Pat甲级题目刷题分享+算法笔记提炼 ---------------第三部分 树专题
一、二叉树(重点掌握BST树和AVL树)
1、一般二叉树的存储结构
采用的是类似链表的方式,每个节点都有两个指针,分别指向其左右孩子节点。
①节点的定义
struct node{
int data; //int 当然是可以变为其他数据类型,这里只是举个常见的例子
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
};
//新建一个节点
node * newNode(int v){
node * root= new node;
root->data=v;
root->lchild=NULL;
root->rchild=NULL;
return root;
}②二叉树节点的查找
bool search(node * root,int v){
if(root ==NULL) return false;
if(root->data==v) return true;
else if(search(root->lchild,v)) return true;
else return search(root->rchild,v);
}?二叉树的插入
void insert(node *&root ,int data){
if(root==NULL){
root = newNode(data);
return;
}
if(完全取决于实际种二叉树的性质决定插入左还是右)
//比如对于查找二叉树,就需要左边的树比根小,右边要大于等于根
{
insert(root->lchild,data);
}else{
insert(root->rchild,data);
}
}④所以二叉树的创建就完全依赖与插入操作即可
node * create(int data[],int n){
node *root = NULL;
for(int i=0;i2、完全二叉树的存储 采用一维数组
对于一个节点的下标x,其左孩子的下标是2x,其右孩子的下标为2*x+1,0下标不存储,其父节点的下标为x/2,以上均是针对节点存在的情况,所以事先要确认要找的节点是存在的。
3、二叉树的遍历
①先序遍历
void preOrder(node * root){
if(root==NULL) return;
printf("%d ",root->data);
preOrder(root->lchild);
preOrder(root->rchild);
}②中序遍历
void inOrder(node *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
inOrder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inOrder(root->rchild);
}?后序遍历
void postOrder(node *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
postOrder(root->lchild);
postOrder(root->rchild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}④层序遍历
void LayerOrder(node *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node *now= q.front();
q.pop();
printf("%d ",now->data);
if(now->lchild!=NULL) q.push(now->lchild);
if(now->rchild!=NULL) q.push(now->rchild);
}
} 如果想知道每个节点所属的层次,就需要稍微修改一下node结构体
struct node{
int data;
int layer;
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
};层次遍历时候就可以确定每个节点的层号
void LayerOrder(node *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
queue q;
root->layer=1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node *now = q.front();
q.pop();
if(now->lchild!=NULL){
now->lchild->layer=now->layer+1;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild!=NULL){
now->rchild->layer=now->layer+1;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
} 问题:给定一棵二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历序列,重建这棵二叉树。
首先,先序序列的起始节点就是根节点,在中序中找到根节点,序列左边就是左子树,序列右边就是右子树,然后对左序列和右序列进行同样操作,就可以构建出一棵二叉树了
node * create(int preL,int preR,int inL,int inR){
if(preL>preR) return NULL;
node *root = new node;
root->data=pre[preL]
int k;
for(k=inL;i<=inR;i++){
if(pre[preL]==in[k]){
break;
}
}
int numLeft=k-inL;
root->lchild=create(preL+1,preL+numLeft,inL,k-1);
root->rchild=create(preL+numleft+1,preR,k+1,inR);
return root;
}中序序列可以与先序序列、后序序列、层次序列中的任意一个来构建唯一的二叉树,而后三者两两搭配在一起都无法构建一个唯一的二叉树。
题二:根据后序序列与中序序列构建一棵二叉树,同理。
node* create(int postL,int postR,int inL,int inR){
if(postL>postR) return NULL;
node *root = new node;
root->data=post[postR];
int k;
for(k=inL;k<=inR;k++){
if(in[k]==post[postR]){
break;
}
}
int numLeft=k-inL;
root->lchild=create(postL,postL+numleft-1,inL,k-1);
root->lchild=create(postL+numleft,postR-1,k+1,inR);
}题目三:通过中序遍历和层次遍历创建二叉树
算法核心关键:
首先添加一个结构体
struct Sq
{
int level;//在层次序列中的下标
int low, high; //在中序序列中的下标区间
int lr;//判断是左孩子还是右孩子 1为左,2为右
node *parent;//该节点的父亲节点指针
};举例说明,方便读者清楚算法实现步骤,层次遍历序列A,在中序序列中的下标为3,在[]0-7]之间,说明其有左右孩子,此时A的左孩子的中序序列区间为[0,2],右孩子的中序序列区间为[4,7],左右孩子在层次序列中的下标为1和2,其父节点为A。
所以写成代码为:
node * root = new node;
root->data = lev[0];
root->lchild = NULL;
root->rchild = NULL;
int i = 0;
int s = 0;
Sq q;
queue Q;
while (in[i] != lev[0]) i++; //in数组为中序序列,lev数组为层次序列
if (i == 0) {//只有右子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 1;
q.high = n - 1; //n是数组大小
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
}
else if (i == n - 1) {//只有左子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 0;
q.high = n - 2;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
}
else { //左右子树均有
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 0;
q.high = i-1;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
q.level = ++s;
q.low = i+1;
q.high = n-1;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
} 从上述可以看出,队列Q中存储的Sq结构体最大的level就是某个节点的最后一个孩子,为什么会这样呢,那是因为,如果节点右两个孩子则s加了两下,有一个孩子则s加了一下。再加上记录了孩子的父亲节点,实现起来就方便了。完整代码如下:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *lchild;
node *rchild;
};
struct Sq
{
int level;
int low, high;
int lr;//判断是左子树还是右孩子 1为左,2为右
node *parent;
};
//数组下标从0开始
node * create(int lev[], int in[], int n) {
if (n == 0) return NULL;
node * root = new node; root->data = lev[0]; root->lchild = NULL; root->rchild = NULL;
if (n == 1) { return root; }
int i = 0;
int s = 0;
Sq q;
queue Q;
while (in[i] != lev[0]) i++;
if (i == 0) {//只有右子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 1;
q.high = n - 1;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
}
else if (i == n - 1) {//只有左子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 0;
q.high = n - 2;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
}
else { //左右子树均有
q.level = ++s;
q.low = 0;
q.high = i-1;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
q.level = ++s;
q.low = i+1;
q.high = n-1;
q.parent = root;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
}
while (!Q.empty())
{
Sq temp = Q.front(); Q.pop();
node *p = temp.parent;
node *Node = new node;
Node->data = lev[temp.level];
Node->lchild = Node->rchild = NULL;
if (temp.lr == 1) p->lchild = Node;
else if (temp.lr == 2) p->rchild = Node;
int i = temp.low;
while (in[i] != lev[temp.level]) i++;
if (i == temp.low&&i == temp.high) { //说明是叶子节点
continue; //防止下面错入队列
}
else if (i == temp.low) {//只有右子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = i+1;
q.high = temp.high;
q.parent = Node;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
}
else if (i ==temp.high) {//只有左子树
q.level = ++s;
q.low = temp.low;
q.high = i-1;
q.parent = Node;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
}
else { //左右子树均有
q.level = ++s;
q.low = temp.low;
q.high = i - 1;
q.parent = Node;
q.lr = 1;
Q.push(q);
q.level = ++s;
q.low = i + 1;
q.high = temp.high;
q.parent = Node;
q.lr = 2;
Q.push(q);
}
}
return root;
}
void inOrder(node *root) {
if (root == NULL) return;
inOrder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inOrder(root->rchild);
}
int main() {
int level[8] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int in[8] = {7,4,2,1,8,5,3,6};
node *root= create(level,in,8);
inOrder(root);
return 0;
} 4、二叉查找树(BST)
定义:左子树的所有节点的数据域均小于根节点的数据域,右子树的所有节点的数据域均大于等于根节点的数据域。且左右子树也是二叉查找树。所以二叉查找树的中序遍历是有序的。
①BST的查找
void search(node *root,int x){
if(root==NULL){printf("search failed!");return;}
if(x==root->data) {printf("%d",x);return;}
else if(xdata) search(root->lchild,x);
else search(root->rchild,x);
} ②BST的插入
void insert(node *&root,int x){
if(root==NULL){
root = new node;
root->data=x;
root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL;
return;
}else if(xdata){
insert(root->lchild,x);
}else{
insert(root->rchild,x);
}
} ?BST的建立
node *create(int data[],int n){
node *root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i5、平衡二叉树(AVL树)
AVL树仍然是一个二叉查找树,只是增加一个平衡属性,即左子树与右子树的高的差值的绝对值<=1
1)介绍AVL树的基本操作之前,首先需要介绍与AVL树性质相关的一些结构体和基本函数
struct node{
int v,height;
node *lchild,*rchild;
}
node * newNode(int x){
node *root= new node;
root->v=x;
root->height=1;
root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL;
return root;
}
int getHeight(node *root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
return root->height;
}
int getBalanceFactor(node *root){
return getHeight(root->lchild)-getHeight(root->rchild);
}
//更新节点的成员height的值
void updateHeight(node *root){
root->height=max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild))+1;
}
2)AVL树的基本操作
①查找操作
bool search(node *root,int x){
if(root == NULL) return false;
if(root->v==x) return true;
else if(xv) search(root->lchild,x);
else search(root->rchild,x);
} ②插入操作,显然插入后,很容易到AVL树失去平衡,所以在插入完成后,根据最终结果来判定接下来该进行什么样的操作使二叉树重新回归平衡
插入后会产生以下四种形态:BF(root)是指root节点的平衡因子
| 树形 | 判定条件 | 调整方法 |
| LL | BF(root)==2,BF(root->lchild)==1 | 对root进行右旋 |
| LR | BF(root)==2,BF(root->lchild=-1) | 先对root->lchild进行左旋,再对root进行右旋 |
| RR | BF(root)==-2,BF(root->rchild)==-1 | 对root进行左旋 |
| RL | BF(root)==-2,BF(root->rchild)==1 | 先对root->rchild进行右旋,再对root进行左旋 |
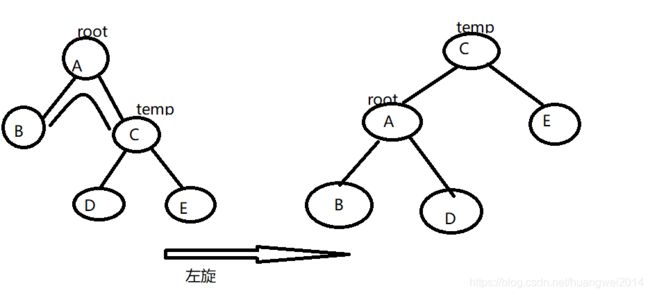
接下来介绍右旋和左旋的操作
右旋同理
那为什么会出现插入后失去平衡的情况呢,就比如在E的后面插入一个孩子节点,右子树的高就为3显然BF(root)=-2,所以通过左旋root,显然只是在上图的右边图中E的后面有个节点,BF(temp)=0
以下是右旋和左旋的代码以及AVL树的插入代码。
void L(node *&root){
node *temp=root->rchild;
root->rchild=temp->lchild;
temp->lchild=root;
//修改每个节点的height
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(temp);
root=temp;
}
void R(node *&root){
node *temp=root->lchild;
root->lchild=temp->rchild;
temp->rchild=root;
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(temp);
root=temp;
}
void insert(node *&root,intx){
if(root==NULL){
root=newNode(x);
return;
}
if(xv){
insert(root->lchild,x);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root)==2){
if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild)==1){ //LL
R(root);
}else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild)==-1){ //LR
L(root->lchild);
R(root);
}
}
}
else{
insert(root->rchild,x);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root)==-2){
if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild)==-1){ //RR
L(root);
}else if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild)==1){ //RL
R(root->rchild);
L(root);
}
}
}
}
?AVL树的创建
node* create(int data[],int n){
node * root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i