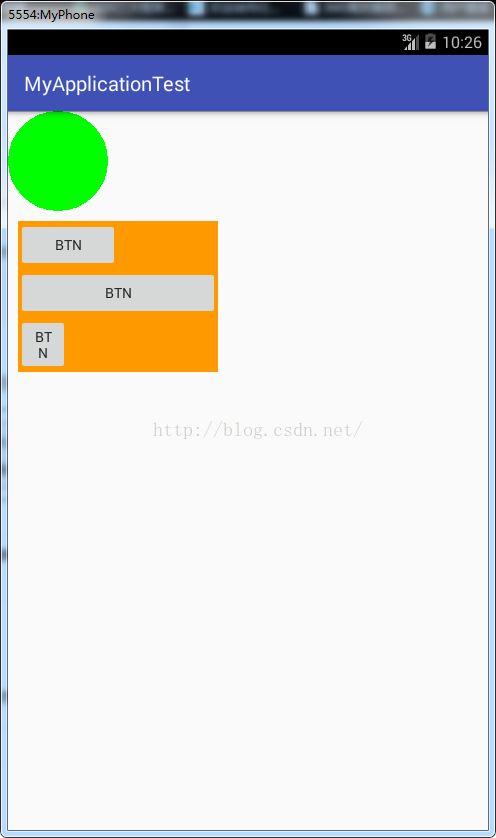
android View的绘制机制
View的绘制机制
应用场景
android内置的view无法满足我们的需求,这时我们需要开发自定义的view,再开发之前我们需要先了解android view的绘制机制,这样可以更加便于我们的开发。以下是view绘制机制的简单讲解以及自定义view的代码示例。
view的绘制机制
这里我们首先要讲的就是View这个类,其中常用的是View以及ViewGroup,View的绘制分三步走,也就是三个重要的重写方法。onMeasure负责测量、Layout负责view的显示位置、onDraw负责view的绘制。ViewGroup是View的子类,它也是view的容器,不仅需要管理好它自己也需要兼顾View,所以onLayout方法是它必须要进行重写的。说到这里大家一定会很蒙吧,那下面来看代码。
自定义view
package com.example.administrator.myapplicationtest.views;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import com.example.administrator.myapplicationtest.R;
/**
* Created by LiHaiNan on 2016/11/10 0010.
*/
public class MyView extends View {
//设置默认大小
private int defaultSize;
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* @param context 上下文环境 attrs styles.xml文件中的标签
* @Title: MyView
* @Description 构造方法(获取XML中配置的自定义大小)
*/
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
//属性集合的标签,在R文件中名称为R.styleable+name
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView);
//第一个参数为属性集合里面的属性,R文件名称:R.styleable+属性集合名称+下划线+属性名称
//第二个参数为,如果没有设置这个属性,则设置的默认的值
defaultSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.MyView_default_size, 100);
//在执行完之后,一定要确保调用recycle()
// 用于检索从这个结构对应于给定的属性位置到obtainStyledAttributes中的值
a.recycle();
}
/**
* @param defaultSize 默认大小 measureSpec 尺寸信息
* @Title: MyView
* @Description 大小的重新设定
*/
private int getMySize(int defaultSize, int measureSpec) {
int mySize = defaultSize;
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (mode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: {//如果没有指定大小,就设置为默认大小
mySize = defaultSize;
break;
}
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: {//如果测量模式是最大取值为size
//我们将大小取最大值,你也可以取其他值
mySize = size;
break;
}
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: {//如果是固定的大小,那就不要去改变它
mySize = size;
break;
}
}
return mySize;
}
/**
* @Description view的测量
* @param widthMeasureSpec 宽度信息(包括测量模式与尺寸) heightMeasureSpec 高度信息(包括测量模式与尺寸)
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = getMySize(defaultSize, widthMeasureSpec);
int height = getMySize(defaultSize, heightMeasureSpec);
//这个地方其决定性作用,重新测绘的高宽
if (width < height) {
height = width;
} else {
width = height;
}
//设置重新测绘的高宽
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
/**
* @Description view的绘制
* @param canvas 画布
*/
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//调用父View的onDraw函数,因为View这个类帮我们实现了一些
// 基本的而绘制功能,比如绘制背景颜色、背景图片等
super.onDraw(canvas);
//得到圆的半径
int r = getMeasuredWidth() / 2;
//圆心的横坐标为当前的View的左边起始位置+半径
int centerX = getLeft() + r;
//圆心的纵坐标为当前的View的顶部起始位置+半径
int centerY = getTop() + r;
//创建画笔对象
Paint paint = new Paint();
//设置画笔颜色
paint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
//开始绘制
canvas.drawCircle(centerX, centerY, r, paint);
}
} 自定义ViewGroup
1.首先,我们得知道各个子View的大小吧,只有先知道子View的大小,我们才知道当前的ViewGroup该设置为多大去容纳它们。
2.根据子View的大小,以及我们的ViewGroup要实现的功能,决定出ViewGroup的大小
3.ViewGroup和子View的大小算出来
4.已经知道怎么去摆放还不行啊,决定了怎么摆放就是相当于把已有的空间”分割”成大大小小的空间,每个空间对应一个子View,我们接下来就是把子View对号入座了,把它们放进它们该放的地方去。
下面是模仿实现垂直布局
package com.example.administrator.myapplicationtest.views;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Created by LiHaiNan on 2016/11/11 0011.
*/
public class MyViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
public MyViewGroup(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/***
* 获取子View中宽度最大的值
*/
private int getMaxChildWidth() {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int maxWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > maxWidth)
maxWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
return maxWidth;
}
/***
* 将所有子View的高度相加
**/
private int getTotleHeight() {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int height = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
height += childView.getMeasuredHeight();
}
return height;
}
//先进行测绘
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//将所有的子View进行测量,这会触发每个子View的onMeasure函数
//注意要与measureChild区分,measureChild是对单个view进行测量
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//获取子view的数量
int childCount = getChildCount();
if (childCount == 0) {
//如果没有子View,当前ViewGroup没有存在的意义,不用占用空间
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
} else {
//如果宽高都是包裹内容
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//我们将高度设置为所有子View的高度相加,宽度设为子View中最大的宽度
int height = getTotleHeight();
int width = getMaxChildWidth();
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有高度是包裹内容
//宽度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量宽度,高度设置为所有子View的高度总和
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, getTotleHeight());
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {//如果只有宽度是包裹内容
//宽度设置为子View中宽度最大的值,高度设置为ViewGroup自己的测量值
setMeasuredDimension(getMaxChildWidth(), heightSize);
}
}
}
//onLayout是必须要重写的方法
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
//记录当前的高度位置,因为在xml中设置过布局dp所以要减去设置的
int curHeight = t - 110;
int curLeft = l - 10;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
child.layout(curLeft, curHeight, curLeft + width, curHeight + height);
curHeight += height;
}
}
}布局文件
部分名词解释
| 测量模式 | 表示意思 |
|---|---|
| UNSPECIFIED | 父容器没有对当前View有任何限制,当前View可以任意取尺寸 |
| EXACTLY | 当前的尺寸就是当前View应该取的尺寸 |
| AT_MOST | 当前尺寸是当前View能取的最大尺寸 |
而上面的测量模式跟我们的布局时的wrap_content、match_parent以及写成固定的尺寸有什么对应关系呢?
match_parent—>EXACTLY。怎么理解呢?match_parent就是要利用父View给我们提供的所有剩余空间,而父View剩余空间是确定的,也就是这个测量模式的整数里面存放的尺寸。
wrap_content—>AT_MOST。怎么理解:就是我们想要将大小设置为包裹我们的view内容,那么尺寸大小就是父View给我们作为参考的尺寸,只要不超过这个尺寸就可以啦,具体尺寸就根据我们的需求去设定。
固定尺寸(如100dp)—>EXACTLY。用户自己指定了尺寸大小,我们就不用再去干涉了,当然是以指定的大小为主啦。