Bellman-Ford算法原理及练习 || LeetCode 787
There are n cities connected by m flights. Each fight starts from city u and arrives at v with a price w.
Now given all the cities and flights, together with starting city src and the destination dst, your task is to find the cheapest price from src to dst with up to k stops. If there is no such route, output -1.
Example 1:
Input:
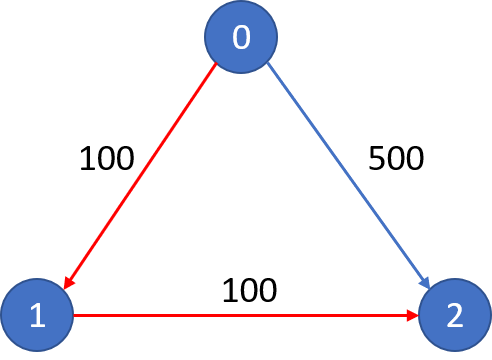
n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 1 stop costs 200, as marked red in the picture.
Example 2:
Input:
n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:The cheapest price from city 0 to city 2 with at most 0 stop costs 500, as marked blue in the picture.
Note:
- The number of nodes
nwill be in range[1, 100], with nodes labeled from0ton- 1. - The size of
flightswill be in range[0, n * (n - 1) / 2]. - The format of each flight will be
(src,dst, price). - The price of each flight will be in the range
[1, 10000]. kis in the range of[0, n - 1].- There will not be any duplicated flights or self cycles.
根据Bellman-Ford算法很容易就写出:
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vectorcost(n,1e6);cost[src]=0;
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){
for(auto&e:flights){
cost[e[1]]=min(cost[e[1]],cost[e[0]]+e[2]);
}
}
return cost[dst]==1e6?-1:cost[dst];
}
}; 但会出错,为什么呢?要注意到转机次数要小于等于k,而对一个点利用所有边进行松弛的时候,会出现利用多条边即多次转机的情况。为了控制转机次数,我们需要稍微调整一下代码:
//bellman-ford
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
vectorcost(n,1e6);cost[src]=0;///将所有权值设为inf,考虑到取值范围为[1, 10000].设为1e6即可。
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){
vectorc(cost);//控制每次大循环最多只会增加一次转机次数
for(auto&e:flights)
c[e[1]]=min(c[e[1]],cost[e[0]]+e[2]);//松弛,注意顺序是:c,c,cost
cost=c;
}
return cost[dst]==1e6?-1:cost[dst];
}
}; 另:由于本题中要求了边的权值为正,因此也可使用Dijkstra算法
参考资料:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/36295603
https://leetcode.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/discuss/128776/5-ms-AC-Java-Solution-based-on-Dijkstra's-Algorithm