计算机视觉:基于YOLO-V3林业病虫害目标检测
计算机视觉:基于YOLO-V3林业病虫害目标检测
- 卷积神经网络提取特征
- 根据输出特征图计算预测框位置和类别
- 建立输出特征图与预测框之间的关联
- 计算预测框是否包含物体的概率
- 计算预测框位置坐标
- 计算物体属于每个类别概率
- 损失函数
- 多尺度检测
- 开启端到端训练
- 预测
- 模型效果及可视化展示
卷积神经网络提取特征
在上一节图像分类的课程中,我们已经学习过了通过卷积神经网络提取图像特征。通过连续使用多层卷积和池化等操作,能得到语义含义更加丰富的特征图。在检测问题中,也使用卷积神经网络逐层提取图像特征,通过最终的输出特征图来表征物体位置和类别等信息。
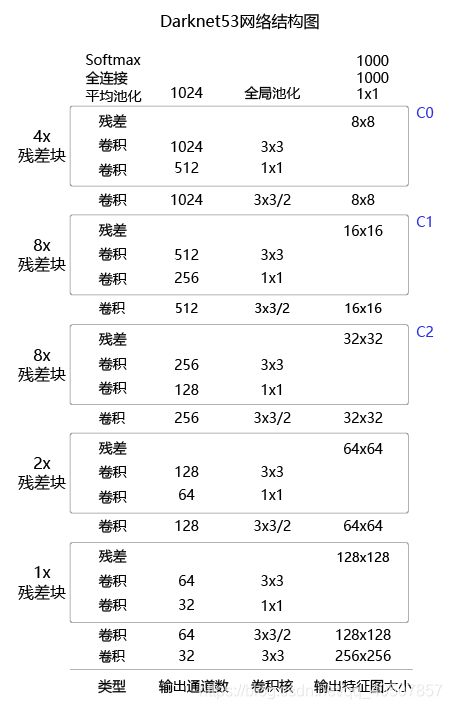
YOLO-V3算法使用的骨干网络是Darknet53。Darknet53网络的具体结构如 图16 所示,在ImageNet图像分类任务上取得了很好的成绩。在检测任务中,将图中C0后面的平均池化、全连接层和Softmax去掉,保留从输入到C0部分的网络结构,作为检测模型的基础网络结构,也称为骨干网络。YOLO-V3模型会在骨干网络的基础上,再添加检测相关的网络模块。
图16:Darknet53网络结构
下面的程序是Darknet53骨干网络的实现代码,这里将上图中C0、C1、C2所表示的输出数据取出,并查看它们的形状分别是, C 0 [ 1 , 1024 , 20 , 20 ] C0 [1, 1024, 20, 20] C0[1,1024,20,20], C 1 [ 1 , 512 , 40 , 40 ] C1 [1, 512, 40, 40] C1[1,512,40,40], C 2 [ 1 , 256 , 80 , 80 ] C2 [1, 256, 80, 80] C2[1,256,80,80]。
- 名词解释:特征图的步幅(stride)
在提取特征的过程中通常会使用步幅大于1的卷积或者池化,导致后面的特征图尺寸越来越小,特征图的步幅等于输入图片尺寸除以特征图尺寸。例如C0的尺寸是 20 × 20 20\times20 20×20,原图尺寸是 640 × 640 640\times640 640×640,则C0的步幅是 640 20 = 32 \frac{640}{20}=32 20640=32。同理,C1的步幅是16,C2的步幅是8。
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from paddle.fluid.param_attr import ParamAttr
from paddle.fluid.regularizer import L2Decay
from paddle.fluid.dygraph.nn import Conv2D, BatchNorm
from paddle.fluid.dygraph.base import to_variable
# YOLO-V3骨干网络结构Darknet53的实现代码
class ConvBNLayer(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
"""
卷积 + 批归一化,BN层之后激活函数默认用leaky_relu
"""
def __init__(self,
ch_in,
ch_out,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
groups=1,
padding=0,
act="leaky",
is_test=True):
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
self.conv = Conv2D(
num_channels=ch_in,
num_filters=ch_out,
filter_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=False,
act=None)
self.batch_norm = BatchNorm(
num_channels=ch_out,
is_test=is_test,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02),
regularizer=L2Decay(0.)),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=L2Decay(0.)))
self.act = act
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv(inputs)
out = self.batch_norm(out)
if self.act == 'leaky':
out = fluid.layers.leaky_relu(x=out, alpha=0.1)
return out
class DownSample(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
"""
下采样,图片尺寸减半,具体实现方式是使用stirde=2的卷积
"""
def __init__(self,
ch_in,
ch_out,
filter_size=3,
stride=2,
padding=1,
is_test=True):
super(DownSample, self).__init__()
self.conv_bn_layer = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
filter_size=filter_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
is_test=is_test)
self.ch_out = ch_out
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv_bn_layer(inputs)
return out
class BasicBlock(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
"""
基本残差块的定义,输入x经过两层卷积,然后接第二层卷积的输出和输入x相加
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, is_test=True):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=is_test
)
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
is_test=is_test
)
def forward(self, inputs):
conv1 = self.conv1(inputs)
conv2 = self.conv2(conv1)
out = fluid.layers.elementwise_add(x=inputs, y=conv2, act=None)
return out
class LayerWarp(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
"""
添加多层残差块,组成Darknet53网络的一个层级
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, count, is_test=True):
super(LayerWarp,self).__init__()
self.basicblock0 = BasicBlock(ch_in,
ch_out,
is_test=is_test)
self.res_out_list = []
for i in range(1, count):
res_out = self.add_sublayer("basic_block_%d" % (i), #使用add_sublayer添加子层
BasicBlock(ch_out*2,
ch_out,
is_test=is_test))
self.res_out_list.append(res_out)
def forward(self,inputs):
y = self.basicblock0(inputs)
for basic_block_i in self.res_out_list:
y = basic_block_i(y)
return y
DarkNet_cfg = {53: ([1, 2, 8, 8, 4])}
class DarkNet53_conv_body(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
def __init__(self,
is_test=True):
super(DarkNet53_conv_body, self).__init__()
self.stages = DarkNet_cfg[53]
self.stages = self.stages[0:5]
# 第一层卷积
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=3,
ch_out=32,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
is_test=is_test)
# 下采样,使用stride=2的卷积来实现
self.downsample0 = DownSample(
ch_in=32,
ch_out=32 * 2,
is_test=is_test)
# 添加各个层级的实现
self.darknet53_conv_block_list = []
self.downsample_list = []
for i, stage in enumerate(self.stages):
conv_block = self.add_sublayer(
"stage_%d" % (i),
LayerWarp(32*(2**(i+1)),
32*(2**i),
stage,
is_test=is_test))
self.darknet53_conv_block_list.append(conv_block)
# 两个层级之间使用DownSample将尺寸减半
for i in range(len(self.stages) - 1):
downsample = self.add_sublayer(
"stage_%d_downsample" % i,
DownSample(ch_in=32*(2**(i+1)),
ch_out=32*(2**(i+2)),
is_test=is_test))
self.downsample_list.append(downsample)
def forward(self,inputs):
out = self.conv0(inputs)
#print("conv1:",out.numpy())
out = self.downsample0(out)
#print("dy:",out.numpy())
blocks = []
for i, conv_block_i in enumerate(self.darknet53_conv_block_list): #依次将各个层级作用在输入上面
out = conv_block_i(out)
blocks.append(out)
if i < len(self.stages) - 1:
out = self.downsample_list[i](out)
return blocks[-1:-4:-1] # 将C0, C1, C2作为返回值
# 查看Darknet53网络输出特征图
import numpy as np
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
print(C0.shape, C1.shape, C2.shape)
[1, 1024, 20, 20] [1, 512, 40, 40] [1, 256, 80, 80]
上面这段示例代码,指定输入数据的形状是 ( 1 , 3 , 640 , 640 ) (1, 3, 640, 640) (1,3,640,640),则3个层级的输出特征图的形状分别是 C 0 ( 1 , 1024 , 20 , 20 ) C0 (1, 1024, 20, 20) C0(1,1024,20,20), C 1 ( 1 , 1024 , 40 , 40 ) C1 (1, 1024, 40, 40) C1(1,1024,40,40)和 C 2 ( 1 , 1024 , 80 , 80 ) C2 (1, 1024, 80, 80) C2(1,1024,80,80)。
根据输出特征图计算预测框位置和类别
YOLO-V3中对每个预测框计算逻辑如下:
-
预测框是否包含物体。也可理解为objectness=1的概率是多少,可以用网络输出一个实数 x x x,可以用 S i g m o i d ( x ) Sigmoid(x) Sigmoid(x)表示objectness为正的概率 P o b j P_{obj} Pobj
-
预测物体位置和形状。物体位置和形状 t x , t y , t w , t h t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h tx,ty,tw,th可以用网络输出4个实数来表示 t x , t y , t w , t h t_x, t_y, t_w, t_h tx,ty,tw,th
-
预测物体类别。预测图像中物体的具体类别是什么,或者说其属于每个类别的概率分别是多少。总的类别数为C,需要预测物体属于每个类别的概率 ( P 1 , P 2 , . . . , P C ) (P_1, P_2, ..., P_C) (P1,P2,...,PC),可以用网络输出C个实数 ( x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x C ) (x_1, x_2, ..., x_C) (x1,x2,...,xC),对每个实数分别求Sigmoid函数,让 P i = S i g m o i d ( x i ) P_i = Sigmoid(x_i) Pi=Sigmoid(xi),则可以表示出物体属于每个类别的概率。
对于一个预测框,网络需要输出 ( 5 + C ) (5 + C) (5+C)个实数来表征它是否包含物体、位置和形状尺寸以及属于每个类别的概率。
由于我们在每个小方块区域都生成了K个预测框,则所有预测框一共需要网络输出的预测值数目是:
[ K ( 5 + C ) ] × m × n [K(5 + C)] \times m \times n [K(5+C)]×m×n
还有更重要的一点是网络输出必须要能区分出小方块区域的位置来,不能直接将特征图连接一个输出大小为 [ K ( 5 + C ) ] × m × n [K(5 + C)] \times m \times n [K(5+C)]×m×n的全连接层。
建立输出特征图与预测框之间的关联
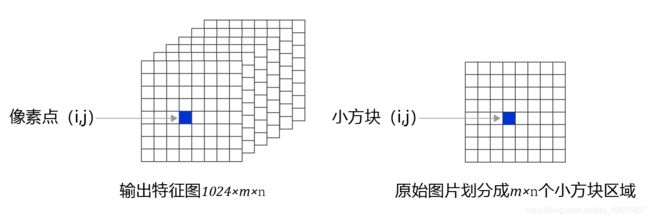
现在观察特征图,经过多次卷积核池化之后,其步幅stride=32, 640 × 480 640 \times 480 640×480大小的输入图片变成了 20 × 15 20\times15 20×15的特征图;而小方块区域的数目正好是 20 × 15 20\times15 20×15,也就是说可以让特征图上每个像素点分别跟原图上一个小方块区域对应。这也是为什么我们最开始将小方块区域的尺寸设置为32的原因,这样可以巧妙的将小方块区域跟特征图上的像素点对应起来,解决了空间位置的对应关系。
图17:特征图C0与小方块区域形状对比
下面需要将像素点 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)与第i行第j列的小方块区域所需要的预测值关联起来,每个小方块区域产生K个预测框,每个预测框需要 ( 5 + C ) (5 + C) (5+C)个实数预测值,则每个像素点相对应的要有 K ( 5 + C ) K(5 + C) K(5+C)个实数。为了解决这一问题,对特征图进行多次卷积,并将最终的输出通道数设置为 K ( 5 + C ) K(5 + C) K(5+C),即可将生成的特征图与每个预测框所需要的预测值巧妙的对应起来。
骨干网络的输出特征图是C0,下面的程序是对C0进行多次卷积以得到跟预测框相关的特征图P0。
# 从骨干网络输出特征图C0得到跟预测相关的特征图P0
class YoloDetectionBlock(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
# define YOLO-V3 detection head
# 使用多层卷积和BN提取特征
def __init__(self,ch_in,ch_out,is_test=True):
super(YoloDetectionBlock, self).__init__()
assert ch_out % 2 == 0, \
"channel {} cannot be divided by 2".format(ch_out)
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=is_test
)
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
is_test=is_test
)
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out*2,
ch_out=ch_out,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=is_test
)
self.conv3 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
is_test=is_test
)
self.route = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out*2,
ch_out=ch_out,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=is_test
)
self.tip = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
filter_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
is_test=is_test
)
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv0(inputs)
out = self.conv1(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
route = self.route(out)
tip = self.tip(route)
return route, tip
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
print(P0.shape)
[1, 36, 20, 20]
如上面的代码所示,可以由特征图C0生成特征图P0,P0的形状是 [ 1 , 36 , 20 , 20 ] [1, 36, 20, 20] [1,36,20,20]。每个小方块区域生成的锚框或者预测框的数量是3,物体类别数目是7,每个区域需要的预测值个数是 3 × ( 5 + 7 ) = 36 3 \times (5 + 7) = 36 3×(5+7)=36,正好等于P0的输出通道数。
图18:特征图P0与候选区域的关联
将 P 0 [ t , 0 : 12 , i , j ] P0[t, 0:12, i, j] P0[t,0:12,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框所需要的12个预测值对应, P 0 [ t , 12 : 24 , i , j ] P0[t, 12:24, i, j] P0[t,12:24,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第2个预测框所需要的12个预测值对应, P 0 [ t , 24 : 36 , i , j ] P0[t, 24:36, i, j] P0[t,24:36,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第3个预测框所需要的12个预测值对应。
P 0 [ t , 0 : 4 , i , j ] P0[t, 0:4, i, j] P0[t,0:4,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框的位置对应, P 0 [ t , 4 , i , j ] P0[t, 4, i, j] P0[t,4,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框的objectness对应, P 0 [ t , 5 : 12 , i , j ] P0[t, 5:12, i, j] P0[t,5:12,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框的类别对应。
如 图18 所示,通过这种方式可以巧妙的将网络输出特征图,与每个小方块区域生成的预测框对应起来了。
计算预测框是否包含物体的概率
根据前面的分析, P 0 [ t , 4 , i , j ] P0[t, 4, i, j] P0[t,4,i,j]与输入的第t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框的objectness对应, P 0 [ t , 4 + 12 , i , j ] P0[t, 4+12, i, j] P0[t,4+12,i,j]与第2个预测框的objectness对应,…,则可以使用下面的程序将objectness相关的预测取出,并使用fluid.layers.sigmoid计算输出概率。
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = fluid.layers.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = fluid.layers.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
print(pred_objectness.shape, pred_objectness_probability.shape)
[1, 3, 20, 20] [1, 3, 20, 20]
上面的输出程序显示,预测框是否包含物体的概率pred_objectness_probability,其数据形状是$[1, 3, 20, 20] $,与我们上面提到的预测框个数一致,数据大小在0~1之间,表示预测框为正样本的概率。
计算预测框位置坐标
P 0 [ t , 0 : 4 , i , j ] P0[t, 0:4, i, j] P0[t,0:4,i,j]与输入的第 t t t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框的位置对应, P 0 [ t , 12 : 16 , i , j ] P0[t, 12:16, i, j] P0[t,12:16,i,j]与第2个预测框的位置对应,…,使用下面的程序可以从 P 0 P0 P0中取出跟预测框位置相关的预测值。
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = fluid.layers.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = fluid.layers.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
print(pred_location.shape)
[1, 3, 4, 20, 20]
网络输出值是 ( t x , t y , t h , t w ) (t_x, t_y, t_h, t_w) (tx,ty,th,tw),还需要将其转化为 ( x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 ) (x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2) (x1,y1,x2,y2)这种形式的坐标表示。使用飞桨fluid.layers.yolo_box API可以直接计算出结果,但为了给读者更清楚的展示算法的实现过程,我们使用Numpy来实现这一过程。
# 定义Sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1./(1.0 + np.exp(-x))
# 将网络特征图输出的[tx, ty, th, tw]转化成预测框的坐标[x1, y1, x2, y2]
def get_yolo_box_xxyy(pred, anchors, num_classes, downsample):
"""
pred是网络输出特征图转化成的numpy.ndarray
anchors 是一个list。表示锚框的大小,
例如 anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],表示有三个锚框,
第一个锚框大小[w, h]是[116, 90],第二个锚框大小是[156, 198],第三个锚框大小是[373, 326]
"""
batchsize = pred.shape[0]
num_rows = pred.shape[-2]
num_cols = pred.shape[-1]
input_h = num_rows * downsample
input_w = num_cols * downsample
num_anchors = len(anchors) // 2
# pred的形状是[N, C, H, W],其中C = NUM_ANCHORS * (5 + NUM_CLASSES)
# 对pred进行reshape
pred = pred.reshape([-1, num_anchors, 5+num_classes, num_rows, num_cols])
pred_location = pred[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
pred_location = np.transpose(pred_location, (0,3,4,1,2))
anchors_this = []
for ind in range(num_anchors):
anchors_this.append([anchors[ind*2], anchors[ind*2+1]])
anchors_this = np.array(anchors_this).astype('float32')
# 最终输出数据保存在pred_box中,其形状是[N, H, W, NUM_ANCHORS, 4],
# 其中最后一个维度4代表位置的4个坐标
pred_box = np.zeros(pred_location.shape)
for n in range(batchsize):
for i in range(num_rows):
for j in range(num_cols):
for k in range(num_anchors):
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 0] = j
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 1] = i
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 2] = anchors_this[k][0]
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 3] = anchors_this[k][1]
# 这里使用相对坐标,pred_box的输出元素数值在0.~1.0之间
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] = (sigmoid(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 0]) + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0]) / num_cols
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] = (sigmoid(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 1]) + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1]) / num_rows
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] = np.exp(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 2]) * pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] / input_w
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] = np.exp(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 3]) * pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] / input_h
# 将坐标从xywh转化成xyxy
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] - pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] / 2.
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] - pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] / 2.
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2]
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3]
pred_box = np.clip(pred_box, 0., 1.0)
return pred_box
通过调用上面定义的get_yolo_box_xxyy函数,可以从 P 0 P0 P0计算出预测框坐标来,具体程序如下:
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = fluid.layers.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = fluid.layers.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32) # 由输出特征图P0计算预测框位置坐标
print(pred_boxes.shape)
(1, 20, 20, 3, 4)
上面程序计算出来的pred_boxes的形状是 [ N , H , W , n u m _ a n c h o r s , 4 ] [N, H, W, num\_anchors, 4] [N,H,W,num_anchors,4],坐标格式是 [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 ] [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2] [x1,y1,x2,y2],数值在0~1之间,表示相对坐标。
计算物体属于每个类别概率
P 0 [ t , 5 : 12 , i , j ] P0[t, 5:12, i, j] P0[t,5:12,i,j]与输入的第 t t t张图片上小方块区域 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j)第1个预测框包含物体的类别对应, P 0 [ t , 17 : 24 , i , j ] P0[t, 17:24, i, j] P0[t,17:24,i,j]与第2个预测框的类别对应,…,使用下面的程序可以从 P 0 P0 P0中取出那些跟预测框类别相关的预测值。
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = to_variable(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = fluid.layers.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
# 取出与objectness相关的预测值
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = fluid.layers.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
# 取出与位置相关的预测值
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
# 取出与类别相关的预测值
pred_classification = reshaped_p0[:, :, 5:5+NUM_CLASSES, :, :]
pred_classification_probability = fluid.layers.sigmoid(pred_classification)
print(pred_classification.shape)
[1, 3, 7, 20, 20]
上面的程序通过 P 0 P0 P0计算出了预测框包含的物体所属类别的概率,pred_classification_probability的形状是 [ 1 , 3 , 7 , 20 , 20 ] [1, 3, 7, 20, 20] [1,3,7,20,20],数值在0~1之间。
损失函数
上面从概念上将输出特征图上的像素点与预测框关联起来了,那么要对神经网络进行求解,还必须从数学上将网络输出和预测框关联起来,也就是要建立起损失函数跟网络输出之间的关系。下面讨论如何建立起YOLO-V3的损失函数。
对于每个预测框,YOLO-V3模型会建立三种类型的损失函数:
-
表征是否包含目标物体的损失函数,通过pred_objectness和label_objectness计算。
loss_obj = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_objectness, label_objectness) -
表征物体位置的损失函数,通过pred_location和label_location计算。
pred_location_x = pred_location[:, :, 0, :, :] pred_location_y = pred_location[:, :, 1, :, :] pred_location_w = pred_location[:, :, 2, :, :] pred_location_h = pred_location[:, :, 3, :, :] loss_location_x = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_location_x, label_location_x) loss_location_y = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_location_y, label_location_y) loss_location_w = fluid.layers.abs(pred_location_w - label_location_w) loss_location_h = fluid.layers.abs(pred_location_h - label_location_h) loss_location = loss_location_x + loss_location_y + loss_location_w + loss_location_h -
表征物体类别的损失函数,通过pred_classification和label_classification计算。
loss_obj = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_classification, label_classification)
我们已经知道怎么计算这些预测值和标签了,但是遗留了一个小问题,就是没有标注出哪些锚框的objectness为-1。为了完成这一步,我们需要计算出所有预测框跟真实框之间的IoU,然后把那些IoU大于阈值的真实框挑选出来。实现代码如下:
# 挑选出跟真实框IoU大于阈值的预测框
def get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_box, gt_boxes, iou_threshold):
batchsize = pred_box.shape[0]
num_rows = pred_box.shape[1]
num_cols = pred_box.shape[2]
num_anchors = pred_box.shape[3]
ret_inds = np.zeros([batchsize, num_rows, num_cols, num_anchors])
for i in range(batchsize):
pred_box_i = pred_box[i]
gt_boxes_i = gt_boxes[i]
for k in range(len(gt_boxes_i)): #gt in gt_boxes_i:
gt = gt_boxes_i[k]
gtx_min = gt[0] - gt[2] / 2.
gty_min = gt[1] - gt[3] / 2.
gtx_max = gt[0] + gt[2] / 2.
gty_max = gt[1] + gt[3] / 2.
if (gtx_max - gtx_min < 1e-3) or (gty_max - gty_min < 1e-3):
continue
x1 = np.maximum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 0], gtx_min)
y1 = np.maximum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 1], gty_min)
x2 = np.minimum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 2], gtx_max)
y2 = np.minimum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 3], gty_max)
intersection = np.maximum(x2 - x1, 0.) * np.maximum(y2 - y1, 0.)
s1 = (gty_max - gty_min) * (gtx_max - gtx_min)
s2 = (pred_box_i[:, :, :, 2] - pred_box_i[:, :, :, 0]) * (pred_box_i[:, :, :, 3] - pred_box_i[:, :, :, 1])
union = s2 + s1 - intersection
iou = intersection / union
above_inds = np.where(iou > iou_threshold)
ret_inds[i][above_inds] = 1
ret_inds = np.transpose(ret_inds, (0,3,1,2))
return ret_inds.astype('bool')
上面的函数可以得到哪些锚框的objectness需要被标注为-1,通过下面的程序,对label_objectness进行处理,将IoU大于阈值,但又不是正样本的锚框标注为-1。
def label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices):
# 注意:这里不能简单的使用 label_objectness[iou_above_thresh_indices] = -1,
# 这样可能会造成label_objectness为1的点被设置为-1了
# 只有将那些被标注为0,且与真实框IoU超过阈值的预测框才被标注为-1
negative_indices = (label_objectness < 0.5)
ignore_indices = negative_indices * iou_above_thresh_indices
label_objectness[ignore_indices] = -1
return label_objectness
下面通过调用这两个函数,实现如何将部分预测框的label_objectness设置为-1。
# 读取数据
reader = multithread_loader('/home/aistudio/work/insects/train', batch_size=2, mode='train')
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(reader())
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = to_variable(img)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32)
iou_above_thresh_indices = get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_boxes, gt_boxes, iou_threshold=0.7)
label_objectness = label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices)
print(label_objectness.shape)
(2, 3, 12, 12)
使用这种方式,就可以将那些没有被标注为正样本,但又与真实框IoU比较大的样本objectness标签设置为-1了,不计算其对任何一种损失函数的贡献。计算总的损失函数的代码如下:
def get_loss(output, label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scales, num_anchors=3, num_classes=7):
# 将output从[N, C, H, W]变形为[N, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, H, W]
reshaped_output = fluid.layers.reshape(output, [-1, num_anchors, num_classes + 5, output.shape[2], output.shape[3]])
# 从output中取出跟objectness相关的预测值
pred_objectness = reshaped_output[:, :, 4, :, :]
loss_objectness = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_objectness, label_objectness, ignore_index=-1)
## 对第1,2,3维求和
#loss_objectness = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(loss_objectness, dim=[1,2,3], keep_dim=False)
# pos_samples 只有在正样本的地方取值为1.,其它地方取值全为0.
pos_objectness = label_objectness > 0
pos_samples = fluid.layers.cast(pos_objectness, 'float32')
pos_samples.stop_gradient=True
#从output中取出所有跟位置相关的预测值
tx = reshaped_output[:, :, 0, :, :]
ty = reshaped_output[:, :, 1, :, :]
tw = reshaped_output[:, :, 2, :, :]
th = reshaped_output[:, :, 3, :, :]
# 从label_location中取出各个位置坐标的标签
dx_label = label_location[:, :, 0, :, :]
dy_label = label_location[:, :, 1, :, :]
tw_label = label_location[:, :, 2, :, :]
th_label = label_location[:, :, 3, :, :]
# 构建损失函数
loss_location_x = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(tx, dx_label)
loss_location_y = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(ty, dy_label)
loss_location_w = fluid.layers.abs(tw - tw_label)
loss_location_h = fluid.layers.abs(th - th_label)
# 计算总的位置损失函数
loss_location = loss_location_x + loss_location_y + loss_location_h + loss_location_w
# 乘以scales
loss_location = loss_location * scales
# 只计算正样本的位置损失函数
loss_location = loss_location * pos_samples
#从ooutput取出所有跟物体类别相关的像素点
pred_classification = reshaped_output[:, :, 5:5+num_classes, :, :]
# 计算分类相关的损失函数
loss_classification = fluid.layers.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_classification, label_classification)
# 将第2维求和
loss_classification = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(loss_classification, dim=2, keep_dim=False)
# 只计算objectness为正的样本的分类损失函数
loss_classification = loss_classification * pos_samples
total_loss = loss_objectness + loss_location + loss_classification
# 对所有预测框的loss进行求和
total_loss = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(total_loss, dim=[1,2,3], keep_dim=False)
# 对所有样本求平均
total_loss = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(total_loss)
return total_loss
# 计算损失函数
# 读取数据
reader = multithread_loader('/home/aistudio/work/insects/train', batch_size=2, mode='train')
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(reader())
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body(is_test=False)
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512, is_test=False)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(num_channels=1024, num_filters=num_filters, filter_size=1)
x = to_variable(img)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32)
iou_above_thresh_indices = get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_boxes, gt_boxes, iou_threshold=0.7)
label_objectness = label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices)
label_objectness = to_variable(label_objectness)
label_location = to_variable(label_location)
label_classification = to_variable(label_classification)
scales = to_variable(scale_location)
label_objectness.stop_gradient=True
label_location.stop_gradient=True
label_classification.stop_gradient=True
scales.stop_gradient=True
total_loss = get_loss(P0, label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scales,
num_anchors=NUM_ANCHORS, num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
total_loss_data = total_loss.numpy()
print(total_loss_data)
[444.7182]
上面的程序计算出了总的损失函数,看到这里,读者已经了解到了YOLO-V3算法的大部分内容,包括如何生成锚框、给锚框打上标签、通过卷积神经网络提取特征、将输出特征图跟预测框相关联、建立起损失函数。
多尺度检测
目前我们计算损失函数是在特征图P0的基础上进行的,它的步幅stride=32。特征图的尺寸比较小,像素点数目比较少,每个像素点的感受野很大,具有非常丰富的高层级语义信息,可能比较容易检测到较大的目标。为了能够检测到尺寸较小的那些目标,需要在尺寸较大的特征图上面建立预测输出。如果我们在C2或者C1这种层级的特征图上直接产生预测输出,可能面临新的问题,它们没有经过充分的特征提取,像素点包含的语义信息不够丰富,有可能难以提取到有效的特征模式。在目标检测中,解决这一问题的方式是,将高层级的特征图尺寸放大之后跟低层级的特征图进行融合,得到的新特征图既能包含丰富的语义信息,又具有较多的像素点,能够描述更加精细的结构。
具体的网络实现方式如 图19 所示:
图19:生成多层级的输出特征图P0、P1、P2
YOLO-V3在每个区域的中心位置产生3个锚框,在3个层级的特征图上产生锚框的大小分别为P2 [(10×13),(16×30),(33×23)],P1 [(30×61),(62×45),(59× 119)],P0[(116 × 90), (156 × 198), (373 × 326]。越往后的特征图上用到的锚框尺寸也越大,能捕捉到大尺寸目标的信息;越往前的特征图上锚框尺寸越小,能捕捉到小尺寸目标的信息。
因为有多尺度的检测,所以需要对上面的代码进行较大的修改,而且实现过程也略显繁琐,所以推荐大家直接使用飞桨 fluid.layers.yolov3_loss API,关键参数说明如下:
paddle.fluid.layers.yolov3_loss(x, gt_box, gt_label, anchors, anchor_mask, class_num, ignore_thresh, downsample_ratio, gt_score=None, use_label_smooth=False, name=None)
- x: 输出特征图。
- gt_box: 真实框。
- gt_label: 真实框标签。
- ignore_thresh,预测框与真实框IoU阈值超过ignore_thresh时,不作为负样本,YOLO-V3模型里设置为0.7。
- downsample_ratio,特征图P0的下采样比例,使用Darknet53骨干网络时为32。
- gt_score,真实框的置信度,在使用了mixup技巧时用到。
- use_label_smooth,一种训练技巧,如不使用,设置为False。
- name,该层的名字,比如’yolov3_loss’,默认值为None,一般无需设置。
对于使用了多层级特征图产生预测框的方法,其具体实现代码如下:
# 定义上采样模块
class Upsample(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
def __init__(self, scale=2):
super(Upsample,self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, inputs):
# get dynamic upsample output shape
shape_nchw = fluid.layers.shape(inputs)
shape_hw = fluid.layers.slice(shape_nchw, axes=[0], starts=[2], ends=[4])
shape_hw.stop_gradient = True
in_shape = fluid.layers.cast(shape_hw, dtype='int32')
out_shape = in_shape * self.scale
out_shape.stop_gradient = True
# reisze by actual_shape
out = fluid.layers.resize_nearest(
input=inputs, scale=self.scale, actual_shape=out_shape)
return out
# 定义YOLO-V3模型
class YOLOv3(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7, is_train=True):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.is_train = is_train
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = DarkNet53_conv_body(
is_test = not self.is_train)
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=512//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 512//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i),
is_test = not self.is_train))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
Conv2D(num_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
num_filters=num_filters,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
act=None,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=(not self.is_train)))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = fluid.layers.concat(input=[route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
"""
使用fluid.layers.yolov3_loss,直接计算损失函数,过程更简洁,速度也更快
"""
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs): # 对三个层级分别求损失函数
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = fluid.layers.yolov3_loss(
x=out, # out是P0, P1, P2中的一个
gt_box=gtbox, # 真实框坐标
gt_label=gtlabel, # 真实框类别
gt_score=gtscore, # 真实框得分,使用mixup训练技巧时需要,不使用该技巧时直接设置为1,形状与gtlabel相同
anchors=anchors, # 锚框尺寸,包含[w0, h0, w1, h1, ..., w8, h8]共9个锚框的尺寸
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i, # 筛选锚框的mask,例如anchor_mask_i=[3, 4, 5],将anchors中第3、4、5个锚框挑选出来给该层级使用
class_num=self.num_classes, # 分类类别数
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh, # 当预测框与真实框IoU > ignore_thresh,标注objectness = -1
downsample_ratio=downsample, # 特征图相对于原图缩小的倍数,例如P0是32, P1是16,P2是8
use_label_smooth=False) # 使用label_smooth训练技巧时会用到,这里没用此技巧,直接设置为False
self.losses.append(fluid.layers.reduce_mean(loss)) #reduce_mean对每张图片求和
downsample = downsample // 2 # 下一级特征图的缩放倍数会减半
return sum(self.losses) # 对每个层级求和
开启端到端训练
训练过程如 图20 所示,输入图片经过特征提取得到三个层级的输出特征图P0(stride=32)、P1(stride=16)和P2(stride=8),相应的分别使用不同大小的小方块区域去生成对应的锚框和预测框,并对这些锚框进行标注。
-
P0层级特征图,对应着使用 32 × 32 32\times32 32×32大小的小方块,在每个区域中心生成大小分别为 [ 116 , 90 ] [116, 90] [116,90], [ 156 , 198 ] [156, 198] [156,198], [ 373 , 326 ] [373, 326] [373,326]的三种锚框。
-
P1层级特征图,对应着使用 16 × 16 16\times16 16×16大小的小方块,在每个区域中心生成大小分别为 [ 30 , 61 ] [30, 61] [30,61], [ 62 , 45 ] [62, 45] [62,45], [ 59 , 119 ] [59, 119] [59,119]的三种锚框。
-
P2层级特征图,对应着使用 8 × 8 8\times8 8×8大小的小方块,在每个区域中心生成大小分别为 [ 10 , 13 ] [10, 13] [10,13], [ 16 , 30 ] [16, 30] [16,30], [ 33 , 23 ] [33, 23] [33,23]的三种锚框。
将三个层级的特征图与对应锚框之间的标签关联起来,并建立损失函数,总的损失函数等于三个层级的损失函数相加。通过极小化损失函数,可以开启端到端的训练过程。
图20:端到端训练流程
训练过程的具体实现代码如下:
############# 这段代码在本地机器上运行请慎重,容易造成死机#######################
import time
import os
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
IGNORE_THRESH = .7
NUM_CLASSES = 7
def get_lr(base_lr = 0.0001, lr_decay = 0.1):
bd = [10000, 20000]
lr = [base_lr, base_lr * lr_decay, base_lr * lr_decay * lr_decay]
learning_rate = fluid.layers.piecewise_decay(boundaries=bd, values=lr)
return learning_rate
if __name__ == '__main__':
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = YOLOv3(num_classes = NUM_CLASSES, is_train=True) #创建模型
learning_rate = get_lr()
opt = fluid.optimizer.Momentum(
learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=0.9,
regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005),
parameter_list=model.parameters()) #创建优化器
train_loader = multithread_loader(TRAINDIR, batch_size= 10, mode='train') #创建训练数据读取器
valid_loader = multithread_loader(VALIDDIR, batch_size= 10, mode='valid') #创建验证数据读取器
MAX_EPOCH = 200
for epoch in range(MAX_EPOCH):
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = to_variable(gt_scores)
img = to_variable(img)
gt_boxes = to_variable(gt_boxes)
gt_labels = to_variable(gt_labels)
outputs = model(img) #前向传播,输出[P0, P1, P2]
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False) # 计算损失函数
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
opt.minimize(loss) # 更新参数
model.clear_gradients()
if i % 1 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[TRAIN]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
# save params of model
if (epoch % 5 == 0) or (epoch == MAX_EPOCH -1):
fluid.save_dygraph(model.state_dict(), 'yolo_epoch{}'.format(epoch))
# 每个epoch结束之后在验证集上进行测试
model.eval()
for i, data in enumerate(valid_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = to_variable(gt_scores)
img = to_variable(img)
gt_boxes = to_variable(gt_boxes)
gt_labels = to_variable(gt_labels)
outputs = model(img)
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False)
if i % 1 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[VALID]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
model.train()
预测
预测过程流程 图21 如下所示:
图21:端到端训练流程
预测过程可以分为两步:
- 通过网络输出计算出预测框位置和所属类别的得分。
- 使用非极大值抑制来消除重叠较大的预测框。
对于第1步,前面我们已经讲过如何通过网络输出值计算pred_objectness_probability, pred_boxes以及pred_classification_probability,这里推荐大家直接使用fluid.layers.yolo_box,关键参数含义如下:
paddle.fluid.layers.yolo_box(x, imgsize, anchors, classnum, confthresh, downsampleratio, clipbbox=True, name=None)
- x,网络输出特征图,例如上面提到的P0或者P1、P2。
- img_size,输入图片尺寸。
- anchors,使用到的anchor的尺寸,如[10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
- anchor_mask: 每个层级上使用的anchor的掩码,[[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
- class_num,物体类别数。
- conf_thresh, 置信度阈值,得分低于该阈值的预测框位置数值不用计算直接设置为0.0。
- downsample_ratio, 特征图的下采样比例,例如P0是32,P1是16,P2是8。
- name=None,名字,例如’yolo_box’,一般无需设置,默认值为None。
返回值包括两项,boxes和scores,其中boxes是所有预测框的坐标值,scores是所有预测框的得分。
预测框得分的定义是所属类别的概率乘以其预测框是否包含目标物体的objectness概率,即
s c o r e = P o b j ⋅ P c l a s s i f i c a t i o n score = P_{obj} \cdot P_{classification} score=Pobj⋅Pclassification
在上面定义的类YOLO-V3下面添加函数,get_pred,通过调用fluid.layers.yolo_box获得P0、P1、P2三个层级的特征图对应的预测框和得分,并将他们拼接在一块,即可得到所有的预测框及其属于各个类别的得分。
# 定义YOLO-V3模型
class YOLOv3(fluid.dygraph.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7, is_train=True):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.is_train = is_train
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = DarkNet53_conv_body(
is_test = not self.is_train)
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=512//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 512//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i),
is_test = not self.is_train))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
Conv2D(num_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
num_filters=num_filters,
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
act=None,
param_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=ParamAttr(
initializer=fluid.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
filter_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
is_test=(not self.is_train)))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = fluid.layers.concat(input=[route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs):
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = fluid.layers.yolov3_loss(
x=out,
gt_box=gtbox,
gt_label=gtlabel,
gt_score=gtscore,
anchors=anchors,
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i,
class_num=self.num_classes,
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh,
downsample_ratio=downsample,
use_label_smooth=False)
self.losses.append(fluid.layers.reduce_mean(loss))
downsample = downsample // 2
return sum(self.losses)
def get_pred(self,
outputs,
im_shape=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
valid_thresh = 0.01):
downsample = 32
total_boxes = []
total_scores = []
for i, out in enumerate(outputs):
anchor_mask = anchor_masks[i]
anchors_this_level = []
for m in anchor_mask:
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m])
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m + 1])
boxes, scores = fluid.layers.yolo_box(
x=out,
img_size=im_shape,
anchors=anchors_this_level,
class_num=self.num_classes,
conf_thresh=valid_thresh,
downsample_ratio=downsample,
name="yolo_box" + str(i))
total_boxes.append(boxes)
total_scores.append(
fluid.layers.transpose(
scores, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
downsample = downsample // 2
yolo_boxes = fluid.layers.concat(total_boxes, axis=1)
yolo_scores = fluid.layers.concat(total_scores, axis=2)
return yolo_boxes, yolo_scores
第1步的计算结果会在每个小方块区域都会产生多个预测框,输出预测框中会有很多重合度比较大,需要消除重叠较大的冗余预测框。
下面示例代码中的预测框是使用模型对图片预测之后输出的,这里一共选出了11个预测框,在图上画出预测框如下所示。在每个人像周围,都出现了多个预测框,需要消除冗余的预测框以得到最终的预测结果。
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = '/home/aistudio/work/images/section3/000000086956.jpg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
# 预测框位置
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
# 预测框得分
scores = np.array([0.5247661 , 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175 , 0.39170712,
0.9297706 , 0.5115228 , 0.270992 , 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
# 画出所有预测框
for box in boxes:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box)
这里使用非极大值抑制(non-maximum suppression, nms)来消除冗余框。基本思想是,如果有多个预测框都对应同一个物体,则只选出得分最高的那个预测框,剩下的预测框被丢弃掉。
如何判断两个预测框对应的是同一个物体呢,标准该怎么设置?
如果两个预测框的类别一样,而且他们的位置重合度比较大,则可以认为他们是在预测同一个目标。非极大值抑制的做法是,选出某个类别得分最高的预测框,然后看哪些预测框跟它的IoU大于阈值,就把这些预测框给丢弃掉。这里IoU的阈值是超参数,需要提前设置,YOLO-V3模型里面设置的是0.5。
比如在上面的程序中,boxes里面一共对应11个预测框,scores给出了它们预测"人"这一类别的得分。
- Step0:创建选中列表,keep_list = []
- Step1:对得分进行排序,remain_list = [ 3, 5, 10, 2, 9, 0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8],
- Step2:选出boxes[3],此时keep_list为空,不需要计算IoU,直接将其放入keep_list,keep_list = [3], remain_list=[5, 10, 2, 9, 0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8]
- Step3:选出boxes[5],此时keep_list中已经存在boxes[3],计算出IoU(boxes[3], boxes[5]) = 0.0,显然小于阈值,则keep_list=[3, 5], remain_list = [10, 2, 9, 0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8]
- Step4:选出boxes[10],此时keep_list=[3, 5],计算IoU(boxes[3], boxes[10])=0.0268,IoU(boxes[5], boxes[10])=0.0268 = 0.24,都小于阈值,则keep_list = [3, 5, 10],remain_list=[2, 9, 0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8]
- Step5:选出boxes[2],此时keep_list = [3, 5, 10],计算IoU(boxes[3], boxes[2]) = 0.88,超过了阈值,直接将boxes[2]丢弃,keep_list=[3, 5, 10],remain_list=[9, 0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8]
- Step6:选出boxes[9],此时keep_list = [3, 5, 10],计算IoU(boxes[3], boxes[9]) = 0.0577,IoU(boxes[5], boxes[9]) = 0.205,IoU(boxes[10], boxes[9]) = 0.88,超过了阈值,将boxes[9]丢弃掉。keep_list=[3, 5, 10],remain_list=[0, 1, 6, 4, 7, 8]
- Step7:重复上述Step6直到remain_list为空。
最终得到keep_list=[3, 5, 10],也就是预测框3、5、10被最终挑选出来了,如下图所示。
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = '/home/aistudio/work/images/section3/000000086956.jpg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
scores = np.array([0.5247661 , 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175 , 0.39170712,
0.9297706 , 0.5115228 , 0.270992 , 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
left_ind = np.where((boxes[:, 0]<60) * (boxes[:, 0]>20))
left_boxes = boxes[left_ind]
left_scores = scores[left_ind]
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k']
# 画出最终保留的预测框
inds = [3, 5, 10]
for i in range(3):
box = boxes[inds[i]]
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor=colors[i])
非极大值抑制的具体实现代码如下面的nms函数的定义,需要说明的是数据集中含有多个类别的物体,所以这里需要做多分类非极大值抑制,其实现原理与非极大值抑制相同,区别在于需要对每个类别都做非极大值抑制,实现代码如下面的multiclass_nms所示。
# 非极大值抑制
def nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=0, c=0):
"""
nms
"""
inds = np.argsort(scores)
inds = inds[::-1]
keep_inds = []
while(len(inds) > 0):
cur_ind = inds[0]
cur_score = scores[cur_ind]
# if score of the box is less than score_thresh, just drop it
if cur_score < score_thresh:
break
keep = True
for ind in keep_inds:
current_box = bboxes[cur_ind]
remain_box = bboxes[ind]
iou = box_iou_xyxy(current_box, remain_box)
if iou > nms_thresh:
keep = False
break
if i == 0 and c == 4 and cur_ind == 951:
print('suppressed, ', keep, i, c, cur_ind, ind, iou)
if keep:
keep_inds.append(cur_ind)
inds = inds[1:]
return np.array(keep_inds)
# 多分类非极大值抑制
def multiclass_nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh=0.01, nms_thresh=0.45, pre_nms_topk=1000, pos_nms_topk=100):
"""
This is for multiclass_nms
"""
batch_size = bboxes.shape[0]
class_num = scores.shape[1]
rets = []
for i in range(batch_size):
bboxes_i = bboxes[i]
scores_i = scores[i]
ret = []
for c in range(class_num):
scores_i_c = scores_i[c]
keep_inds = nms(bboxes_i, scores_i_c, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=i, c=c)
if len(keep_inds) < 1:
continue
keep_bboxes = bboxes_i[keep_inds]
keep_scores = scores_i_c[keep_inds]
keep_results = np.zeros([keep_scores.shape[0], 6])
keep_results[:, 0] = c
keep_results[:, 1] = keep_scores[:]
keep_results[:, 2:6] = keep_bboxes[:, :]
ret.append(keep_results)
if len(ret) < 1:
rets.append(ret)
continue
ret_i = np.concatenate(ret, axis=0)
scores_i = ret_i[:, 1]
if len(scores_i) > pos_nms_topk:
inds = np.argsort(scores_i)[::-1]
inds = inds[:pos_nms_topk]
ret_i = ret_i[inds]
rets.append(ret_i)
return rets
下面是完整的测试程序,在测试数据集上的输出结果将会被保存在pred_results.json文件中。
import json
import os
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train/images'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES, is_train=False)
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/work/yolo_epoch50'
model_state_dict, _ = fluid.load_dygraph(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = test_data_loader(TESTDIR, batch_size= 1, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = to_variable(img_data)
img_scale = to_variable(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
result = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
for j in range(len(result)):
result_j = result[j]
img_name_j = img_name[j]
total_results.append([img_name_j, result_j.tolist()])
print('processed {} pictures'.format(len(total_results)))
print('')
json.dump(total_results, open('pred_results.json', 'w'))
json文件中保存着测试结果,是包含所有图片预测结果的list,其构成如下:
[[img_name, [[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2], ..., [label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]]],
[img_name, [[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2], ..., [label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]]],
...
[img_name, [[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2],..., [label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]]]]
list中的每一个元素是一张图片的预测结果,list的总长度等于图片的数目,每张图片预测结果的格式是:
[img_name, [[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2],..., [label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]]]
其中第一个元素是图片名称image_name,第二个元素是包含该图片所有预测框的list, 预测框列表:
[[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2],..., [label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]]
预测框列表中每个元素[label, score, x1, x2, y1, y2]描述了一个预测框,label是预测框所属类别标签,score是预测框的得分;x1, x2, y1, y2对应预测框左上角坐标(x1, y1),右下角坐标(x2, y2)。每张图片可能有很多个预测框,则将其全部放在预测框列表中。
模型效果及可视化展示
上面的程序展示了如何读取测试数据集的读片,并将最终结果保存在json格式的文件中。为了更直观的给读者展示模型效果,下面的程序添加了如何读取单张图片,并画出其产生的预测框。
- 创建数据读取器以读取单张图片的数据
# 读取单张测试图片
def single_image_data_loader(filename, test_image_size=608, mode='test'):
"""
加载测试用的图片,测试数据没有groundtruth标签
"""
batch_size= 1
def reader():
batch_data = []
img_size = test_image_size
file_path = os.path.join(filename)
img = cv2.imread(file_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
H = img.shape[0]
W = img.shape[1]
img = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size))
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
out_img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
out_img = out_img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
img = out_img #np.transpose(out_img, (2,0,1))
im_shape = [H, W]
batch_data.append((image_name.split('.')[0], img, im_shape))
if len(batch_data) == batch_size:
yield make_test_array(batch_data)
batch_data = []
return reader
- 定义绘制预测框的画图函数,代码如下。
# 定义画图函数
INSECT_NAMES = ['Boerner', 'Leconte', 'Linnaeus',
'acuminatus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'linnaeus']
# 定义画矩形框的函数
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
# 定义绘制预测结果的函数
def draw_results(result, filename, draw_thresh=0.5):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k', 'y', 'c', 'purple']
for item in result:
box = item[2:6]
label = int(item[0])
name = INSECT_NAMES[label]
if item[1] > draw_thresh:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor = colors[label])
plt.text(box[0], box[1], name, fontsize=12, color=colors[label])
- 使用上面定义的single_image_data_loader函数读取指定的图片,输入网络并计算出预测框和得分,然后使用多分类非极大值抑制消除冗余的框。将最终结果画图展示出来。
import json
import paddle
import paddle.fluid as fluid
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_name = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images/2599.jpeg'
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/work/yolo_epoch50'
with fluid.dygraph.guard():
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES, is_train=False)
model_state_dict, _ = fluid.load_dygraph(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = single_image_data_loader(image_name, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = to_variable(img_data)
img_scale = to_variable(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
results = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
result = results[0]
draw_results(result, image_name, draw_thresh=0.5)
通过上面的程序,清晰的给读者展示了如何使用训练好的权重,对图片进行预测并将结果可视化。最终输出的图片上,检测出了每个昆虫,标出了它们的边界框和具体类别。