编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
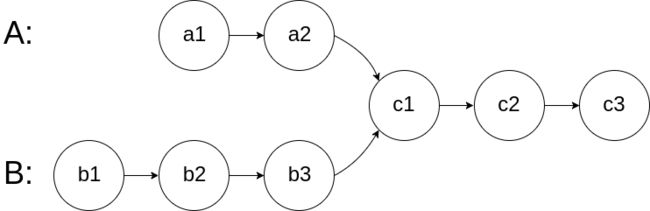
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
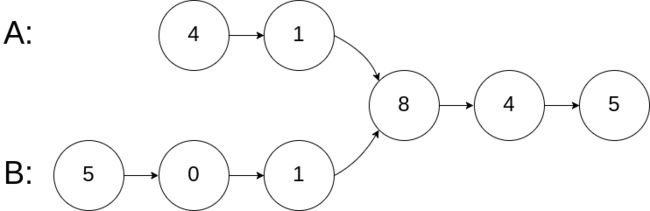
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
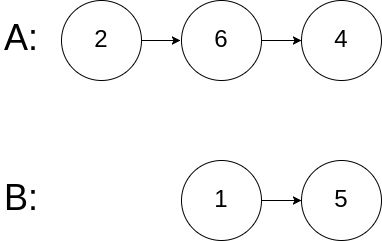
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
C
int getlength(struct ListNode *Node) {
int len = 0;
while(Node != NULL) {
len++;
Node = Node->next;
}
return len;
}
struct ListNode* func(struct ListNode *node, int movelen) {
while(movelen--) {
node = node->next;
}
return node;
}
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode *listA=headA;
struct ListNode *listB=headB;
int Alength=getlength(headA);
int Blength=getlength(headB);
if(Alength>=Blength){
listA=func(headA,Alength-Blength);
}else{
listB=func(headB,Blength-Alength);
}
while(listA!=listB&&listA!=NULL&&listB!=NULL){
listA=listA->next;
listB=listB->next;
}
return listA;
}