springCloud微服务常用组件使用
springcloud
cloud与其说是一个框架,它更像一个为微服务提供解决方案的架构,提供了为实现微服务功能与解决微服务产生问题的所有组件
- 微服务的特点:
- 单一职责:微服务中每一个服务都对应唯一的业务能力,做到单一职责
- 微:微服务的服务拆分粒度很小,例如一个用户管理就可以作为一个服务。每个服务虽小,但“五脏俱全”。面向服务:面向服务是说每个服务都要对外暴露Rest风格服务接口API。并不关心服务的技术实现,做到与平台和语言无关,也不限定用什么技术实现,只要提供Rest的接口即可。
- 自治:自治是说服务间互相独立,互不干扰
- 团队独立:每个服务都是一个独立的开发团队,人数不能过多。
- 技术独立:因为是面向服务,提供Rest接口,使用什么技术没有别人干涉
- 前后端分离:采用前后端分离开发,提供统一Rest接口,后端不用再为PC、移动段开发不同接口
- 数据库分离:每个服务都使用自己的数据源
- 部署独立,服务间虽然有调用,但要做到服务重启不影响其它服务。有利于持续集成和持续交付。每个服务都是独立的组件,可复用,可替换,降低耦合,易维护
架构图
boot整合cloud对应的版本
详细网址:https://start.spring.io/actuator/info
| cloud | boot |
|---|---|
| Finchley.M2 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.M3 and <2.0.0.M5” |
| Finchley.M3 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.M5 and <=2.0.0.M5” |
| Finchley.M4 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.M6 and <=2.0.0.M6” |
| Finchley.M5 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.M7 and <=2.0.0.M7” |
| Finchley.M6 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.RC1 and <=2.0.0.RC1” |
| Finchley.M7 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.RC2 and <=2.0.0.RC2” |
| Finchley.M9 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.0.RELEASE and <=2.0.0.RELEASE” |
| Finchley.RC1 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.1.RELEASE and <2.0.2.RELEASE” |
| Finchley.RC2 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.2.RELEASE and <2.0.3.RELEASE” |
| Finchley.SR4 | “Spring Boot >=2.0.3.RELEASE and <2.0.999.BUILD-SNAPSHOT” |
| Finchley.BUILD-SNAPSHOT | “Spring Boot >=2.0.999.BUILD-SNAPSHOT and <2.1.0.M3” |
| Greenwich.M1 | “Spring Boot >=2.1.0.M3 and <2.1.0.RELEASE” |
| Greenwich.SR2 | “Spring Boot >=2.1.0.RELEASE and <2.1.9.BUILD-SNAPSHOT” |
| Greenwich.BUILD-SNAPSHOT | “Spring Boot >=2.1.9.BUILD-SNAPSHOT and <2.2.0.M4” |
| Hoxton.SR1 | Spring Boot >=2.2.0.M4 and <2.2.3.BUILD-SNAPSHOT |
| Hoxton.BUILD-SNAPSHOT | Spring Boot >=2.2.3.BUILD-SNAPSHOT |
1、服务调用方式
RPC:远程过程调用,类似的还有RMI,自定义数据格式,基于原生TCP通信,速度快、效率高,webservice、dubbo 都是使用这类通信
HTTP:一种网络传输协议,基于TCP,规定了数据格式
缺点:消息封装臃肿
优点:对服务的提供和调用没有技术限定,自由灵活,更加的复合微服务理念
2、http 客户端
httpclient:
OKhttp
URLconnection
3、spring的restTemplate
spring提供的一个http请求模板,自带对象序列化,和反序列化。可以抽象实现以上三种http请求方式,默认URLconnection
4、eureka注册中心
Eureka架构中的三个核心角色:
- 服务注册中心
Eureka的服务端应用,提供服务注册和发现功能,就是刚刚我们建立的itcast-eureka。
- 服务提供者
提供服务的应用,可以是SpringBoot应用,也可以是其它任意技术实现,只要对外提供的是Rest风格服务即可。本例中就是我们实现的itcast-service-provider。
- 服务消费者
消费应用从注册中心获取服务列表,从而得知每个服务方的信息,知道去哪里调用服务方。

使用该客户端可以获取注册中心上面的所有实例信息包括名称,端口号,地址

不过现在推荐使用feign替换该方式进行服务之间的调用
-
服务注册
服务提供者在启动时,会检测配置属性中的:eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true参数是否正确,事实上默认就是true。如果值确实为true,则会向EurekaServer发起一个Rest请求,并携带自己的元数据信息,Eureka Server会把这些信息保存到一个双层Map结构中。
第一层Map的Key就是服务id,一般是配置中的spring.application.name属性
第二层Map的key是服务的实例id。一般host+ serviceId + port,例如:locahost:service-provider:8081
值则是服务的实例对象,也就是说一个服务,可以同时启动多个不同实例,形成集群。 -
服务续约
在注册服务完成以后,服务提供者会维持一个心跳(定时向EurekaServer发起Rest请求),告诉EurekaServer:“我还活着”。这个我们称为服务的续约(renew);
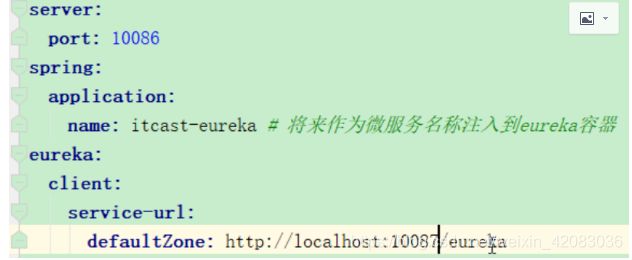
eureka:
instance:
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 90 //开发建议10秒
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 30 //开发建议5秒
-
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds:服务续约(renew)的间隔,默认为30秒
-
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds:服务失效时间,默认值90秒
也就是说,默认情况下每个30秒服务会向注册中心发送一次心跳,证明自己还活着。如果超过90秒没有发送心跳,EurekaServer就会认为该服务宕机,会从服务列表中移除,这两个值在生产环境不要修改,默认即可。
5、高可用的注册中心——注册中心相互注册
euraka默认配置是开启的(true)
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true //开启服务注册中心注册自己
失效剔除
有些时候,我们的服务实例并不一定会正常下线,可能由于内存溢出、网络故障等原因使服务不能正常运作。而服务注册中心并未收到“服务下线”的请求,为了从服务列表中将这些无法提供服务的实例剔除,Eureka Server在启动的时候会创建一个定时任务,默认每隔一段时间(默认为60秒)将当前清单中超时(默认为90秒)没有续约的服务剔除出去。
为什么?——CAP定理
CAP定理又称CAP原则,指的是在一个分布式系统中,Consistency(一致性)、 Availability(可用性)、Partition tolerance(分区容错性),最多只能同时三个特性中的两个,三者不可兼得。
符合AP理论的注册中心——euraka
euraka为了保证可用性和容错性,拥有失效服务检验,与失效剔除、以及相互注册功能。
6、ribbon负载均衡
一路源码跟踪:RestTemplate.getForObject --> RestTemplate.execute -->RestTemplate.doExecute:点击进入AbstractClientHttpRequest.execute --> AbstractBufferingClientHttpRequest.executeInternal --> InterceptingClientHttpRequest.executeInternal --> InterceptingClientHttpRequest.execute:
继续跟入:LoadBalancerInterceptor.intercept方法
继续跟入execute方法:发现获取了8082端口的服务
再跟下一次,发现获取的是8081:
@Autowired
private RibbonLoadBalancerClient client;
负载均衡策略
默认轮询:可改为随机
server:
port: 80
spring:
application:
name: service-consumer
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:10086/eureka
service-provider:
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
7、Hystrix(豪猪)断路器

作用:保护机制 防止上游服务调用下游服务失败而导致整个微服务异常
雪崩问题:当用户发送请求,由于某个服务响应速度慢/失败导致该请求无法快速应答,从而导致后续的所有请求无法正常响应堆积在内存中最终OOM 服务挂了
解决手段:
- 线程隔离
- 服务熔断
示意图解读:
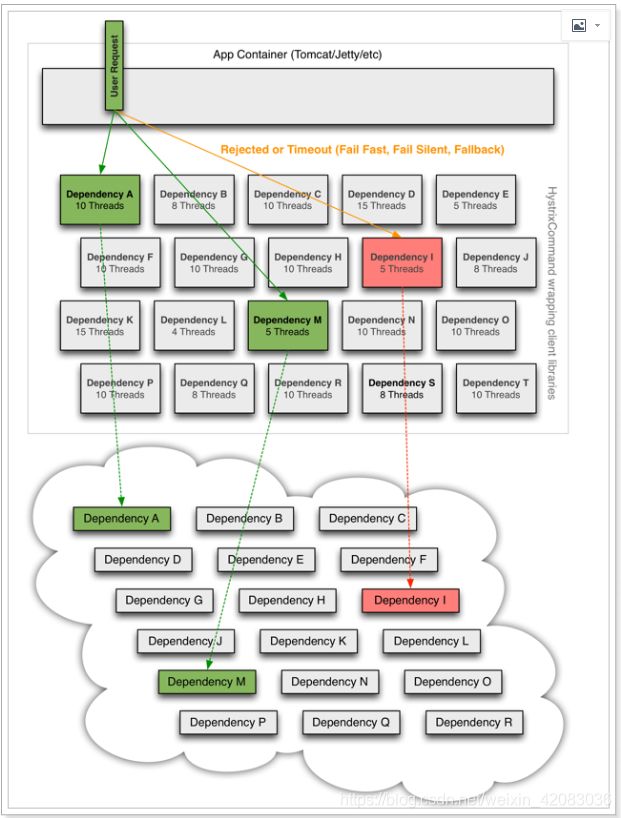
Hystrix为每个依赖服务调用分配一个小的线程池,如果线程池已满调用将被立即拒绝,默认不采用排队.加速失败判定时间。
用户的请求将不再直接访问服务,而是通过线程池中的空闲线程来访问服务,如果线程池已满,或者请求超时,则会进行降级处理,什么是服务降级?
服务降级:优先保证核心服务,而非核心服务不可用或弱可用。
一旦线程池满、请求超时 就会触发服务降级
7.1 Hystrix 具体实现
7.1.1、引入依赖:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix
7.1.2、加入注解:
@EnableCircuitBreaker 如果闲注解太多可以使用 @SpringCloudApplication组合注解替换
7.1.3、开始编写降级接口 一般写在feign调用接口下方
@Controller
@RequestMapping("consumer/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping
@ResponseBody
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "queryUserByIdFallBack")
public String queryUserById(@RequestParam("id") Long id) {
String user = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/user/" + id, String.class);
return user;
}
public String queryUserByIdFallBack(Long id){
return "请求繁忙,请稍后再试!";
}
}
要注意,因为熔断的降级逻辑方法必须跟正常逻辑方法保证:相同的参数列表和返回值声明。失败逻辑中返回User对象没有太大意义,一般会返回友好提示。所以我们把queryById的方法改造为返回String,反正也是Json数据。这样失败逻辑中返回一个错误说明,会比较方便。
可以设置全局降级方法
@Controller
@RequestMapping("consumer/user")
@DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = "fallBackMethod") // 指定一个类的全局熔断方法
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping
@ResponseBody
@HystrixCommand // 标记该方法需要熔断
public String queryUserById(@RequestParam("id") Long id) {
String user = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/user/" + id, String.class);
return user;
}
/**
* 熔断方法
* 返回值要和被熔断的方法的返回值一致
* 熔断方法不需要参数
* @return
*/
public String fallBackMethod(){
return "请求繁忙,请稍后再试!";
}
}
@DefaultProperties(defaultFallback = “defaultFallBack”):在类上指明统一的失败降级方法
@HystrixCommand:在方法上直接使用该注解,使用默认的降级方法。
defaultFallback:默认降级方法,不用任何参数,以匹配更多方法,但是返回值一定一致
注:局部降级方法需要入参和返回都必修和熔断方法一致,全局的返回参数必须和被熔断方法一致参数列表必须为空
7.2、设置超时时间
在之前的案例中,请求在超过1秒后都会返回错误信息,这是因为Hystix的默认超时时长为1,我们可以通过配置修改这个值:
我们可以通过hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds来设置Hystrix超时时间。该配置没有提示。
hystrix:
command:
default:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 6000 # 设置hystrix的超时时间为6000ms
7.3、熔断原理
当服务正常,熔断处于闭合状态,所有的请求都可以通过。如果当请求失败次数比例超过50%开启熔断,后面的所有请求(无论是正常请求还是不正常请求)均被熔断,无法访问服务。进入休眠期,随后进入半开状态,释放一部分请求,假如此时的请求健康,断路器关闭,请求可以正常访问服务但是如果后续请求都是不健康则再次打开断路器,再次休眠计时如此进行循环。
熔断状态:
- Closed:关闭状态,所有请求都正常访问。
- Open:打开状态,所有请求都会被降级。Hystix会对请求情况计数,当一定时间内失败请求百分比达到阈值,则触发熔断,断路器会完全打开。默认失败比例的阈值是50%,请求次数最少不低于20次。
- HalfOpen:半开状态,open状态不是永久的,打开后会进入休眠时间(默认是5S)。随后断路器会自动进入半开状态。此时会释放部分请求通过,若这些请求都是健康的,则会完全关闭断路器,否则继续保持打开,再次进行休眠计时
@GetMapping("{id}")
@HystrixCommand
public String queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
if(id == 1){
throw new RuntimeException("太忙了");
}
String user = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/user/" + id, String.class);
return user;
}
我们准备两个请求窗口:
一个请求:http://localhost/consumer/user/1,注定失败 //如果请求1设置休眠超时
一个请求:http://localhost/consumer/user/2,肯定成功 //不做任何超时
当我们疯狂访问id为1的请求时(超过20次),就会触发熔断。断路器会断开,一切请求都会被降级处理。
此时你访问id为2的请求,会发现返回的也是失败,而且失败时间很短,只有几毫秒左右:
不过,默认的熔断触发要求较高,休眠时间窗较短,为了测试方便,我们可以通过配置修改熔断策略:
circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold=10
circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds=10000
circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage=50
解读:
- requestVolumeThreshold:触发熔断的最小请求次数,默认20
- errorThresholdPercentage:触发熔断的失败请求最小占比,默认50%
- sleepWindowInMilliseconds:休眠时长,默认是5000毫秒
8、feign
项目主页:https://github.com/OpenFeign/feign
导入:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
启动类添加@EnableFeignClients
创建接口
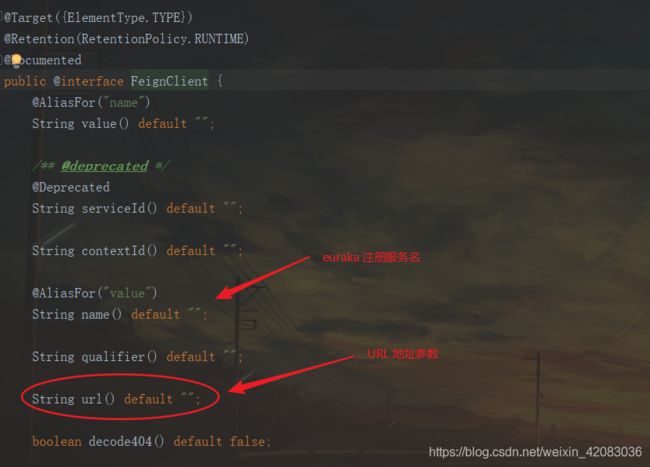
@FeignClient(value = "service-provider") // 标注该类是一个feign接口
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("user/{id}")
User queryById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
首先这是一个接口,Feign会通过动态代理,帮我们生成实现类。这点跟mybatis的mapper很像
@FeignClient,声明这是一个Feign客户端,类似@Mapper注解。同时通过value属性指定服务名称
接口中的定义方法,完全采用SpringMVC的注解,Feign会根据注解帮我们生成URL,并访问获取结果
注:全局访问路径必须加到每个方法的路径里面而不可以加到接口上面添加一个@RequestMapping
改造原来的调用逻辑,调用UserClient接口:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("consumer/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserClient userClient;
@GetMapping
@ResponseBody
public User queryUserById(@RequestParam("id") Long id){
User user = this.userClient.queryUserById(id);
return user;
}
}
feign集成了ribbon所以有负载均衡的功能
8.1、feign集成Hystrix断路器
默认情况下是关闭的。我们需要通过下面的参数来开启:
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true # 开启Feign的熔断功能
8.1.1)首先,我们要定义一个类UserClientFallback,实现刚才编写的UserClient,作为fallback的处理类
@Component
public class UserClientFallback implements UserClient {
@Override
public User queryById(Long id) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("服务器繁忙,请稍后再试!");
return user;
}
}
8.1.2)然后在UserFeignClient中,指定刚才编写的实现类
@FeignClient(value = "service-provider", fallback = UserClientFallback.class) // 标注该类是一个feign接口
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("user/{id}")
User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
使用feign需要注意问题!
1、feigin客户端无法多继承只允许单继承接口 如需要解决代码冗余只能单继承 所以尽量继承接口多的那个接口
public interface SlideshowtimeInterface {
@RequestMapping(value = "/slideshowtime/updateTime", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map updatetime(@RequestBody(required = false)String json)throws UnsupportedEncodingException;
@RequestMapping(value = "/slideshowtime/loadtime", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map loadtime(@RequestBody(required = false)String json)throws UnsupportedEncodingException;
}
public interface PictureInterface {
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/initializeAdPosition", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Map initializeAdPosition(@RequestBody(required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/saveOrUpdate", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Map save(@RequestBody(required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/load", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Map load(@RequestBody( required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/queryBannerOfproduct", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Map queryBannerOfproduct(@RequestBody( required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/queryBannerOfproducts", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public Map queryBannerOfproducts(@RequestBody( required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/move", method = {RequestMethod.POST})
public Map move(@RequestBody(required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/delete", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map delete(@RequestBody(required = false)String json);
@RequestMapping(value = "/picture/isEffect", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map isEffect(@RequestBody(required = false)String json);
}
错误写法
调用方书写
@FeignClient(value = "djslideshow-server",path = "/djslideshowserver" )
public interface FeiginClient extends PictureInterface,SlideshowtimeInterface{
}
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Only single inheritance supported: PayfeiginClient
正确写法
调用方书写
@FeignClient(value = "djslideshow-server",path = "/djslideshowserver" )
public interface FeiginClient extends PictureInterface {
@RequestMapping(value = "/slideshowtime/updateTime", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map updatetime(@RequestBody(required = false)String json)throws UnsupportedEncodingException;
@RequestMapping(value = "/slideshowtime/loadtime", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Map loadtime(@RequestBody(required = false)String json)throws UnsupportedEncodingException;
}
为什么?
原因在于 接口是可以对接口进行继承的 但是spring对于使用@feiginClient 注解修饰的接口会对其进行实现并注入bean 其就相当于是一个类 类是不允许多继承的
而且 不建议继承这种服务器端和客户端之间共享接口方式,因为这种方式会造成服务器端和客户端代码的紧耦合。并且,Feign本身并不使用Spring MVC的工作机制(方法参数映射不被继承)
2、feigin调用的请求类型以及参数。
- 当参数比较复杂时,feign即使声明为get请求也会强行使用post请求
- 不支持@GetMapping类似注解声明请求,需使用@RequestMapping(value = “url”,method = RequestMethod.GET)
- 使用@RequestParam注解时必须要在后面加上参数名
- TbItem对象,使用@RequestBody来声明
- String字符串,使用@RequestParam(“xxx”)来声明
@PostMapping(value = "bankCard/judgeCardFroPreNumber")
public HttpResult judgeCardPreNumber(@RequestParam(value = "faccountNumber") String faccountNumber);
如果不加 则报错
feign.FeignException: status 500 reading PayfeiginClient#judgeCardPreNumber(String)
3、feigin调用的方法建议不要用 多实体参数 因为不支持 如果一定需要 你要对方法进行重写编码器修饰包装再使用feign
SpringCloud Feign重写编码器支持pojos多实体与文件数组参数传递的方法 请看博客 :https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34523427/article/details/88863800
4、feigin的调用方与被调用方都必须在同一个注册中心 并且被调用方一定要先启动 当然后启动也行 不过需要等待30秒eureka 注册中心对被调用服务进行心跳机制判断
毕竟feigin适合euraka注册中心混合使用的,如果单独提出feign那边不是那么很有意义了。但feign依旧集成了ribbon的 底层是rest调用 所以并非feigin离开eureka就无法使用 而是只能充当restHttp使用 也就是说他不高大上了
而且使用时需要注明url 接口名 相关使用 看feign源码:
5、一个项目里面准确的说时一个服务里面 不允许feigin客户端覆盖代理同一个服务 即不允许一个服务里面同时出现两个代理同一个服务的feign客户端
@FeignClient(value = "pay-server")
public interface PaybankFeiginClient extends BalanceModuleInterface {
}
@FeignClient(name = "pay-server")
public interface PayfeiginClient extends BankCardModuleInterface {
当实现feigin时会出现以下错误:
The bean ‘pay-server.FeignClientSpecification’, defined in null, could not be registered. A bean with that name has already been defined in null and overriding is disabled.
无法注册以null定义的bean“pay-server / djpay.FeignClientSpecification”。 具有该名称的bean已在null中定义,并且已禁用覆盖。
9、zuul网关

zuul网关的作用
服务网关是微服务架构中一个不可或缺的部分。通过服务网关统一向外系统提供REST API的过程中,除了具备服务路由、均衡负载功能之外,它还具备了权限控制等功能。Spring Cloud Netflix中的Zuul就担任了这样的一个角色,为微服务架构提供了前门保护的作用,同时将权限控制这些较重的非业务逻辑内容迁移到服务路由层面,使得服务集群主体能够具备更高的可复用性和可测试性。
9.1、zuul的快速运用
导入依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-netflix-zuul
因为zuul的使用伴随着负载均衡 所以需要注册到eureka上使用才有意义
9.2、zuul网关的四种路由配置
- 使用路径名直接访问 容易出错 需要把负载均衡关闭 因为此时没有负载均衡效果
zuul:
routes:
service-provider: #路由名称 随意取名 习惯取服务名
path: /service-leyou/**
url: http//localhost:8087
- 通过服务ID(首先得注册eureka 由eureka中心的注册服务ID)
zuul:
routes:
service-provider: #路由名称 随意取名 习惯取服务名
path: /service-leyou/**
#url: http//localhost:8087
#serviceID: service-leyou
- 直接通过路由名称和eureka服务ID一致 (推荐)
zuul:
routes:
service-leyou: /service-leyou/** #此时 前面的事服务ID 后面是路径前缀
prefix: /api #指定路由前缀 用以区分网关与服务
- 不配置路由 默认第三种服务ID寻找路径
9.3、zuul过滤器——ZuulFilter
public abstract ZuulFilter implements IZuulFilter{
abstract public String filterType();
abstract public int filterOrder();
boolean shouldFilter();// 来自IZuulFilter
Object run() throws ZuulException;// IZuulFilter
}
- shouldFilter:返回一个Boolean值,判断该过滤器是否需要执行。返回true执行,返回false不执行。
- run:过滤器的具体业务逻辑。
- filterType:返回字符串,代表过滤器的类型。包含以下4种:
- pre:请求在被路由之前执行
- route:在路由请求时调用
- post:在route和errror过滤器之后调用
- error:处理请求时发生错误调用
- filterOrder:通过返回的int值来定义过滤器的执行顺序,数字越小优先级越高。
- 当 pre 出现异常 ——>error ——>post——>HTTP
- 当 routing 出现异常——>error——>post——>HTTP
- 当 error 出现异常——>post——>HTTP
- 当 post 出现异常——>error——>HTTP
自定义filter
/**
* @program: leyou
* @description: //zuul网关
* @author: Mr.Wang
* @create: 2020-01-05 17:28
**/
@Component
public class LoginFilter extends ZuulFilter {
/**
* 过滤器类型 pre、route、post、error
* @return
*/
@Override
public String filterType() {
return "pre";
}
/**
* 执行顺序 数字越小优先级越高
* @return
*/
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return 10;
}
/**
* 是否执行该过滤器 如果true则执行run方法 false不执行run方法
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
/**
* 编写过滤器的业务逻辑
* @return
* @throws ZuulException
*/
@Override
public Object run() throws ZuulException {
//获取zuul上下文
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
//获取request请求对象
HttpServletRequest request = context.getRequest();
//判断是否存在令牌
String token = request.getHeader("token");
if(StringUtils.isBlank(token)){
String token1 = request.getParameter("token");
if(StringUtils.isBlank(token1)){
//false 拦截不转发请求
context.setSendZuulResponse(false);
//设置响应状态码 身份未认证
context.setResponseStatusCode(HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
//设置响应体
context.setResponseBody("request error!");
}
}
//返回值为null 表示该过滤器什么都不做
return null;
}
}
9.4、自定义熔断时间——zuul自动集成了负载均衡和熔断功能默认熔断时间是1S
hystrix:
command:
default:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 2000 # 设置hystrix的超时时间为6000ms
9.5、使用zuul网关整合guava 框架实现接口限流
实现原理图:

流程图剖析:
使用zuul过滤器filter实现请求拦截,在filter设置一个全局变量令牌容器,创造令牌一般是1000个,每一次请求都会从容器中带走一个令牌,拥有令牌的请求是可以正常通过的,但是没有令牌的就必须等待容器重新生成令牌.
实现源码:
/**
* 使用guava限流框架
* @author wyy
* @date
*/
public class OrderRateLimitFilter extends ZuulFilter {
//每一秒生成1000个令牌 根据接口的压力来规定有多少个令牌
private static final RateLimiter RATE_LIMITER = RateLimiter.create(1000);
@Override
public String filterType() {
return PRE_TYPE;
}
@Override
public int filterOrder() {
return -4;
}
@Override
public boolean shouldFilter() {
RequestContext requestContext = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
HttpServletRequest request = requestContext.getRequest();
/* System.out.println(request.getRequestURI());*/
//需要对那个接口限流就把哪个接口写下去
//ACL 拦截下面的接口 忽略大小写
if ("/apigateway/order/api/v1/order/save".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getRequestURI())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Object run() throws ZuulException {
RequestContext requestContext = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
if (!RATE_LIMITER.tryAcquire()) {
requestContext.setSendZuulResponse(false);
requestContext.setResponseStatusCode(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS.value());
}
return null;
}
}