297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
- 方法1: ASCII
- 易错点
- 方法2: level-order traversal/BFS
- 易错点
- Complexity
- 方法3: bytes
- 易错点
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Example:
You may serialize the following tree:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
as "[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
Clarification: The above format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
Note:
Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your serialize and deserialize algorithms should be stateless.
方法1: ASCII
花花酱: https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/tree/leetcode-297-serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
思路:
用字符来记录每一节点,如果是null就记“#”。
易错点
- 空格, 即使是“# ”后面也跟着一个空格,这样stringstream读取的时候才能分开。
- stringstream的使用。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out;
serializeHelper(root, out);
return out.str();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream in(data);
TreeNode * root = deserializeHelper(in);
return root;
}
private:
void serializeHelper(TreeNode* root, ostringstream & out){
if (!root) {
out << "# ";
return;
}
out << root -> val << " ";
serializeHelper(root -> left, out);
serializeHelper(root -> right, out);
return;
}
TreeNode* deserializeHelper(istringstream & in){
string s;
in >> s;
if (s == "#") return nullptr;
TreeNode* current = new TreeNode(stoi(s));
current -> left = deserializeHelper(in);
current -> right = deserializeHelper(in);
return current;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));
方法2: level-order traversal/BFS
grandyang:http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4913869.html
思路:
用bfs的方法
易错点
- serialize和deserialize的时候,都需要判空。
- deserialize的时候,每次的要判断有没有需要连接的左右孩子,并且将孩子入队。
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if (root) q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()){
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t){
out << t -> val << " ";
q.push(t -> left);
q.push(t -> right);
}
else {
out << "# ";
}
}
return out.str();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
if (data.empty()) return nullptr;
istringstream in(data);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
string val;
in >> val;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
TreeNode* current = root;
q.push(current);
while (!q.empty()){
TreeNode* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (!(in >> val)) break;
if (val != "#") {
current = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
q.push(current);
t -> left = current;
}
if (!(in >> val)) break;
if (val != "#") {
current = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
q.push(current);
t -> right = current;
}
}
return root;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));
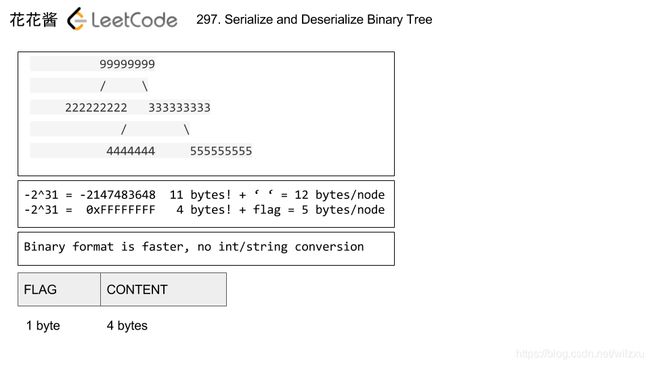
方法3: bytes
思路:
往压缩方向思考的第一步。所有int可以被存储在4 bytes以内,相比都用string来存储可以大幅度节省空间。通过设置enum status的方法,用一个byte来表示root,root->left, root->right有没有值。那么在serialize的时候一共最多有5 bytes。在deserialize时,先读入一个status byte,来判断接下来需要读入多少个byte,分别是什么。
易错点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
ostringstream out;
serializeHelper(root, out);
return out.str();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
istringstream in(data);
TreeNode* root = deserializeHelper(in);
return root;
}
private:
enum STATUS {
ROOT_NULL = 0x0,
ROOT = 0x1,
LEFT = 0x2,
RIGHT = 0x4
};
void serializeHelper(TreeNode* root, ostringstream& out) {
char status = 0;
if (root) status |= ROOT;
if (root && root->left) status |= LEFT;
if (root && root->right) status |= RIGHT;
out.write(&status, sizeof(char));
if (!root) return;
out.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&(root->val)), sizeof(root->val));
if (root->left) serializeHelper(root->left, out);
if (root->right) serializeHelper(root->right, out);
}
TreeNode* deserializeHelper(istringstream& in) {
char status;
in.read(&status, sizeof(char));
if (!status & ROOT) return nullptr;
auto root = new TreeNode(0);
in.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&root->val), sizeof(root->val));
root->left = (status & LEFT) ? deserializeHelper(in) : nullptr;
root->right = (status & RIGHT) ? deserializeHelper(in) : nullptr;
return root;
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec;
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));