谷歌论文Weight Agnostic Neural Networks(WANN)权重无关神经网络
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04358
项目及代码地址:
https://weightagnostic.github.io/
目录
一、概览
1.1 贡献点
1.2 背景
二、方法
2.1 本文做法
2.2 相关工作
2.3 方法
网络结构搜寻
结构搜索 Topology search
2.4 性能与复杂度评估
三、实验及结果
3.1 任务描述
3.2 比较标准
3.3 实验结果
3.4 分类任务结果
四、结论及个人总结
一、概览
1.1 贡献点
在“权重无关神经网络”(Weight Agnostic Neural Networks, WANN) 中,谷歌踏出了第一步:使用随机共享权重执行各种任务的神经网络架构。一些早熟动物天生就可以进行反捕食行为,并且可以做出一系列复杂的运动和感官活动。受到此启发,本文希望设计出神经网络可以运用随机初始的weight来达到较好的效果。
- 来探讨一个问题,权重与网络结构对于神经网络而言,哪个更重要。
- 不训练weight的情况下在强化学习任务上进行实验
- 不训练weight的情况下,在监督学习领域使用目标,比random weight在MINST数据集上取得了更高的准确率。
1.2 背景
Random-initialized的CNN可以很好的在superresolution, inpainting and style transfer中表现很好。
- K. He, Y. Wang, and J. Hopcroft. A powerful generative model using random weights for the deepimage representation. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 631–639, 2016. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.04801.
- D. Ulyanov, A. Vedaldi, and V. Lempitsky. Deep image prior. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 9446–9454, 2018. https://dmitryulyanov.github.io/deep_image_prior.
Random-initialized的LSTM加上一个learned linear output也可以在时间序列的预测中完成一些的reservior-based RNN不能完成的任务。
- S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber. Long short-term memory. Neural computation, 9(8):1735–1780, 1997 . http://people.idsia.ch/~juergen/rnn.html.
- H. Jaeger and H. Haas. Harnessing nonlinearity: Predicting chaotic systems and saving energy in wireless communication. science, 304(5667):78–80, 2004. http://tiny.cc/t3wd8y.
A. Roli and L. Melandri. Introduction to reservoir computing methods, 2014. https://amslaurea.unibo.it/8268/1/melandri_luca_tesi.pdf
其他在self-attention和capsule networks的工作也希望有一个成型的building block来实现专门的网络结构与任务对应。
- S. Sabour, N. Frosst, and G. E. Hinton. Dynamic routing between capsules. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pages 3856–3866, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.09829.
A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, Ł. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin. Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pages 5998–6008, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762.
二、方法
2.1 本文做法
- Assigning a single shared weight parameter to every network connection固定的权重分配
- Evaluating the network on a wide range of this single weight parameter.
对比于 固定网络结构,优化权重,本文采用 固定权重,优化网络结构。
结果:
- 强化学习中,本文的网络可以运用random weight parameter执行continuous control tasks
- 监督学习中,本文的网络可以在MNIST识别上达到将近92%的准确率。
- 需要注意的是,本文的网络依然不可以达到运用梯度下降算法所达的相匹敌的准确率。
2.2 相关工作
论文中提到了大量的参考文献,需要的话直接查阅原论文。
Architecture Search
Search algorithms for neural network topologies originated from the field of evolutionary computing,本文的方法是基于NEAT的方法,这种方法是同时优化权重和网络结构。
- K. O. Stanley and R. Miikkulainen. Evolving neural networks through augmenting topologies. Evolutionary computation, 10(2):99–127, 2002. http://www.cs.ucf.edu/~kstanley/neat.html.
为了得到SOTA的准确率,近期的工作将网络结构的搜索空间降低。本文直接去除掉权重训练的步骤。
Bayesian Neural Networks
The weight parameters of a BNN并不是fixed value,但是会遵从一个distribution,这个distribution的参数是通过学习得到的。近期的工作发现,运用0均值,学习得到的方差的初始化权重可以改善 image recognition tasks的performance。
- K. Neklyudov, D. Molchanov, A. Ashukha, and D. Vetrov. Variance networks: When expectation does not meet your expectations. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2019. https://openreview.net/forum?id=B1GAUs0cKQ.
Algorithmic Information Theory (AIT)
这部分背景知识偏理论化。
In AIT [ 108 ], the Kolmogorov complexity [ 56 ] of a computable object is the minimum length of the program that can compute it. The Minimal Description Length (MDL) [ 35 , 97 , 98 ] is a formalization of Occam’s razor, in which a good model is one that is best at compressing its data, including the cost of describing of the model itself.
前面提到的工作focus on the information capacity required to represent the weights of a predefined network architecture, 本文的工作 focus on finding minimal architectures that can represent solutions to various tasks。
Network Pruning
网络剪枝是指将一个训练好的网络中的部分权重连接删掉。我们的工作中,网络初始化时没有任何链接,然后逐步增加网络的复杂程度。 Compared to our approach, pruning requires prior training of the full network to obtain useful information about each weight in advance. the architectures produced by pruning are limited by the full network, while in our method there is no upper bound on the network’s complexity
Neuroscience
A connectome [ 105 ] is the “wiring diagram” or mapping of all neural connections of the brain.可以被看作一个graph,
Like the connectome of simple organisms, the networks discovered by our approach are small enough to be analyzed.
2.3 方法
Neural architecture search (NAS),是指创建一个网络可以胜任之前人工设计的神经网络结构。但是NAS创建的神经网络依然需要训练权重,The weights are the solution; the found architectures merely a better substrate for the weights to inhabit.
本文采用的方法是用随机的权重作为网络的权重, 因为所有的权重在高维空间, curse of dimensionality,因此本文采用weight-sharing on all weights
网络结构搜寻
- 最简单的网络结构被创建
- 每个网络结构都被评估,且网络运用不同的随机初始化权重
- 网络结构根据输出的performance和复杂程度进行排序
- 将评分最高的网络作为初始化网络生成一系列网络,重复步骤2
这种方法即同一个网络结构运用不同的随机初始化权重,从而得到一个更全面的评估。
结构搜索 Topology search
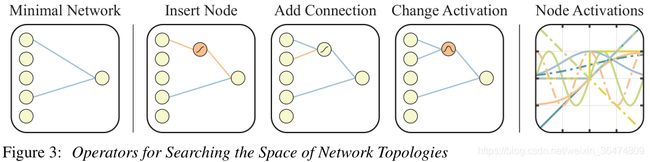
初始的网络只有输入与输出、稀疏连接。剩下的有三种操作
- 加入节点,Insert node,we split an existing connection into two connections that pass through this new hidden node. 加入节点的时候,激活函数是随机分配的
- 加入连接,Add connection,New connections are added between previously unconnected nodes, respecting the feed-forward property of the network.
- 更改激活函数,Change activation, Activation functions include both the common (e.g. linear, sigmoid, ReLU) and more exotic (Gaussian, sinusoid, step), encoding a variety of relationships between inputs and outputs
2.4 性能与复杂度评估
对于每种网络结构,都有一系列固定的权重被用于此结构,平均的准确率为网络的准确率。权值包括 [−2,−1,−0.5,+0.5,+1,+2] 。
这里详细理解为,所有权重固定为一个值,比如所有权值均为-2,然后一系列权值被应用于网络用于评估网络性能。
此外,基于信息论而言,网络结构的优劣不止用准确率来衡量,也需要用网络结构是否精简来衡量networks that can be described with a minimal description length。
为了保证网络 简单simple、分单元modular、可展开evolvable, 有三个标准对网络进行评价,平均准确率、某个固定权值下的最佳性能、最多连接的数量。
三、实验及结果
3.1 任务描述
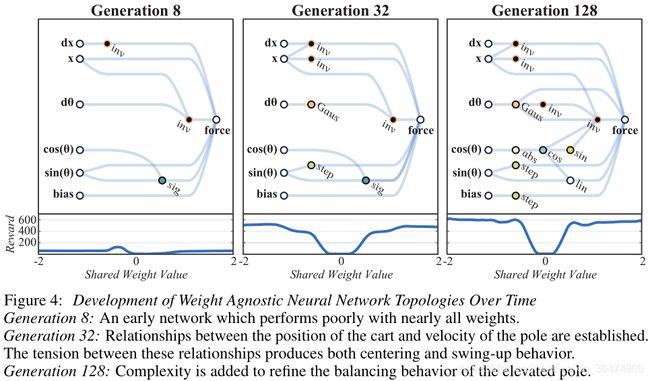
第一个任务:CartPoleSwingUp,这是一个典型的控制问题,在给定的推车连杆系统下,杆必须从静止位置摆动到直立位置然后平衡,而推车不会越过轨道的边界。这个问题无法用线性控制器解决。每个时间步长上的奖励都是基于推车与轨道边缘的距离和杆的角度决定的。
第二个任务是BipedalWalker-v2 ,目的是引导一个双腿智能体跨越随机生成的地形。奖励是针对成功行进距离,以及电动机扭矩的成本确定。每条腿都由髋关节和膝关节控制,响应24个输入。与低维的CartPoleSwingUp任务相比,BipedalWalker-v2的可能连接数更多更复杂,WANN需要选择输入到输出的路线。
第三个任务CarRacing-v0是一个从像素环境中自上而下行驶的赛车问题。赛车由三个连续命令(点火,转向,制动)控制,任务目标是在一定时限内行驶过尽量长的随机生成的道路。我们将任务的像素解释元素交给经过预训练的变分自动编码器(VAE),后者将像素表示压缩为16个潜在维度,将这些信息作为网络的输入。这个任务测试了WANN学习抽象关联的能力,而不是编码输入之间的显式几何关系
3.2 比较标准
在实验中,我们比较了以下4种情况下100次试验的平均表现:
- 随机权重:从μ(-2,2)范围内抽取的单个权重。
- 随机共享权重:从μ(- 2,2)范围内中抽取的单个共享权重。
- 调整共享权重:在μ(-2,2)范围内表现最好的共享权重值。
- 调整权重:使用基于人口信息的强化调整的个体权重。
3.3 实验结果
我们比较了过往研究中常用的标准前馈网络的最佳权重无关网络架构的平均性能(测试次数超过100次)。通过均匀分布采样的共享权重来测量其性能,从结果中可以观察到网络拓扑的固有偏差。通过调整此共享权重参数,可以测出其最佳性能。为了便于与基线架构进行比较,允许网络获得独特的权重参数,并对其进行调整。
结果如上表所示,作为基线的传统固定拓扑网络在经过大量调整后只产生有用行为,相比之下,WANN甚至可以使用随机共享权重。虽然WANN架构编码强烈偏向解决方案,但并不完全独立于权重值,当单个权重值随机分配时,模型就会失败。WANN通过编码输入和输出之间的关系来起作用,因此,虽然权重大小并不重要,但它们的一致性,特别是符号的一致性,是非常重要的。单个共享权重的另一个好处是,调整单个参数变得非常容易,无需使用基于梯度的方法。
3.4 分类任务结果
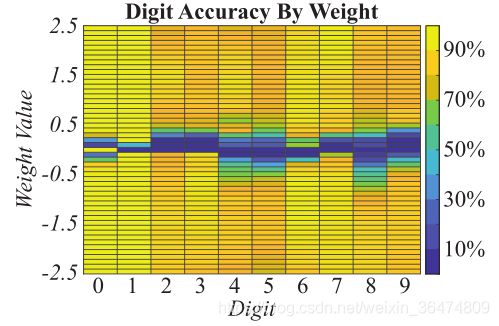
WANN在4种权重设定下在MNIST图像数据集上的分类表现,WANN的分类精度用多个权重值作为集合进行实例化,其性能远远优于随机采样权重
即使在高维分类任务中,WANN的表现也非常出色。 只使用单个权重值,WANN就能够对MNIST上的数字以及具有通过梯度下降训练的数千个权重的单层神经网络进行分类,产生的架构灵活性很高,仍然可以继续进行权重,进一步提高准确性。
四、结论及个人总结
创新点在于设计权值无关神经网络,非常具有开创性。