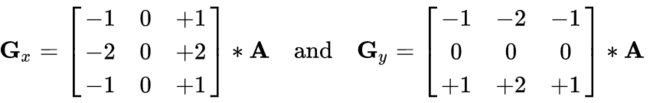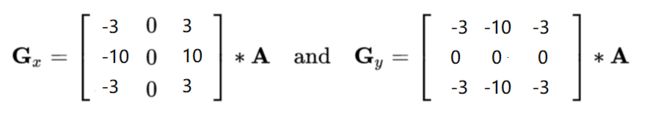Opencv计算机视觉入门——图像的处理(一)
接上次的笔记,开始图像操作的第二段学习旅程~~~
图像的处理(一)
图像阈值
拿到一张图像,图像是由众多像素点组成的,我们要对每一个像素点的值进行判断,用像素点的值与阈值进行比较,对于大于或小于阈值分别做不同的处理。
ret,dist = cv2.threshold(src,thresh,maxval,type)src:输入图,只能输入单通道图像,通常来说为灰度图
dist:输出图
thresh:阈值
maxval:当像素值超过了阈值(或者小于阈值,根据type来决定),所赋予的值
type:二值化操作的类型,包括以下5种类型:cv2.THRESH_BINARY;cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV;cv2.THRESH_TRUNC;cv2.THRESH_TOZERO;cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV
cv2.THRESH_BINARY:超过阈值部分取maxval(最大值),否则取0
cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV:THRESH_BINARY的反转,即超过阈值部分取0,否则取maxval(最大值)
cv2.THRESH_TRUNC:大于阈值部分设为阈值,否则不变
cv2.THRESH_TOZERO:大于阈值部分不改变,否则设为0
cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV:THRESH_TOZERO的反转
#图像阈值
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img_gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img_gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ret, thresh3 = cv2.threshold(img_gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TRUNC)
ret, thresh4 = cv2.threshold(img_gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
ret, thresh5 = cv2.threshold(img_gray,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
title = ['Original Image','BINARY','BINARY_INV','TRUNC','TOZERO','TOZERO_INV']
images = [img,thresh1,thresh2,thresh3,thresh4,thresh5]
for i in range(6):
plt.subplot(2,3,i + 1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(title[i])
plt.xticks()
plt.yticks()
plt.show()图像平滑
当前输入数据,如上lena图像上有很多噪音点,现在我们想通过滤波、平滑处理等操作尽可能的去掉这些噪音点。
#图像平滑
img = cv2.imread('lenaNoise.png')
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#均值滤波
#简单的平均卷积操作
blur = cv2.blur(img,(3,3))
cv2.imshow('blur',blur)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#方框滤波
#基本和滤波一样,可以选择归一化
box = cv2.boxFilter(img,-1,(3,3),normalize=True)
cv2.imshow('box',box)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#方框滤波
#基本和滤波一样,可以选择归一化,容易越界
box = cv2.boxFilter(img,-1,(3,3),normalize=False)
cv2.imshow('box',box)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#高斯滤波
#高斯模糊的卷积核里的数值是满足高斯分布的,相当于更重视中间的
aussian = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),1)
cv2.imshow('aussian',aussian)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#中值滤波
#相当于用中值代替,利用中值滤波处理后,椒盐噪声几乎完全被去除掉
median = cv2.medianBlur(img,5)
cv2.imshow('median',median)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#展示所有的
res = np.hstack((blur,aussian,median))
print(res)
cv2.imshow('median vs average',res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()均值滤波相当于低通滤波,有将图像模糊化的趋势,对椒盐噪声计基本无能为力。中值滤波的优点是可以很好的过滤掉椒盐噪声,缺点是易造成图像的不连续性。
形态学-腐蚀操作
#形态学—腐蚀操作
img = cv2.imread('dige.png')
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
kernel_1 = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel_1,iterations=1)
cv2.imshow('erosion',erosion)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
pie = cv2.imread('pie.png')
cv2.imshow('pie',pie)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
kernel_2 = np.ones((30,30),np.uint8)
erosion_1 = cv2.erode(pie,kernel_2,iterations=1)
erosion_2 = cv2.erode(pie,kernel_2,iterations=2)
erosion_3 = cv2.erode(pie,kernel_2,iterations=3)
res = np.hstack((erosion_1,erosion_2,erosion_3))
cv2.imshow('res',res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()形态学-膨胀操作
#形态学—膨胀操作
img = cv2.imread('dige.png')
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
dige_erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations=1)
cv2.imshow('erosion',dige_erosion)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
dige_dilate = cv2.dilate(dige_erosion,kernel,iterations=1)
cv2.imshow('dilate',dige_dilate)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
pie = cv2.imread('pie.png')
kernel = np.ones((30,30),np.uint8)
dilate_1 = cv2.dilate(pie,kernel,iterations=1)
dilate_2 = cv2.dilate(pie,kernel,iterations=2)
dilate_3 = cv2.dilate(pie,kernel,iterations=3)
res = np.hstack((dilate_1,dilate_2,dilate_3))
cv2.imshow('res',res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()开运算与闭运算
开运算:先腐蚀,再膨胀
闭运算:先膨胀,再腐蚀
#开运算与闭运算
#开:先腐蚀,再膨胀
img = cv2.imread('dige.png')
kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(img,cv2.MORPH_OPEN,kernel)
cv2.imshow('opening',opening)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#闭:先膨胀,再腐蚀
img =cv2.imread('dige.png')
kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(img,cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel)
cv2.imshow('closing',closing)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#梯度运算
#梯度=膨胀-腐蚀
pie = cv2.imread('pie.png')
kernel = np.ones((7,7),np.uint8)
dilate = cv2.dilate(pie,kernel,iterations=5)
erossion = cv2.erode(pie,kernel,iterations=5)
res = np.hstack((dilate,erossion))
cv2.imshow('res',res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
gradient = cv2.morphologyEx(pie,cv2.MORPH_GRADIENT,kernel)
cv2.imshow('gradient',gradient)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#礼帽和黑帽
#礼帽=原始输入-开运算结果
#黑帽=闭运算-原始输入
#礼帽
img = cv2.imread('dige.png')
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(img,cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT,kernel)
cv2.imshow('topcat',tophat)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#黑帽
img = cv2.imread('dige.png')
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
blackhat = cv2.morphologyEx(img,cv2.MORPH_BLACKHAT,kernel)
cv2.imshow('blackhat',blackhat)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
图像梯度-Sobel算子
梯度简单来说就是求导。OpenCV提供了三种不同的梯度滤波器,或者说高通滤波器:Sobel,Scharr和Lapacian。Sobel,Scharr其实就是求一阶或二阶导。Scharr是对Sobel的部分优化。Laplacian是求二阶导。
#图像梯度-Sobel算子
img = cv2.imread('pie.png',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()dist = cv2.Sobel(src,ddepth,dx,dy,ksize)
ddepth:图像深度
dx和dy分别表示水平和竖直方向
ksize是Sobel算子的大小
#图像梯度-Sobel算子
img = cv2.imread('pie.png',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def cv_show(img,name):
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#cv2.CV_64F,64F代表每一个像素点元素占64位浮点数
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3)
sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx)
cv_show(sobelx,'sobelx')
#白到黑是正数,黑到白是负数,所有的负数都会被截断为0,所以要取绝对值
sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3)
sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
cv_show(sobely,'sobely')
sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3)
sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
cv_show(sobely,'sobely')
#分别计算x和y,再求和
sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0)
cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy')
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3)
sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3)
sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0)
cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy')
#整体计算存在重影,不建议
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
sobelxy = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,1,ksize=3)
sobelxy = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelxy)
cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy')图像梯度-Scharr算子
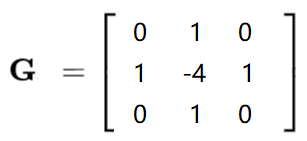
图像梯度-laplacian算子
拉普拉斯算子可以使用二阶导数的形式定义,可假设其离散实现类似于二阶Sobel导数。
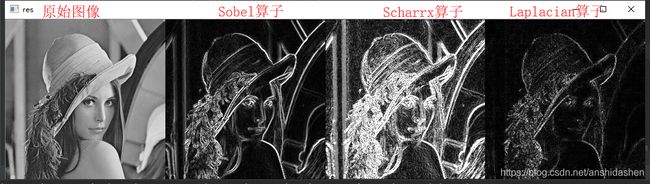
#不同算子的差异
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3)
sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx)
sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely)
sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0)
scharrx = cv2.Scharr(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0)
scharry = cv2.Scharr(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1)
scharrx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(scharrx)
scharry = cv2.convertScaleAbs(scharry)
scharrxy = cv2.addWeighted(scharrx,0.5,scharry,0.5,0)
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img,cv2.CV_64F)
laplacian = cv2.convertScaleAbs(laplacian)
res = np.hstack((img,sobelxy,scharrxy,laplacian))
cv_show(res,'res')