Netty介绍及NIO详解
Netty简介
Netty是一个异步、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架
BIO、NIO、AIO的简介
应用场景
- 分布式系统中各节点远程过程调用(RPC:Dubbo)
- 游戏服务器
- Hadoop通信
NIO
三大组件
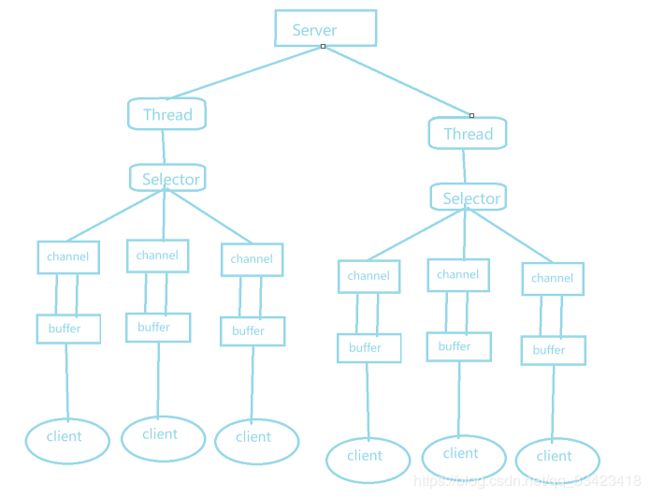
NIO三大组件:Selector、Channel、Buffer
- 一个Channel对应一个Buffer,一个Selector管理多个Channel,一个线程对应一个Selector
- 程序切换到哪个Channel由事件决定,Event
- Buffer就是一个内存块,底层是数组。Client通过Buffer进行数据的读写,NIO中的Buffer是双向的,BIO中的输入流、输出流不是双向的。
- Channel也是双向的
Buffer
抽象类Buffer中的属性:
- mark : 标记
- position : 位置,下一次要读写的元素的位置。
- limit : 缓冲区的终点,不能超过缓冲区的最大位置,可以修改
- capacity :容量,缓冲区创建时指定
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
// 将元素插入position位置
intBuffer.put(i << 10);
}
// 读写翻转
intBuffer.flip();
// 将limit指定为3,只能获取索引小于3的元素
intBuffer.limit(3);
System.out.println(intBuffer.capacity());
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
// 获取position位置的元素
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
基本类型中除了bool,其他类型都有对应的Buffer类。
IntegerBuffer类中的重要属性:
// 存储数据的数组
final int[] hb; // Non-null only for heap buffers
final int offset;
// 是否只读
boolean isReadOnly;
Channel
Channel可以同时读写,可以异步读写数据。
- FileChannel:文件读写
FileOutPutStream和FileInputStream中包含了FileChannel属性,可以通过这两个类的实例获得Channel。
实例:
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D://hello.txt");
// 从FileOutPutStream获取FileChannelImpl
FileChannel channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String s = "hello,World";
// 将byte数组放入缓冲区,buffer的position等于数组长度
buffer.put(s.getBytes());
// 读写翻转,limit=position,而position置0
buffer.flip();
// 写入
channel.write(buffer);
outputStream.close();
channel.close();
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D://hello.txt");
// FileInputStream获取FileChannel,实际类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel channel = inputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(read);
String s = new String(buffer.array(), 0, read,"utf-8");
System.out.println(s);
inputStream.close();
channel.close();
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D://hello.txt");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D://hello2.txt");
FileChannel inChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);
while (true){
// clear不重置的话,position=limit,则read一直等于0
// 标志位重置,position重置为0,limit设为capacity
buffer.clear();
int read = inChannel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1){
break;
}
buffer.flip();
outputChannel.write(buffer);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
// 使用transfrom拷贝文件
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D://a.jpg");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("D://a2.jpg");
FileChannel inChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = outputStream.getChannel();
// transferFrom拷贝
outputChannel.transferFrom(inChannel,0,inChannel.size());
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
Buffer和Channel注意事项
-
ByteBuffer,put什么类型,取得时候就要相应的类型去get。
-
Buffer可以设置为只读
// 只读Buffer,不可写,否则会报ReadOnlyBufferException ByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer(); -
MappedByteBuffer可以直接在内存(堆外内存)中修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次
// 直接在内存中修改,不用操作系统再拷贝一次 RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile("D://a.txt", "rw"); FileChannel channel = accessFile.getChannel(); /** * 参数说明; * 1.FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE 使用读写模式 * 2.直接修改的起始位置 * 3.从起始位置映射到内存的大小(不是索引),超过字节大小将不能修改 */ MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5); mappedByteBuffer.put(0,(byte) 'a'); mappedByteBuffer.put(3,(byte) '9'); accessFile.close(); -
NIO支持多个Buffer的Scatting和Gathering
/** * Scatting:将数据写入到buffer时,可以使用buffer数组,依次写入 * Gathering:从buffer读取数据时,可以采用buffer数组,依次读取 */ ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000); serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(socketAddress); // 创建buffer数组 ByteBuffer[] buffers = new ByteBuffer[2]; buffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5); buffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(8); int messageLength = 10; // 等待连接 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); // 循环读取 while (true) { int byteRead = 0; while (byteRead < messageLength){ long l = socketChannel.read(buffers); byteRead += l; System.out.println("byteRead = "+byteRead); Arrays.asList(buffers).stream().map(buffer -> "position = "+buffer.position() +",limit = "+buffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println); } Arrays.asList(buffers).forEach(byteBuffer -> byteBuffer.flip()); int byteWrite = 0; while (byteWrite < messageLength){ long l = socketChannel.write(buffers); byteWrite += l; } Arrays.asList(buffers).forEach(byteBuffer -> byteBuffer.clear()); System.out.println("byteRead = "+byteRead + ",byteWrite = "+byteWrite +",messageLength = "+messageLength);
Selector
- Channel注册到Selector,Selector能够检测到Channel是否有事件发生。如果有事件发生,则进行相应的处理。这样可以实现一个线程管理多个Channel(即多个连接和请求)
- 只有通道真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写。减少了创建的线程数,降低了系统开销
- 减少了上下文的切换,用户态和系统态的切换
以ServerSocketChannel为例说明:
- 当有客户端连接时,ServerSocketChannel会返回一个SocketChannel
- SocketChannel注册到Selector。(register方法)
- register方法会返回一个SelectionKey,SelectionKey与Channel关联
- Selector监听select方法,返回有事件的个数
- 进一步得到SelectionKey
- 通过SelectionKey获取SocketChannel(SelectionKey中的channel方法)
- 通过获取的channel,执行业务处理
代码说明:
SeverSocketChannel端:
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 绑定ip
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
// 设置为不阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将ServerSocketChannel注册到selector。指定关心的事件为OP_ACCEPT,
// 当有关心的事件发生时,会返回这个SelectionKey,通过SelectionKey可以拿到Channel
serverSocketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true){
// Selector监听,等于0说明此时没有事件发生。
if (selector.select(1000) == 0) {
System.out.println("Selector监听了一秒");
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = keys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()){
// 获得SocketChannel,此处的accept不会阻塞
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 此处socketChannel也要设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册Selector。第三个参数是连接的对象,通过SelectionKey可以连接到这个对象
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ,ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
int read = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("客户端 : "+new String(buffer.array(),0,read));
}
// 手动删除避免重复
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
SocketClient端;
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
boolean connect = socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9000));
if (!connect){
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做一些其他工作");
}
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("This is a message!".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();