论文阅读笔记-《Pose-Based View Synthesis for Vehicles: A Perspective Aware Method》
论文阅读笔记-《Pose-Based View Synthesis for Vehicles: A Perspective Aware Method》
前言
算是开了一个新的栏目?
一直看论文不分享,只输入,不输出,效果总感觉不太好。
那就尽量每天分享一篇自己的阅读笔记?我看好多大佬都是这么操作的。
今天先看看能不能找到一个合适的模式,便于记录,也能让更好的理解文章的思路?
行文逻辑用平时汇报的思路?
- 论文背景,领域,作者,发表的期刊会议,被引用数,一句话介绍论文;
- 创新点和贡献;
- 相关领域的概述(related work);
- 主要的信息流(approach)
- 总结
以及中间穿插一些,我觉得可以摘录的句子(英语还是太差,无脑auto-encoder也许有用)
一. 论文简介
1. 作者:
北航的团队,这个团队和我们组的研究方向不太相关,所以之前不熟。
2. 期刊杂志:
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 29, 2020 5163
知乎搜了一下,顶刊
3. 引用数:
目前还没有。
4. 论文背景,领域
新视角合成(novel view synthesis),这个操作我之前都没想过会有用。
然后我们的项目可能会用上,多番搜索之后发现了这篇。
看了一下他们的介绍,可以用于**数据增强、虚拟现实(VR)**上面。
emmm,姑且有用吧。
5. 一句话介绍论文解决的问题:
给定一张pose-a 的汽车A的RGB图,和一张pose-b的另一辆汽车B的RGB图,根据pose-b,生成一张汽车A的新图。(看第三行的图,比较明显。)
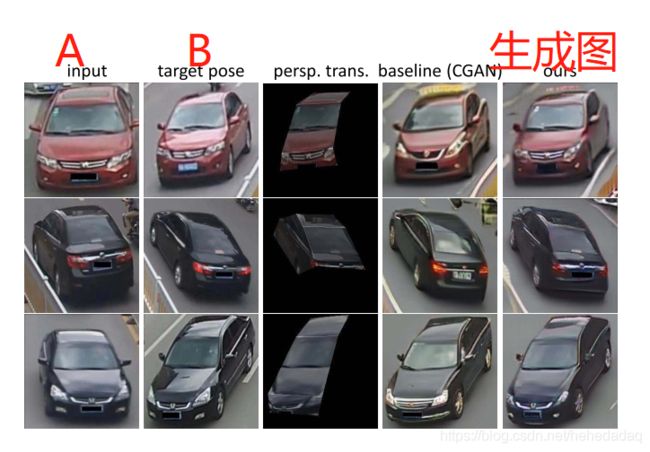

二. 创新点和贡献:
将视角转换(perspective transformation)和生成模型结合起来,将细节纹理信息和生成模型都利用上了。
(considering the complementary properties of the perspective transformation and GAN, a natural idea is to leverage their respective strengths.)
在利用视角转换的时候,有一个先验知识–汽车是方块状的,所有汽车都有特定的一些关键点。
有这些特征点,才能进行视角转换…
三. 相关领域的概述(related work)
1. 图像生成
GAN和CGAN炼就完事儿了。
我到现在都还没自己练过。
2. Novel View Synthesis(新视角合成)
a. geometry-based:
先用多张图,显式的生成3D场景,然后再合成新视角视图。有点费劲。
b. appearance flow:
这个是新的概念,我需要去看一下参考文献【12】–《View synthesis by appearance flow》–ECCV2016。
先来一张插图:

一句话介绍:将原图和旋转矩阵(3*4)输入,输出一个“流场–那个箭头一样的东西”,将这个和原图结合,进行双线性采样,生成新图。
至于流场如何训练,双线性采样如何计算,我目前的理解是,将新图与真图进行loss最小化(看他有ground truth,那么应该是可以直接有监督训练的?)
整体来说就是生成一个原图的像素该怎么变换的一个趋势图。
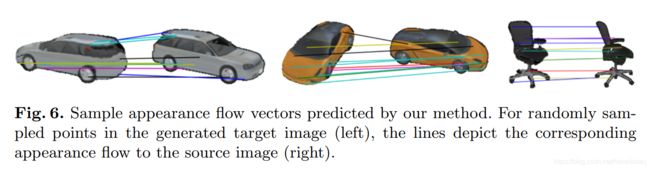
但是看最终的效果图,发现图像的线条畸变比较严重。

这个是利用了传统的几何方法,限度比较明显,遮挡问题可以通过多视角输入来弥补,但应该仍然有不少的问题。
参考[14]–“Transformationgrounded image generation network for novel 3D view synthesis”,在【12】的基础上加了一个完成网络,用了生成对抗等花里胡哨的技术,进一步优化。

19年最新的【34】就更花哨了,用了已知物体的3D模型,以及各种操作,就不解析了,反正很复杂。
c. 作者的方案
3D模型和相机的视角比较难获取,但是可以用之前已有的方案去pose 提取。这样极大的提高了应用范围。
3. 人体姿态转换(Person Pose Transfer)
这篇文章介绍的主要是人体的姿态转换,大家用一些生成模型,将输入的原图和姿态产生新的图。
引文【40】和这篇工作的主要区别在于,【40】针对的是非刚体(non-rigid objects),比如人体和衣服。这篇主要是针对汽车等刚体。
且之前大家用的都是仿射变换(affine transformation),变换矩阵23,只能将一个平行四边形变成另外一个平行四边形。他们用的是视角转换(perspective transformation),变换矩阵33,有8个参数,可以将一个不规则四边形变换为另一个四边形。其实这里我不太理解具体含义。
4. 汽车图片生成
这个没什么好说的。
主要的信息流(approach)
1. 输入输出:
详细的见下图,输入为当前视角图s和目标视角图t,输出为目标图中姿态的视角图的汽车。
详细的信息流用语言描述感觉很奇怪,直接看下文就好了。
指出几个需要关注的点:

2.姿态提取:
用的已知的模型-stack hourglass,文中将汽车分为20个关键点,8个四边形。
然后 P s P_s Ps指的是关键点,实际用的是Response Maps,就是关键点提取中的heat map,用高斯map 表示,一般一张图代表一个关键点,维度和原图一样大小,原图有该点则正常显示,没有则是黑图。
因此 R s R_s Rs是一个image_sizeimage_size20的图。
感知loss(perceptual loss)
这个loss是风格迁移网络中的一个概念,对中间的特征图也进行约束,目的是为了让生成图的风格和目标图尽可能的相似。
约束目标是:

3. PTC是啥?(附上交互式代码)
PTC是将源图的四边形区域 r s i r_si rsi和目标图对应的 r t i r_ti rti做一个映射,映射矩阵为 T i T_i Ti,源四边形的内容通过这个 T i T_i Ti转换之后,就可以拿到一个新的图。
我写了一个简单的demo,去实现透视变换的脚本。
https://github.com/kaixindelele/image-perspective-transformation-
可以试试,操作起来真滴蛮方便的!:

讨论:
作者列出了四个讨论,还是蛮有意思的,研究做的非常细致。
1. What Is the Relationship Between View Synthesis and Pose Transfer?
- As a human body is a non-rigid object, different poses always imply
that the relative positions of the joints are not consistent. - Meanwhile, different views refer that the view of the observer has
changed and the relative positions of joints should keep the same. - Vehicle pose transfer can be regarded as view synthesis for vehicles.
A vehicle is a rigid object, whose different poses are the same with
different views.
2. Why Doesn’t Conditional GAN Preserve Local Details?:
The output of the encoder is a vector, whose dimension is too low to maintain all the details of the input image.
Because GAN is optimized on some training set, the generated images are, to some extent, biased towards the training data.
For example, the GAN generated images usually have a visible license plate, because the license plates of most training images are visible.

3. Why Don’t U-Net Skip Connections Work?:
The feature maps of the encoder, which have the same spatial distribution with the ones of the decoder, are strong constraints while the misaligned ones are not qualified for strong constraints.
4. Why Does PTC Work?:
- PTC takes the misaligned feature maps as input and aligns the maps by using perspective transformation.
- By adopting PTC, the pixel-to-pixel misaligned task (input and target have different poses) is converted to the pixel-to-pixel aligned task to some extent.
- On the other hand, the PTC also filters out the background by the region masks.

总结:
- PTC: 看到的地方细节保留清晰 看不到的地方无法转换
- CGAN: 对固定目标生成比较容易,但是会忽略背景,以及当前图片的信息;
- 综合来看,这篇工作性能不错,分析很透彻,充分利用了先验知识对生成模型的优化,但是模型结构好复杂;
- 对我来说解惑了PTC并不能解决我的项目。
- 另外汽车的pose变换,就对应着视角转换吗?他这个的前提是将坐标系放在了汽车的质心?
- 得尽快学一手CGAN了~
