01 力反馈 OpenHaptics ConsoleExamples-FrictionlessPlane
HDAPI Overview
本文目的: 分析 HDAPI demo,如何产生一个触碰平面的力
Haptic Device(触觉设备)API 包含两个主要的部分:设备以及调度程序。设备抽象化就可以让任何支持3维触觉的机器在 HDAPI 下使用。调度程序回调允许程序员输入在伺服循环线程内执行的命令。
HDAPI 典型用途:
- 初始化设备
- 初始化调度程序
- 启动调度程序
- 使用调度程序执行一些触觉命令
- 完成时退出
开始
HDAPI 需要一个安装驱动的 3D 触觉设备,以及安装的 HDAPI
项目应该包含 HDAPI 的头文件以及 HDAPI 库文件以及实用工具(utility)的库文件
由于3维触觉设备不易表示出来,下面采用语言描述
ConsoleExamples 中的 FrictionlessPlane:
创建一个高度为0的平面,触觉设备从上或者从下碰到平面时产生推力,当触觉设备的力大于阈值时会发生穿透。
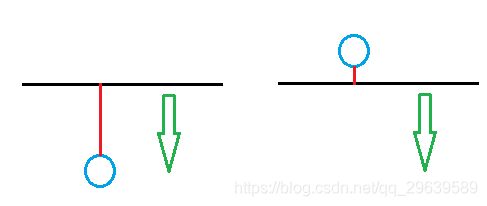
力的判定

如图(左侧),当触觉设备位置在平面法向量(绿色部分)上方,此时投影为正,表示没有发生穿透现象
接着设备朝着平面运动(图右侧),当投影为负时表示发生穿透。
现在用穿透的位移(点到平面的距离)当作弹簧形变,根据胡可定律产生力,力的方向和当前平面的法向量一致(所以产生排斥力)。
当力大于阈值时设置力为0,同时改变朝向(directionFlag)如下图
这样当设备朝着上方移动时(重复上述过程)仍然可以感受到平面,符合实际情况。
demo源码解析
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
HDErrorInfo error;
// 初始化默认的 haptic device.
HHD hHD = hdInitDevice(HD_DEFAULT_DEVICE);
if (HD_DEVICE_ERROR(error = hdGetError()))
{
hduPrintError(stderr, &error, "Failed to initialize haptic device");
fprintf(stderr, "\nPress any key to quit.\n");
getch();
return -1;
}
// 创建一个随动调度程序并施夹力
hdEnable(HD_FORCE_OUTPUT);
hdStartScheduler();
if (HD_DEVICE_ERROR(error = hdGetError()))
{
hduPrintError(stderr, &error, "Failed to start the scheduler");
fprintf(stderr, "\nPress any key to quit.\n");
getch();
return -1;
}
// 安排一个无摩擦平面的回调, 会运行在servoloop 中,当刺破平面时施加力
HDCallbackCode hPlaneCallback = hdScheduleAsynchronous(
FrictionlessPlaneCallback, 0, HD_DEFAULT_SCHEDULER_PRIORITY);
printf("Plane example.\n");
printf("Move the device up and down to feel a plane along Y=0.\n");
printf("Push hard against the plane to popthrough to the other side.\n");
printf("Press any key to quit.\n\n");
while (!_kbhit())
{
if (!hdWaitForCompletion(hPlaneCallback, HD_WAIT_CHECK_STATUS))
{
fprintf(stderr, "\nThe main scheduler callback has exited\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\nPress any key to quit.\n");
getch();
break;
}
}
// 清理并关闭 haptic device, 清除所有的回调函数.
hdStopScheduler();
hdUnschedule(hPlaneCallback);
hdDisableDevice(hHD);
return 0;
}
// 平面在y=0处,当穿破物体时提供一个排斥力
HDCallbackCode HDCALLBACK FrictionlessPlaneCallback(void *data)
{
// 硬度,值越大平面越硬
const double planeStiffness = 2.85;
// 穿透平面时最大的力
const double popthroughForceThreshold = 30.0;
// 朝向:穿破平面时改变,1和-1表示面对平面的正面和背面
// 这个例子中,1表示位于平面上方,-1表示位于平面下方
static int directionFlag = 1;
hdBeginFrame(hdGetCurrentDevice());
// device 的位置.
hduVector3Dd position;
hdGetDoublev(HD_CURRENT_POSITION, position);
// 如果用户穿透平面, 设置一个沿着平面法向量上排斥的力
// 当平面法向量+y但位置为负时,发生穿透
if ((position[1] <= 0 && directionFlag > 0) ||
(position[1] > 0) && (directionFlag < 0))
{
double penetrationDistance = fabs(position[1]);
hduVector3Dd forceDirection(0,directionFlag,0);
// 胡克定律
double k = planeStiffness;
hduVector3Dd x = penetrationDistance*forceDirection;
hduVector3Dd f = k*x;
// 发生穿刺时力归0,更改朝向
if (f.magnitude() > popthroughForceThreshold)
{
f.set(0.0,0.0,0.0);
directionFlag = -directionFlag;
}
hdSetDoublev(HD_CURRENT_FORCE, f);
}
hdEndFrame(hdGetCurrentDevice());
// 发生错误时结束回调函数
HDErrorInfo error;
if (HD_DEVICE_ERROR(error = hdGetError()))
{
hduPrintError(stderr, &error, "Error detected during main scheduler callback\n");
if (hduIsSchedulerError(&error))
{
return HD_CALLBACK_DONE;
}
}
return HD_CALLBACK_CONTINUE;
}
效果
可以看到整个过程中间有明显的阻力,当继续施加力之后会直接穿透平面
bug
- 速度太快时无法感受到力,此时会直接刺破平面,感觉是碰撞检测出了问题