Android动画绘制原理(源码解析)
个人博客地址 http://dandanlove.com/
前言
Android 平台提供了三类动画,一类是 Tween 动画-Animation,即通过对场景里的对象不断做图像变换 ( 平移、缩放、旋转 ) 产生动画效果;第二类是 Frame 动画,即顺序播放事先做好的图像,跟电影类似。最后一种就是3.0之后才出现的属性动画PropertyAnimator(在下文我们讲帧动画和补间动画统一称为View动画)。如果有人对ViewGroup内部View使用过View动画的还知道有layout-animation。
大家对这三种动画基本都能熟练的使用,那么……?
- 想知道动画与界面渲染与屏幕刷新有着什么样的关系?
- 想知道属性动画为什么会发生内存泄露么?
因为本文章中会有一些屏幕刷新、Vsync信号相关的知识点,读过我写的 Android的16ms和垂直同步以及三重缓存 和Android系统的编舞者Choreographer 这两篇文章的同学会可能会更容易了解本文章。
接下来拿起我们的键盘、鼠标和显示器,我们将探索从Android源码(android-23)的角度去探索动画的实现~!
动画的介绍
Drawable Animation
也就是所谓的帧动画,Frame动画。指通过指定每一帧的图片和播放时间,有序的进行播放而形成动画效果。
Tween Animation
视图动画,也就是所谓补间动画,Tween动画。指通过指定View的初始状态、变化时间、方式,通过一系列的算法去进行图形变换,从而形成动画效果,主要有Alpha、Scale、Translate、Rotate四种效果。注意:只是在视图层实现了动画效果,并没有真正改变View的属性。
Property Animation
属性动画,通过不断的改变View的属性,不断的重绘而形成动画效果。相比于视图动画,View的属性是真正改变了。注意:Android 3.0(API 11)以上才支持。
接下来我们按照倒叙来揭开一个一个动画的神秘面纱_。
Property Animation
属性动画的优点
- 属性动画顾名思义就是改变了View的属性,而不仅仅是绘制的位置。
- 属性动画可以操作的属性相比于补间动画大大增加,除了常用的平移、旋转、缩放、透明度还有颜色等,基本上能通过View.setXX来设置的属性,属性动画都可以操作,这大大增加了我们在使用动画时的灵活性。
- 属性动画分为ObjectAnimator和ValueAnimator,其中ObjectAnimator是继承于ValueAnimator。
ValueAnimator
ValueAnimator并不会改变属性的大小,他只是在一段时间生成某些值。我们需要做的是监听这些值得改变从而该改变View的属性,进而产生动画效果。
下边的动画就是对mView进行平移:
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1000);
anim.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
mView.setTranslationX(animation.getAnimatedValue());
}
});
animator.setDuration(1000).start()
ObjectAnimator
在ValueAnimator的基础之上,对控件的某个属性执行一次动画。
相同的对mView进行平移的动画ObjectAnimator是这样实现的:
ObjectAnimator animator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat (mView,"translationX",0,1000);
animator.setDuration (1000);
animator.start ();
PropertyAnimation流程图
属性动画代码的执行过程
start
ObjectAnimator.start
public final class ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
public void start() {
//首先依次判断了当前动画、等待的动画、延迟的动画中是否有和当前动画相同的动画
//若有就把相同的动画取消掉
// See if any of the current active/pending animators need to be canceled
AnimationHandler handler = sAnimationHandler.get();
if (handler != null) {
int numAnims = handler.mAnimations.size();
for (int i = numAnims - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (handler.mAnimations.get(i) instanceof ObjectAnimator) {
ObjectAnimator anim = (ObjectAnimator) handler.mAnimations.get(i);
if (anim.mAutoCancel && hasSameTargetAndProperties(anim)) {
anim.cancel();
}
}
}
/***部分代码省略***/
}
/***部分代码省略***/
//然后调用ValueAnimator.start()方法
super.start();
}
}
ValueAnimator.start
public class ValueAnimator extends Animator {
/***部分代码省略***/
protected static ThreadLocal sAnimationHandler =
new ThreadLocal();
//保证每个线程有且只有一个AnimationHandler
private static AnimationHandler getOrCreateAnimationHandler() {
AnimationHandler handler = sAnimationHandler.get();
if (handler == null) {
handler = new AnimationHandler();
sAnimationHandler.set(handler);
}
return handler;
}
@Override
public void start() {
start(false);
}
private void start(boolean playBackwards) {
if (Looper.myLooper() == null) {
throw new AndroidRuntimeException("Animators may only be run on Looper threads");
}
/***部分代码省略***/
//创建或者获取animationHandler实例
AnimationHandler animationHandler = getOrCreateAnimationHandler();
animationHandler.mPendingAnimations.add(this);
if (mStartDelay == 0) {
// This sets the initial value of the animation, prior to actually starting it running
if (prevPlayingState != SEEKED) {
setCurrentPlayTime(0);
}
mPlayingState = STOPPED;
mRunning = true;
//回调监听器,通知动画开始
notifyStartListeners();
}
//开始动画
animationHandler.start();
}
//回调监听器,通知动画开始
private void notifyStartListeners() {
if (mListeners != null && !mStartListenersCalled) {
ArrayList tmpListeners =
(ArrayList) mListeners.clone();
int numListeners = tmpListeners.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
tmpListeners.get(i).onAnimationStart(this);
}
}
mStartListenersCalled = true;
}
public void setCurrentPlayTime(long playTime) {
float fraction = mUnscaledDuration > 0 ? (float) playTime / mUnscaledDuration : 1;
setCurrentFraction(fraction);
}
public void setCurrentFraction(float fraction) {
//初始化动画
initAnimation();
if (fraction < 0) {
fraction = 0;
}
/***部分代码省略***/
}
}
AnimationHandler.start
public class ValueAnimator extends Animator {
/***部分代码省略***/
protected static class AnimationHandler implements Runnable {
/***部分代码省略***/
//开始动画
public void start() {
scheduleAnimation();
}
//发送VSYNC信号回调请求
private void scheduleAnimation() {
if (!mAnimationScheduled) {
mChoreographer.postCallback(Choreographer.CALLBACK_ANIMATION, this, null);
mAnimationScheduled = true;
}
}
// Called by the Choreographer.
//Choreographer的VSYNC信号回调
@Override
public void run() {
mAnimationScheduled = false;
doAnimationFrame(mChoreographer.getFrameTime());
}
private void doAnimationFrame(long frameTime) {
/***部分代码省略***/
// Now process all active animations. The return value from animationFrame()
// tells the handler whether it should now be ended
int numAnims = mAnimations.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numAnims; ++i) {
mTmpAnimations.add(mAnimations.get(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < numAnims; ++i) {
ValueAnimator anim = mTmpAnimations.get(i);
//执行动画
//doAnimationFrame方法返回ture,则该动画添加在mEndingAnims队列中进行end操作
if (mAnimations.contains(anim) && anim.doAnimationFrame(frameTime)) {
mEndingAnims.add(anim);
}
}
/***部分代码省略***/
//循环执行,直到endAnimation将mAnimations置空
if (!mAnimations.isEmpty() || !mDelayedAnims.isEmpty()) {
scheduleAnimation();
}
}
}
}
init
ObjectAnimator.initAnimation
public final class ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
void initAnimation() {
if (!mInitialized) {
// mValueType may change due to setter/getter setup; do this before calling super.init(),
// which uses mValueType to set up the default type evaluator.
final Object target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
final int numValues = mValues.length;
for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) {
mValues[i].setupSetterAndGetter(target);
}
}
super.initAnimation();
}
}
}
setupSetterAndGetter
public final class ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
/***部分代码省略***/
void setupSetterAndGetter(Object target) {
mKeyframes.invalidateCache();
if (mProperty != null) {
/***部分代码省略***/
}
// We can't just say 'else' here because the catch statement sets mProperty to null.
if (mProperty == null) {
Class targetClass = target.getClass();
if (mSetter == null) {
//初始化mSetter
setupSetter(targetClass);
}
/***部分代码省略***/
}
}
//初始化mSetter用于以后反射执行get、set操作
void setupSetter(Class targetClass) {
Class propertyType = mConverter == null ? mValueType : mConverter.getTargetType();
mSetter = setupSetterOrGetter(targetClass, sSetterPropertyMap, "set", propertyType);
}
}
animation
ValueAnimator.doAnimationFrame
public class ValueAnimator extends Animator {
/***部分代码省略***/
final boolean doAnimationFrame(long frameTime) {
/***部分代码省略***/
return animationFrame(currentTime);
}
boolean animationFrame(long currentTime) {
boolean done = false;
switch (mPlayingState) {
case RUNNING:
case SEEKED:
/***部分代码省略***/
if (fraction >= 1f) {
//mCurrentIteration是否等于mRepeatCount
if (mCurrentIteration < mRepeatCount || mRepeatCount == INFINITE) {
// Time to repeat
/***部分代码省略***/
} else {
//执行完这次,该动画结束
done = true;
fraction = Math.min(fraction, 1.0f);
}
}
if (mPlayingBackwards) {
fraction = 1f - fraction;
}
//设置View的属性值
animateValue(fraction);
break;
}
return done;
}
}
ValueAnimator.animateValue
public class ValueAnimator extends Animator {
/***部分代码省略***/
void animateValue(float fraction) {
fraction = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
mCurrentFraction = fraction;
int numValues = mValues.length;
for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) {
//PropertyValuesHolder.calculateValue就是计算每帧动画所对应的值
mValues[i].calculateValue(fraction);
}
if (mUpdateListeners != null) {
int numListeners = mUpdateListeners.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
//属性值得改变的回调
mUpdateListeners.get(i).onAnimationUpdate(this);
}
}
}
}
ObjectAnimator.animateValue
public final class ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
void animateValue(float fraction) {
final Object target = getTarget();
if (mTarget != null && target == null) {
// We lost the target reference, cancel and clean up.
cancel();
return;
}
//ValueAnimator.animateValue方法
super.animateValue(fraction);
int numValues = mValues.length;
for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) {
//设置target的属性值,进行View的移动,产生动画
mValues[i].setAnimatedValue(target);
}
}
}
PropertyValuesHolder
PropertyValuesHolder这个类的意义就是,它其中保存了动画过程中所需要操作的属性和对应的值。我们通过ofFloat(Object target, String propertyName, float… values)构造的动画,ofFloat()的内部实现其实就是将传进来的参数封装成PropertyValuesHolder实例来保存动画状态。在封装成PropertyValuesHolder实例以后,后期的各种操作也是以PropertyValuesHolder为主的。
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat
我们先看看我们之前的代码中构造ObjectAnimator的方法:
public final class ObjectAnimator extends ValueAnimator {
/***部分代码省略***/
private ObjectAnimator(Object target, String propertyName) {
setTarget(target);
setPropertyName(propertyName);
}
public static ObjectAnimator ofFloat(Object target, String propertyName, float... values) {
//构造ObjectAnimator
ObjectAnimator anim = new ObjectAnimator(target, propertyName);
anim.setFloatValues(values);
return anim;
}
//设置属性值
public void setPropertyName(@NonNull String propertyName) {
/***部分代码省略***/
mPropertyName = propertyName;
// New property/values/target should cause re-initialization prior to starting
mInitialized = false;
}
@Override
public void setFloatValues(float... values) {
if (mValues == null || mValues.length == 0) {
// No values yet - this animator is being constructed piecemeal. Init the values with
// whatever the current propertyName is
if (mProperty != null) {
setValues(PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat(mProperty, values));
} else {
setValues(PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat(mPropertyName, values));
}
} else {
super.setFloatValues(values);
}
}
}
构造FloatPropertyValueHolder
public class PropertyValuesHolder implements Cloneable {
/***部分代码省略***/
public static PropertyValuesHolder ofFloat(String propertyName, float... values) {
return new FloatPropertyValuesHolder(propertyName, values);
}
}
public class PropertyValuesHolder implements Cloneable {
/***部分代码省略***/
static class FloatPropertyValuesHolder extends PropertyValuesHolder {
public FloatPropertyValuesHolder(String propertyName, float... values) {
super(propertyName);
setFloatValues(values);
}
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
public void setFloatValues(float... values) {
super.setFloatValues(values);
mFloatKeyframes = (Keyframes.FloatKeyframes) mKeyframes;
}
@Override
void setAnimatedValue(Object target) {
/***部分代码省略***/
if (mSetter != null) {
try {
mTmpValueArray[0] = mFloatAnimatedValue;
//反射操作target的属性,通过set、get方法
mSetter.invoke(target, mTmpValueArray);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Log.e("PropertyValuesHolder", e.toString());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
Log.e("PropertyValuesHolder", e.toString());
}
}
}
}
}
属性动画的内存泄露
- 上面讲述到
ValueAnimator.AnimationHandler.doAnimationFrame的时候说过,这个方法会循环执行。 - 因为
ValueAnimator.AnimationHandler.doAnimationFrame每次执行完动画(如果动画没有结束),都在再一次请求Vsync同步信号回调给自己。 Choreographer的回调都配post进入了当前线程的looper队列中。mRepeatCount无穷大,会导致该循环会一直执行下去,即使关闭当前的页面也不会停止。
Drawable Animation
帧动画使用
animalist.xml
layout.xml
java类使用
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
AnimationDrawable animationDrawable = (AnimationDrawable) image.getDrawable();
animationDrawable.start();
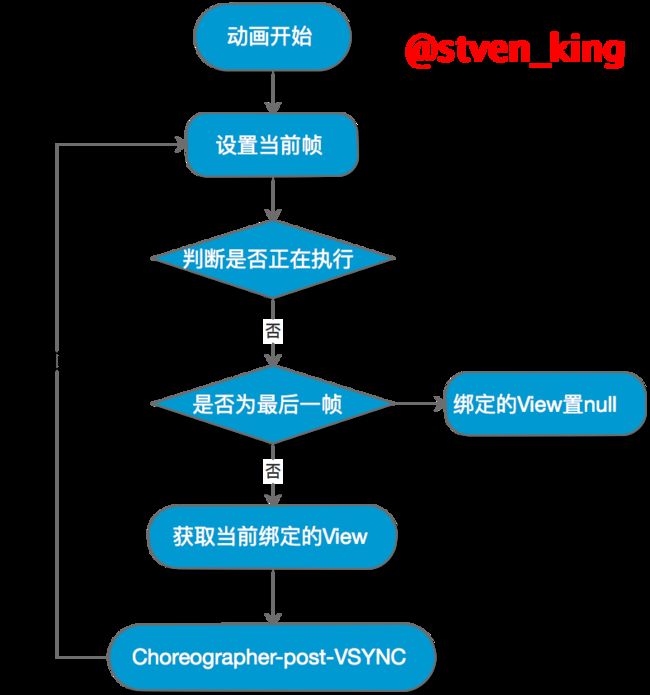
DrawableAnimation流程图
帧动画代码执行过程
start
public class AnimationDrawable extends DrawableContainer implements Runnable, Animatable {
/***代码部分省略***/
@Override
public void start() {
mAnimating = true;
if (!isRunning()) {
// Start from 0th frame.
setFrame(0, false, mAnimationState.getChildCount() > 1
|| !mAnimationState.mOneShot);
}
}
//设置当前展示第几帧
private void setFrame(int frame, boolean unschedule, boolean animate) {
if (frame >= mAnimationState.getChildCount()) {
return;
}
mAnimating = animate;
mCurFrame = frame;
selectDrawable(frame);
//如果取消下一帧任务,或者这已经是当前最后一帧,则取消当帧动画任务
if (unschedule || animate) {
unscheduleSelf(this);
}
if (animate) {
// Unscheduling may have clobbered these values; restore them
mCurFrame = frame;
mRunning = true;
scheduleSelf(this, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + mAnimationState.mDurations[frame]);
}
}
//安排动画绘制任务
public void scheduleSelf(Runnable what, long when) {
//该Callback是当前AnimationDrawable绑定的View
final Callback callback = getCallback();
//判断当前绑定的View是否被销毁
if (callback != null) {
callback.scheduleDrawable(this, what, when);
}
}
}
scheduleDrawable
-
ViewRootImpl的独白,我不是一个View(布局篇)
-
Android系统的编舞者Choreographer
public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
AccessibilityEventSource {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
public void scheduleDrawable(Drawable who, Runnable what, long when) {
if (verifyDrawable(who) && what != null) {
final long delay = when - SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (mAttachInfo != null) {
//请求Vsync信号同步
mAttachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mChoreographer.postCallbackDelayed(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_ANIMATION, what, who,
Choreographer.subtractFrameDelay(delay));
} else {
ViewRootImpl.getRunQueue().postDelayed(what, delay);
}
}
}
}
run
public class AnimationDrawable extends DrawableContainer implements Runnable, Animatable {
/***代码部分省略***/
//Choreographer的Vsync同步回调
@Override
public void run() {
nextFrame(false);
}
//继续执行下一帧动画
private void nextFrame(boolean unschedule) {
int nextFrame = mCurFrame + 1;
final int numFrames = mAnimationState.getChildCount();
final boolean isLastFrame = mAnimationState.mOneShot && nextFrame >= (numFrames - 1);
// Loop if necessary. One-shot animations should never hit this case.
if (!mAnimationState.mOneShot && nextFrame >= numFrames) {
nextFrame = 0;
}
//新一轮的循环又开始
setFrame(nextFrame, unschedule, !isLastFrame);
}
}
其他
CallBack的绑定
public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
AccessibilityEventSource {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Deprecated
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//清除之前的背景
if (mBackground != null) {
mBackground.setCallback(null);
unscheduleDrawable(mBackground);
}
if (background != null) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//Drawable绑定当前的View
background.setCallback(this);
if (background.isStateful()) {
background.setState(getDrawableState());
}
background.setVisible(getVisibility() == VISIBLE, false);
mBackground = background;
applyBackgroundTint();
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) != 0) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW;
requestLayout = true;
}
} else {
/***部分代码省略***/
}
computeOpaqueFlags();
if (requestLayout) {
requestLayout();
}
mBackgroundSizeChanged = true;
invalidate(true);
}
}
内存方面
帧动画相比较属性动画而言可能会出现OOM,因为在家的每一帧的图片会占用很大的内存空间。
帧动画不会出现内存泄露的问题:
public abstract class Drawable {
/***部分代码省略***/
//持有当前View的弱引用,当View回收之后,没办法继续下一帧的展示
private WeakReference mCallback = null;
public Callback getCallback() {
if (mCallback != null) {
return mCallback.get();
}
return null;
}
}
Tween Animation
补间动画的使用
Animation translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(0, 100, 0, 0);
translateAnimation.setDuration(500);
translateAnimation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true);//设置动画结束后保持当前的位置(即不返回到动画开始前的位置)
imageView.startAnimation(translateAnimation);
TweenAnimation流程图
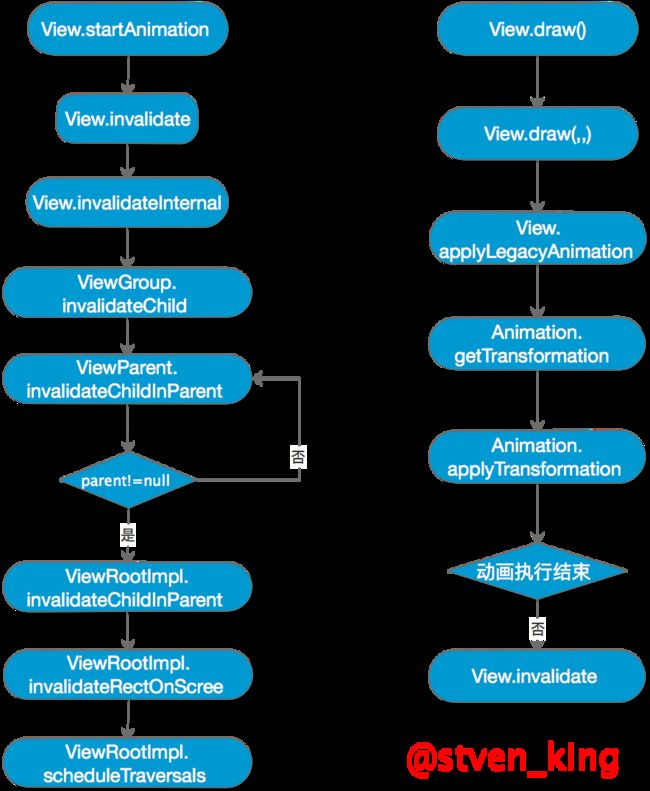
补间动画代码的执行过程
start
View:
public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
AccessibilityEventSource {
//部分代码省略
public void startAnimation(Animation animation) {
animation.setStartTime(Animation.START_ON_FIRST_FRAME);
setAnimation(animation);
invalidateParentCaches();
invalidate(true);
}
void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) {
invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,
boolean fullInvalidate) {
if (mGhostView != null) {
mGhostView.invalidate(true);
return;
}
if (skipInvalidate()) {
return;
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)
|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED
|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {
//部分代码省略
// Propagate the damage rectangle to the parent view.
final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;
final ViewParent p = mParent;
if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {
final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
damage.set(l, t, r, b);
//执行ViewParent的invalidateChild方法
p.invalidateChild(this, damage);
}
//部分代码省略
}
}
}
ViewGroup
public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
/***部分代码省略***/
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
ViewParent parent = this;
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
/***部分代码省略***/
do {
/***部分代码省略***/
//向顶部的View便利找到根View,即:ViewRootImpl
//执行ViewRootImpl的invalidateChildInParent方法
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
if (view != null) {
// Account for transform on current parent
Matrix m = view.getMatrix();
if (!m.isIdentity()) {
RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect;
boundingRect.set(dirty);
m.mapRect(boundingRect);
dirty.set((int) (boundingRect.left - 0.5f),
(int) (boundingRect.top - 0.5f),
(int) (boundingRect.right + 0.5f),
(int) (boundingRect.bottom + 0.5f));
}
}
/***部分代码省略***/
} while (parent != null);
}
}
}
ViewRootImpl
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, HardwareRenderer.HardwareDrawCallbacks {
/***部分代码省略***/
@Override
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) {
checkThread();
/***部分代码省略***/
invalidateRectOnScreen(dirty);
return null;
}
private void invalidateRectOnScreen(Rect dirty) {
/***部分代码省略***/
if (!mWillDrawSoon && (intersected || mIsAnimating)) {
//开始View的绘制任务
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
}
之前写过一篇文章 ViewRootImpl的独白,我不是一个View(布局篇) 其中 ViewRootImpl对mView进行操作 讲述了再ViewRootImpl 中View的绘制。
draw
public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback,
AccessibilityEventSource {
//部分代码省略
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//如果有子 View(DecorView当然有子View),就会调用dispatchDraw() 将绘制事件通知给子 View。
//ViewGroup 重写了 dispatchDraw(),调用了 drawChild()
//drawChild() 调用了子 View 的 draw(Canvas, ViewGroup, long)
}
boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) {
final boolean hardwareAcceleratedCanvas = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated();
/***部分代码省略***/
Transformation transformToApply = null;
boolean concatMatrix = false;
final boolean scalingRequired = mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired;
final Animation a = getAnimation();
if (a != null) {
more = applyLegacyAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired);
concatMatrix = a.willChangeTransformationMatrix();
if (concatMatrix) {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM;
}
transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation();
} else {
/***部分代码省略***/
}
/***部分代码省略***/
}
private boolean applyLegacyAnimation(ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime,
Animation a, boolean scalingRequired) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//绘制动画的当前帧,并获取当前动画的状态(是否继续运行)
boolean more = a.getTransformation(drawingTime, t, 1f);
if (scalingRequired && mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale != 1f) {
if (parent.mInvalidationTransformation == null) {
parent.mInvalidationTransformation = new Transformation();
}
invalidationTransform = parent.mInvalidationTransformation;
a.getTransformation(drawingTime, invalidationTransform, 1f);
} else {
invalidationTransform = t;
}
//如果动画没有结果
if (more) {
if (!a.willChangeBounds()) {
if ((flags & (ViewGroup.FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE | ViewGroup.FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)) ==
ViewGroup.FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE) {
parent.mGroupFlags |= ViewGroup.FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED;
} else if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == 0) {
// The child need to draw an animation, potentially offscreen, so
// make sure we do not cancel invalidate requests
parent.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION;
//进行绘制
parent.invalidate(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
}
} else {
/***部分代码省略***/
//进行绘制
parent.invalidate(left, top, left + (int) (region.width() + .5f),
top + (int) (region.height() + .5f));
}
}
return more;
}
}
running
public abstract class Animation implements Cloneable {
/***部分代码省略***/
public boolean getTransformation(long currentTime, Transformation outTransformation) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//执行时间是否过期
final boolean expired = normalizedTime >= 1.0f;
mMore = !expired;
//动画进度为0.0~1.0之间
if (!mFillEnabled) normalizedTime = Math.max(Math.min(normalizedTime, 1.0f), 0.0f);
if ((normalizedTime >= 0.0f || mFillBefore) && (normalizedTime <= 1.0f || mFillAfter)) {
/***部分代码省略***/
//插值器计算动画执行进度
final float interpolatedTime = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(normalizedTime);
//真正的动画效果代码执行处(通过矩阵变化)
applyTransformation(interpolatedTime, outTransformation);
}
//如果动画绘制完成
if (expired) {
//判断动画是否需要继续循环
if (mRepeatCount == mRepeated) {
if (!mEnded) {
mEnded = true;
guard.close();
fireAnimationEnd();
}
} else {
if (mRepeatCount > 0) {
mRepeated++;
}
if (mRepeatMode == REVERSE) {
mCycleFlip = !mCycleFlip;
}
mStartTime = -1;
mMore = true;
fireAnimationRepeat();
}
}
if (!mMore && mOneMoreTime) {
mOneMoreTime = false;
return true;
}
return mMore;
}
}
其他
通过代码分析可以证明补间动画也不会存在内存泄露的问题,因为他是靠着View的绘制来完成每一帧动效的展示。
使用动画的注意事项
OOM的问题
这个问题主要出现在帧动画中,当图片数量过多的且图片较大的时候就极易出现OOM,这个在实际的开发中要尤其注意,尽量避免使用帧动画。
内存泄漏的问题
在属性动画中有一类无限循环的动画,这类动画需要在Activity退出时及时停止,否则导致Activity无法释放从而造成内存泄露,通过验证发现View动画(帧动画和补间动画)并不存在此问题。
兼容性问题
动画在3.0以下的系统上有兼容性问题,在某些特殊场景可能无法正常工作,因此要做好适配工作。
View动画的问题
View动画对View的影像做动画,并不是真正的改变View的状态,因此有时候会出现动画完成后View无法影藏的现象,即
setVisibility(View.GONE)失效了,这个时候只要调用view.clearAnimation()清除View动画即可解决此问题。
不要使用px
在进行动画的过程中,要尽量使用dp,使用px会导致在不同的设备上有不同的效果。
动画元素的交互
将View移动(平移)后,在Android3.0之前的系统上,不管是View动画还是属性动画,新位置均无法触发单击事件,同时老位置任然可以触发单击事件。尽管View已经在视觉上不存在了,将View移回原位置以后,原位置的单击事件继续生效。从3.0开始,属性动画的单击事件触发位置为移动以后的位置,但View动画仍然在原位置。
硬件加速
使用动画的过程中,建议开启硬件加速,这样会提交动画的流畅性。
文章到这里就全部讲述完啦,若有其他需要交流的可以留言哦!!
想阅读作者的更多文章,可以查看我 个人博客 和公共号:
![]()