KMP算法(fail优化) Trie树 AC自动机(指针 ,数组写法)
注意,模式串匹配是处理小串,再用大串去跑
KMP算法:
对于目标串和模式串的匹配问题,暴力做法为枚举每一个位置查看是否匹配
KMP就是对模式串做预处理,每个位置添加一个fail指针,避免过多的重复匹配
寻找模式串中长度最大且相等的前缀和后缀
f a i l [ i ] = j fail[i]=j fail[i]=j表示当匹配到 i i i时失配( i + 1 i+1 i+1不能匹配),让 i i i跳到 j j j继续匹配(查看 j + 1 j+1 j+1是否可配)
当然,如果 i = 0 i=0 i=0时 i + 1 i+1 i+1都不能匹配,当然要跳出这个串( f a i l ( 0 ) = − 1 fail(0)=-1 fail(0)=−1)避免死循环了
eg:
有模式串ababa,给你一个目标串abacabcbc,问模式串是不是目标串的子串
暴力做法就是枚举每个位置看看ababa是不是那个位置接下来的子串
字 符 a b a b a 下 标 0 1 2 3 4 指 针 − 1 0 0 1 2 \begin{matrix}字符&a&b&a&b&a\\下标&0&1&2&3&4\\指针&-1&0&0&1&2 \end{matrix} 字符下标指针a0−1b10a20b31a42
f a i l ( 0 ) = − 1 fail(0)=-1 fail(0)=−1上面有解释, f a i l ( 3 ) = 1 fail(3)=1 fail(3)=1表示已经匹配 a b a b abab abab的情况下下一个不是a不能匹配就要跳到1
即 a b a b abab abab变成 a b ab ab再继续判断2是不是可配
代码:
void KMP(char *x,int *fail){
fail[0]=-1,fail[1]=0;
int len=strlen(x);
int i=1,j=0;
while(i<len&&j<len){
if(j==-1||x[i]==x[j])fail[++i]=++j;
else j=fail[j];
}
}
KMP的查询
int len=strlen(a);//目标串
KMP(str,fail);//模式串
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
while(str[j]!=a[i]&&j!=-1)j=fail[j];
//题目查询 if(j==len-1)...
j++;
}
\\\;
KMP指针数组优化
假设你当前的位置为temp,son为temp的下一个节点,temp的fail指针跳向p,p的儿子为sonp
如果son和sonp相同有什么结论呢?
说明temp因为下一个匹配的不是son而跳到p,结果sonp和son一样,即还会不匹配,p也会跳到p的fail指针那里.
很明显的优化就是出现这种情况的时候继续更新temp的fail指针直到不需要跳多次为止
void KMP(char *x,int *fail){
int len=strlen(x);
int i=0,j=-1;
fail[0]=-1;
while(i<len){
while(j!=-1&&x[i]!=x[j]) j=fail[j];
fail[++i]=++j;
if(x[i]==x[j]) fail[i]=fail[j];
}
}
\\\;
\\\;
Trie树:
Trie树,即字典树,又称单词查找树或键树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。
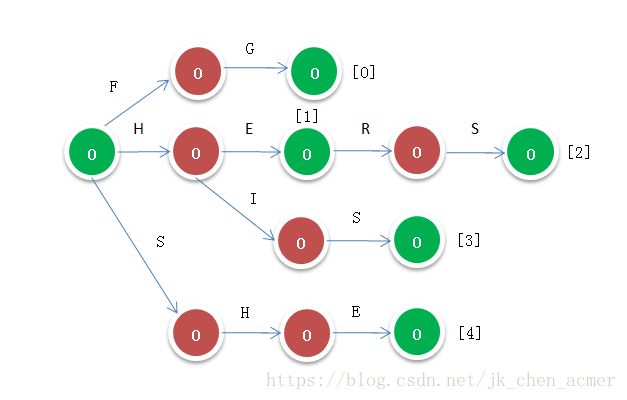
图中从根节点到任何一个绿色节点途径的字母的累加就是一个单词
每个节点有2种基本数据:
- count:以此节点为结尾的单词的个数
- next[26]:记录连接的下一个字母
代码:
struct node{
node *next[kind];
int count;
node(){
count=0;
memset(next,0,sizeof(next));
}
};
void build(char *x,node *root){
node *p=root;
int i=0,index;
while(x[i]){
index=x[i]-'a';
if(p->next[index]==NULL)
p->next[index]=new node();
p=p->next[index]; //p指向i字符相等的节点
i++;
}
p->count++;
}
\\\;
\\\;
\\\;
AC自动机:
一个常见的例子就是给出n个单词,再给出一段包含m个字符的文章,让你找出有多少个单词在文章里出现过。
要搞懂AC自动机,先得有Tire树(字典树)和KMP模式匹配算法的基础知识。AC自动机算法分为3步:构造一棵Trie树,构造失败指针和模式匹配过程。
简单得说就是在Trie树的结构上实现KMP算法,以快速实现让一个大串去匹配多个小串
L1.数据结构
略
const int kind=26;
struct node {
node *fail; //失败指针
node *next[kind];//Tire树每个节点的子节点个数
int count;
node(){
fail=NULL;
count=0;
memset(next,0,sizeof(next));
}
}*q[500002]; //队列,方便用于bfs构造失败指针
char str[1000001]; //模式串
int head,tail; //队列的头尾指针
L2.建Trie树
略
void build(char *str,node *root){
node *p=root;
int i=0,index;
while(str[i]) {
index=str[i]-'a';
if(p->next[index]==NULL)
p->next[index]=new node();
p=p->next[index]; //p指向i字符相等的节点
i++;
}
p->count++;
}
L3.构建失败指针
和KMP算法一样,失败指针是用来在失配时往前跳转用的,不过在KMP中是在串中一个往前跳,而在AC自动机中,因为数据结构是一棵Trie树,所以是往树根的方向跳
使失配时跳转到另一段从root开始每个字符都与当前已匹配字符段某个后缀完全相同的最长的位置,并继续匹配
因为一定是往前跳,所以当跳到一个位置的时候,必须把所有前面的都处理好,所以自然而然的就想到了BFS
构造失败指针:
对一个字符C,沿着其父亲节点的失败指针走,知道 走到根节点 或是 失败指针所指的节点有个儿子而为C
eg:
a ⇒ b ⇒ a ⇒ b ⇒ a ⇒ c a\Rightarrow b\Rightarrow a\Rightarrow b\Rightarrow a\Rightarrow c a⇒b⇒a⇒b⇒a⇒c
很显然,第二个a指向了第一个a,那么在找第二个b的失败指针时就跳到了第一个a,发现第一个a有一个儿子也是b,那么就指向第一个b
代码:
void build_ac_automatio(node *root){ //写出fail的指向
int i;
root->fail=NULL;
q[head++]=root; //bfs
while(head!=tail){
node *temp=q[tail++];
node *p=NULL;
for(i=0;i<26;i++){
if(temp->next[i]!=NULL){ //当前的子节点i不为空
if(temp==root)
temp->next[i]->fail=root;
else{
p=temp->fail; //记录一下当前节点失败节点指向那个节点
while(p!=NULL){ //直到找到
if(p->next[i]!=NULL){
temp->next[i]->fail=p->next[i]; break;
}
p=p->fail;
}
if(p==NULL)
temp->next[i]->fail=root;
}
q[head++]=temp->next[i]; //先把失败节点指向,再进入队列
}
}
}
}
L4.查询匹配
我觉得最核心的应该是这部分,因为query()函数并不是像上面几部分一样靠模板就行了,很多地方都得自己改
下面有一个查询大串有几个小串作为子串的模板
代码:
int query(node *root){ //查询
int i=0,cnt=0,index,len=strlen(str);
node *p=root;
while(str[i]){
index =str[i]-'a';
while(p->next[index]==NULL&&p!=root) //当前节点失败,&& 第root节点
p=p->fail;
p=p->next[index];
p=(p==NULL)?root:p;
//走到有效点
//计算这个有效点及比这个点浅的其他有效点中作为串结尾的点的数量
node *temp=p;
while(temp!=root&&temp->count!=-1){
cnt+=temp->count;
if(temp->count>0)
temp->count=-1;
temp=temp->fail;
}
i++;
}
return cnt;
}
AC自动机模板(指针版):
#includeAC自动机模板(数组版):
#include
const LL mod=1e9+7;
LL rd() {
LL ans=0;
char last=' ',ch=getchar();
while(!(ch>='0' && ch<='9'))
last=ch,ch=getchar();
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9')
ans=ans*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
if(last=='-')
ans=-ans;
return ans;
}
/*_________________________________________________________head*/
const int maxn=109;
namespace AC {
const int K=2;
int nex[maxn<<1][K],fail[maxn<<1],End[maxn<<1],root,cnt; //数组开字符串长度之和
int newnode() {
++cnt;
for(int i=0; i<K; i++)
nex[cnt][i]=-1;
End[cnt]=0;
return cnt;
// 1~ cnt
}
void init() {
cnt=0;
root=newnode(); // 1
}
void insert(char *str,int len) {
int now=root;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
if(nex[now][str[i]-'a']==-1)
nex[now][str[i]-'a']=newnode();
now=nex[now][str[i]-'a'];
}
End[now]++;
}
void build() { //建立ac自动机
queue<int>que;
for(int i=0; i<K; i++) {
if(nex[root][i]==-1)
nex[root][i]=root;
else {
fail[nex[root][i]]=root;
que.push(nex[root][i]);
}
}
while(!que.empty()) {
int now=que.front();
que.pop();
for(int i=0; i<K; i++) {
if(nex[now][i]==-1)
nex[now][i]=nex[fail[now]][i];
else {
fail[nex[now][i]]=nex[fail[now]][i];
que.push(nex[now][i]);
}
}
}
}
}
例题:Fleet of the Eternal Throne
原题:hdu 6138
题意:
有n个字符串,m个询问,每次询问选择n中的两个字符串a,b,求a和b的最长子串使之是1~n中某个字符串的前缀
解析:
AC自动机本身比较好处理模式串的前缀问题,因为每次跳到有效位置后,从root到当前节点所形成的串即为某个模式串的前缀
所以现在所需要处理的问题就是怎么找满足要求的两个串的最长公共子串
这个时候想到了AC自动机的另一个性质,在查询的过程中,在每次跳到有效位置之后,从root到当前节点所形成的串必定是查询目标串的子串,所以我们可以对两个串用AC自动机跑一遍,某个节点被两个串跑过,那么这个节点所形成的串就是两个串的公共串
| 怎么实现呢? 我们在建树的时候记录下每个节点到root的距离,即为这个子串(前缀)的长度,在AC自动机跑两个字符串的时候取max维护ans就行了 |
代码:
| 代码细节: 1. 最多1e5个字符串但是总长度只有1e5,不能开1e5个char数组,需要记录到一个char数组里面,用pos数组来表示每个字符串的位置 2. 如果在怕跑第二个字符串的时候用vis=0\1来判断是否被第一个跑过,显然会比较麻烦,所以通过vis的累加来解决(第一次vis变成1判断是否为1,第二次vis变成2判断是否为2...),从而省去清空vis的时间 |
#include