NestJS学习与实践
前言
之前一直想写后端,但是对于php python golang 学习成本比较大。nodejs 也作为一种服务器语言,接触比较久的,学习起来成本不大,而且性能也不错。所有我打算先从这入手。
开始时用纯nodejs写后端,发现写起来一堆api要记,写起来麻烦,所有用了nodejs的一个框架:Nest.js。
NestJS 简介
Nest 是一个用于构建高效,可扩展的 Node.js 服务器端应用程序的框架。
学习资料: 官网 https://nestjs.com/
中文 https://docs.nestjs.cn
建议中英文对照的看,有些翻译有点怪
ps: 本文下面不是按照官网的顺序,也不讲官网语法,要看官网语法的请看上面,而是以本人实际开发的步骤写的:
就是把官网里面用到的知识抽出来,方便以后看·····
安装
通过npm 或者yarn安装cli工具构建项目快速
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
// 或者 yarn
yarn global add @nestjs/cli
$ nest new project-name
HMR (不用,框架本身支持)
为了开发方便利用webpack 热模块替换,使代码在开发过程中,实时更新。
- yarn add webpack webpack-cli webpack-node-externals ts-loader --dev 安装包
- 在根目录新建 webpack.config.js 文件 代码如下:
const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
module.exports = {
entry: ['webpack/hot/poll?100', './src/main.ts'],
watch: true,
target: 'node',
externals: [
nodeExternals({
whitelist: ['webpack/hot/poll?100'],
}),
],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.tsx?$/,
use: 'ts-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
},
{
test: /.schema?$/,
use: 'json-schema-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
}
],
},
mode: 'development',
resolve: {
extensions: ['.tsx', '.ts', '.js'],
},
plugins: [new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin()],
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'server.js',
},
};
- 改/src/main.ts的代码,如下:
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
declare const module: any;
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
if (module.hot) {
module.hot.accept();
module.hot.dispose(() => app.close());
}
}
bootstrap();
- 在package.json的文件下加如:
"server": "node dist/server",
"webpack": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
- 同时运行 yarn webpack ;yarn server;
连接mysql数据库
开始运行 nest g mo users新建一个users.module
- 安装包 yarn add @nestjs/typeorm typeorm mysql
- 在/src/app.module.ts 文件里面加入
import ormconfig from '../ormconfig';
@Module({
imports: [
TypeOrmModule.forRoot(ormconfig),
],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [],
})
export class AppModule {
constructor(private readonly connection: Connection) {
console.warn(__dirname);
console.warn(connection.isConnected ? '数据库连接成功' : '数据库连接失败');
}
}
import { UserEntity } from './src/users/user.entity';
import { TypeOrmModuleOptions } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
const ormconfig: TypeOrmModuleOptions = {
keepConnectionAlive: true,
type: 'mysql',
host: '*****',
port: '*****,
username: ''*****',
password: ''*****',
database: '*****',
synchronize: true,
entities: [UserEntity],
};
export default ormconfig;
- 新建实体 新建 /src/users/user.entity.ts文件
import { Column, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity({ name: 'user-info' })
export class UserEntity {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
name: string;
@Column()
password: string;
@Column()
email: string;
}
- module里面加入entity 修改 /src/users/user.module.ts
import { UserEntity } from './user.entity';
....
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forFeature([UserEntity])],
....
})
export class UsersModule {}
- nest g s users 新建users.service.ts,使用 @InjectRepository() 修饰器向 UsersService 注入 userRepository:
.....
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(
@InjectRepository(UserEntity)
private readonly userRepository: Repository<UserEntity>,
) {}
findAll(): Promise<UserEntity[]> {
return this.userRepository.find();
}
}
- nest g co users 新建users.controller.ts
@Controller('users')
export class UsersController {
constructor(private readonly usersService: UsersService) {}
@Get('all-user')
getAllUser(@Req() req) {
return this.usersService.findAll();
}
}
Authorization 登陆认证
- 安装passport passport 是目前最流行的 node.js 认证库 passport-local:密码/用户名 的认证策略
npm install --save @nestjs/passport passport passport-local
npm install --save-dev @types/passport-local
2.新建 auth 模块 users 模块
nest g module auth
nest g service auth
nest g module users
nest g service users
3.在users module里面注入TypeOrmModule;
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forFeature([UserEntity])],
providers: [UsersService],
exports: [UsersService],
controllers: [UsersController],
})
export class UsersModule {}
在 users service 里面 查询用户名和密码 以及新增用户 采用Repository提供的方法
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(
@InjectRepository(UserEntity)
private readonly userRepository: Repository<UserEntity>,
) {}
async findOneByUserName(username): Promise<UserEntity> {
return this.userRepository.findOne({ name: username });
}
async addUser(param: UserDTO) {
const salt = Math.random()
.toString(36)
.substr(2);
const password = CreateMD5(param.password, salt);
return this.userRepository.save({
name: param.name,
email: param.email,
password,
salt,
});
}
}
在auth service里面调用userservice方法去验证用户名和密码,下面的代码对密码进行了MD5加密,每个用户新建时生成一个随机sal用于加密密码,数据库存入的是,确保数据库存入的密码的安全。
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
constructor(
private readonly usersService: UsersService
) {}
async validateUser(username: string, pass: string): Promise<any> {
const user = await this.usersService.findOneByUserName(username);
if (!user) {
throw new BadRequestException('用户名不存在');
}
if (user && user.password === CreateMD5(pass, user.salt)) {
const { password, ...result } = user;
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
- 在auth 文件新建local.strategy.ts文件 调用service对方法进行用户名验证
@Injectable()
export class LocalStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor(private readonly authService: AuthService) {
super();
}
async validate(username: string, password: string): Promise<any> {
console.warn(username, password);
if (!username || !password) {
throw new BadRequestException('请用户名和密码');
}
const user = await this.authService.validateUser(username, password);
if (!user) {
throw new BadRequestException('用户名或者密码不正确');
}
return user;
}
}
在auth module 里面注入 PassportModule LocalStrategy AuthService
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
PassportModule
],
providers: [AuthService, LocalStrategy]
exports: [AuthService],
controllers: [AuthController],
})
export class AuthModule {}
新建auth controller ,AuthGuard 是 @nestjs/passport 包中提供的
@Controller('auth')
export class AuthController {
constructor(
private readonly authService: AuthService,
private readonly usersService: UsersService,
) {}
// 登陆
@UseGuards(AuthGuard('local'))
@Post('login')
async login(@Req() req) {
return this.authService.login(req.user);
}
}
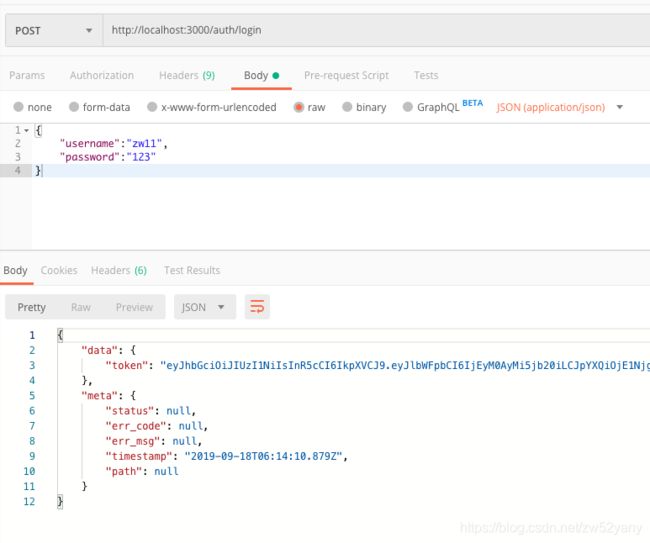
5.下面进行 jwt 认证 (jwt对原理可以看我对另一篇文章https://blog.csdn.net/zw52yany/article/details/100081326)
首先安装passport-jwt
npm install @nestjs/jwt passport-jwt
npm install @types/passport-jwt --save-dev
再在auth.service 文件里面加入login方法,生成jwt 并返回给客户端
...
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
constructor(
private readonly usersService: UsersService,
private readonly jwtService: JwtService,
) {}
...
async login(user: UserEntity) {
const payload = { username: user.name, email: user.email };
return {
token: this.jwtService.sign(payload),
};
}
}
export const jwtSecretKey = 'zw';
同时在auth.module里面注册jwt策略,注入JwtModule
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
PassportModule.register({ defaultStrategy: 'jwt' }),
JwtModule.register({
secret: jwtSecretKey,
signOptions: { expiresIn: '1h' }, // 这里是jwt失效时间
}),
],
providers: [AuthService, LocalStrategy, JwtStrategy],
exports: [AuthService],
controllers: [AuthController],
})
export class AuthModule {}
- 下面进行api 的登陆认证
新建 jwt.strategy文件 validate 方法的作用是:先获得jwt解析后的payload,调用validate 方法验证用户名和密码存不存在。
@Injectable()
export class JwtStrategy extends PassportStrategy(Strategy) {
constructor(private readonly usersService: UsersService) {
super({
jwtFromRequest: ExtractJwt.fromAuthHeaderAsBearerToken(), // 从header bearer 里面获得jwt
ignoreExpiration: false,
secretOrKey: jwtSecretKey,
});
}
async validate(payload: UserInfo) {
const user = await this.usersService.findOneByUserName(payload.username);
if (!user) {
throw new BadRequestException('用户名不存在');
}
return { username: payload.username, email: payload.email };
}
}
在auth module providers 里面注入 JwtStrategy
@Module({
imports: [
...
],
providers: [AuthService, LocalStrategy, JwtStrategy],
exports: [AuthService],
controllers: [AuthController],
})
export class AuthModule {}
- nest js提供了路由守卫,可以用来针对每个接口,判断用户是否登陆,对用户接口进行访问权限控制
新建jwtAuth.guard.ts ,JwtAuthGuard继承AuthGuard,并做了一些错误判断
@Injectable()
export class JwtAuthGuard extends AuthGuard('jwt') {
canActivate(
context: ExecutionContext,
): boolean | Promise<boolean> | Observable<boolean> {
const request = context.switchToHttp().getRequest();
if (request.url === '/auth/login' || request.url === '/auth/register') {
return true;
} else {
return super.canActivate(context);
}
}
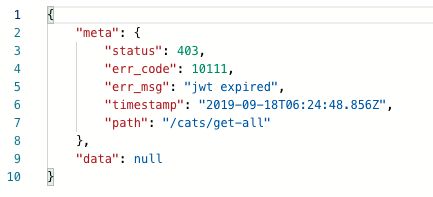
handleRequest(err, user, info) {
if (err || !user) {
if (info.message === 'jwt expired') {
throw new JwtException(ErrorCode.jwtExpired, info.message);
} else if (info.message === 'No auth token') {
throw new JwtException(ErrorCode.jwtNotFound, info.message);
} else {
throw new JwtException(ErrorCode.jwtInvalid, info.message);
}
}
return user;
}
}
Exception
- 异常处理
nestjs/common中公开了一个内置的 HttpException 类,使用方式,直接调用基础类:
@Get()
async findAll() {
throw new HttpException('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
throw new HttpException({
status: HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN,
error: 'This is a custom message',
}, 403);
}
或者扩展基础类:
export class ForbiddenException extends HttpException {
constructor() {
super('Forbidden', HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN);
}
}
@Get()
async findAll() {
throw new ForbiddenException();
}
下面一些例子:在jwt对验证,过期对错误提示可以
// jwt 过期
export class JwtException extends HttpException {
constructor(private readonly errCode, private readonly msg) {
super(
{
status: errCode,
error: msg,
},
403,
);
}
}
统一BadrEquestException 可以这样
export class BadRequestException extends HttpException {
constructor(private readonly msg: string) {
super(
{
status: HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, // error code
error: msg,
},
500, // status code
);
}
}
- 异常过滤器:就是一个异常中间件,捕获到所有异常进行一些处理,例如可以对抛出对异常进行统一格式化处理:
@Catch(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost): any {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse();
const request = ctx.getRequest();
const status = exception.getStatus();
console.warn(exception);
response.status(status).json({
meta: {
status: exception.getStatus(),
err_code: exception.message.status,
err_msg: exception.message.error,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
},
data: null,
});
}
}
拦截器
拦截器是一个请求中间件,拦截请求做一些处理,一般可以用来:
- 在函数执行之前/之后绑定额外的逻辑
- 转换从函数返回的结果
- 转换从函数抛出的异常
- 扩展基本函数行为
- 根据所选条件完全重写函数 (例如, 缓存目的)
下面一个统一response body格式的拦截器:
export interface Response<T> {
data: T;
meta: {
status: number;
err_code: number;
err_msg: string;
timestamp: string;
path: string;
};
}
// 转化请求结果
@Injectable()
export class TransformInterceptor<T>
implements NestInterceptor<T, Response<T>> {
intercept(
context: ExecutionContext,
next: CallHandler<T>,
): Observable<Response<T>> | Promise<Observable<Response<T>>> {
console.log('transform...');
return next.handle().pipe(
map(data => ({
data,
meta: {
status: null,
err_code: null,
err_msg: null,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: null,
},
})),
);
}
}
参数格式验证
- 新建validation.pipe.ts
@Injectable()
export class ValidationPipe implements PipeTransform<any> {
async transform(value, metadata: ArgumentMetadata) {
const { metatype } = metadata;
if (!metatype || !this.toValidate(metatype)) {
return value;
}
const object = plainToClass(metatype, value);
const errors = await validate(object);
if (errors.length > 0) {
let errMsg = '';
for (const err of errors) {
errMsg += err.constraints[Object.keys(err.constraints)[0]] + ';';
}
console.warn(errMsg);
throw new BadRequestException(errMsg);
}
return value;
}
private toValidate(metatype): boolean {
const types = [String, Boolean, Number, Array, Object];
return !types.find(type => metatype === type);
}
}
- 在app module中导入
@Module({
providers: [
{
provide: APP_PIPE,
useClass: ValidationPipe, // 请求参数格式验证
}
]
})
export class AppModule {}
- 使用 以用户注册为例子,新建register.todo.ts
export class UserDTO {
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
readonly name: string;
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
readonly password: string;
@IsString()
@IsNotEmpty()
readonly email: string;
}
然后在auth.controller中使用
// 注册
@Post('register')
async addUser(@Body() user: UserDTO) {
try {
const data = await this.usersService.addUser(user);
return { name: data.name, email: data.email };
} catch (e) {
console.warn(e);
throw new BadRequestException(e.message);
}
}