kw5:1,kw8:3,kw9:1 22 kw1:1,kw3:1,kw4:1,kw5:1,kw6:1,kw7:2,kw9:1 33 kw1:1,kw3:1,kw6:1,kw7:1,kw8:1 35 1,kw3:1,kw6:1 77 kw1:1,kw4:1,kw5:1,kw7:1,kw9:1 99 1,kw3:1,kw6:1 -
将上面聚合结果转换成map
select cc.user_id,str_to_map(concat_ws(',',collect_set(cc.kw_w))) as wm from( select a.user_id, concat_ws(':',b.kw,cast (count(1) as string)) as kw_w from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) group by a.user_id,b.kw ) as cc group by cc.user_id;11 {"kw1":"4","kw4":"1","kw5":"1","kw8":"3","kw9":"1"} 22 {"kw1":"1","kw3":"1","kw4":"1","kw5":"1","kw6":"1","kw7":"2","kw9":"1"} 33 {"kw1":"1","kw3":"1","kw6":"1","kw7":"1","kw8":"1"} 35 {"1":null,"kw3":"1","kw6":"1"} 77 {"kw1":"1","kw4":"1","kw5":"1","kw7":"1","kw9":"1"} 99 {"1":null,"kw3":"1","kw6":"1"} -
将用户的阅读偏好结果保存到表中
create table user_kws as select cc.user_id,str_to_map(concat_ws(',',collect_set(cc.kw_w))) as wm from( select a.user_id, concat_ws(':',b.kw,cast (count(1) as string)) as kw_w from user_actions as a left outer JOIN (select article_id,kw from articles lateral view outer explode(key_words) t as kw) b on (a.article_id = b.article_id) group by a.user_id,b.kw ) as cc group by cc.user_id; -
从表中通过key查询map中的值
select user_id, wm['kw1'] from user_kws;11 4 22 1 33 1 35 NULL 77 1 99 NULL -
从表中获取map中所有的key 和 所有的value
select user_id,map_keys(wm),map_values(wm) from user_kws;11 ["kw1","kw4","kw5","kw8","kw9"] ["4","1","1","3","1"] 22 ["kw1","kw3","kw4","kw5","kw6","kw7","kw9"] ["1","1","1","1","1","2","1"] 33 ["kw1","kw3","kw6","kw7","kw8"] ["1","1","1","1","1"] 35 ["1","kw3","kw6"] [null,"1","1"] 77 ["kw1","kw4","kw5","kw7","kw9"] ["1","1","1","1","1"] 99 ["1","kw3","kw6"] [null,"1","1"] -
用lateral view explode把map中的数据转换成多列
select user_id,keyword,weight from user_kws lateral view explode(wm) t as keyword,weight;11 kw1 4 11 kw4 1 11 kw5 1 11 kw8 3 11 kw9 1 22 kw1 1 22 kw3 1 22 kw4 1 22 kw5 1 22 kw6 1 22 kw7 2 22 kw9 1 33 kw1 1 33 kw3 1 33 kw6 1 33 kw7 1 33 kw8 1 35 1 NULL 35 kw3 1 35 kw6 1 77 kw1 1 77 kw4 1 77 kw5 1 77 kw7 1 77 kw9 1 99 1 NULL 99 kw3 1 99 kw6 1