HDLBits刷题合集—3 Vectors
HDLBits刷题合集—3 Vectors
HDLBits-11 Vector0
Problem Statement
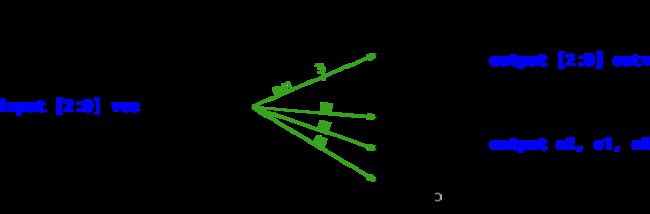
建立一个电路,有一个3位输入,然后输出相同的向量,并把它分成三个独立的1位输出。将输出o0连接到输入向量的位置0,o1连接到位置1,o2连接到位置2。
在下图中,带有数字的标记表示向量(或“总线”)的宽度,而不是向量中的每个位绘制单独的线。
module top_module (
input wire [2:0] vec,
output wire [2:0] outv,
output wire o2,
output wire o1,
output wire o0 ); // Module body starts after module declaration
assign outv = vec;
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
endmodule
HDLBits-12 Vector1
Problem Statement
建立一个组合电路,将一个输入的半个字(即一个32位的字,取16位,[15:0]),分成[7:0]和[15:8]两个字节。
代码如下:
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi = in[15:8];
assign out_lo = in[7:0];
endmodule
HDLBits-13 Vector2
Problem Statement
32位向量可以看作包含4个字节(分别是[31:24]、[23:16]、[15:8]和[7:0]等)。建立一个电路,将4字节字的顺序方向。如下所示:
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd=>DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaa
当需要交换一段数据的顺序时,通常会使用这种操作。
代码如下:
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out[31:24] = in[7:0];
assign out[23:16] = in[15:8];
assign out[15:8] = in[23:16];
assign out[7:0] = in[31:24];
endmodule
HDLBits-13 Vectorgates
Problem Statement
构建一个有两个3位输入的电路,它可以计算两个向量的按位或、两个向量的逻辑或和两个向量的非。将b的非在out_not的高半部分,a的非在out_not的低半部分。
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b;
assign out_or_logical = a || b;
assign out_not[5:3] = ~b;
assign out_not[2:0] = ~a;
endmodule
HDLBits-14 Gates4
Problem Statement
在建立一个有四个输入的组合电路。有3个输出:
out_and: 四输入与门的输出。
out_or: 四输入或门的输出。
out_xor: 四输入异或门的输出。
代码如下:
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = ∈
assign out_or = |in;
assign out_xor = ^in;
endmodule
HDLBits-14 Vector3
Problem Statement
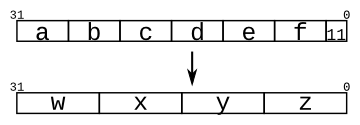
给定几个输入向量,将它们连接在一起,然后将它们分成几个输出向量。有六个5位的输入向量:a、b、c、d、e和f,总共有30位的输入。对于32位的输出,有4个8位的输出向量:w、x、y和z。输出应该包括两个输入的1位向量。
module top_module (
input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f,
output [7:0] w, x, y, z );//
assign {w,x,y,z} = {a,b,c,d,e,f,2'b11};
endmodule
HDLBits-15 Vectorr
Problem Statement
给定一个8位输入向量[7:0],将它的顺序按位颠倒。
代码如下:
module top_module(
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] out
);
//下面一行是简便方法
//assign {out[0],out[1],out[2],out[3],out[4],out[5],out[6],out[7]} = in;
assign out[7] = in[0];
assign out[6] = in[1];
assign out[5] = in[2];
assign out[4] = in[3];
assign out[3] = in[4];
assign out[2] = in[5];
assign out[1] = in[6];
assign out[0] = in[7];
endmodule
HDLBits-15 Vector4
Problem Statement
建立一个能将8位数字扩展到32位的电路。这需要24个符号位(即复制第[7]位24次),然后复制8位数字本身。
代码如下:
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out = {{24{in[7]}},in};
endmodule
HDLBits-16 Vector5
Problem Statement
给定5个1位信号(a、b、c、d和e),计算25位输出向量中所有25个成对的1位向量比较。如果被比较的两位是相等的,输出应该是1。
out[24] = ~a ^ a; // a == a, so out[24] is always 1.
out[23] = ~a ^ b;
out[22] = ~a ^ c;
…
out[ 1] = ~e ^ d;
out[ 0] = ~e ^ e;

如图所示,使用复制和拼接操作符可以更容易地做到这一点。
前部分的向量是每个输入重复5次的拼接;
后部分的向量是5个输入序列的重复5次。
代码如下:
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out
);
wire [24:0] top, bottom;
assign top = { {5{a}}, {5{b}}, {5{c}}, {5{d}}, {5{e}} };
assign bottom = {5{a,b,c,d,e}};
assign out = top ~^ bottom;
// This could be done on one line:
// assign out = { {5{a}}, {5{b}}, {5{c}}, {5{d}}, {5{e}} } ~^ {5{a,b,c,d,e}};
endmodule
Note
新手一枚,主要分享博客,记录学习过程,后期参考大佬代码或思想会一一列出。欢迎大家批评指正!